Anaerobic Bioenergetics: Enzymes, Glycolysis, and Exercise Fuels
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What are enzymes?
Catalysts that regulate the speed of reactions and lower the energy of activation.
What factors regulate enzyme activity?
Temperature and pH.
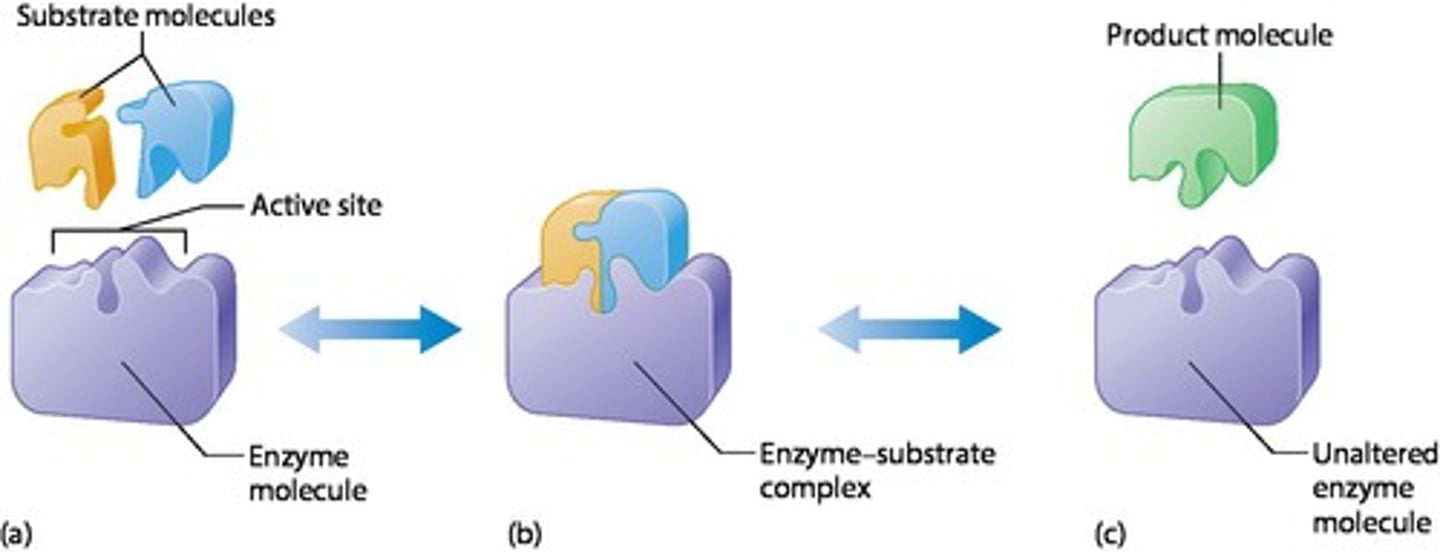
Describe the lock and key model in enzyme activity.
Enzymes interact with specific substrates where two substrates fit into the enzyme's active site.
What happens to enzymes during an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
The enzyme catalyzes the chemical reaction, producing a product molecule while remaining unaltered.
How can enzyme activity in the blood serve as a diagnostic tool?
Damaged cells release enzymes into the blood, and elevated levels can indicate disease or tissue damage.
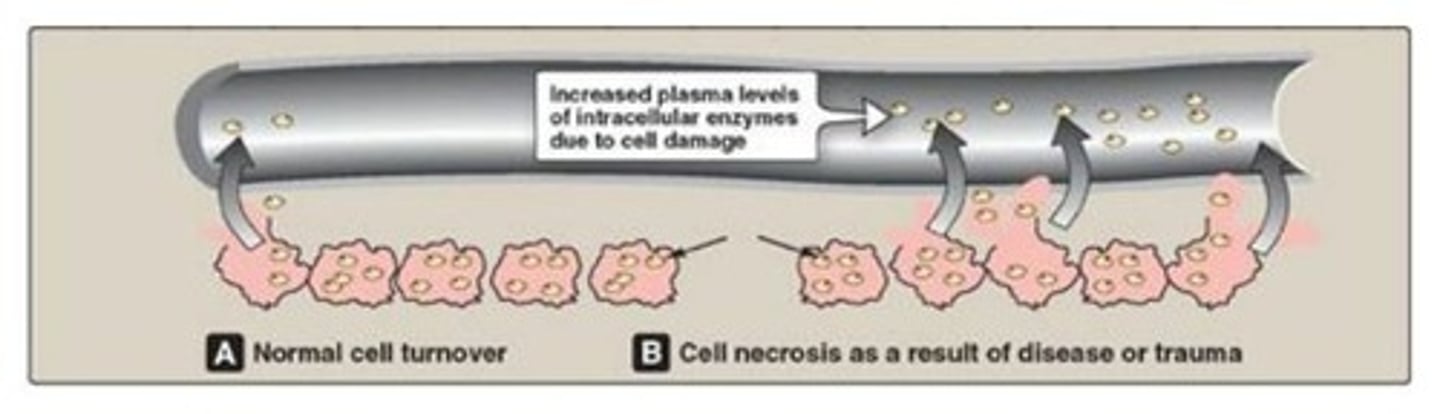
What enzyme levels may indicate a myocardial infarction?
