A+P Lab Quiz 1
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Ventral (anterior)
Toward or at the front of the body; in front of
Ex: The breastbone is ____ to the spine
Dorsal (posterior)
Toward or at the back of the body; behind
Ex: The heart is _____ to the breastbone
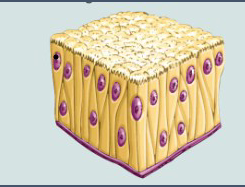
Pseudostratified columnar epithelial
Appears to be multilayered
Squished together
All cells anchored to the BM
Lateral
Away from the middle of the body, on the outer side of
Ex: The arm is ____ to the chest
Epithelial Tissues
Covers/lines
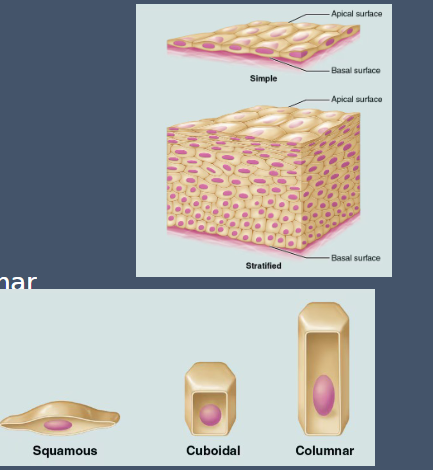
Transitional Epithelium
Bottom cells appear cuboid
Top Cells appear dome shaped or flat
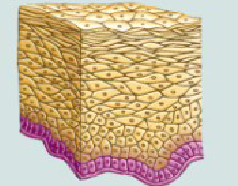
Loose Areolar
Loose arrangement of fibers
A lot of ground substance
Scattered Cells
Located in every organ
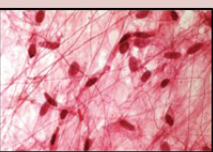
Dense Areolar
Densely packed, parallel fibers
Not much open space
Located in tendons and ligaments
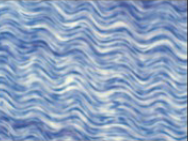
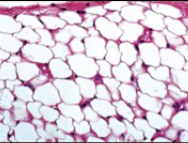
Adipose Areolar
Large empty looking cells
Often pale
Subcutaneous fat
