Year 2 organic sem 1
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What is the ranking of strongest nucleophiles from lowest to highest (negative charge, multiple bonds, lone pair and single bonds)?

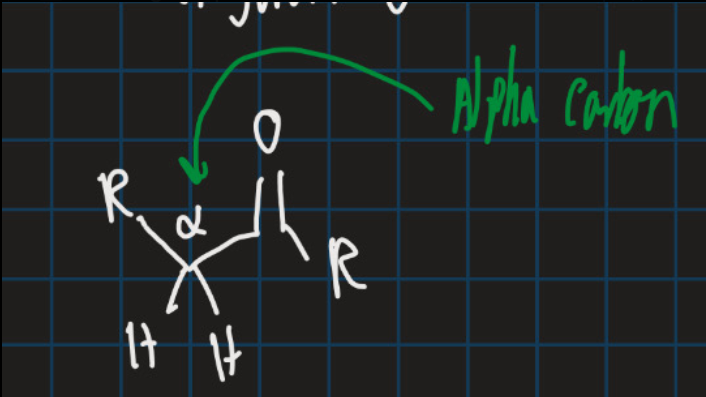
What is the alpha carbon?
The carbon directly attached to the carbonyl carbon C=O
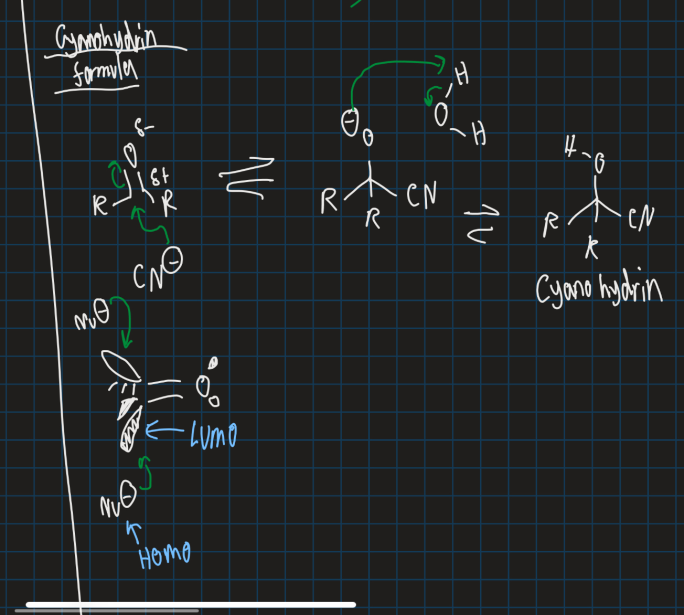
Show the mechanism for making cyanohydrin and show orbital mechanism of adding nucleophile (start from ketone and add solvent (water) and CN- nucleophile)
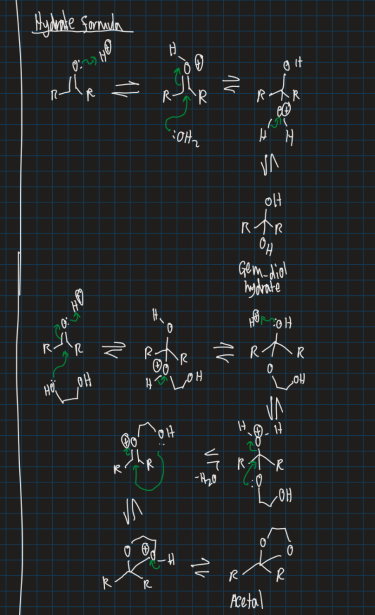
Show the mechanism for creating gem-diol hydrate and acetal starting from ketone (use water solvent)
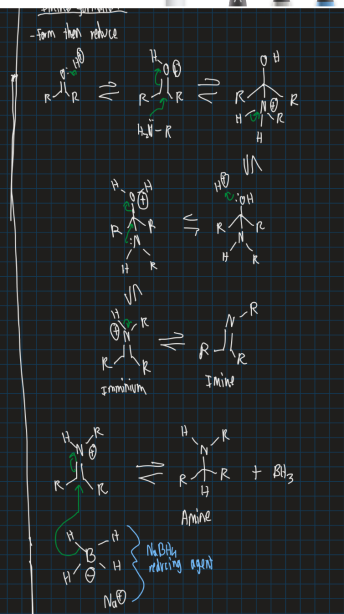
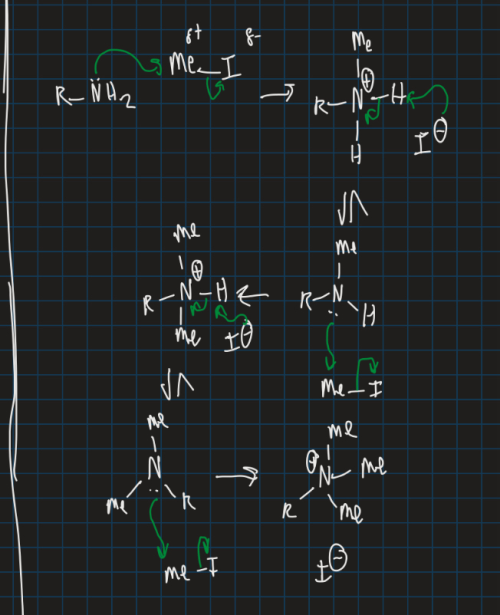
Show the mechanism for forming an imine (start from ketone and use reducing agent)
Show the mechanism for forming an imine (start from Me-I)
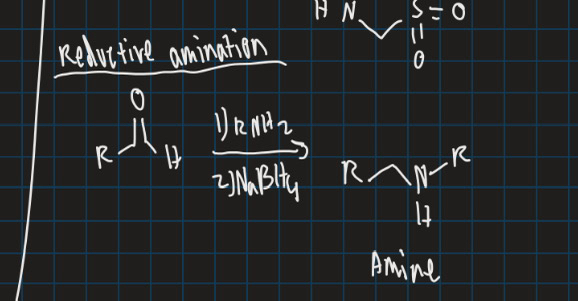
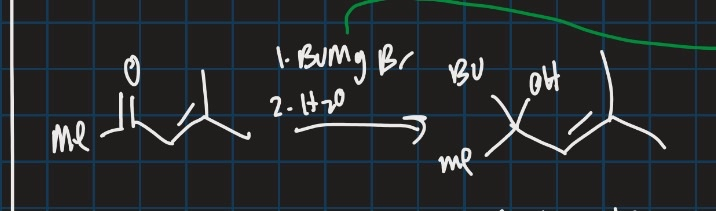
Show the formula for reductive amination (start from ketone and use reducing agent e.g = NaBH4)
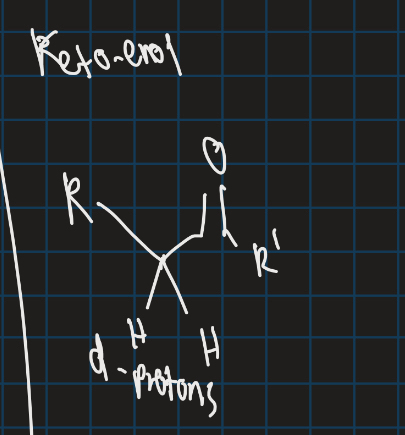
What are alpha protons?
Protons attached to alpha carbon
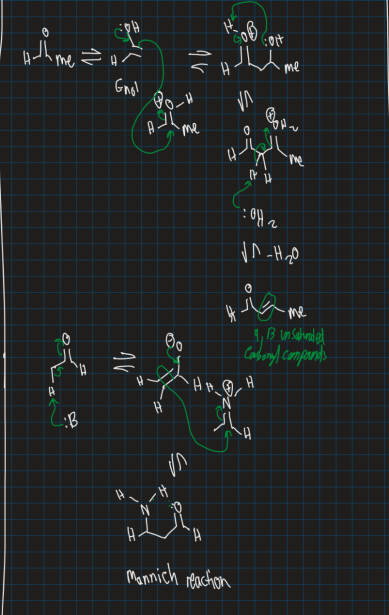
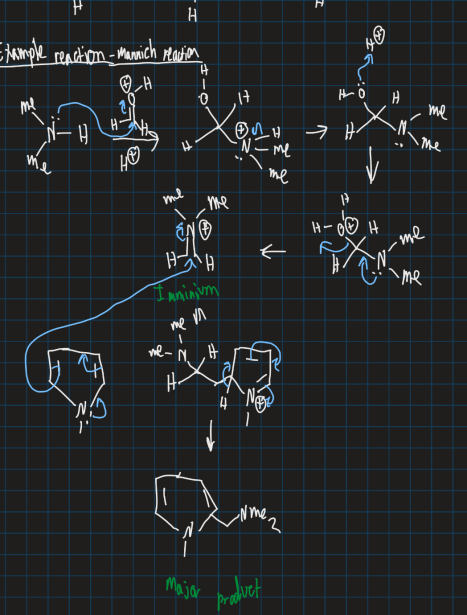
What is the mannich reaction?
Forming a beta-aminocarbonyl compound
→ combines carbonyl compound with at least one alpha-hydrogen
→ Combines formaldehyde
→ Combines primary or secondary amine
Show the mannich reaction starting from ethylaldehyde (add another ethylaldehyde, imine, water solvent and base)
Show the aldol reaction starting from ethyl aldehyde (use OH- base, water solvent and heat)
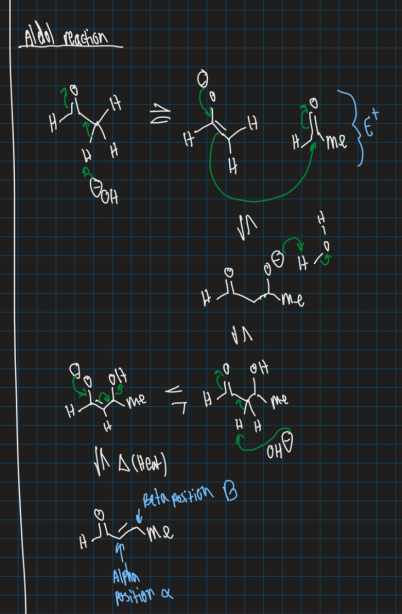
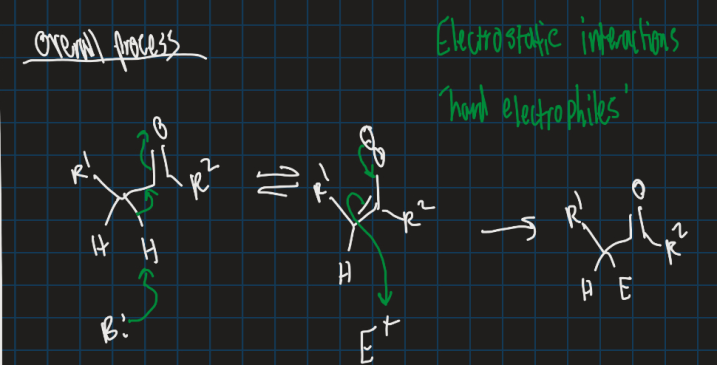
How do you form an enol?
