earth science astronomy test
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Johannes Kepler
(1) planets move in elliptical orbits with the Sun as a focus
(2) a planet covers the same area of space in the same amount of time no matter where it is in its orbit
Galileo
Galileo Galilei's three key discoveries include the moons of Jupiter, the phases of Venus, and sunspots, all observed through his improved telescope, which revolutionized astronomy.
Charles Messier
French astronomer who was the first to compile a systematic catalog of nebulae and star clusters.
Why is the sky blue
Rayleigh scattering
Why are clouds white
Mie scattering
Terrestrial planets
The terrestrial planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. They are called terrestrial because they are rocky and have solid surfaces, similar to Earth.

Gas giants
large, Jovian planets in our solar system, primarily composed of gases like hydrogen and helium, with no solid surface, and include Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Asteroid belts
a region in our solar system, located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, where many asteroids (also called minor planets) orbit the sun.
What is a planet
it must orbit a star, it must be big enough to have enough gravity to force a spherical shape, and it must be big enough that its gravity cleared away any objects of a similar size near its orbit.
Layers of the sun (from inside to outside)
core, radiative zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, transition region, and corona.
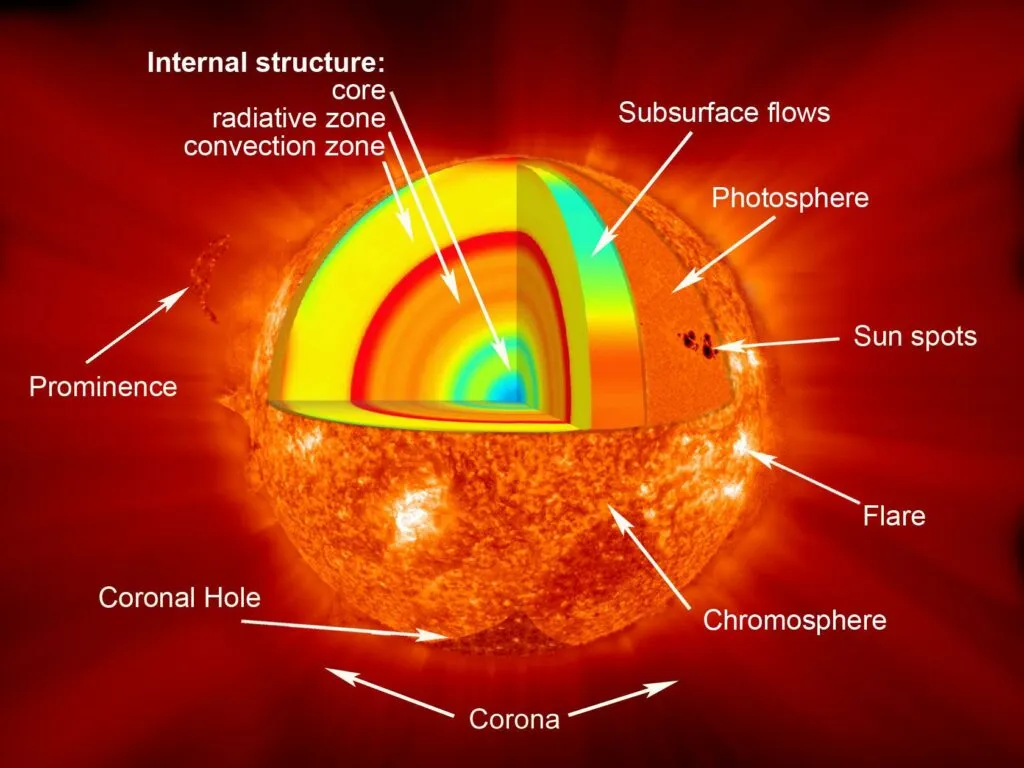
Sun spots
cooler, darker areas on the Sun's surface caused by intense magnetic fields, appearing as spots with a central dark region (umbra) and a lighter outer region (penumbra).
Solar flares
sudden, intense bursts of energy and radiation from the Sun, often associated with regions of strong magnetic fields, that can extend out to the Sun's corona.
Prominences
large, bright, arch-like loops of plasma that extend outward from the Sun's surface, often associated with magnetic fields and can last for days or even months.
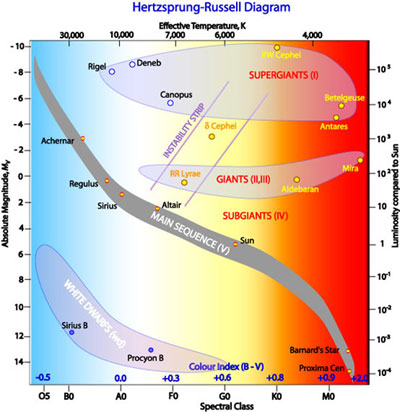
What is this called?
An H-R diagram
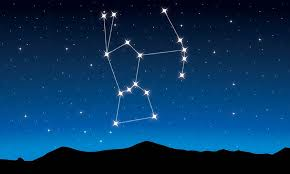
What constellation is this
Orion
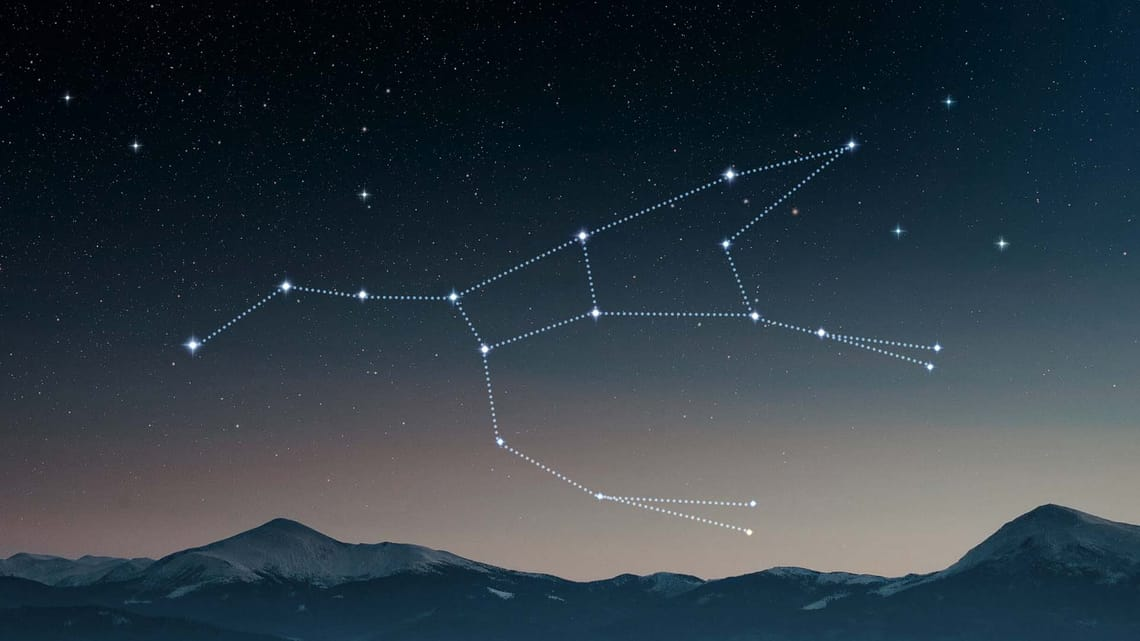

