PH 112 Final Review
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
A suspended Object A is attracted to a neutral wall. It's also attracted to a negatively charged object B. Object A is therefore...
Uncharged
Negatively Charged
Positively Charged
Could be positively or negatively charged
Positively Charged
Which of the following best explains the key difference between conductors and insulators?
Conductors allow heat to move freely, while insulators do not
Conductors allow electric charge to move freely, while insulators do not
Conductors have high density, while insulators have low density.
Conductors are typically metals, while insulators are non-metals
Conductors allow electric charge to move freely, while insulators do not
Object A has a charge of +9 nC, and Object B has a charge of +1 nC. The force between the charges is...
Attractive
Repulsive
Neither Attractive nor Repulsive
Cannot be Determined
Repulsive
Object A has a charge of +9 nC, and Object B has a charge of +1 nC. The magnitude force on Object A is _____ on Object B.
9x stronger than
81x stronger than
9x weaker than
81x weaker than
equal to that
equal to that
Two objects initially experience an electrical force F. If the distance between the two objects is halved, by what factor does the force change?
1/4
1/2
2
4
4
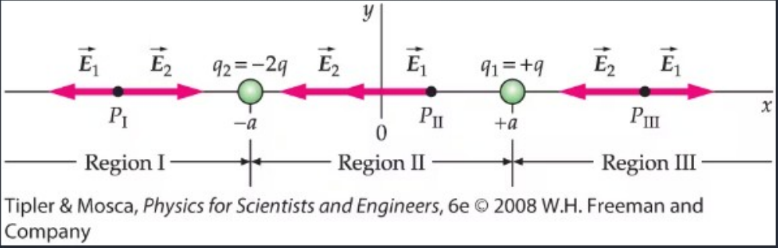
In which region would you expect to find a point where the electric field is zero?
Region I
Region II
Region III
Region III
A negative charge is placed in an electric field. The force on this negative charge is _______ to the electric field.
perpendicular
a parallel
anti-parallel
out of phase
anti-parallel
A negative test charge is put in an external electric field. The negative test charge is then replaced with positive test charge of equal magnitude.
It has the same magnitude but changes direction
It increases in magnitude and changes direction.
It decreases in magnitude and changes direction
It remains the same.
It remains the same.
A free electron and a free proton are placed one-at-a-time in an external electric field. The particles experience the same acceleration.
True
False
False
A free electron and a free proton are placed one-at-a-time in an external electric field. The particles experience the same force.
True
False
True
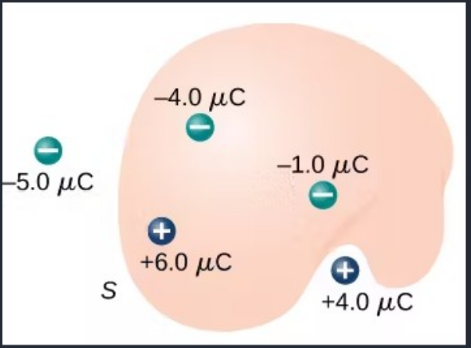
What is the electric flux through the closed surface in the image?
-1 µC/eps0
0
+1 µC/eps0
+1 µC/eps0
Consider an arbitrary closed surface. Charges outside the surface affect the net flux through the surface.
True
False
False
If a proton is released from rest in a uniform electric field, the proton would begin moving such that the electric potential energy...
Increases
Decreases
Remains the same
Decreases
If an electron is released from rest in a uniform electric field, the electron would move toward electric potential.
Higher
Lower
an equipotential
Higher
Electric potential can increase while potential energy decreases.
True
False
True
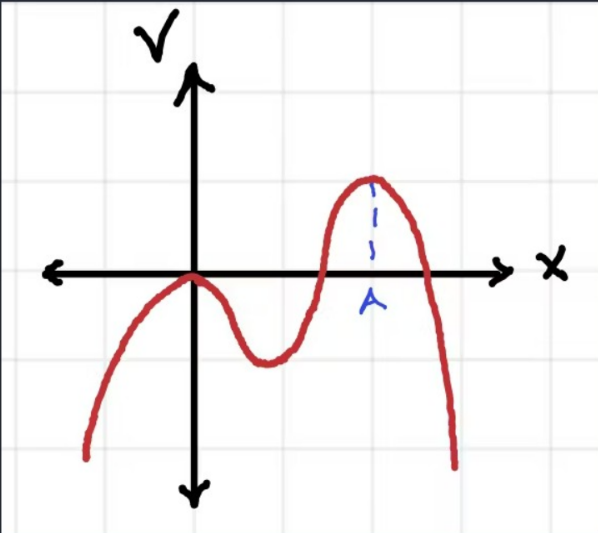
An electron is placed at Point A and given a small kick to the right. What will its subsequent motion be?
it will go to the right and not return
It will go to the left
It will remain at Point A
It will oscillate about Point A
It will oscillate about Point A
An object can be accelerated (experience a force) when V = 0.
