DNA Repair Mechanisms and Basis of Cancer Genetics
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Direct Reversal
photoreactivation, methyl group removal
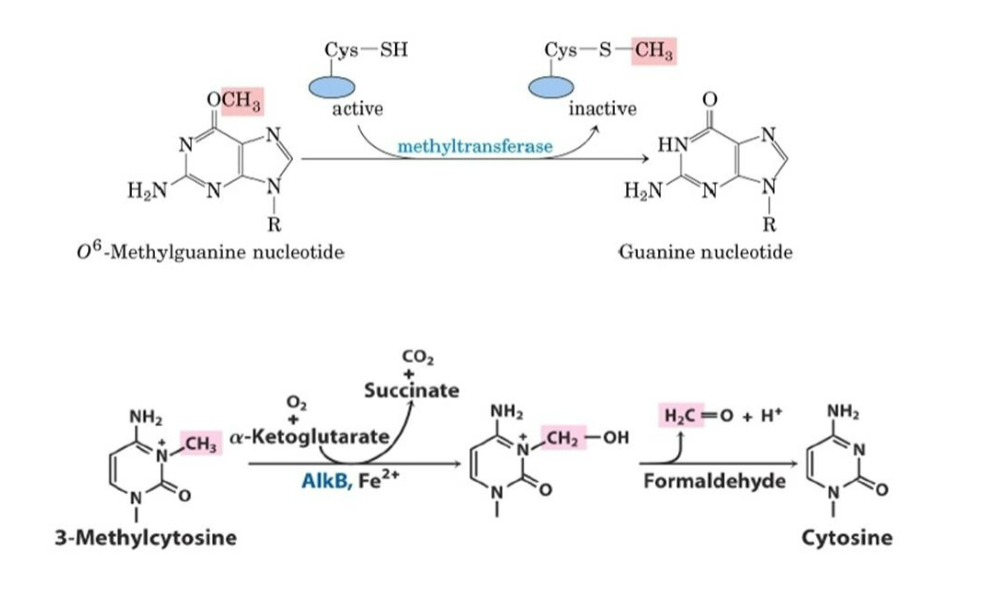
Single Strand Damage, Base Excision Repair
which
repairs damage to a single base caused by oxidation, alkylation, hydrolysis, or deamination.
1- DNA glycosylases remove damaged base (apurinic or apyrimidinic site).
2- DNA polymerase/ligase
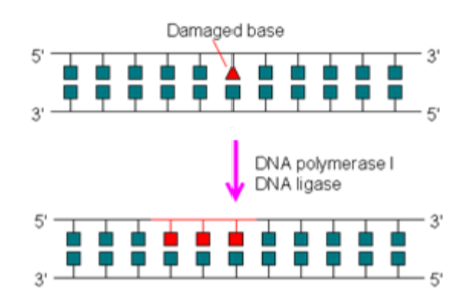
Single Strand Damage, Nucleotide Excision Repair
which recognizes bulky, helix-distorting lesions such as pyrimidine dimers and 6,4 photoproducts.