Use base to attack alpha proton and use electrophile after
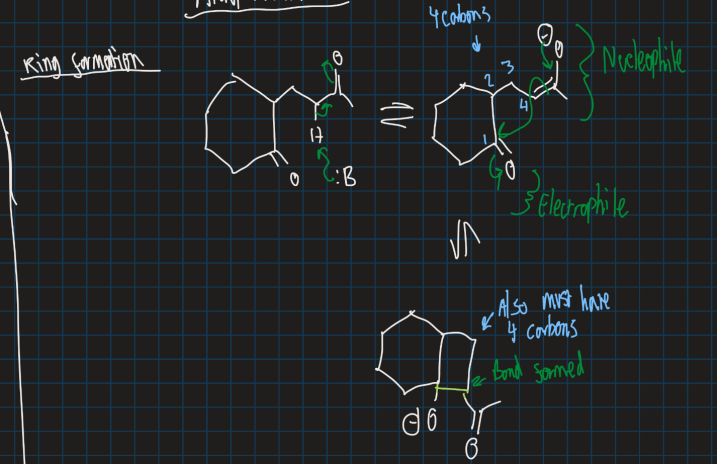
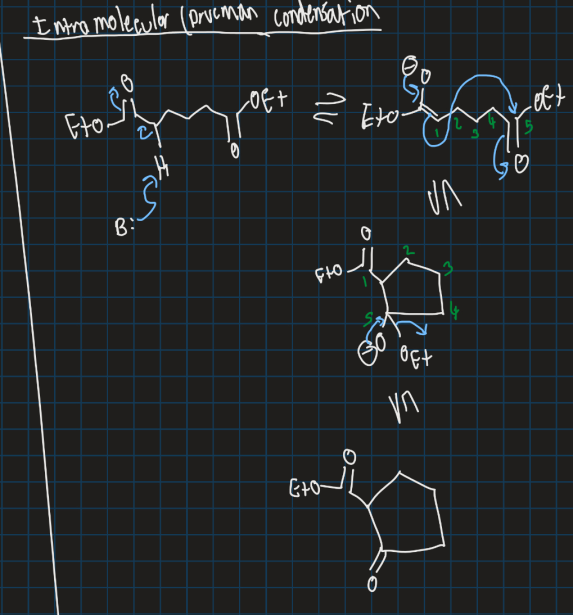
Show ring formation
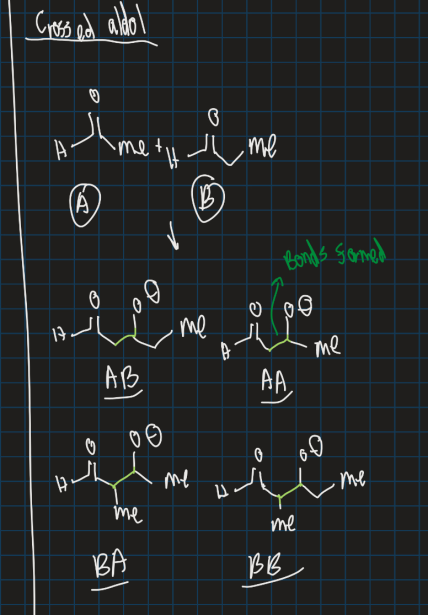
What is a crossed aldol reaction?
When 2 carbonyl compounds have alpha protons and when they react it forms combinations of products
→ USE MOLECULE WITH NO ALPHA PROTONS FOR ALDOL REACTION TO WORK
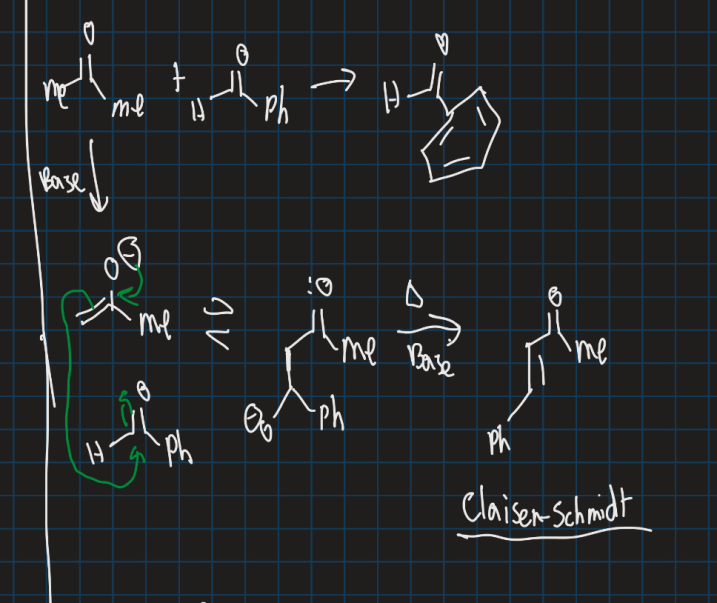
What is the Claisen-Schmidt reaction?
Show the Claisen-Schmidt reaction starting from acetone and benzaldehyde (use base)
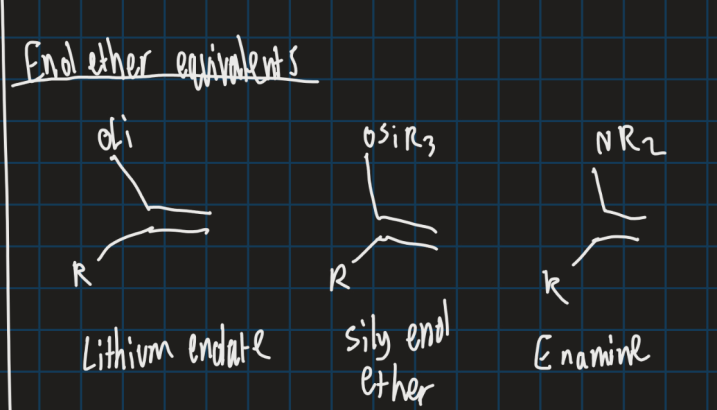
Show the enol ether equivalents
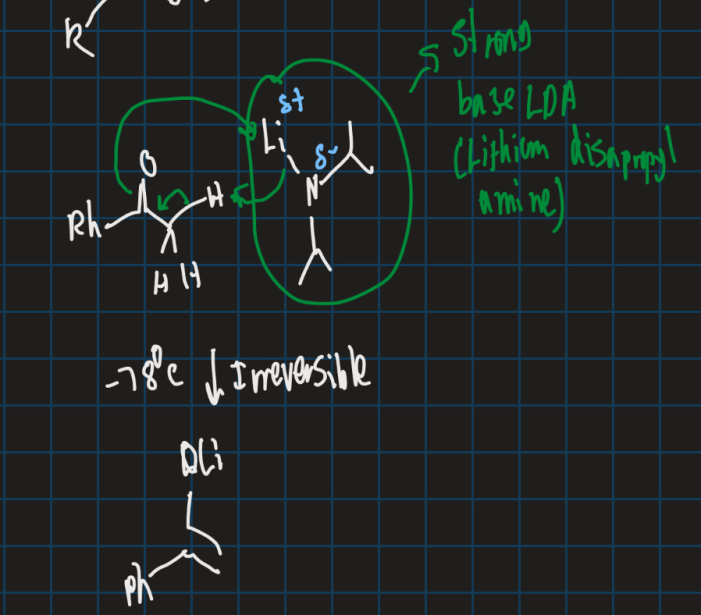
What is LDA (lithium diisopropylamine )?
Strong base
When should you use LDA?
Make reaction irreversible
→ Also use for weak acids
What is trimethylamine?
Hard base (but softer than LDA)
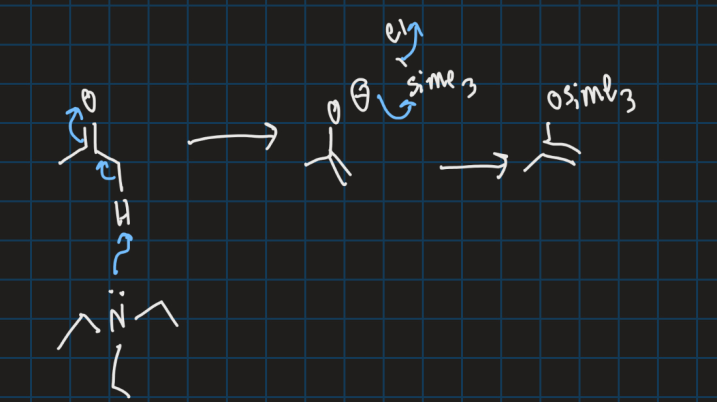
What is HSAB (Hard and soft acid base) theory?
Determines if compound is hard or soft base based on charge density, size and polarizability
How do you determine if a base is hard?
Large size, easily polarizable and low charge density e.g = LDA
Show reaction of formation of alpha,beta carbonyl compound starting from 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, aldehyde ,weak base and heat (Knoevenagel condensation)
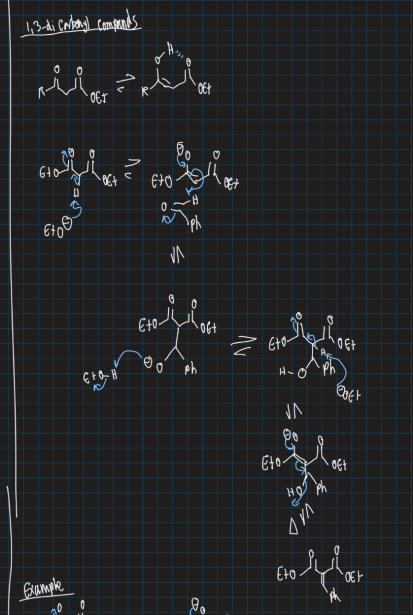
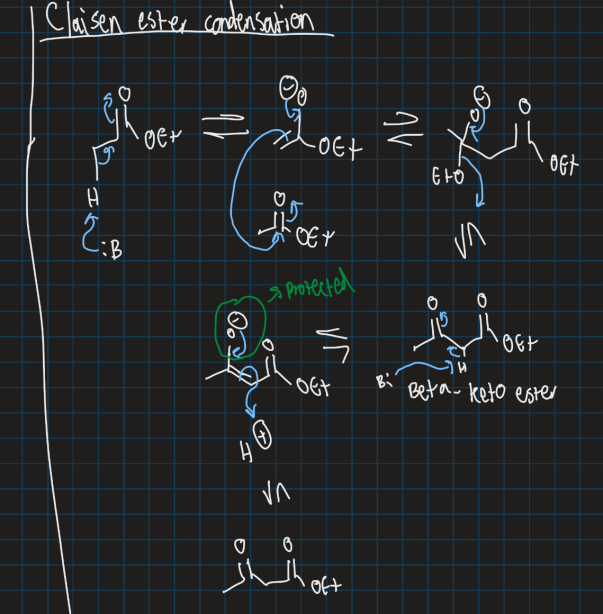
What does claisen ester condensation reaction do?
Forms a beta carbonyl by reacting 2 esters (or one ester and one ketone)
Show claisen ester condensation reaction (formation of carbonyl using 2 esters and strong base
What is the claisen-schmidt reaction?
Crossed aldol reaction between aromatic aldehyde and aliphatic aldehyde or ketone
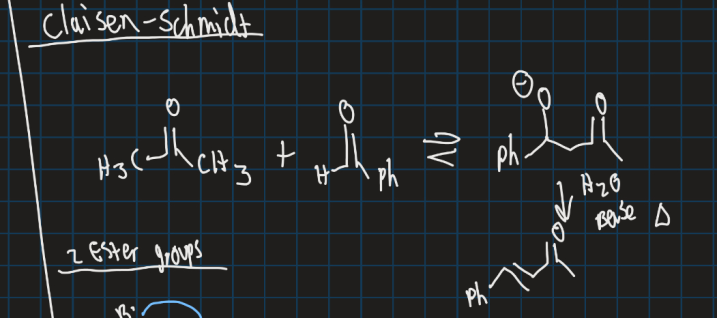
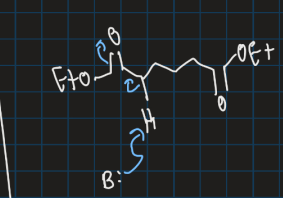
Show mechanism for formation of cyclic ring base
What is haloform reaction?