True
False
True
A spherical balloon contains a positively charged particle at its center. As the balloon is inflated, which of the following statements is true?
The electric potential at the surface of the balloon increases.
The magnitude of the electric field at the surface of the balloon increases.
The electric flux through the balloon remains the same.
None of these.
The electric flux through the balloon remains the same
An electron and a proton are accelerated through a potential difference of 1 V magnitude. Which has the higher KE after this?
The Proton
The Electron
They have the same KE
Cannot be determined.
They have the same KE
An electron and a proton are accelerated through a potential difference of 1 V magnitude. Which has the higher velocity after this?
The Proton
The Electron
They have the same KE
Cannot be determined.
The Electron
A sphere has a capacitance of 1 µF and carries a charge of 20 µC. If the charge is increased to 60 µC, what is the sphere's new capacitance?
Less than 1 µF
Equal to 1 µF
Greater than 1 µF
Not enough information.
Equal to 1 µF
How is the capacitance affected if the potential across a cylindrical capacitor is increased from 20 V to 80 V?
It increases
It decreases.
It remains the same
It remains the same
How is the stored charge affected if the potential across a cylindrical capacitor is increased from 20 V to 80 V?
It increases
It decreases.
It remains the same
It increases
For capacitors connected in parallel, the equivalent capacitance will always be
Greater than the highest individual capacitance
Equal to the median capacitance
Lesser than the lowest individual capacitance
Greater than the highest individual capacitance
For capacitors connected in series, the equivalent capacitance will always be
Greater than the highest individual capacitance
Equal to the median capacitance
Lesser than the lowest individual capacitance
Lesser than the lowest individual capacitance
The current carried by wire A is twice the current carried by the identical wire B. In which wire do the charge carriers have the higher drift speed?
Wire A
Wire B
Wire C
They have the some drift speed
Wire A
Suppose a current-carrying wire has a cross-sectional area that gradually becomes larger along the wire. How does the drift speed vary along the wire?
It slows down as the cross section becomes larger
It speeds up as the cross section becomes smaller.
It doesn't change
Cannot be determined.
It slows down as the cross section becomes larger
If the radius and the length of a wire are reduced to half their original size, the resistance should then.
Increase
Decrease
Remain the same
Increase
Two resistors, A and B, are connected in parallel with a battery and to each other. Resistor B has twice the resistance as A. Which resistor dissipates the most amount of power?
Resistor A
Resistor B
They dissipate the same power
Resistor A
The terminal voltage of a battery is always greater than or equal to the emf of the battery.
True
False
False
For which case(s) do you expect the discharging time of an RC Circuit to increase for a given system.
Increase resistance
Increase capacitance
Decrease resistance
Decrease capacitance.
Increase resistance
Increase capacitance
For a discharging RC circuit, we expect both charge on the capacitor and system current to decrease over time.
True
False
True
For a charging RC circuit, we expect both charge on the capacitor and system current to increase over time.
False
A charged particle is moving in a straight line through a magnetic field. You therefore expect the particle's velocity and the magnetic field to be.....
Parallel
Perpendicular
Parallel or Perpendicular
Between parallel and perpendicular
Not magnetic fields again
Parallel
Since the magnetic force is always perpendicular to the particle's velocity, magnetic forces do ___ work on particles.
Positive
Negative
No
No
Magnetic fields tend to _____ the KE of charged particles moving through them.
increase
decrease
do not change
do not change
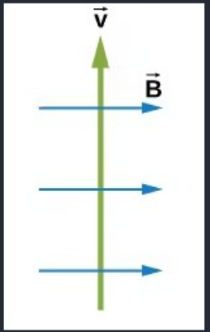
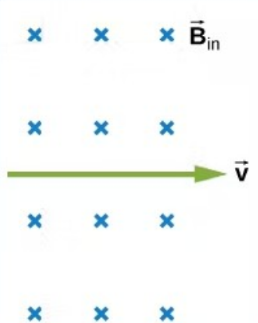
In what direction is the magnetic force on the moving positively charged particle?
