4.27-4.28 Bromination
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:41 AM on 8/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
1
New cards
Halogenation
Addition reaction between a compound and a halogen, resulting in the halogen being added to the compound.
2
New cards
Bromination
Addition reaction between a compound and bromine, resulting in bromine being added to the compound
3
New cards
Addition reactions between bromine and alkenes
* No heat, light, or catalyst required for reaction
* Reaction uses bromine water (an aqueous solution)
* C=C double bond breaks → forms new single bonds
* Carbon atoms of original functional group are now free radicals because they have unpaired valence electrons
* Bromine’s valence electron covalently bonds to unpaired valence electrons of carbon free radicals, the bromine atoms add across to the carbon free radicals
* Halogen atoms always add to carbon atoms across C=C double bond → addition reaction works for any halogen and any alkane
* All halogens exist as diatomic molecules
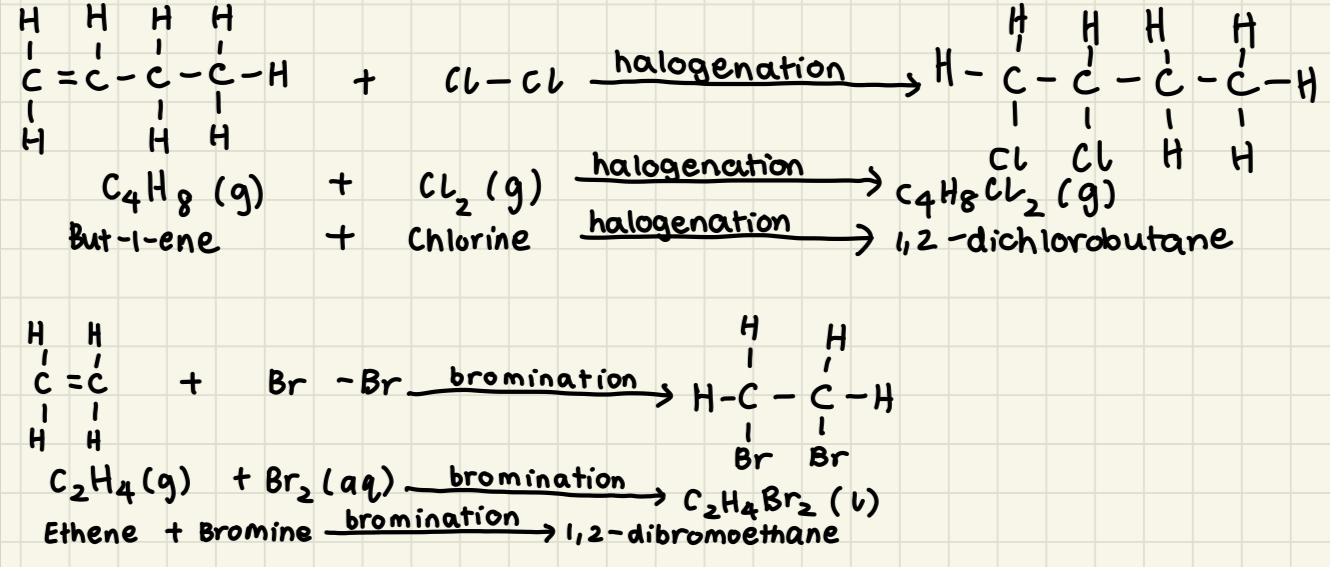
* Alkene (g) + Halogen (g) → x,y-dihaloalkane (g)
* E.g: But-1-ene + Chlorine → 1,2-dichlorobutane
* Alkene (g) + Bromine (aq) → x,y-dibromoalkane (l)
* E.g: Ethene + Bromine → 1,2-dibromoethane
* Reaction uses bromine water (an aqueous solution)
* C=C double bond breaks → forms new single bonds
* Carbon atoms of original functional group are now free radicals because they have unpaired valence electrons
* Bromine’s valence electron covalently bonds to unpaired valence electrons of carbon free radicals, the bromine atoms add across to the carbon free radicals
* Halogen atoms always add to carbon atoms across C=C double bond → addition reaction works for any halogen and any alkane
* All halogens exist as diatomic molecules
* Alkene (g) + Halogen (g) → x,y-dihaloalkane (g)
* E.g: But-1-ene + Chlorine → 1,2-dichlorobutane
* Alkene (g) + Bromine (aq) → x,y-dibromoalkane (l)
* E.g: Ethene + Bromine → 1,2-dibromoethane
4
New cards
Aqueous solution
Solution where water is the solvent
5
New cards
How can bromine water be used to test for the presence or absence of alkenes?