Articulating Surfaces
The smooth, cartilage covered end of a bone within a joint where two bones meet to allow for movement
Non-Articulating Prominences
A bony projection or feature of the skeleton that serves as an attachment point for muscles and ligaments but does not form a joint with a another bone, unlike an articular surface
Depressions
An indentation or hollow area on a bone, like a fossa or a cavity
Openings
Natural holes or gaps within bones, or other dense connective tissue, that allow nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics, and other soft tissues to pass through from one body compartment to another
Hypertonic solution
When water leaves the cell, more water outside than inside
Crenated
Isotonic Solution
equal amounts of water on the inside and outside
Hypotonic solution
More water inside of the cell than outside, lysed
Condyle
A large rounded, articulating knob
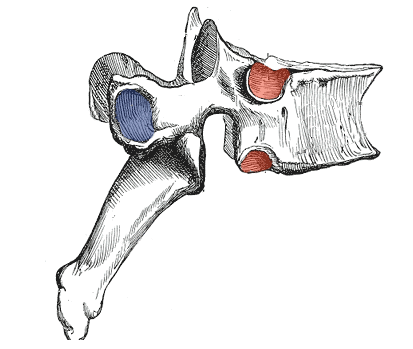
Facet
A flattened or shallow articulating surface
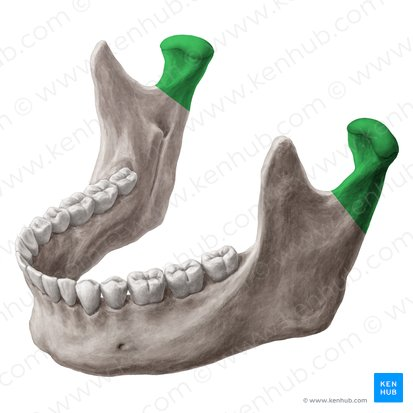
Head
A prominent, rounded, articulating end of a bone
Crest
A narrow, ridgelike projection