Toward the Top of the Screen
Toward the Bottom of the Screen
To the Left
To the Right
Into the Screen
Out of the Screen
Into the Screen
In what direction is the magnetic force on the moving positively charged particle?
Toward the Top of the Screen
Toward the Bottom of the Screen
To the Left
To the Right
Into the Screen
Out of the Screen
Toward the Top of the Screen
A current-carrying loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field. How does the magnetic torque on the loop behave?
The torque is zero if the magnetic field is parallel to the plane of the loop.
The torque is maximum when the magnetic field is parallel to the loop's magnetic moment.
The torque seeks to align the plane of the loop to be perpendicular to the magnetic field.
The torque does not depend on the orientation of the loop relative to the field
The torque seeks to align the plane of the loop to be perpendicular to the magnetic field.
In the Hall effect, what is the primary reason a potential difference is developed across the conductor?
The magnetic field induces an electric field across the conductor
The charge carriers experience a force perpendicular to both the magnetic field and current
The current increases in the presence of the magnetic field.
The conductor's resistance decreases due to the magnetic field
The charge carriers experience a force perpendicular to both the magnetic field and current
A point charge is moving with a constant velocity. What best describes the magnetic field it generates?
The magnetic field is strongest along the direction of motion of the charge
The magnetic field is circular around the path of the moving charge
The magnetic field is uniform and does not depend on the speed of the charge
The magnetic field exists only if the charge is accelerating
The magnetic field is circular around the path of the moving charge
Which of the following best describes the magnetic field inside a long, current-carrying solenoid?
The interior magnetic field is non-uniform and decreases along the length of the solenoid
The interior magnetic field is uniform and directed parallel to the axis of the solenoid
The magnetic field is strongest outside the solenoid and weaker inside
The interior magnetic field is uniform and directed parallel to the axis of the solenoid
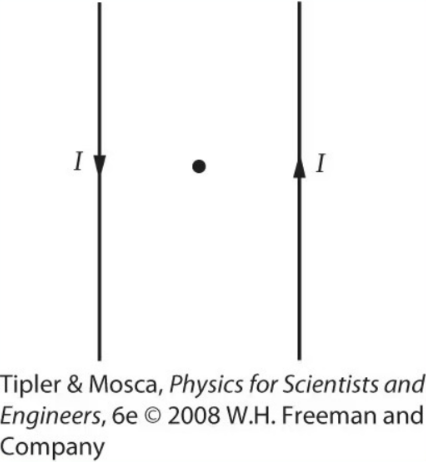
The two wires shown carry equal and opposite currents. At the midpoint between the currents, the magnetic field is...
Zero
Into the Screen
Out of the Screen
Toward the Top of the Screen
Toward the Bottom of the Screen
Out of the Screen
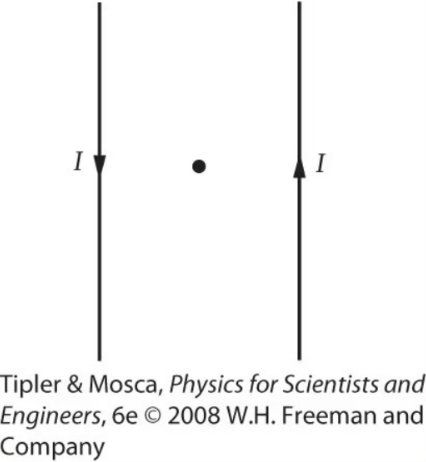
If instead, the currents were in the same direction: At the midpoint between the currents, the magnetic field is...
Zero
Into the Screen
Out of the Screen
Toward the Top of the Screen
Toward the Bottom of the Screen
Zero
Two parallel wires carry current in the same direction. Wire 1 has current I while wire 2 double the current. Which wire experiences greater force?
Wire 1
Wire 2
They experience the same magnitude force.
They experience the same magnitude force.
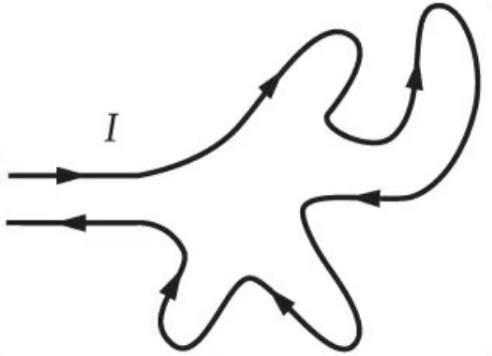
When a current is passed through the wire in the figure, will the wire tend to bunch up or will it tend to form a circle?
