5.3.1 Transition element
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What is a transition element ?
D block element that forms at least one ion with a incomplete d subshell
Which of the period 4 d-block elements are not transition metals?
Scandium and zinc
what is the electron configuration of Cr
[Ar] 4s¹ 3d⁵
what type of ions do transition metals form
positive ions
how to work out electronic configuration for d block ions ?
remove 4s subshell e⁻
remove 3d subshell e⁻
Why is scandium not a transition element?
Scandium only forms Sc³⁺ which has a empty D subshell
Why is zinc not a transition element?
Only forms Zn²⁺ which has a full D subshell
what are some properties of Transition metals?
Form complex ions
Good catalysts
exist in variable oxidation states
Why do they exist in variable oxidation states?
energy levels of 4s and 3d subshell is similar,
different numbers of e⁻ can be lost or gained using similar energy
Disadvantages of using transition metals catalysts?
compounds and metals are toxic --> cause health risks
name 2 transition metal catalyst and there uses ?
Fe - catalyst in the Haber process
MnO₂ - catalyst in the decomposition of H₂O₂
Advantages of using transition metals catalyst?
allow reactions to happen faster at lower temperatures/pressure -- reduces energy usage.
why do transition metals have special chemistry properties
they have a incomplete d subshell
What is a complex ion?
transition Metal ion surrounded by co-ordinately bonded ligands
What is a ligand?
a ion or molecule that donates e- to co-ordinately bond to a central metal ion
what is a coordinate bond?
Covalent bond where both electrons are supplied from the same species
what do all ligands have
a lone pair of e⁻ to form the coordinate bond
what are the different types of ligands
Monodentate ( 1)
Multidentate ( multiply)
Bidentate ( 2)
Examples of monodentate ligands
:NH₃
Cl⁻
:CN⁻
H2O:
monodentate ligand
species with 1 lone pairs that can form co-ordinate bonds
Multidentate ligand
species with more then 1 lone pairs that can form co-ordinate bonds
Bidentate ligand
species with 2 lone pairs that can form co-ordinate bonds
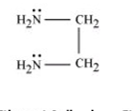
example of a bidentate ligand ( (Cu(en)₂)²⁺ )
2 lone pairs on the Nitrogen so it can 2 coordinate bonds
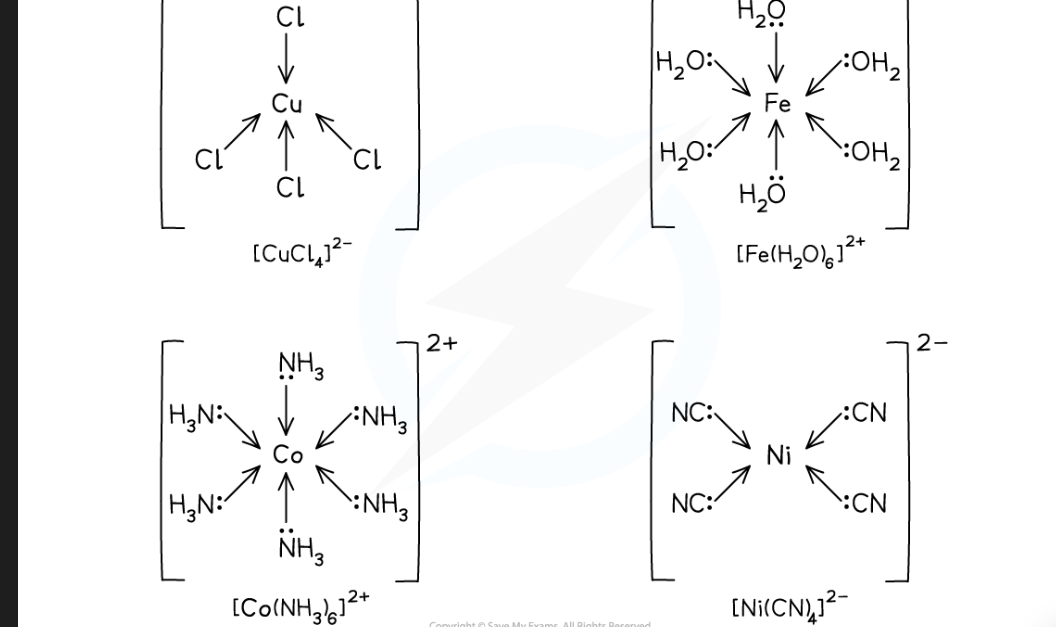
what is the shape of the complex ions based on?