1-recognition of damage,
2-excision of damaged DNA both upstream and downstream of damage by endonucleases
3- and re-synthesis of removed DNA region
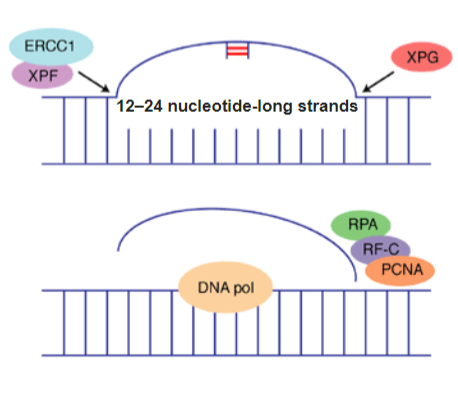
Single Strand Damage, Mismatch Repair
corrects errors of DNA replication and recombination that results in mispaired nucleotides
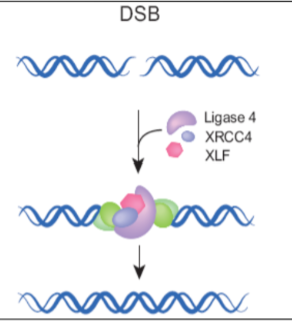
Double Strand Breaks - non-homologous end joining
pathway that repairs double strand breaks in DNA; the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template
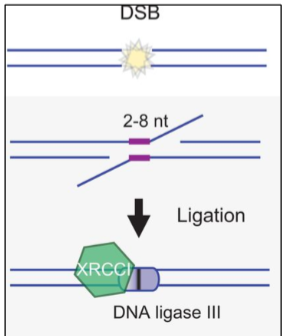
Double Strand Breaks - microhomology-mediated end joining
use of 5-25 base pair micro homologous sequences during the alignment of broken ends before joining; this results in deletions flanking the original break
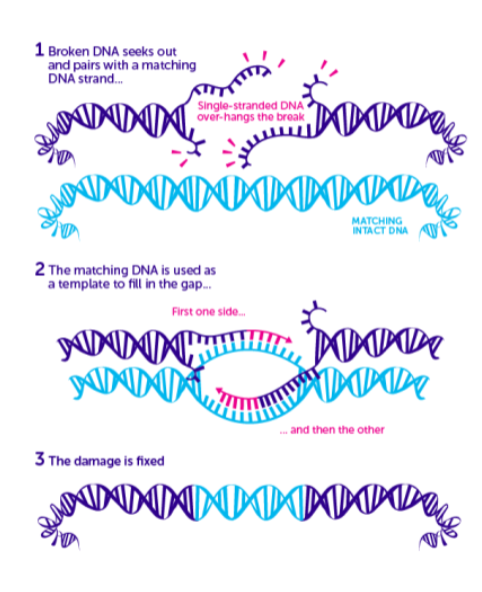
Double Strand Breaks - homologous recombination
requires the presence of an identical or nearly identical sequence to be used as a template for repair of the break
chromosomal crossover during meiosis
sister chromatid or a homologous chromosome as a template
Cancer cells evade normal growth by…
produce cell division signals (autocrine stimulation)
lose contact inhibition
avoid programmed cell death
Hayflick Limit
the number of times a normal cell population will divide before it stops, presumably because the telomeres reach a critical length
Cancer cells interact with the body…
produce substances that encourage blood vessel growth
provide nutrients to tumor
move to other locations
Apoptosis
genetically programmed cell death
essential for normal embryonic development
removes abnormal cells from the body
depends on numerous signals, both inside and outside of the cell
Knudson’s Multistep Model of Cancer
cancer is the result of a multistep process that requires several mutations
if one or more mutations are inherited, fewer mutations are required to produce cancer