Methyl ketone reacts with halogen in presence of base to form haloform and carboxylate salt
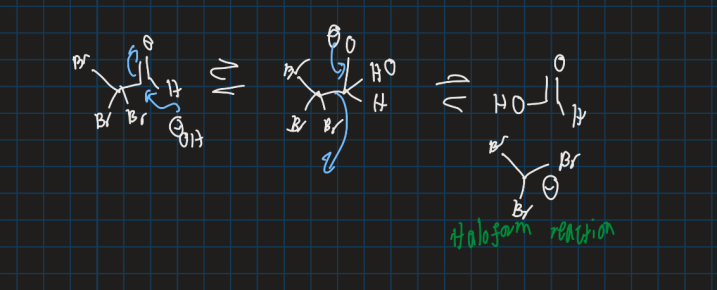
Show mechanism for haloform reaction
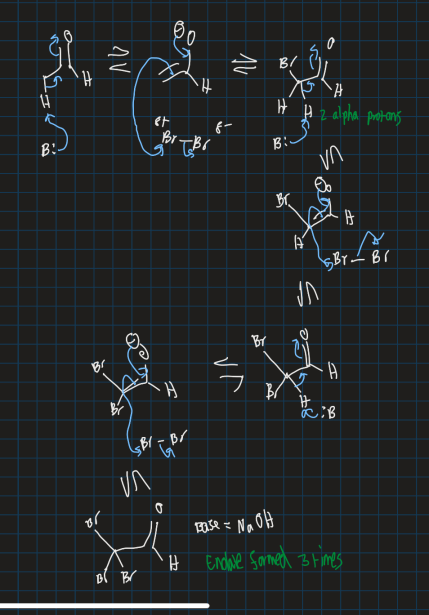
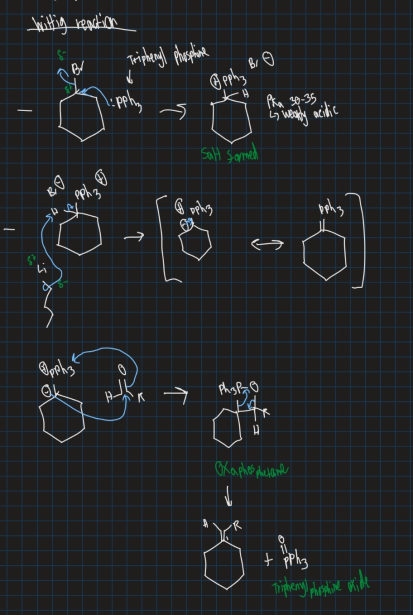
What is the wittig reaction?
Reaction of phosphonium ylide with an aldehyde or ketone to form an alkene → Also use base
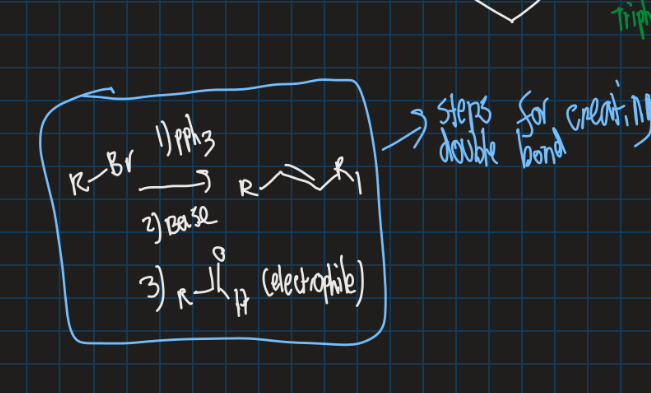
Show wittig reaction on cyclobromide (use aldehyde)
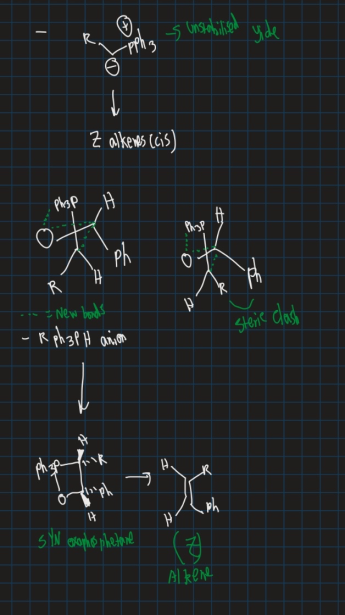
How is a cis (z) alkene formed? Does ylide have to be stable or unstable?
Ylide must be unstable
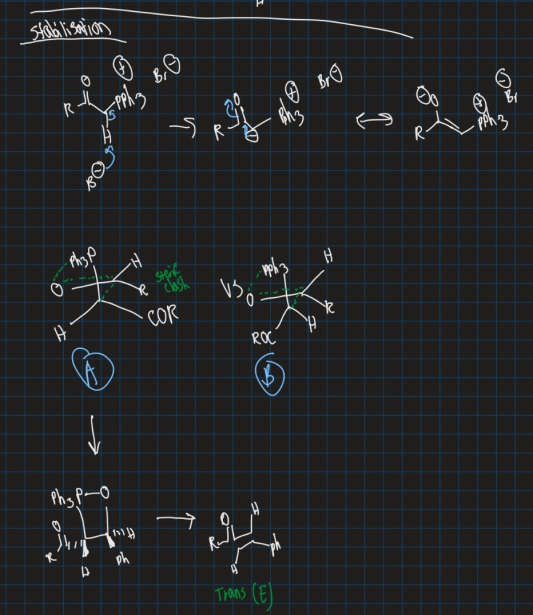
How is a trans (E) alkene formed? Does ylide have to be stable or unstable?
Ylide must be stable
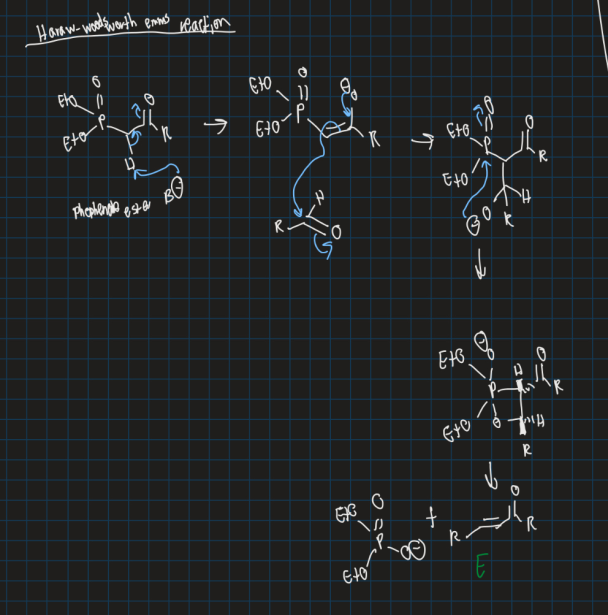
What is the Haraw-woodsworth emms reaction?
Variation of a wittig reaction used to form a double bond
Use Phosphonate ester, base and aldehyde
What is Julia Olefination reaction?
Variation of wittig reaction used to form a double bond
Use sulfone, base, aldehyde and phenylacetyl chloride
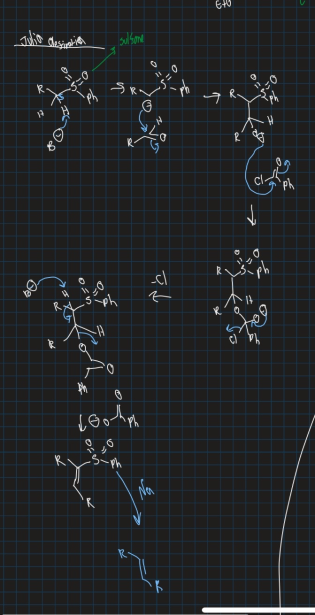
How do you break an epoxide?
Use stronger nucleophile to break
Oxygen then can be used as nucleophile
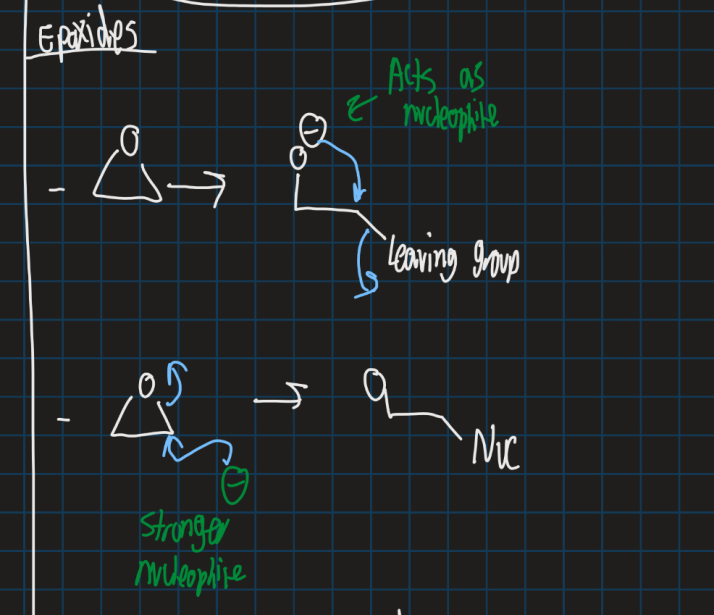
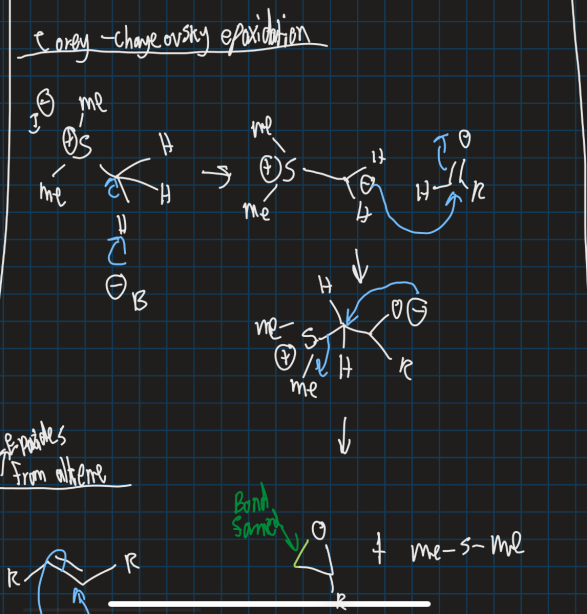
What is the Corey- Chaykovsky epoxidation and show an example?
Used to create an epoxide from an alkene
Sulfur ylide is used
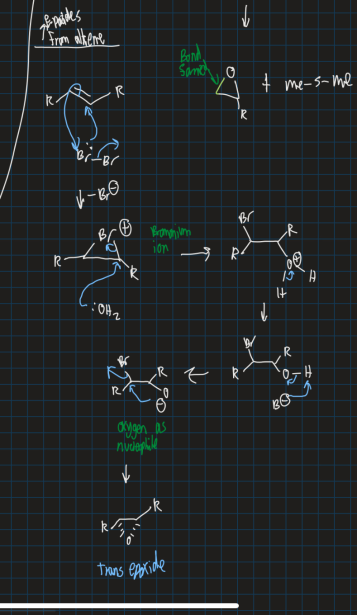
How do you form epoxides from an alkene using bromine, water and base and what isomer will it form?
Trans epoxide formed
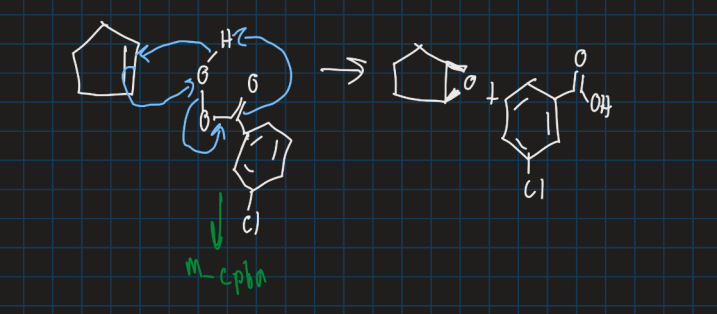
Show the mechanism for formation of an epoxide using m-cpba from pentene
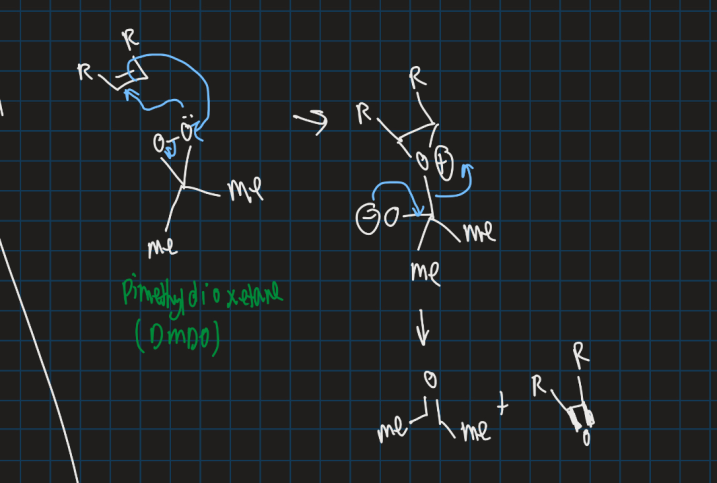
Show the mechanism for formation of an epoxide using DMDO from an alkene
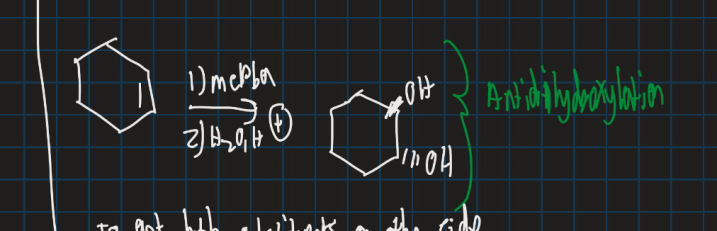
What is anti dihydroxylation ?