Bunch Up
Form a Circle
Not enough information
Form a Circle
Which of the following statements is true about the application of Ampere's Law?
Ampere’s Law can only be applied if the current distribution is uniform
Ampere's Law applies only to circular paths
Amperes Law cannot be used when there is no current enclosed
None of these
None of these
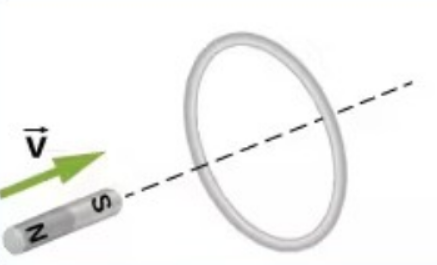
In which direction is the induced emf/current?
Clockwise
Counter-Clockwise
No Induced Current
Clockwise

In which direction is the induced emf/current?
Clockwise
Counter-Clockwise
No Induced Current
Clockwise
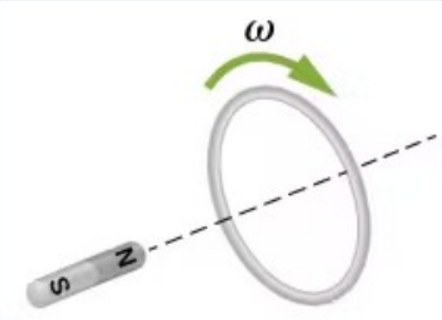
In which direction is the induced emf/current?
Clockwise
Counter-Clockwise
No Induced Current
No Induced Current
Two objects with different sizes, masses, and temperatures are placed in thermal contact. Energy travels
from the larger to the smaller
from the more massive to less massive
from the higher temperature object to lower temperature
It depends on the combination of their relative sizes, masses, and temperatures
from the higher temperature object to lower temperature
When the temperature of an ideal gas in a sealed container is increased, which of the following will happen if the volume is held constant?
The pressure will decrease
The pressure will remain constant
The pressure will increase
The number of gas molecules will decrease
The pressure will increase
If the volume of an ideal gas is doubled while the temperature and amount of gas remain constant. what happens to the pressure?
It doubles
It remains the same
It is halved
It increases by a factor of four
It is halved
Which of the following changes would increase the volume of an ideal gas in a flexible container, assuming constant pressure?
Increasing the number of moles of gas
Decreasing the temperature
Decreasing the number of moles of gas
Increasing the temperature
Increasing the number of moles of gas
Increasing the temperature
Water (highest specific heat), iron, and lead (lowest specific heat) of equal masses are all at 10 Celsius. Which has the greatest heat?
Water
Iron
Lead
Objects do not contain heat.
Objects do not contain heat.
When a solid turns into a liquid at its melting point, which of the following happens to the temperature?
It decreases as the solid absorbs heat
It stays constant until all the solid has melted.
It increases steadily during melting
It stays constant but only if additional heat isn't added
It stays constant until all the solid has melted.
The pressure of a gas must remain constant for work to be done on the gas.
True
False
False
The volume of a gas must change as work is done on/by the gas.
True
False
True
In an isothermal process for an ideal gas, how does the work done by the gas relate to the heat added to the system?
The work done is greater than the heat added
The work done is equal to the heat added
The work done is less than the heat added
No work is done during an isothermal process
The work done is equal to the heat added
During an isobaric expansion of an ideal gas, which describes the work done by the gas?
It is proportional to the change in temperature
It is proportional to the change in pressure.
It is proportional to the change in volume
It is zero because the pressure is constant
It is proportional to the change in volume
For an adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas, what happens to the internal energy of the gas?
It increases because no heat is exchanged
It decreases because the gas does work on its surroundings.
It remains constant because no heat is exchanged.
It depends on the specific heat capacity of the gas
It decreases because the gas does work on its surroundings.
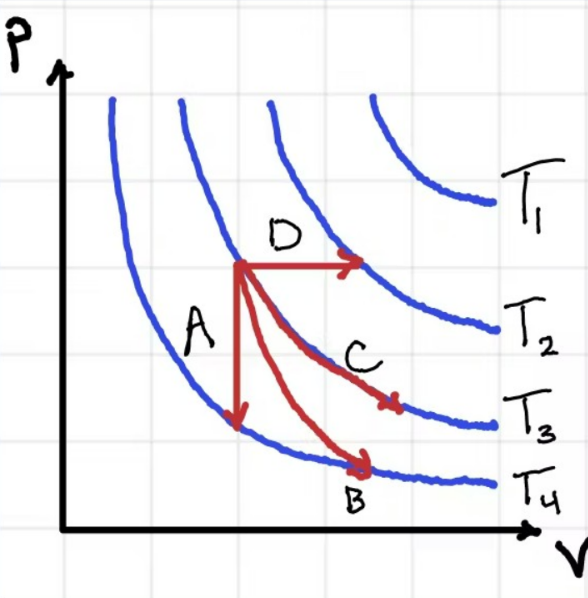
According to the graph attached, Process A is...