What constellation is this?
Ursa major
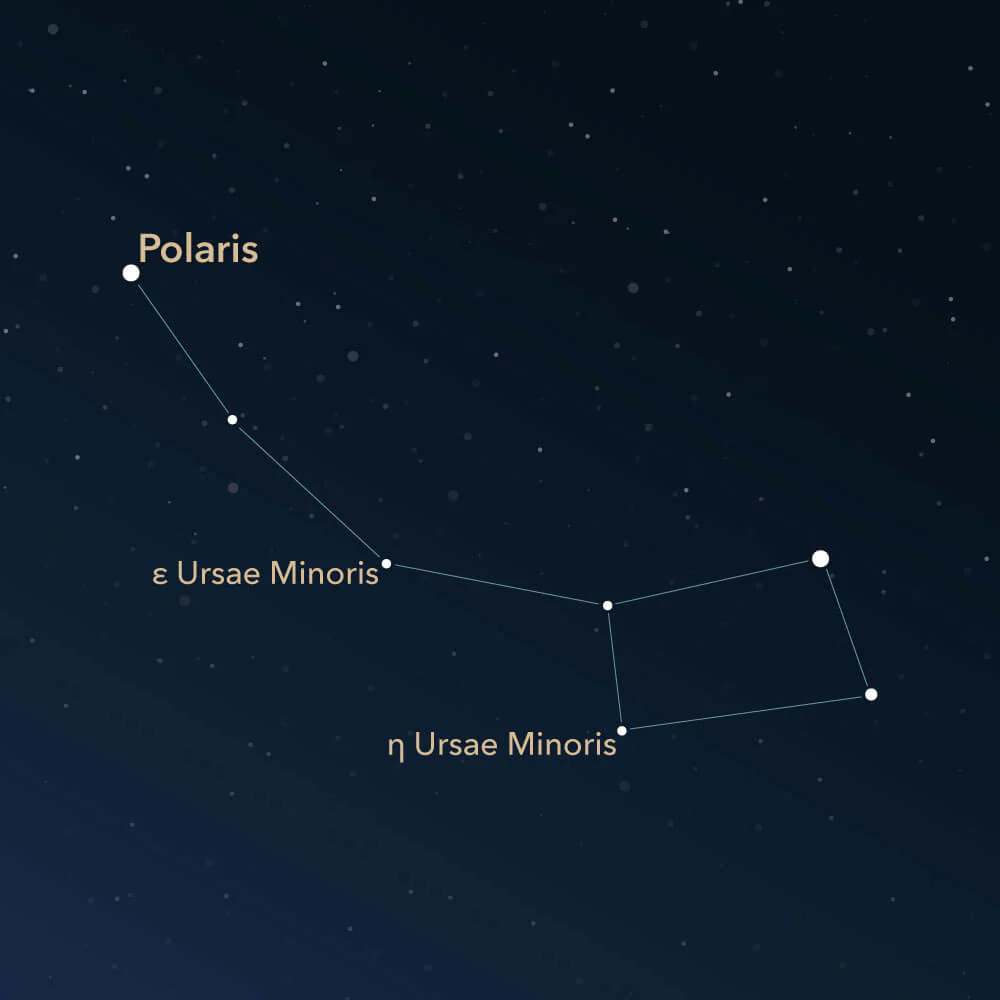
What constellation is this
Ursa minor
Andromeda galaxy
a spiral galaxy, the closest large galaxy to our own Milky Way, and one of the few galaxies visible to the naked eye.
What are the four methods to find exoplanets
Transit Method
Wobble Method
Direct Imaging
Microlensing
Transit method
When we look at distant stars, we can't actually see planets transiting their stars. They're too far away for us to see such small features, even with our best telescopes. However, we can tell that the amount of light coming from the star decreases.