Formation of 2 hydroxy groups using mcpba, water and an acid
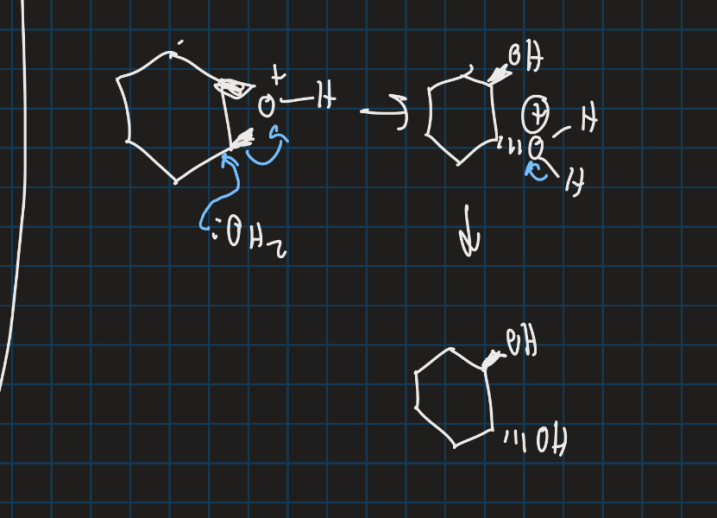
Show the anti dihydroxylation reaction starting from cyclohexane
How do you get both substituents on the same side (SYN dihydroxylation reaction)
Use osmium tetraoxide (dangerous compound)
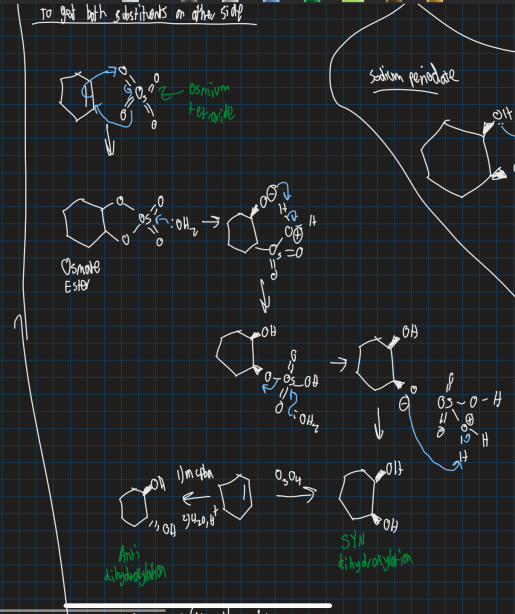
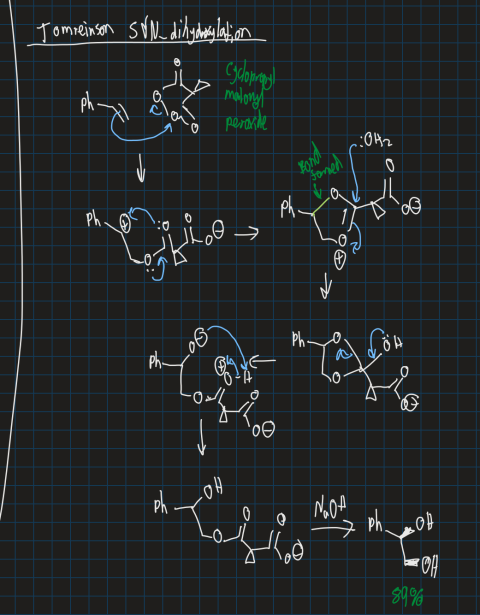
Show the reaction for Upjohn dihydroxylation and what does it do?
Also gets both OH groups on the same side (cis isomer formed)
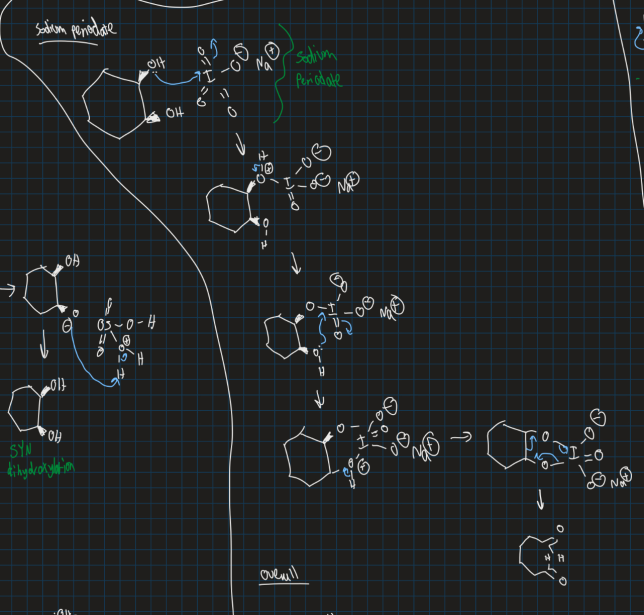
What does sodium periodate do and show the reaction of sodium periodate with 2,3-dihydroxycylohexane
Cleaves diols
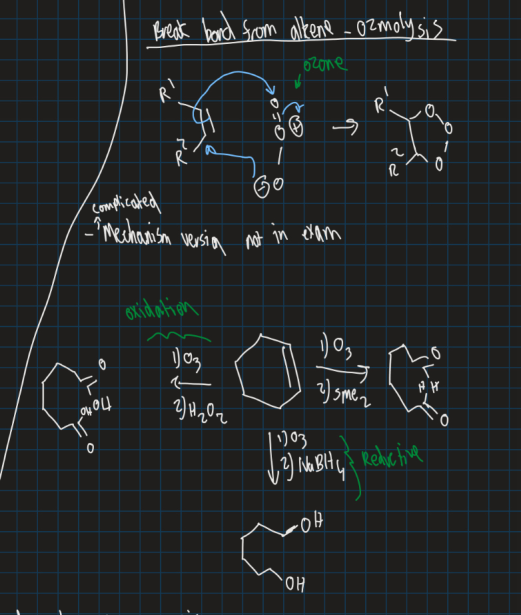
What happens when you react an alkene to ozone (O3)?
Breaks bond from alkene
Can either oxidise or reduce OH in reactant molecule
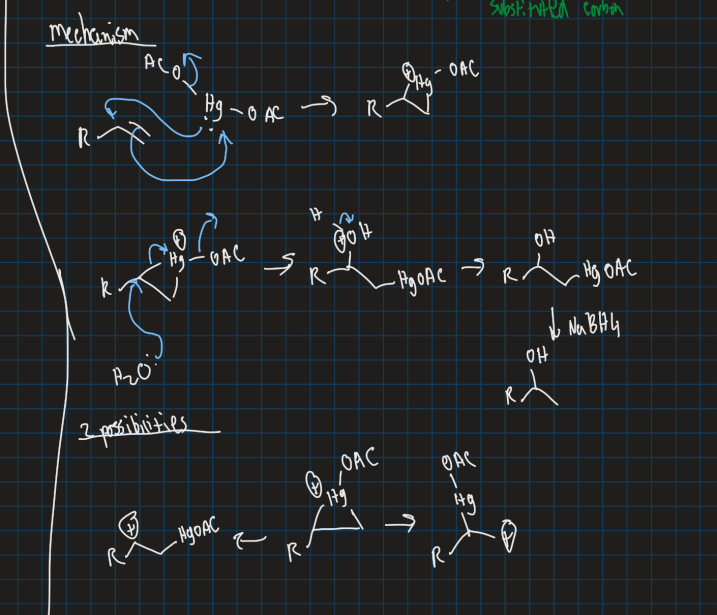
Show markovnikov reaction and anti-markovnikov reaction using mercury acetate (Hg(OAC)2) and reducing agent
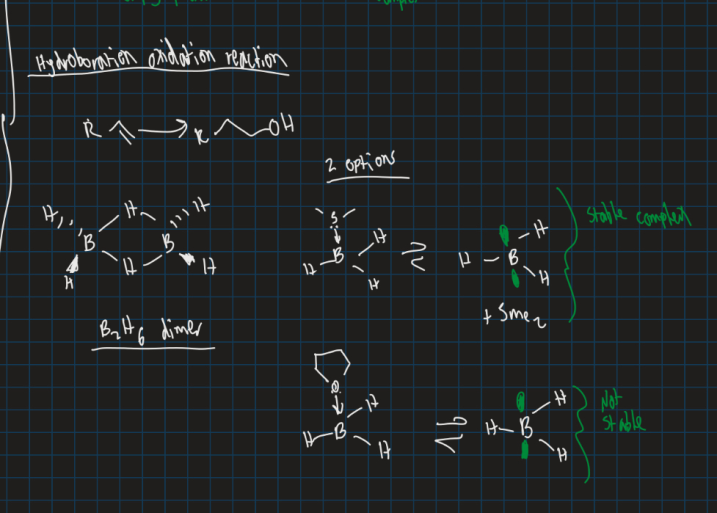
What is the hydroboration oxidation reaction ?
Converts alkene to an alcohol with using anti-markovnikov reaction
Can use BH3 SMe2
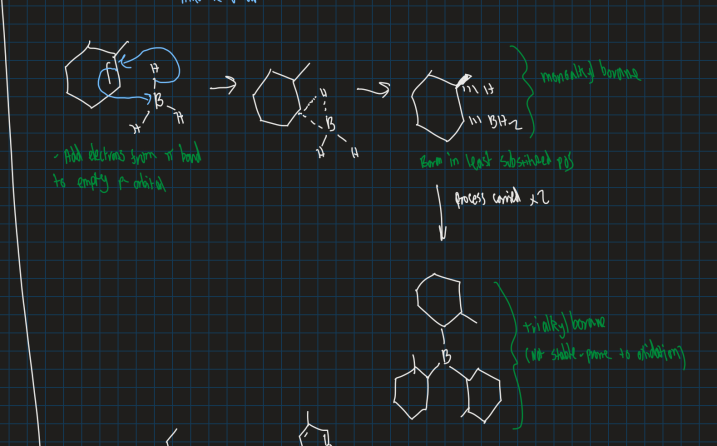
Show reaction of borane reacting with 1-methyl cyclohexene
Boron in least substituted position
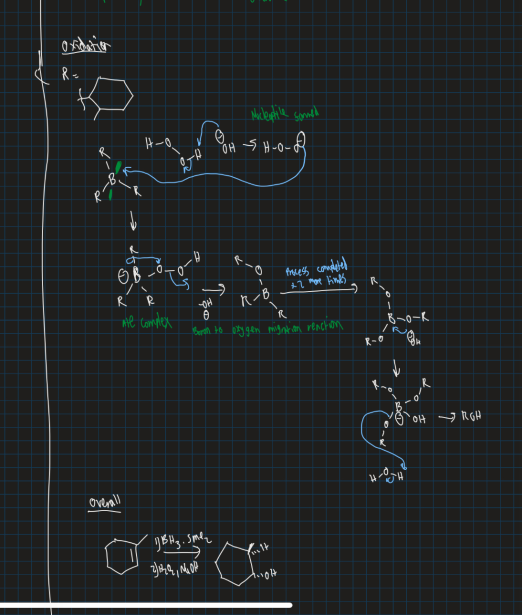
Show reaction of BH3 . SMe2 , H2O2 and NaOH reacting with methyl cyclohexene
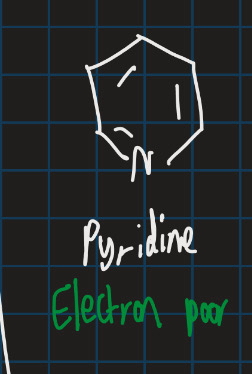
Is pyridine electron rich or poor?