coordination number ( number of coordinate bonds formed with the central metal ion)
what is the shape of a complex ion with 6 coordinate bonds
Octahedral shape
what is the bond angle of a octahedral shape
90°C
what are aqueous metals
hexaaqua complexes
what does `en` stand for
ethane-1,2-diamine ligand
what is the shape of a complex ion with 4 coordinate bonds
Tetrahedral shape
what is the bond angle of a tetrahedral shape
109.5°C
What is the other shape a tetrahedral shape could have
Square planar
what is the bond angle of Square Planar shape
90°C
Bidentate ligand image

monodentate image
how to test for transition metals
Add NaOH (aq)
what colour is Cu²⁺ precipitates
blue precipitate
what colour is Fe²⁺ precipitates
green precipitate
what colour is Fe³⁺ precipitates
Brown precipitate
what colour is Mn²⁺ precipitates
buff precipitate
what colour is Cr³⁺ precipitates
green precipitate
ionic equation for the reaction between Fe²⁺ and NaOH
Fe²⁺(aq) + 2OH⁻( aq) → Fe(OH)₂ (s)
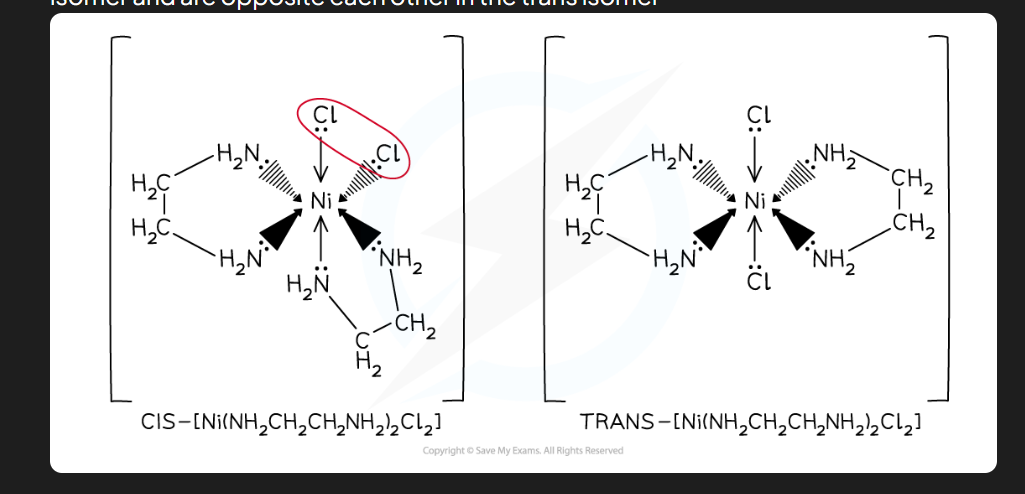
stereoisomerism definition
same structural formula, different arrangement in space
what is a trans isomer in complex ions
Ligands are 180°C apart
what is a CIS isomer in complex ions
ligands are less then 180°C apart
CIS/ Trans isomers ( Image)
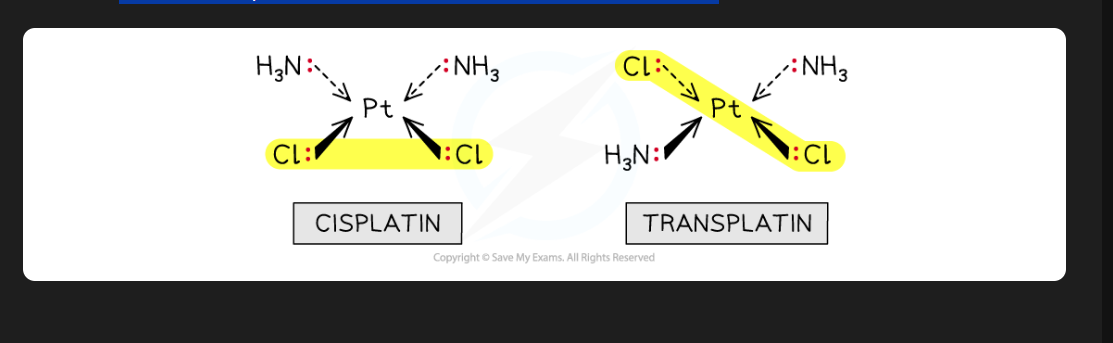
differences between cis and trans platin
CIS platin is a anti-cancer drug ( binds to DNA in cancer cell)
Trans platin is not a anti cancer drug
cis and trans isomerism in square planar molecules ( Image)
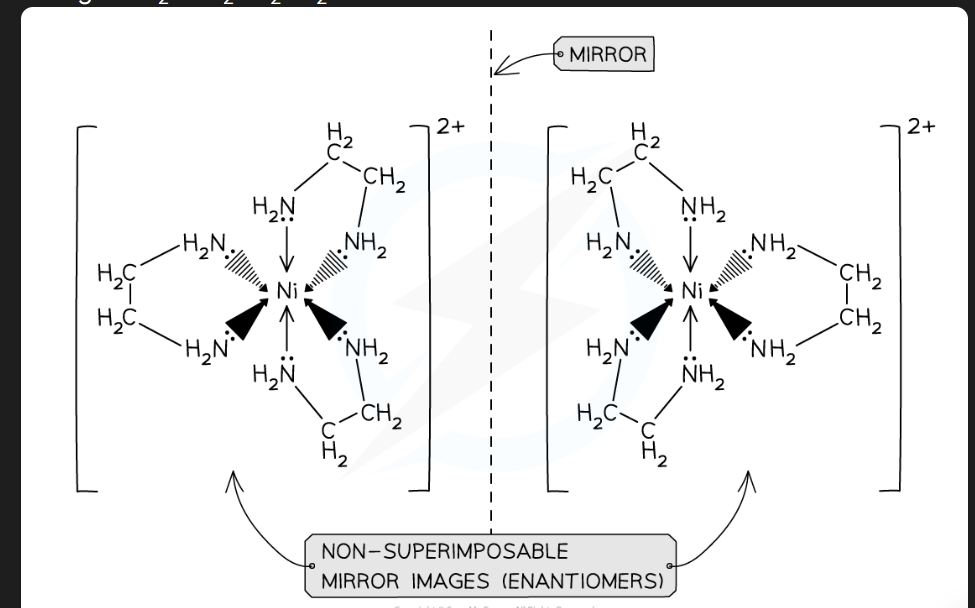
what type of complex ions have optical isomers
Octahedral complexes with bidentate ligands
Non- Superimposable mirror image ( image)
Ligand substitution what do transition metals exist as
