Anatomy and Physiology Exam 1
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Oregon State University A&P
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Hypertonic
Cells lose water and shrink and shrivel up.
Hypotonic
Cells gain water and swells
Isotonic
extracellular fluid solute concentration is the same as inside the cell
Osmosis
The diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane to maintain equilibrium
How does water move relative to the solution gradient?
Low to high solute concentration.
Body fluids are solutions of water and dissolved solutes like ____________.
ions, glucose, amino acids, hormones, potassium, sodium
The plasma membrane is a _______________ barrier that allows some ions and molecules to pass through.
selectively permeable
What are the two mechanisms responsible for moving necessary substances across the membrane?
Active and passive transport
In passive transport, how do solutes move relative to the concentration gradient?
High to Low (down)
In active transport, how do solutes move across their concentration gradient?
Low to high (Up)
What form of transport is diffusion?
Passive transport because of the concentrations.
Diffusion
The movement of any substance from a high to a low concentration.
Is osmosis active or passive?
Passive - no energy is required.
What type of molecules use simple diffusion?
Small, nonpolar molecules like oxygen (O₂), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and lipid-soluble substances.
Osmosis is a type of diffusion.
True
Simple diffusion has no max rate and is not _______.
protein limited
Facilitated diffusion has a lower max rate, and is _______.
limited by the number of transport proteins.
What is the cell membrane made up of?
Phospholipids
What features do phospholipids have?
A hydrophilic (polar) head - loves water
A hydrophobic (non-polar) tail - repels water
What are the two types of passive transport?
simple and facilitated diffusion
Autoregulation
A part of your body self-regulates to maintain homeostasis in that specific area.
Enzymes _______.
do most of the work in cells
There is more Na+ outside of cells than inside. Given this, how does Na+ enter a typical human cell?
facilitated diffusion
Which kind of section would best allow you to see concentric lamellae in bone?
Transverse
Mesenchymal cells can differentiate to become any kind of ______ cell.
connective tissue
Intramembranous ossification
Occurs to form the flat bones of the skull
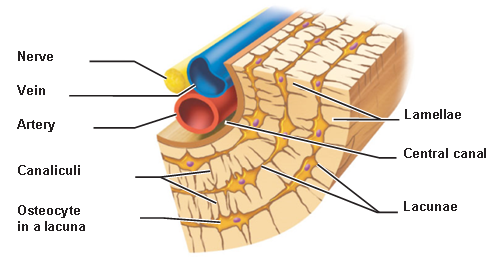
lamelle
Layers of bone matrix that strengthen and organize compact bone.
They help bones handle stress from multiple directions without breaking.
myositis
inflammation of the muscles
Osteoclasts
Large cells that break down bone tissue to help remodel bone and regulate calcium levels.
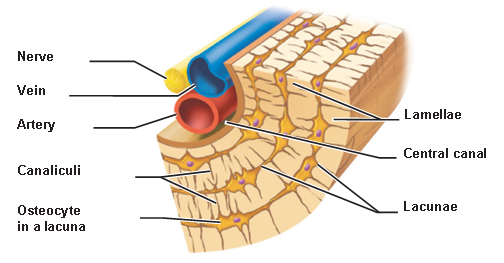
lacunae
Found between the lamellae in compact bone, and store osteocytes.
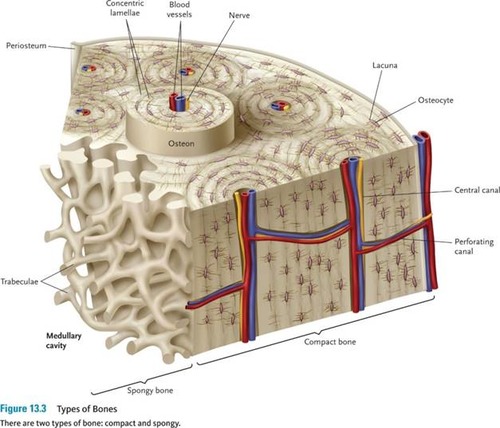
Osteon
Basic structural and functional unit of compact bone.
What molecules utilize facilitated diffusion?
Amino acids, sugars, nucleotides
What kind of diffusion requires no energy from the cell?
simple diffusion
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein fibers that provides structure, shape, and support for the cell; also helps with movement of organelles and the cell itself.
Cillia
Short, hair-like structures on the cell surface that move in waves to help the cell move or move substances along its surface.
Flagella
Long, whip-like tails that propel the cell through fluid; usually one or a few per cell.
Ribosomes
Small structures that build proteins by linking amino acids together; can be free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER.
Rough ER
Network of membranes covered in ribosomes; modifies and transports proteins made by ribosomes.
Smooth ER
Membrane network without ribosomes; makes lipids, detoxifies harmful substances, and stores calcium.
Nucleus
Control center of the cell that contains DNA and coordinates activities like growth and protein production.
Golgi Apparatus
Stack of flattened membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for storage or transport.
Lysosomes
Organelles filled with digestive enzymes that break down waste, old cell parts, and foreign materials.
Transport Vessicles
Small membrane sacs that carry materials between organelles or to and from the cell membrane.
Protein Synthesis
The process by which cells make proteins; includes transcription (DNA → mRNA) and translation (mRNA → protein).
Transcription
The process in the nucleus where a gene’s DNA sequence is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA).
Translation
The process in the cytoplasm where ribosomes read mRNA and assemble amino acids into a protein chain.
Endocytosis
Process by which the cell membrane folds inward to bring substances into the cell.
Exocytosis
Process where vesicles fuse with the cell membrane to release materials outside the cell.
Cellular Respiration
Process by which cells break down glucose to produce ATP, mainly in the mitochondria.
Cartilage is a form of connective tissue.
true
What do lamelle do?
bone remodeling
structural support
organization of bone matrix
positive feedback
Strengthen or amplify a change until a specific event is completed “pushes it farther”.
Negative Feedback
Keep the body stable (maintain homeostasis)
Ribosomes
build proteins
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesis and transport of proteins
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
detoxification, lipid synthesis, calcium storage
The Nucleus
the cells control center
The golgi apparatus
modifies proteins and lipids, produces lysosomes,
lysosomes
digestive enzymes
Basal layer of epithelial tissue
bottom layer of tissue
apical layer
top layer of epithelial tissue
what bones are formed by Intramembranous Bone Formation
clavicle, mandible, and flat bones of the skull
What bones are formed by endochondral bone formation?
All other bones (specifically long bones)
What part of the bone in endochondral bone formation forms first?
The middle (diaphysis)
what appears first in endochondral bone formation? Bone matrix or Blood vessels?
Bone matrix
Osteoblasts __________.
Build bone. They secrete new bone matrix (osteoid)
osteoclasts ________.
Break down bone (resorption). They release enzymes and acids that dissolve bone tissue