Electron poor

Is pyrrole electron rich or poor?
Electron rich
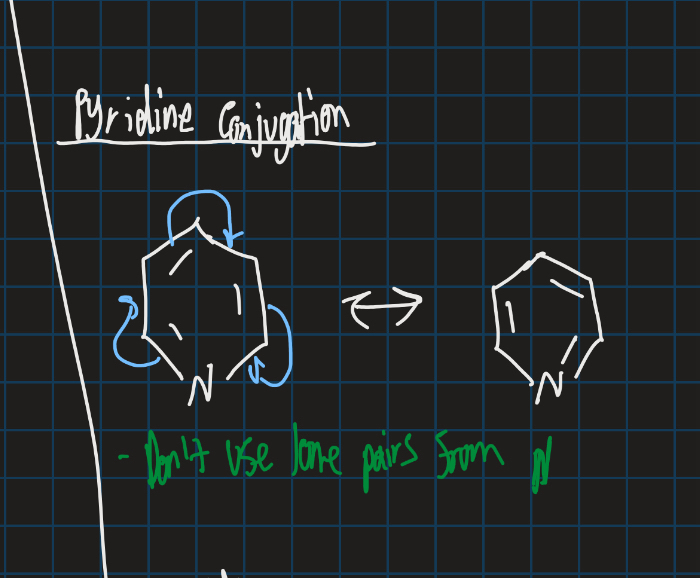
How is pyridine conjugated? (Show resonance structure)
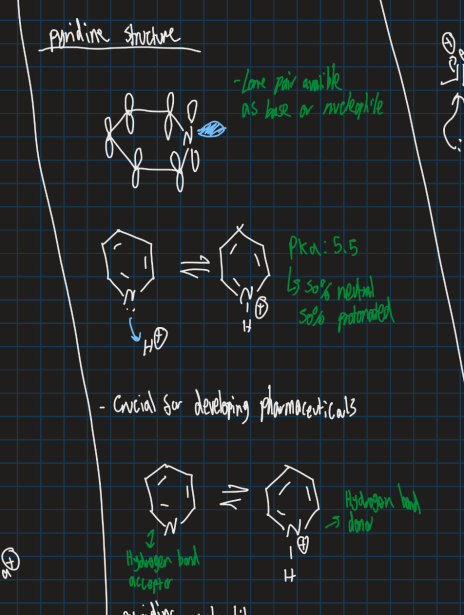
Show the orbital structure of pyridine and its acidity
Pka of 5.5 → Created 50% neutral and 50% protonated product
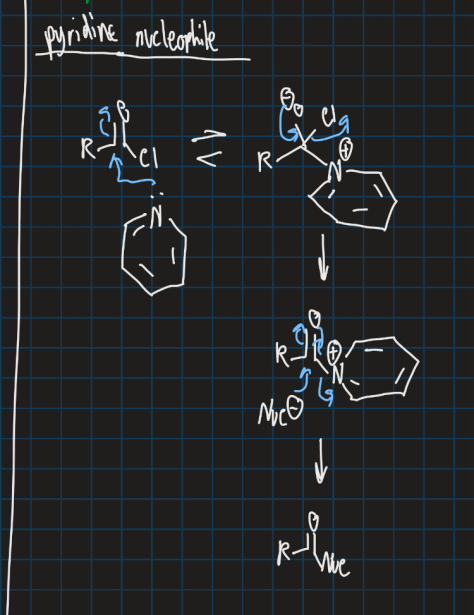
Show pyridine acting as a nucleophile (react with acyl chloride)
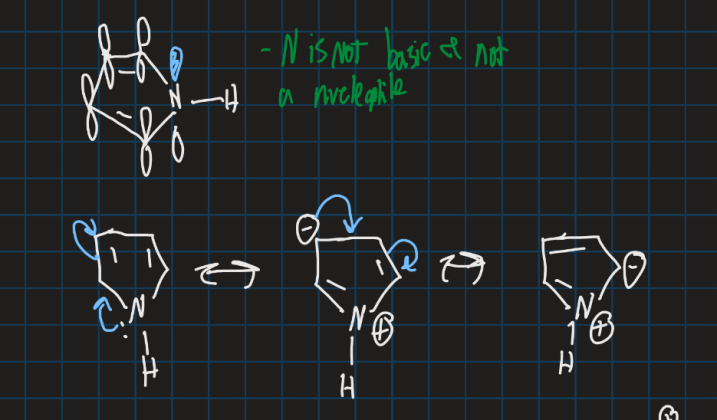
Show how pyrrole is aromatic
Using Huckel’s rule, if n=1 then 6 pi electrons needed for aromaticity

Show how pyrrole is not a nucleophile using resonance structures
Nitrogen atom donates into the aromatic ring so not enough electron density to act as a nucleophile
What is the dimethyl amine reacting with aldehyde to form a pyrrole ring - Mannich reaction
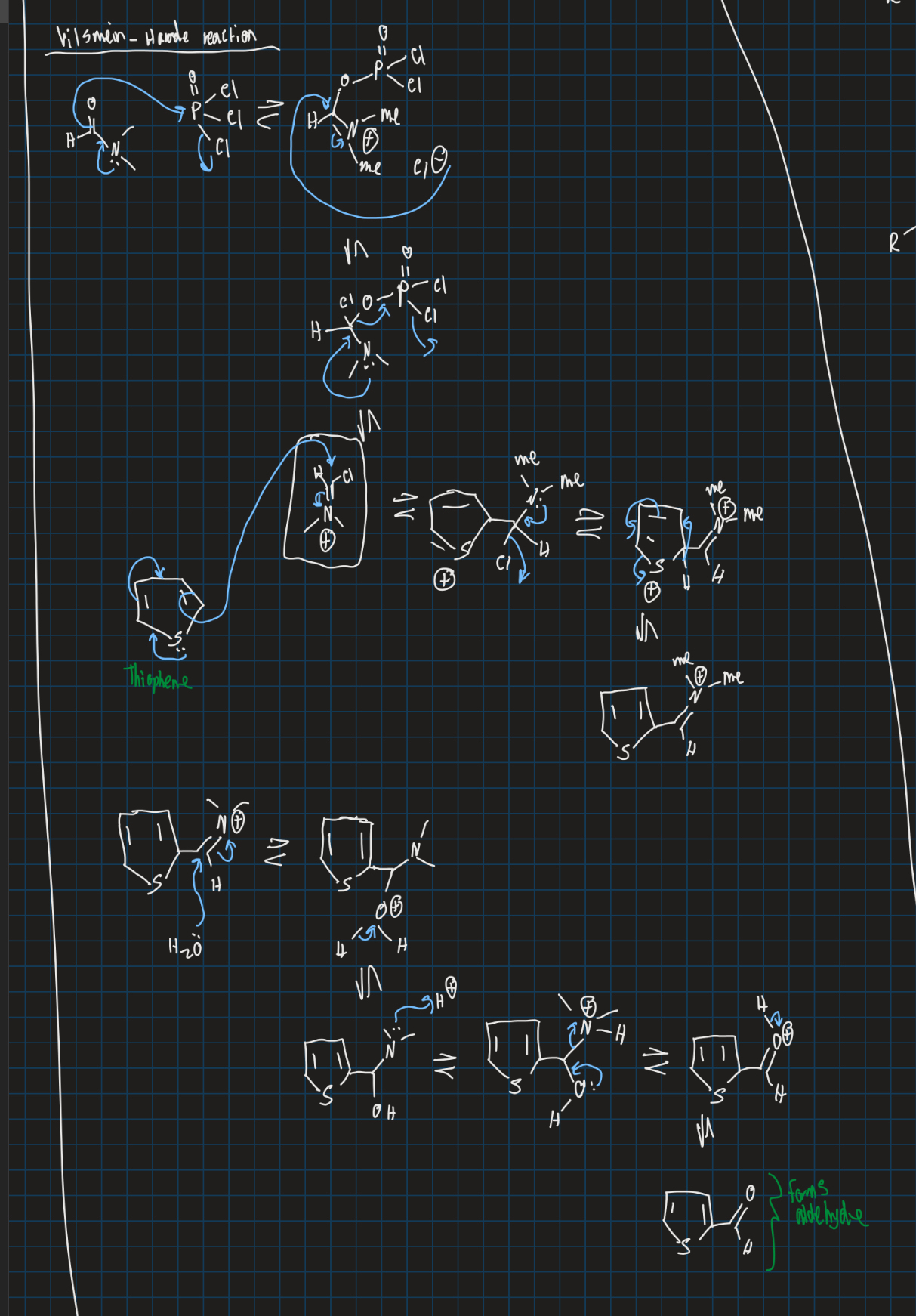
What is the Vilsmeier - Haack reaction and show N,N-dimethyl acetaldehyde reacting with PCl3, thiophene, H2O
Formyl group added to electron rich aromatic rings like pyrrole
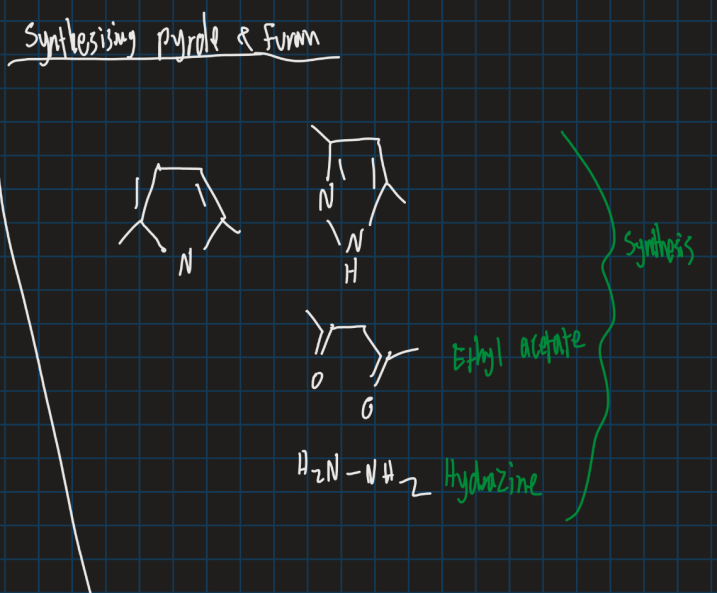
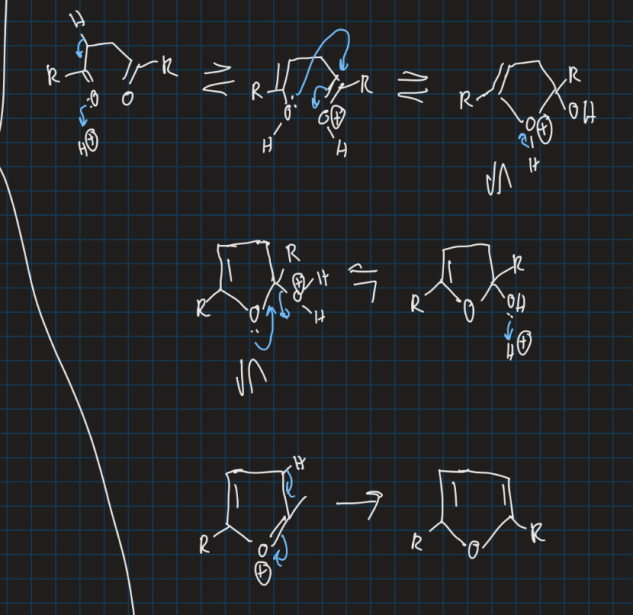
How can pyrrole and furan be synthesised?