Elevated lactate dehydrogenase or creatine kinase.
What is the normal pH range for enzyme activity?
Normal pH is 7.4±0.05, with a survival range of 7.0-7.8.
What are the primary fuels for exercise?
Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
What is glycogen and its role in the body?
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in the liver and muscle, synthesized by glycogen synthase.
What is glycolysis?
The process that converts glucose into 2 pyruvic acid or 2 lactic acid, involving an energy investment and generation phase.
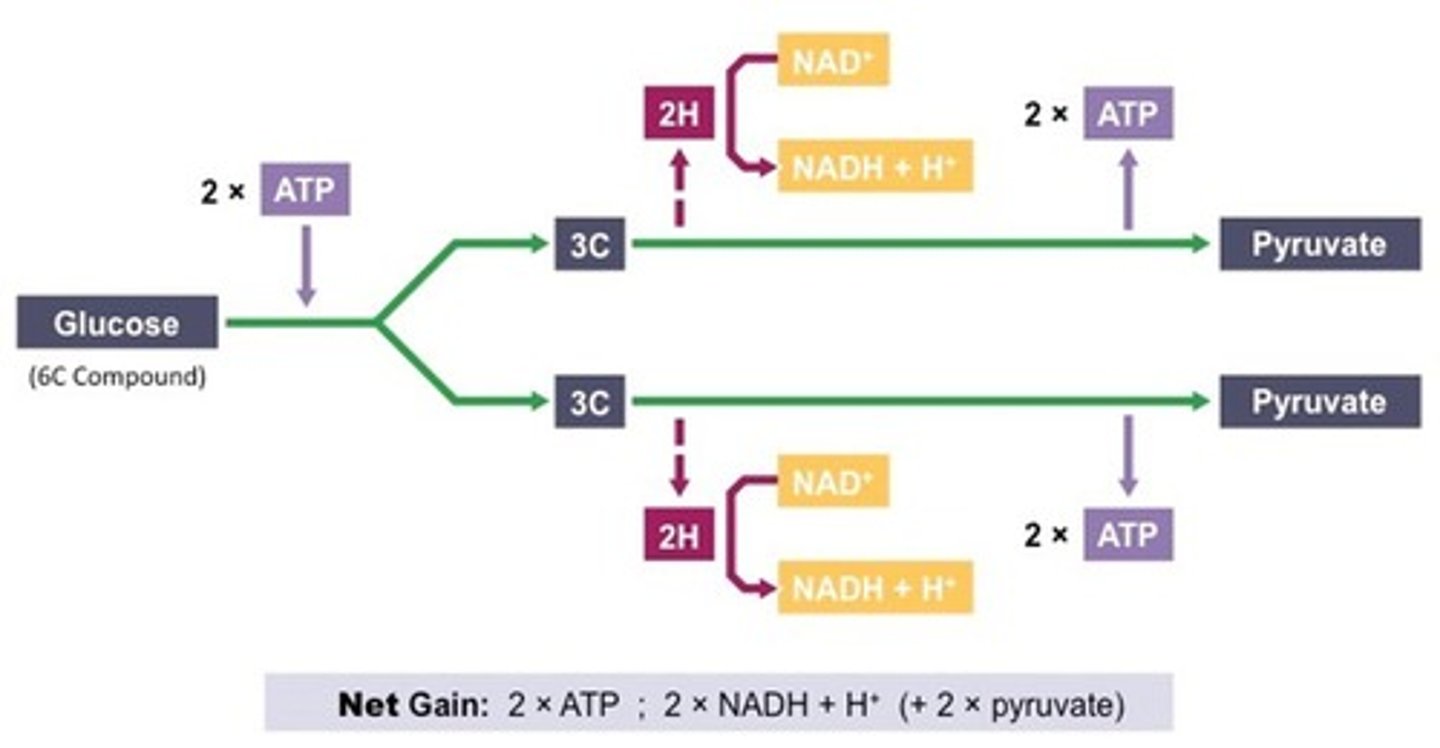
What occurs during the energy investment phase of glycolysis?
It requires 2 ATP to initiate the process.
What are the products of the energy generation phase of glycolysis?
Produces 4 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate or 2 lactate.
What is the difference between lactic acid and lactate?
Lactate is the conjugate base of lactic acid, which is produced in glycolysis and rapidly disassociates to lactate and H+.
What is the ATP-PCr system?
An immediate source of ATP in anaerobic ATP production.
What is the energy currency of the body?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
What are the roles of NAD and FAD in electron transport?
They are coenzymes that play critical roles in the transfer of electrons during metabolic processes.
What is the difference between anaerobic and aerobic pathways in ATP formation?
Anaerobic pathways do not require O2, while aerobic pathways require O2 for oxidative phosphorylation.
What is gluconeogenesis?
The process by which some amino acids are converted to glucose in the liver.
What is the significance of the First Law of Thermodynamics in metabolism?
It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.