hexaaqua complex ions ( has 6 H₂O ligands attached )
what colour is the Cr³⁺ metal aqua ion
green solution
when can ligands be substituted without change to co-ordination / shape
when ligands are similar sized and similar charge
which ligands can be substituted without change to co-ordination / shape and why
NH₃, H₂O, OH⁻ and CN ⁻
all similar size
equation for [ Cr ( H₂O)₆ ]³⁺ + NH₃ ( Ligand substitution)
[ Cr ( H₂O)₆ ]³⁺ (aq) + 6NH₃ (aq) → 6H₂O + [ Cr (NH₃)₆ ]³⁺(aq)
what is the shape when H₂O → Cl⁻ ligands are substituted
Octahedral → Tetrahedral
which ligand is a different size to the others
Cl⁻
equation for [ Cu ( H₂O)₆ ]²⁺ + HCl ( Ligand substitution)
[Cu( H₂O)₆ ]²⁺(aq) + 4Cl⁻(aq) ⇌ [CuCl₄]²⁻ + (aq) 6 H₂O (l)
what is the colour change from [ Cr ( H₂O)₆ ]³⁺ to [ Cr (NH₃)₆ ]³⁺
green→ purple
colour from [ Cu ( H₂O)₆ ]²⁺ to [CuCl₄]²⁻
blue → yellow- green
when does partial substitution of NH₃ happen
when excess NH₃ is added ( Cu )
partial ligand substitution of [ Cu ( H₂O)₆ ]²⁺ and excess NH₃
[ Cu ( H₂O)₆ ]²⁺(aq) + 4NH₃(aq) → 4H₂O(l) + [ Cu ( NH₃)₄ ( H₂O)₂ ]²⁺( aq)
what is the only shape Ag/Pt can form
square planar
what is the only shape Cl₂ can form and why
tetrahedral
Cl₂ is too large
which transition metal always undergoes partial ligand substitution with NH₃
Copper ( Cu)
what is the reactant when forming a chlorine ligand
HCl
what are the type of reactions complex ions undergo
precipitation reactions
ligand substitution
when do transition metals undergo precipitate reactions
when reacted with NaOH or NH₃ (aq)
What is the colour of the precipitate in the reaction between NaOH/ NH₃(aq) and Cu?
Blue precipitate
What is the colour of the precipitate in the reaction between NaOH/ NH₃(aq) and Fe²⁺
Green precipitate