Use ethyl acetate
Use hydrazine
Show formation of hemiaminal by adding ammonia to protonated ketone
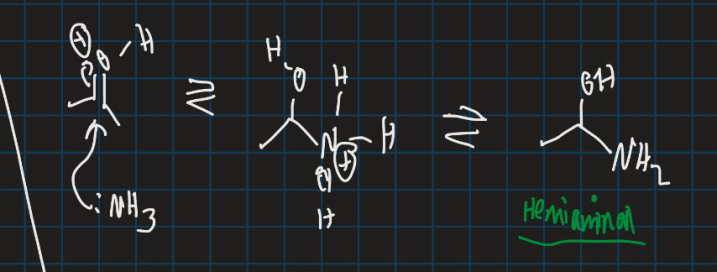
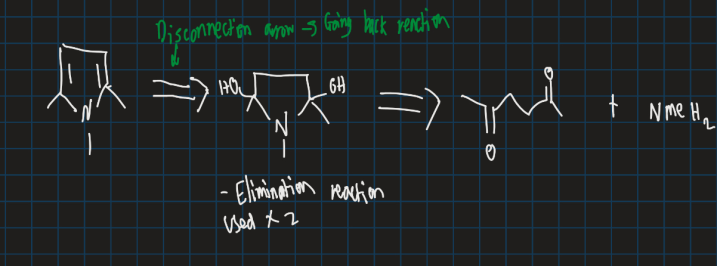
How is pyrrole synthesised?
Form diol first
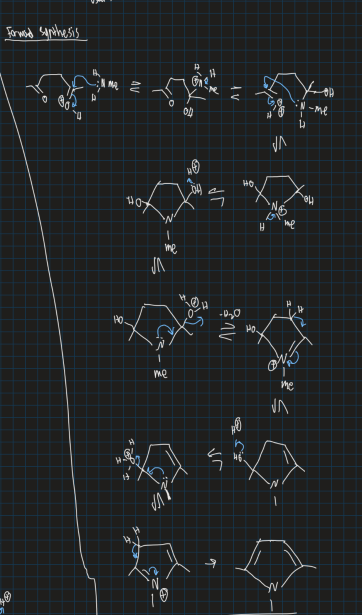
Show mechanism of forming pyrrole from ethyl acetate, hydrazine
How is furan synthesised?
Similar to pyrrole, diol also forms
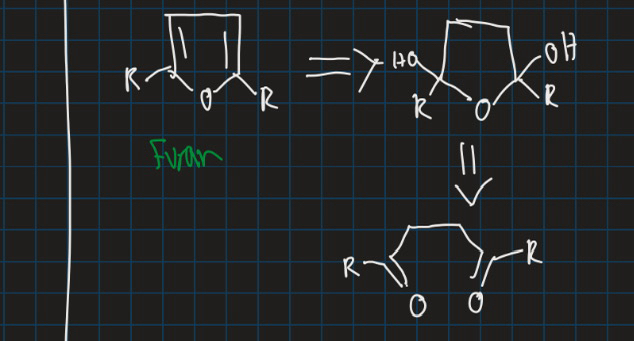
Show mechanism for formation of furan from ethyl acetate using acid
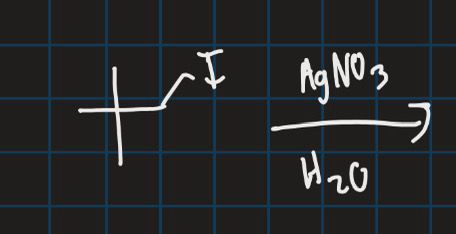
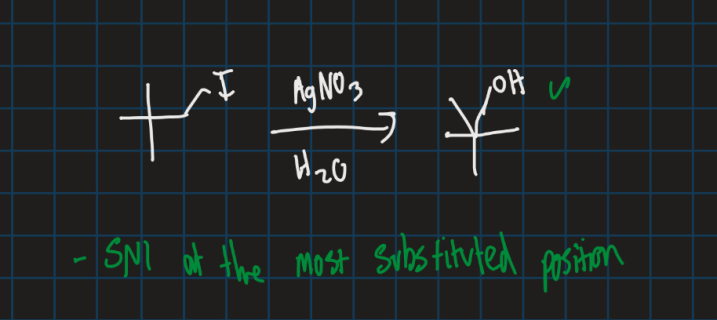
Complete this reaction
Sn1 reaction so OH goes at the most substituted carbon position
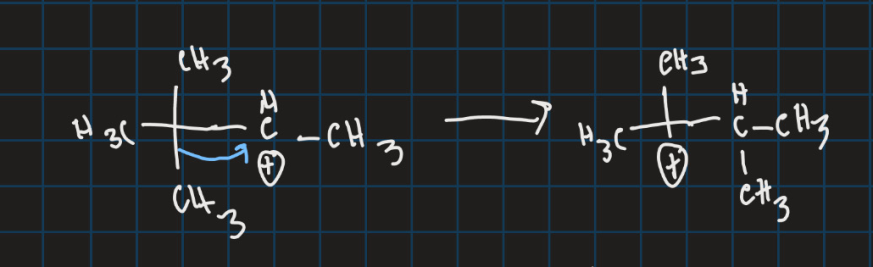
What is the filled orbital and the empty orbital in this reaction?
Filled orbital is the C-C sigma bond
Unfilled orbital is the carbocation p orbital
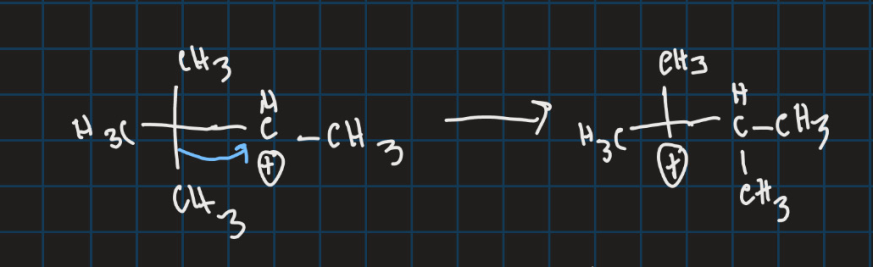
Why does this reaction happen in terms of orbitals?
C-C bond that moves is in same plane as empty orbital for max overlap
Also C-C bond doesn’t break before new bond forms to keep energy low and stable
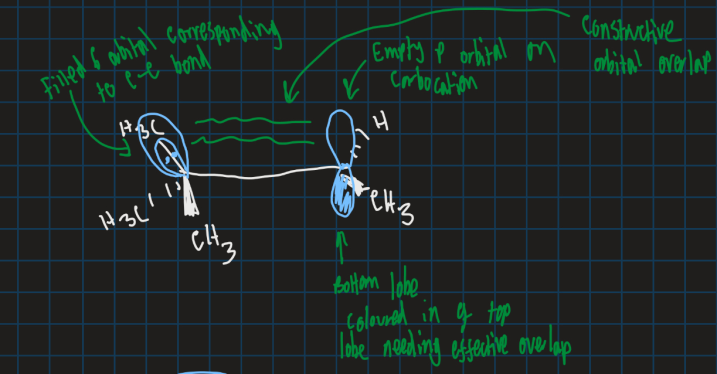
How does SN1 reaction compare with carbon rearrangement?
Carbon rearrangement occurs within a molecule
SN1 reaction requires a strong nucleophile to fill empty orbital in carbocation

Why does carbon rearrangement happen?
Selectivity of rearrangements driven by relative stabilities of carbocations
Thermodynamics and kinetics
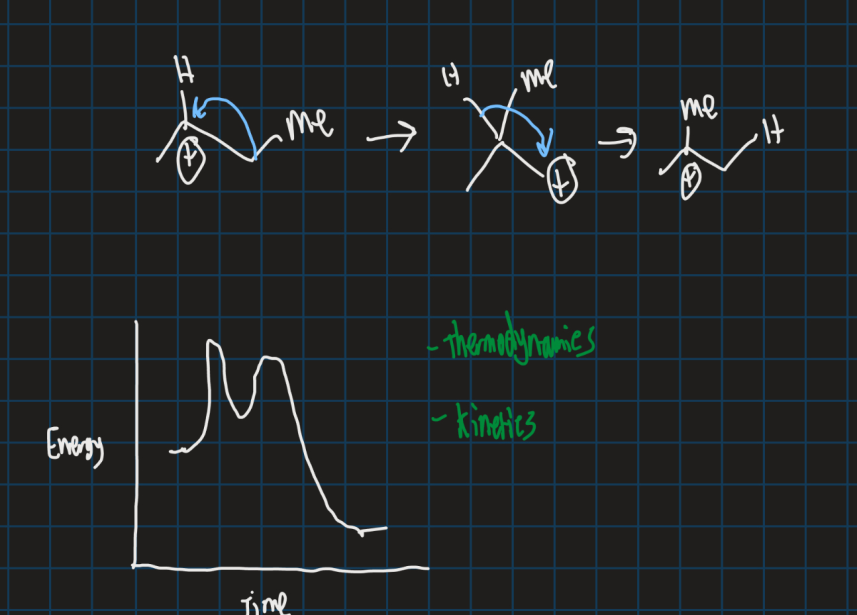
What is Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement?
Alkyl group or hydrogen migrates from one carbon to another carbon forming a more stable carbocation
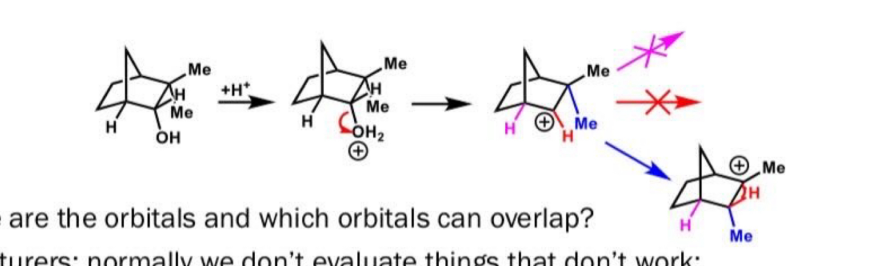
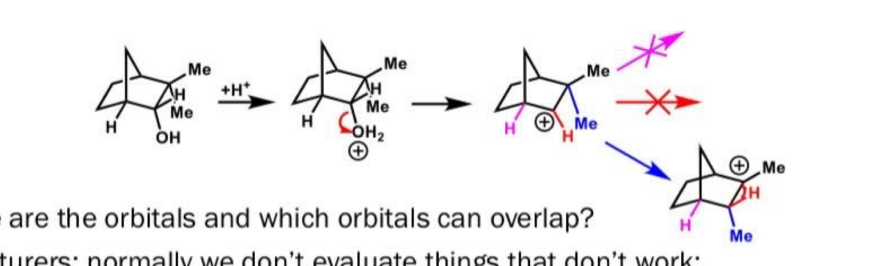
What is the empty orbital and filled orbital in this reaciton?
Empty orbital = Carbocation p-orbital
Filled orbital = Blue C-C sigma orbital (overlaps with empty p- orbital for reaction to proceed )
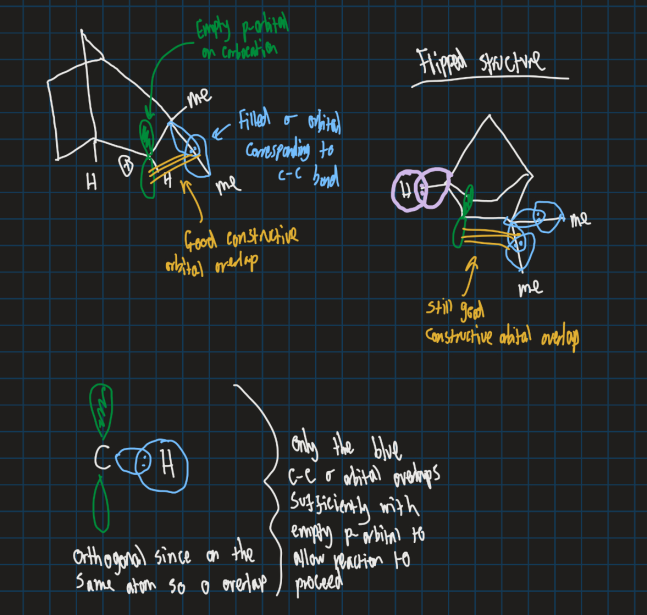
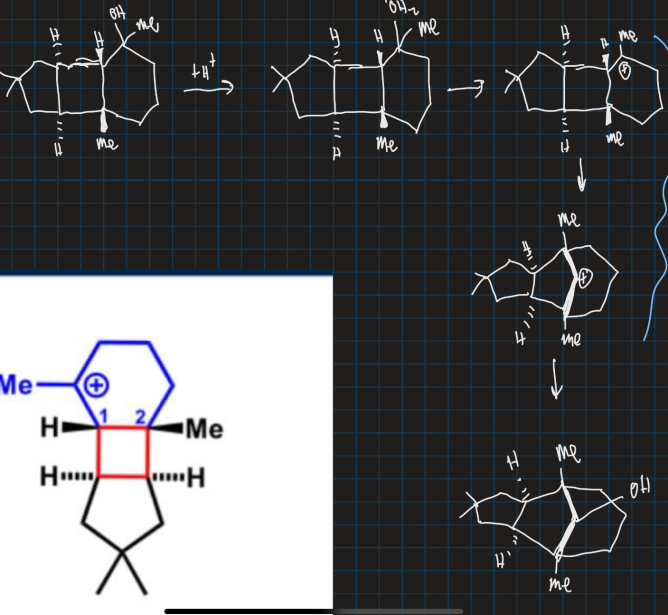
Why does the carbocation go from tertiary to secondary in this reaction?