* Bromine water → orange-colored aqueous solution
* Alkenes can undergo halogenation and bromination because they are unsaturated compounds with a C=C double bond that breaks down when reacting with halogens → halogens add across the carbon atoms of the original C=C functional group
* Dibromoalkanes formed when alkenes react with bromine
* Solid or liquid alkene added to bromine water → bromine reacts with and adds onto alkene → no free bromine left in aqueous solution → bromine water decolorizes and changes from an orange to a colorless solution
* Gaseous alkene bubbled through bromine water → bromine reacts with and adds onto alkene → no free bromine left in aqueous solution → bromine water decolorizes and changes from an orange to a colorless solution
* Alkanes cannot undergo halogenation or bromination because they are saturated compounds (they have no C=C double bond or C☰C triple bond) so the halogens cannot add across any carbon atoms
* Alkanes added to bromine water → no reaction (bromine remains in its aqueous solution) → bromine water remains orange and does not decolorize
* Alkenes can undergo halogenation and bromination because they are unsaturated compounds with a C=C double bond that breaks down when reacting with halogens → halogens add across the carbon atoms of the original C=C functional group
* Dibromoalkanes formed when alkenes react with bromine
* Solid or liquid alkene added to bromine water → bromine reacts with and adds onto alkene → no free bromine left in aqueous solution → bromine water decolorizes and changes from an orange to a colorless solution
* Gaseous alkene bubbled through bromine water → bromine reacts with and adds onto alkene → no free bromine left in aqueous solution → bromine water decolorizes and changes from an orange to a colorless solution
* Alkanes cannot undergo halogenation or bromination because they are saturated compounds (they have no C=C double bond or C☰C triple bond) so the halogens cannot add across any carbon atoms
* Alkanes added to bromine water → no reaction (bromine remains in its aqueous solution) → bromine water remains orange and does not decolorize
6
New cards
Why do … not … with … water?
alkanes
react
bromine
they are saturated compounds and have no C=C double bonds or C☰C triple bonds so the bromine atoms (and any halogen) cannot add across any of the alkane’s carbon atoms. The bromine remains in its aqueous solution → bromine water stays orange and does not decolorize
react
bromine
they are saturated compounds and have no C=C double bonds or C☰C triple bonds so the bromine atoms (and any halogen) cannot add across any of the alkane’s carbon atoms. The bromine remains in its aqueous solution → bromine water stays orange and does not decolorize
7
New cards
Hydrogenation
Addition reaction where hydrogen atoms are added to an unsaturated compound
Alkene (g) + Hydrogen (g) → Alkane (g)
E.g: Ethene + Hydrogen → Ethane
Polyunsaturated (many C=C double bonds) plant oils → hydrogenation → margarine
Alkene (g) + Hydrogen (g) → Alkane (g)
E.g: Ethene + Hydrogen → Ethane
Polyunsaturated (many C=C double bonds) plant oils → hydrogenation → margarine

8
New cards
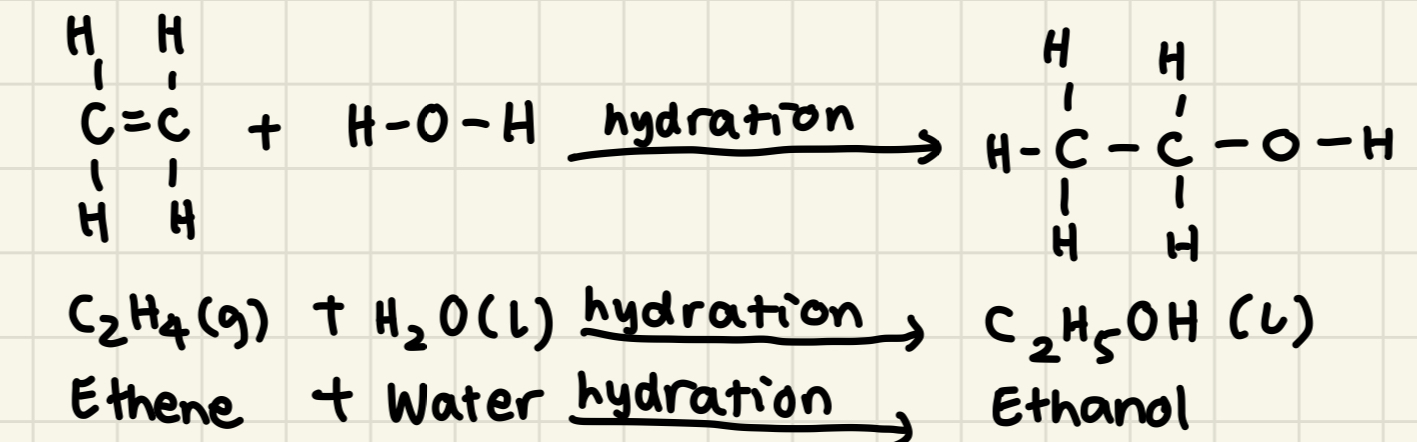
Hydration
Addition reaction where water molecules are added to an unsaturated compound
Alkene (g) + Water (l) → Alcohol (l)
E.g: Ethene + Water → Ethanol
Alkene (g) + Water (l) → Alcohol (l)
E.g: Ethene + Water → Ethanol