Proto-oncogenes
In normal cells
Code for proteins involved in the stimulus of cell division
If altered, may form oncogenes
Alone, do not cause malignant cancer
Require other mutations, including one in a tumor suppressor gene
Mutation in oncogenes/tumor suppressor genes cause
cancerMutation DNA repair genes
Oncogenes act in a…
dominant fashion to promote cancer
nonmutant allele is a…
protooncogene
protooncogenes encode…
proteins needed for cell cycle progression
gain of function mutation
results in increased proliferation
Ras - oncogene (signaling section)
usually active when bound to growth factor
oncogenic point mutation makes constitutively active protei
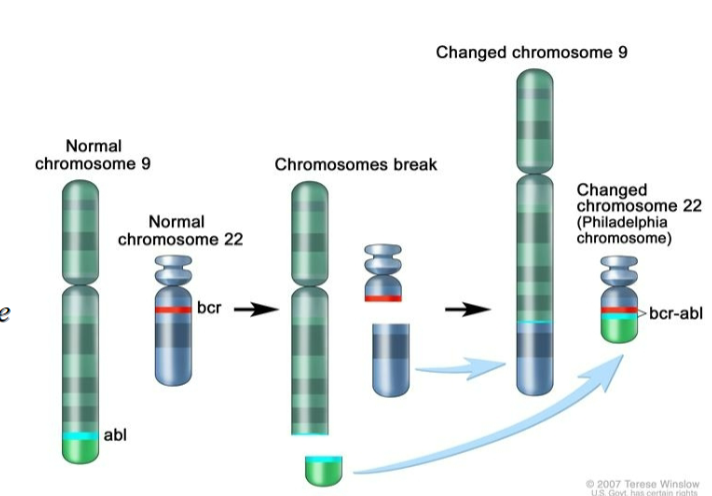
c-Abl - oncogene
Chromosomal translocation fuses the c-abl and bcr genes
Hybrid protein encodes a constitutively active tyrosine kinase
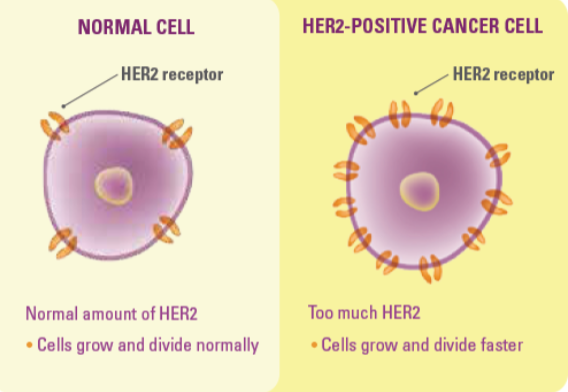
Her2 - oncogene
Found in 20% of all breast cancers
overexpressed growth factor receptor
Philadelphia Chromosome
chromosome 22 of leukemia cancer cells
contains a fusion gene called BCR-ABL1
Tumor Suppressors act…
recessively to promote cancer
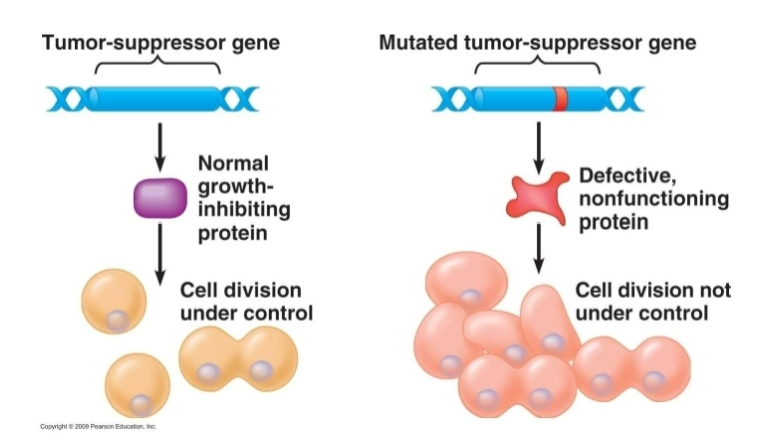
Normal alleles of tumor suppressor genes…
encode proteins that slow down the cell cycle
Loss of function mutations…
in both gene copies results in increased proliferation
Rb (tumor suppressor)
normal protein delays entry into S-phase
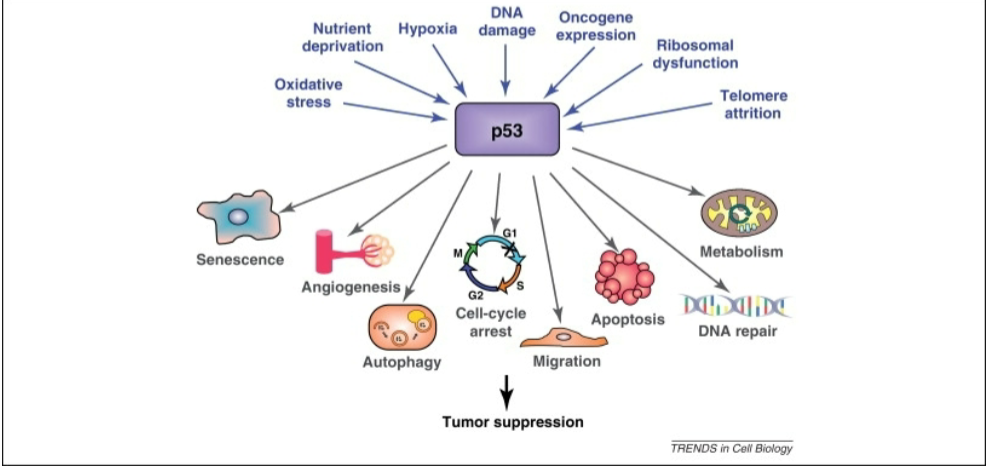
p53 (tumor suppressor)
normal protein functions in G1/S checkpoint
HNPCC (tumor suppressor)
Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer
Caused by mutation in any of DNA mismatch repair genes
Haploinsufficiency
A single functional copy of a gene (with the other copy inactivated by mutation) does not produce enough gene product (typically a protein) to bring about a wild-type condition, leading to an abnormal or diseased state.