Adiabatic
Isochoric
Isobaric
Isothermal
Isochoric
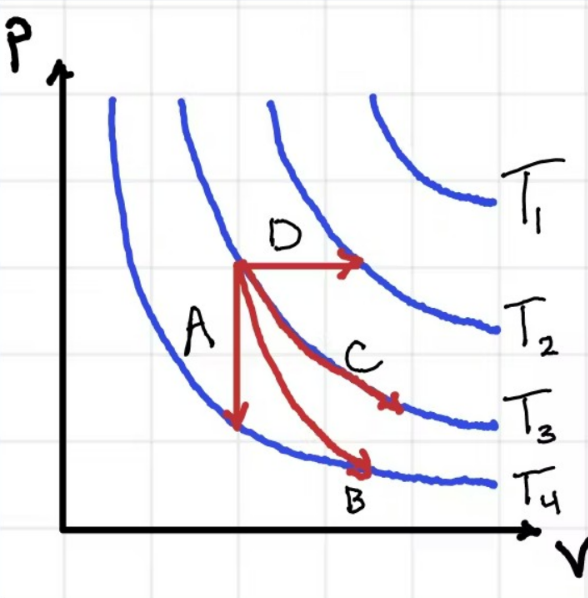
According to the graph attached, Process B is...
Adiabatic
Isochoric
Isobaric
Isothermal
Adiabatic
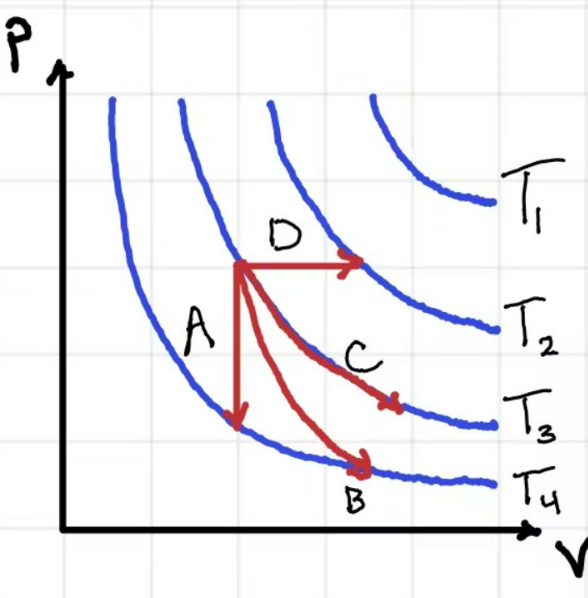
According to the graph attached, Process C is...
Adiabatic
Isochoric
Isobaric
Isothermal
Isothermal
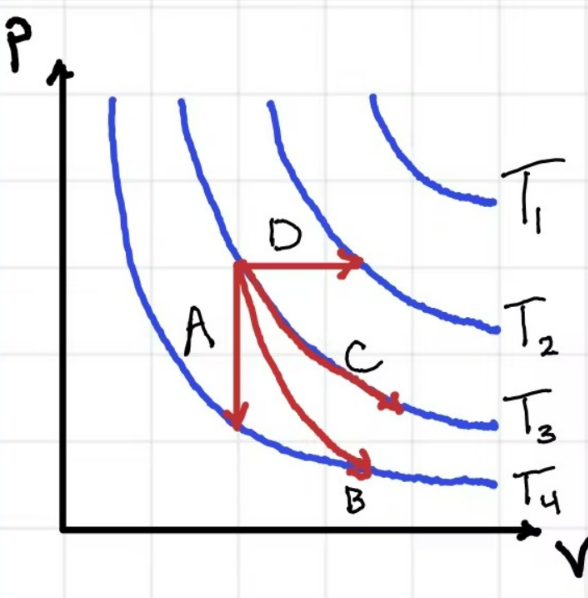
According to the graph attached, Process D is...
Adiabatic
Isochoric
Isobaric
Isothermal
Isobaric