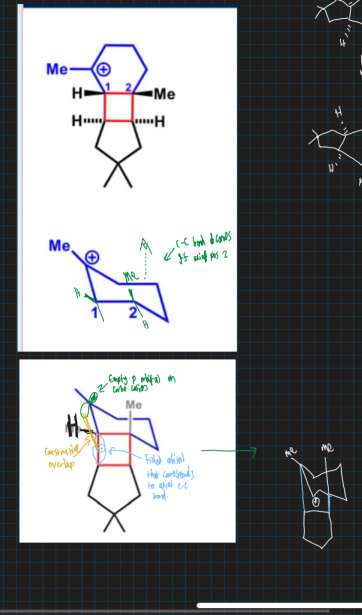
What are pinacol rearrangements?
-Acid-catalysed rearrangements of vicinal diols that produces carbonyl compounds
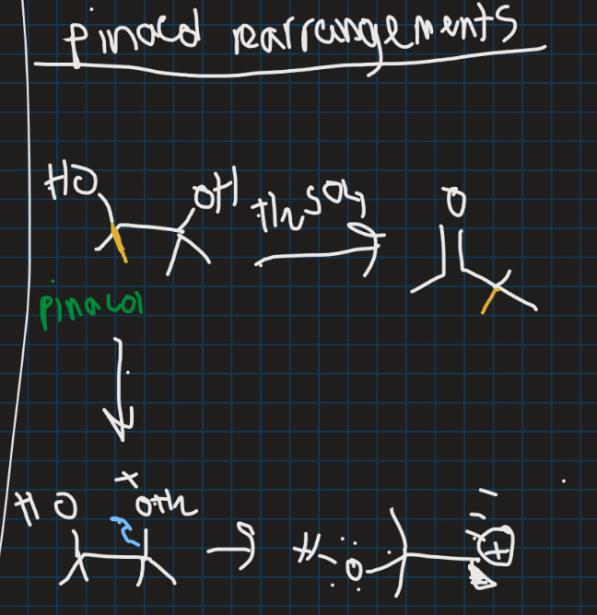
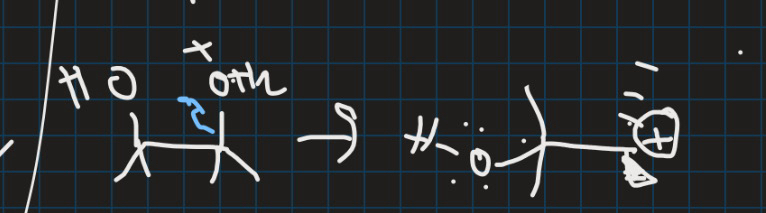
What is the empty and what is the filled orbital in this reaction and why (draw orbital structure)?
Filled = C-C sigma orbital
Empty = Carbocation p-orbital
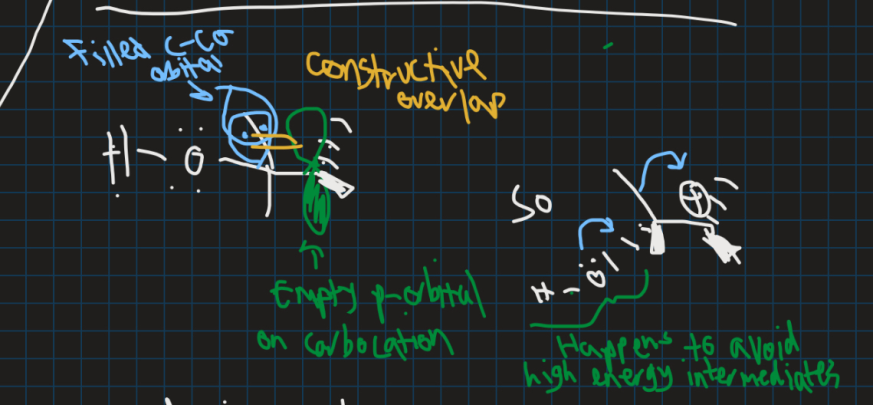
How does this reaction produce cyclopentanecarboxyaldehyde? (use pinacol rearrangement)
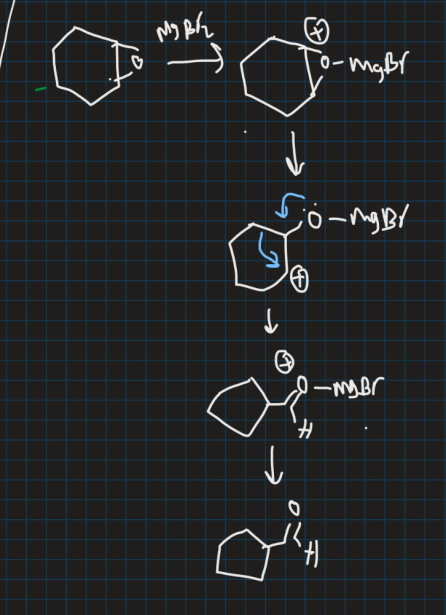
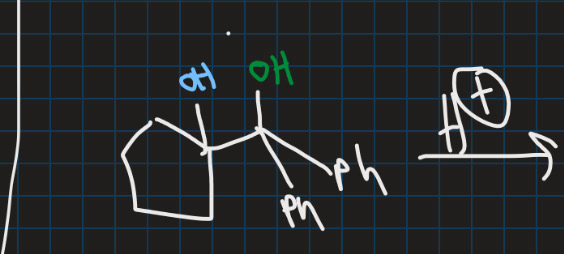
Show asymmetric pinacol rearrangement
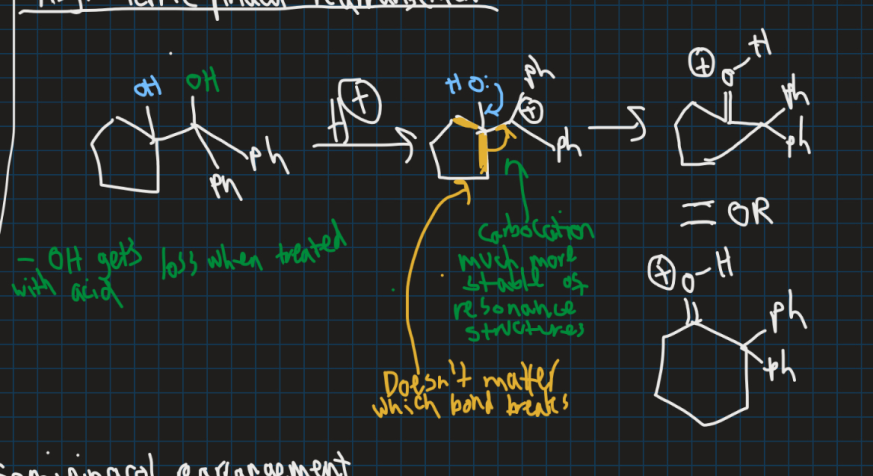
What is asymmetric pinacol rearrangement?
When 2 carbons of 1,2-diol are not equivalent so more than 1 rearrangement pathway is possible → but one major product
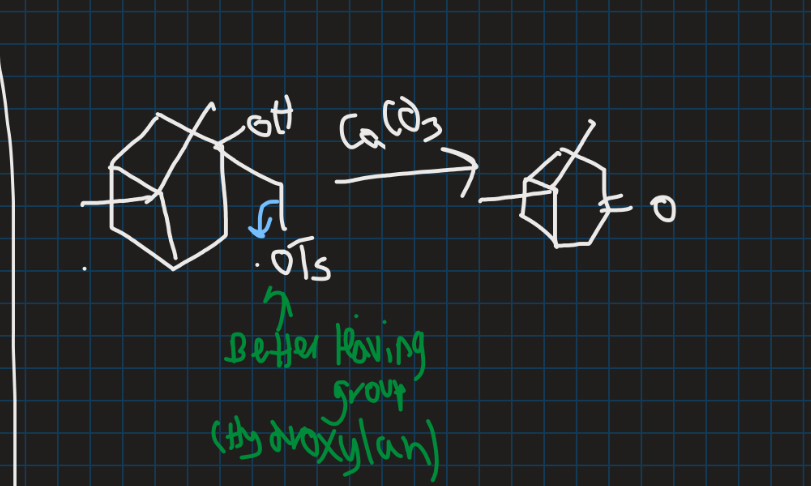
What is semi pinacol rearrangement?
When carbon stability is no longer the deciding factor
→ No longer requires 1,2-diol
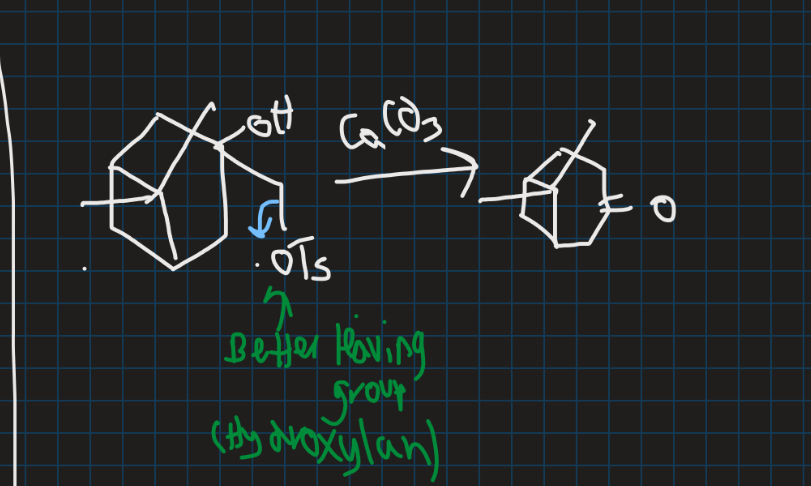
Why does OTs leave and why is there only one product for semi pinacol rearrangement?