Retention of a single functional retinoblastoma susceptibility (RB1) allele is insufficient to maintain genome stability.
Haploinsufficiency of RB1accelerates cancer pathogenesis in concert with inactivation of tumor protein p53
Growth Factors
Extracellular hormones or cell-bound signals that stimulate or
inhibit cell proliferation
Receptors
Comprised of a signal-binding site outside the cell, a transmembrane segment, and an intracellular domain
Signal Transducers
located in cytoplasm
Transcription factors
activate expression of specific genes to either promote or inhibit cell proliferation
Genes that control the cycle of cell division
cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs)
G1/S transition
Retinoblastoma protein (RB)
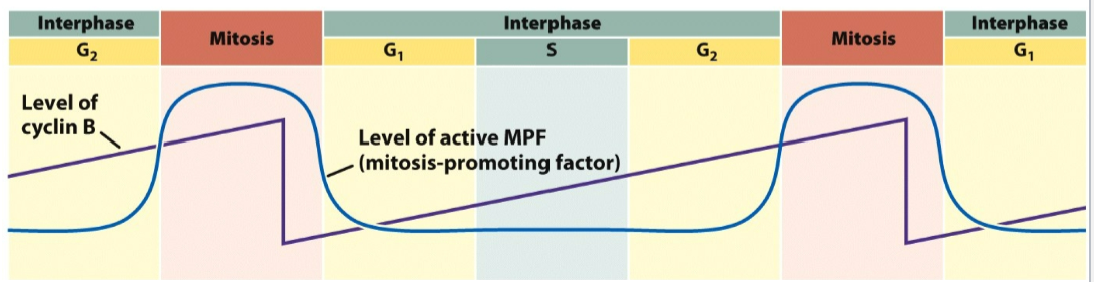