What is the colour of the precipitate in the reaction between NaOH/ NH₃(aq) and Fe³⁺
Brown precipitate
What is the colour of the precipitate in the reaction between NaOH/ NH₃(aq) and Mn²⁺
Buff precipitate
What is the colour of the precipitate in the reaction between NaOH/ NH₃(aq) and Cr³⁺
Dark green precipitate
What is the colour of the precipitate in the reaction between excess NH₃ and Cr³⁺
green precipate
What is the Ionic Equation between Fe³⁺ and NaOH/ NH₃ ( precipitation reaction)
Fe³⁺ (aq) + 3OH⁻ (aq) → Fe(OH)₃(s)
What is the Ionic Equation between Fe²⁺ and NaOH/ NH₃ (precipitation reaction)
Fe²⁺ (aq) + 2OH⁻ (aq) → Fe(OH)₂(s)
What is the Ionic Equation between Mn²⁺ and NaOH/ NH₃ (precipitation reaction)
Mn²⁺ (aq) + 2OH⁻(aq) → Mn(OH)₂(s)
What is the Ionic Equation between Cr³⁺ and NaOH/ NH₃ ( precipitation reaction)
Cr³⁺(aq) + 3OH⁻(aq) → Cr(OH)₃(s)
What is the colour of the precipitate in the reaction between excess NH₃ and Cu²⁺
Dark blue
what is the colour of the chromate ion (Cr₂O₇²⁻)
orange
what are the colour changes in the oxidation of Cr³⁺→CrO₄²⁻ →Cr₂O₇²⁻
Cr³⁺ (green)→CrO₄²⁻ ( yellow) →Cr₂O₇²⁻ ( orange)
what reagnant reduces Fe³⁺
KI
what reagant oxidises Fe²⁺
MnO₄⁻/H⁺
what reduces Cr₂O₇²⁻
Zn/H⁺
what reduces Cu
I⁻
Shape of a central ion with 2 mono-dente ligands
Linear
how does haemoglobin transport O₂ around body
O₂ lone pair forms a co-ordinate bond with Fe (II)
O₂ bonds reversibly (can be replaced with CO₂/H₂O)
what are elements in the periodic table determined by
increasing atomic number
what is a d block element
element with highest energy electron in d subshell
why is CO toxic ?
binds irreversibly to Fe ( II)
what happens to Aqueous ionic molecules during ligand substitution
dissociate into ions
cations are hexa aqua