OTs is a better leaving group → OH is bad leaving group
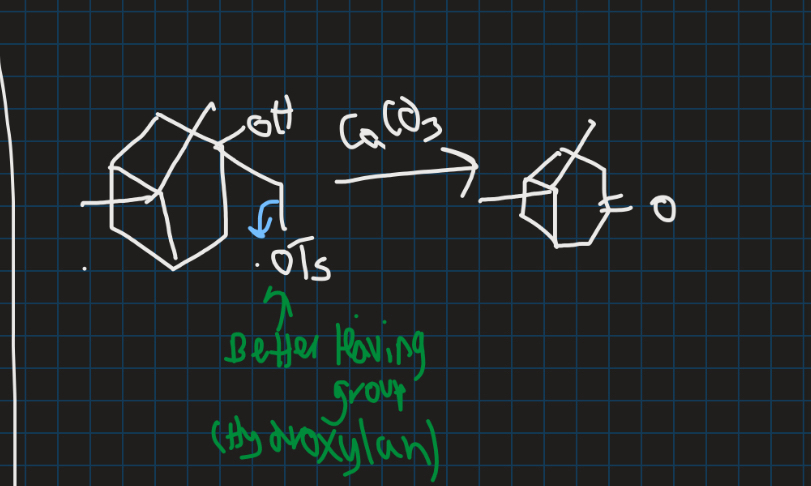
Show the intermediate of this reaction
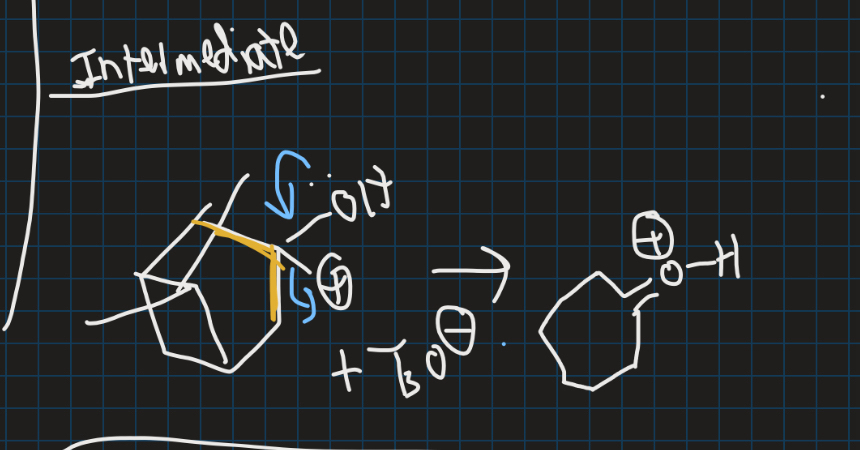
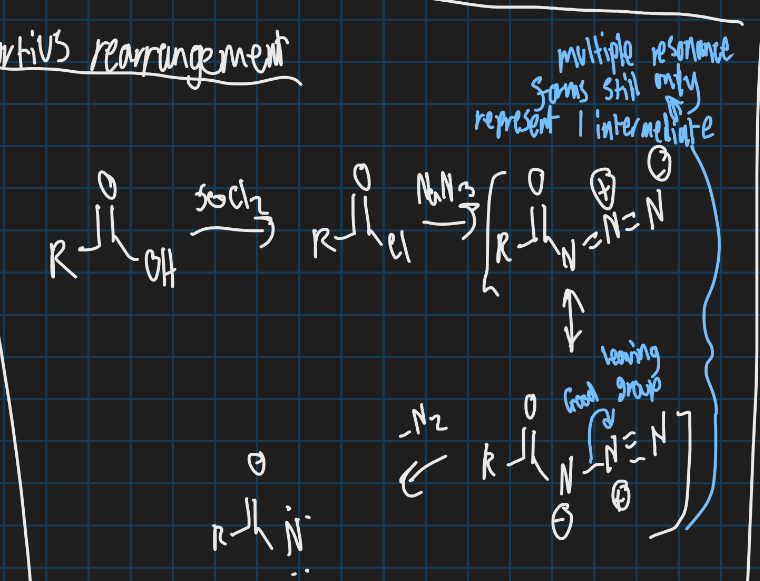
What is the curtius rearrangement?
Converts carboxylic acid into isocyanate with loss of N2
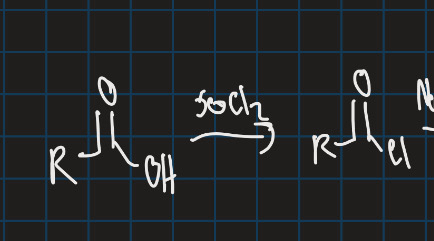
Complete this reaction (use curtius rearrangement)
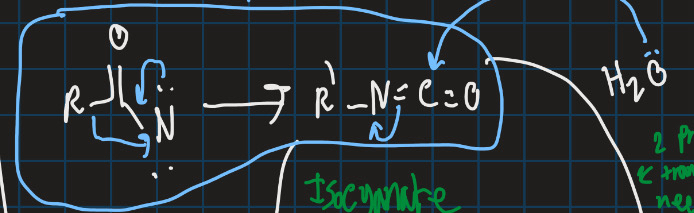
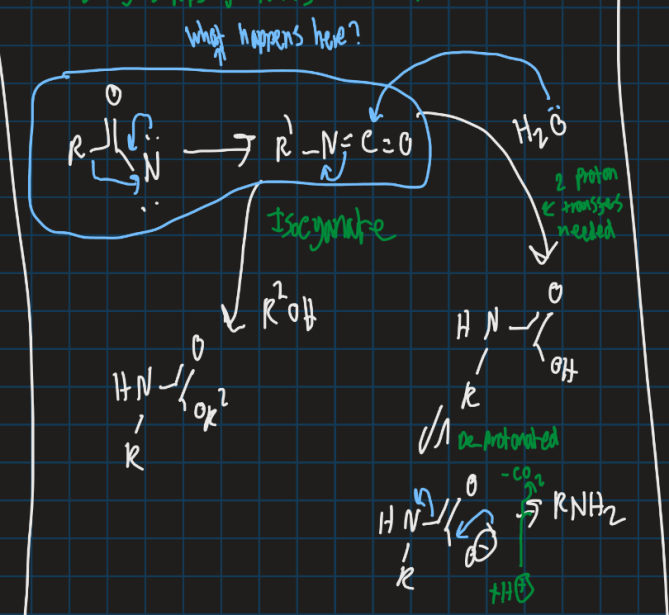
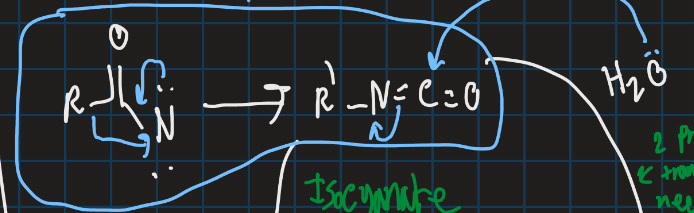
How can isocynate be turned into amine or substitute with ester?
Give orbital structure for this rearrangement step
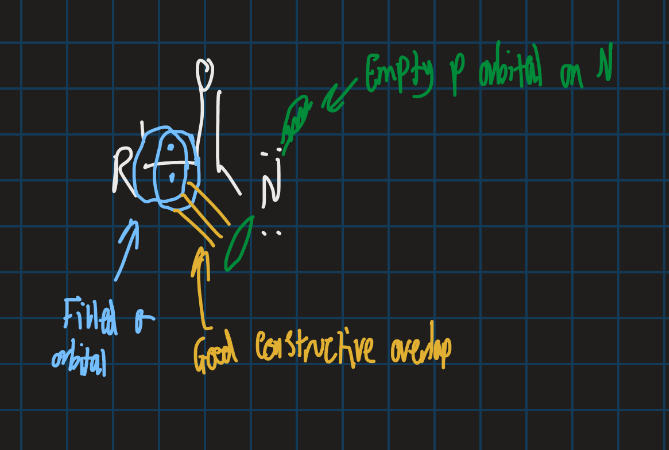
What is the Hoffman rearrangement?
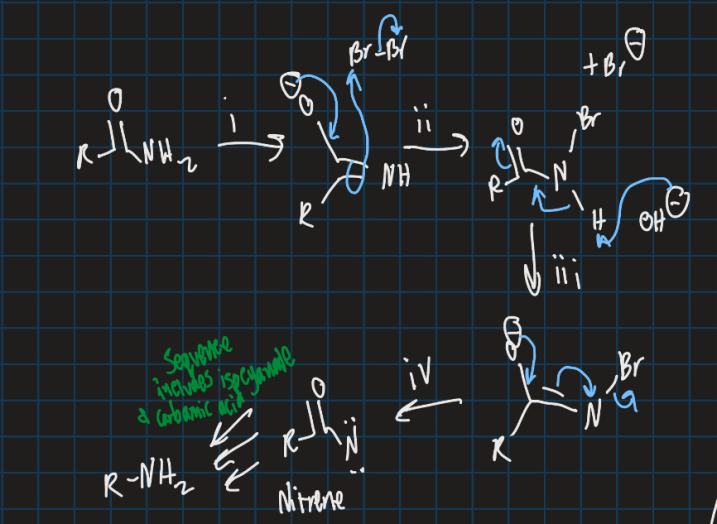
Converts primary amide into primary amine using halogen and strong base
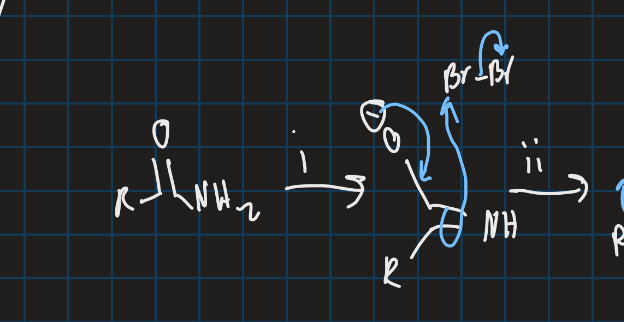
Complete this reaction using the Hoffman rearrangement
1 nitrene formed
How is Lossen rearrangement different from Hoffman rearrangement?
Uses TsCl instead
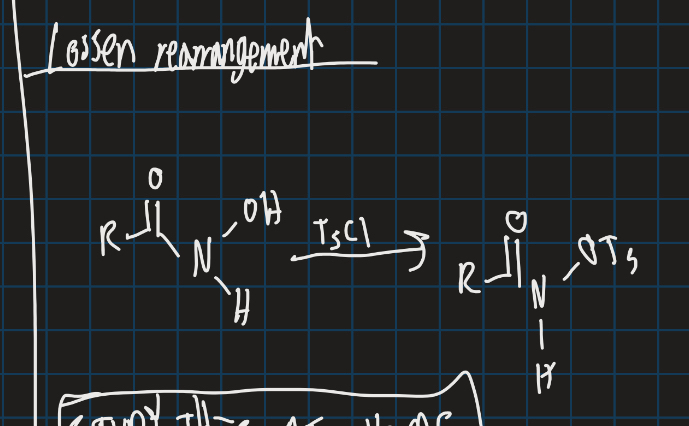
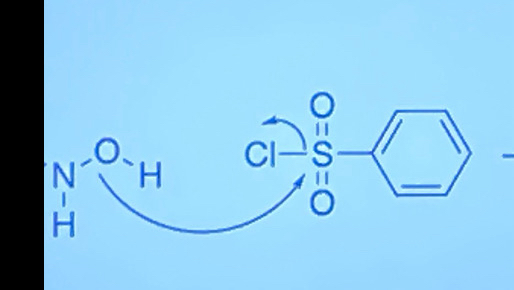
Complete this reaction using Lossen rearrangement mechanism (RCONHOH)

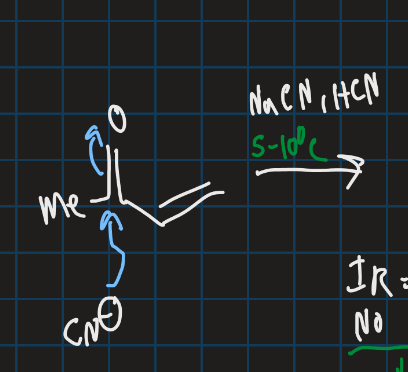
Complete this addition reaction
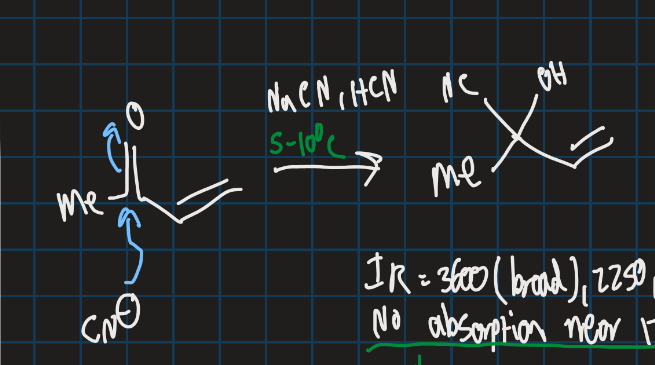
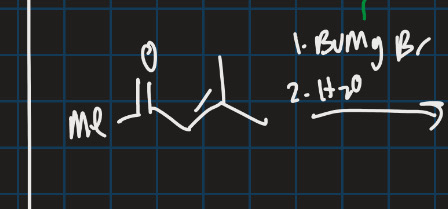
Complete this addition reaction
What is the typical IR spec value for carbonyl groups
Around 1700 cm-1 (varies)
Why doesn’t Me-S attack at carbonyl here?
Alkene turned from nucleophile to electrophile