G2/M Transition
mitosis promoting factor (MPF)
Flowchart of Genes that Control the Cycle of Cell Division
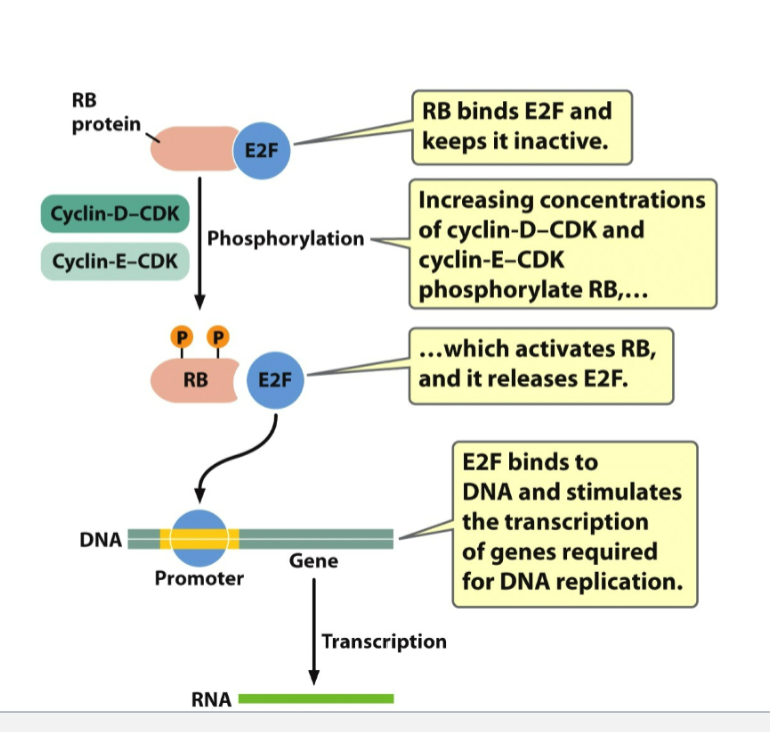
Different CDK-cyclin complexes govern different cell cycle transitions
Presence of each type depends on:
synthesis of specific cyclins at certain times
destruction of cyclins that are not needed
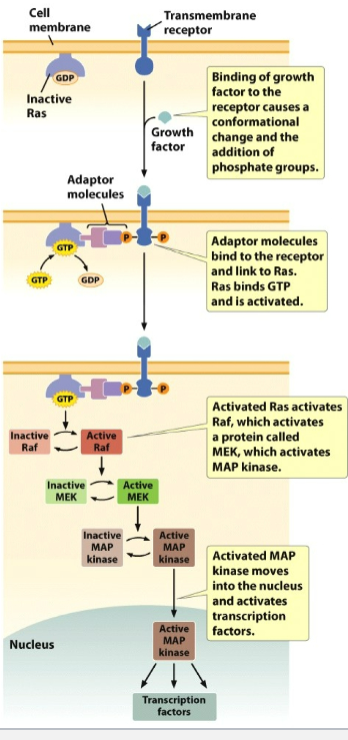
Signal Transduction pathways
external signal triggers a cascade of intracellular reactions producing a specific response
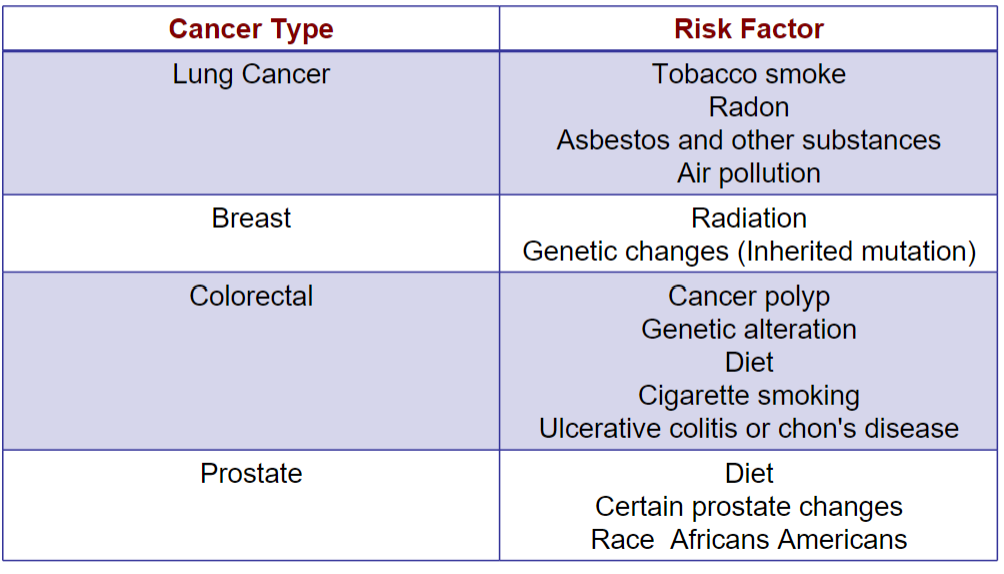
Environmental Risk Factors
Cancer cells can be over-methylated which means that…
hypermethylated
silences the expression of tumor
suppressor genes
Cancer cells can also be under-methylated
hypomethylated
may cause chromosome instability