Epicondyle
A projection above a condyle
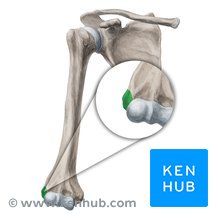
Process
Any marked, body prominence
Spine
A sharp, slender process
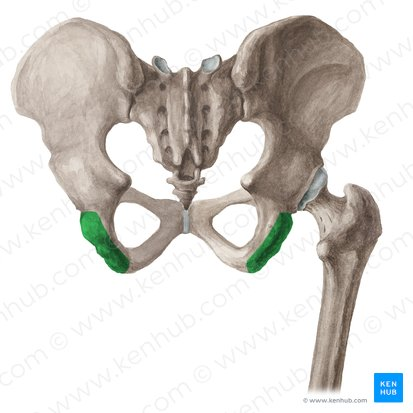
trochanter
A massive process found only on the femur
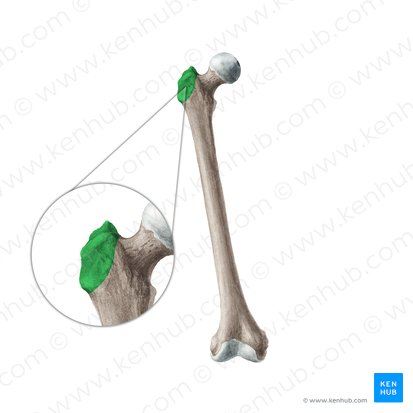
Tubercle
A small rounded process
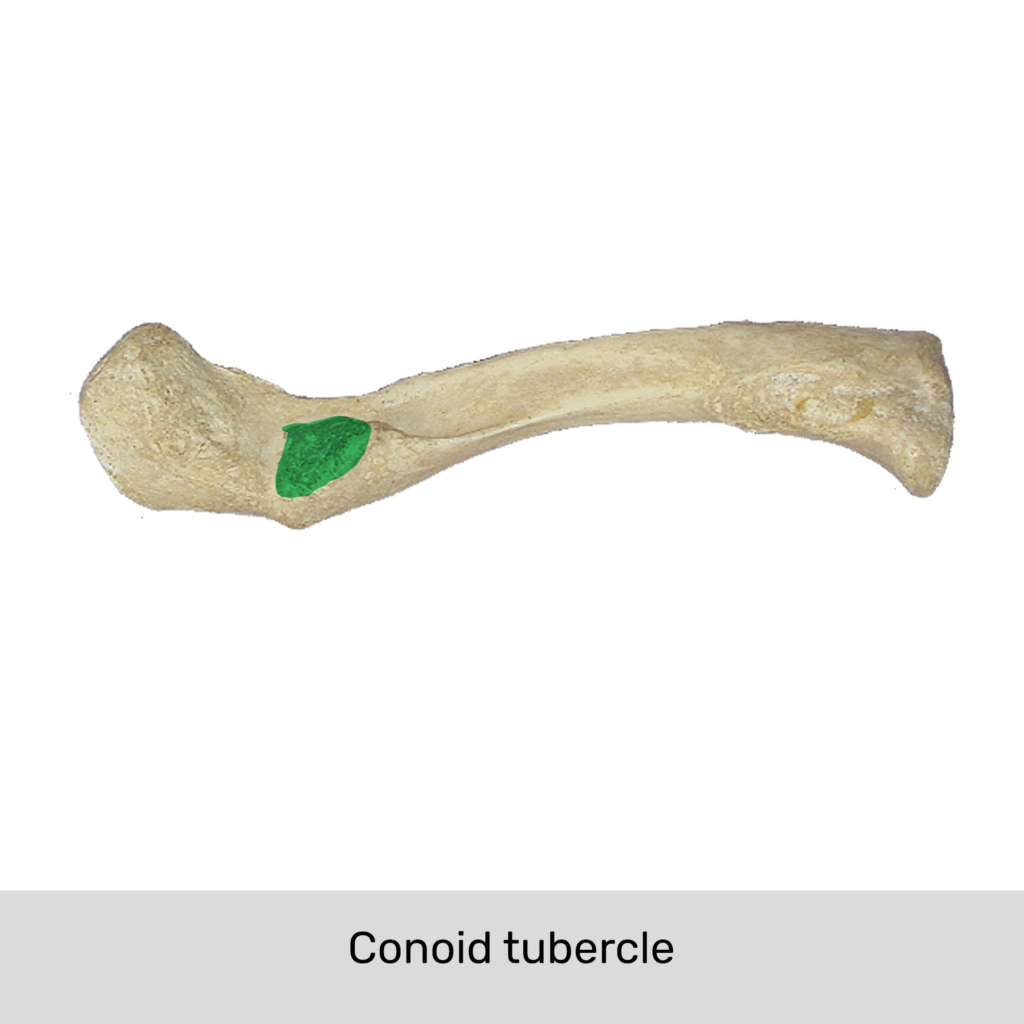
Tuberosity
A large roughened process
Alveolus
A deep pit or socket
Fissure
A narrow, slit-like opening
Foramen
A rounded opening through a bone
Fossa
A flattened or shallow surface
Fovea
A small pit or depression

Meatus
A tube-like passageway through a bone
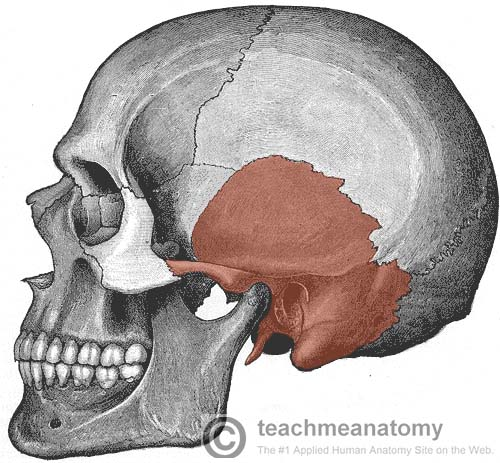
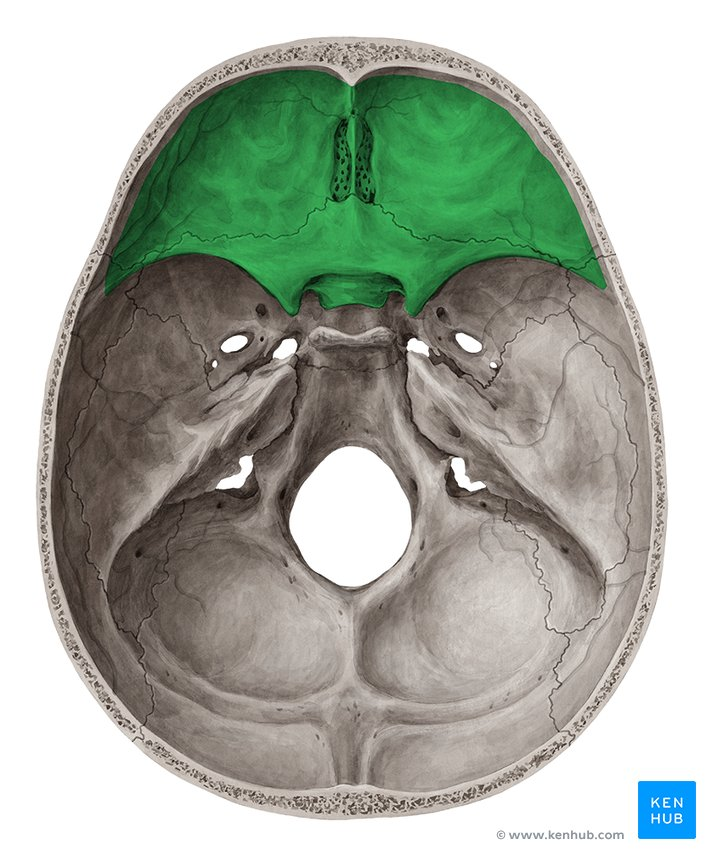
Sinus
A cavity or hollow space in a bone
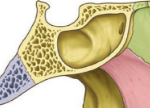
Sulcus
A groove that accommodates a vessel, nerve, or tendon
Nervous Tissue
Controls
Proximal
Closer to the origin of the body part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
The elbow is ____ to the wrist
Distal
Farther from the origin of a body part or the point attachment of a limb to the body trunk
The knee is ____ to the thigh