Wobble method
The movement of a light source, such as a star, changes the frequencies of light that the star emits. If we see this type of rhythmic change in the light frequency emitted by a star, we know the star is being orbited by a significant body.
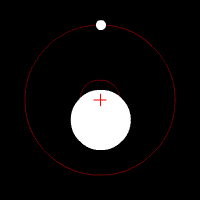
Direct imaging
Taking a photo of the planet while omitting the light from stars
Microlensing
Light from a distant object is bent by gravity as it travels. we can use the presence of gravitational lensing to detect a planet around a star.
Equation of a planets radius:

Equation for a planets mass
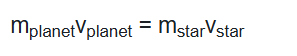
Equation for the density of a planet:

Nebula
a vast cloud of gas and dust in space, often containing the raw materials for new stars and planets.
The sun is ___ from earth
93 million miles
The asteroid belt beyond neptune is the…
Kuiper belt
Sunspots are located in the…
Photosphere
The ___ of the sun is only visible during a solar eclipse
Corona
Lines on the sun that look like long sun spots
filaments
Methods of studying a planets atmosphere
Transmission and emission spectroscopy
Precession
the slow movement of the axis of a spinning body around another axis due to a torque (such as gravitational influence) acting to change the direction of the first axis
Baycenter
the point that serves as the center of mass for a system of two or more bodies orbiting each other. It's the point where their gravitational forces are balanced, and both bodies orbit around it. In simpler terms, it's the balancing point of a system in space.
Nutation
a rocking, swaying, or nodding motion of the axis of rotation of an object, like a gyroscope, planet, or even a bullet in flight
Perihelion
the point in the orbit of a planet, asteroid, or comet at which it is closest to the sun.
Aphelion
the point in an orbiting body's path where it is farthest from the Sun
Tropic of cancer
a line of latitude located at approximately 23.5 degrees north of the Equator. It marks the northernmost point where the sun can appear directly overhead at noon.
Tropic of capicorn
a line of latitude, approximately 23.5 degrees south of the Earth's equator. It marks the southernmost point where the sun can be directly overhead at noon.
Arctic circle
a line of latitude at approximately 66°33′ north, marking the border of the Arctic region
Antarctic circle
s the northernmost latitude in the Southern Hemisphere at which the centre of the sun can remain continuously above the horizon for twenty-four hours
How does the tilt of the earth cause seasons
As the Earth orbits the Sun, the tilt causes different hemispheres to receive varying amounts of direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in seasonal changes in temperature and daylight hours.
how the Earth’s rotation and revolution about the Sun affect its shape and is related to seasons and tides.
As the Earth spins on its axis, the centrifugal force created by this rotation causes the Earth to bulge at the equator and flatten at the poles. This results in a shape that is not a perfect sphere but rather an oblate spheroid (a squashed sphere).
The Moon's gravitational pull is the primary driver of tides. The Moon's gravity creates bulges of water on both sides of the Earth, closest to and farthest from the Moon, which are the high tides.
fusion vs fission
Fission involves splitting a heavy atom, while fusion involves combining light atoms.
how energy flows from the sun to the Earth through space.
through radiation, specifically in the form of electromagnetic radiation, which includes visible light and other frequencies of light