B4.2 - Ecological Niches
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is an ecological niche?
The role of an organism in an ecosystem (their purpose).
How does the niche affect the organism?
The niche has abiotic and biotic factors that affect their growth, survival, reproduction, nutrition, interactions, competition
What are the names for the types of organisms which are affected by oxygen?
Obligate aerobes - organisms which can only survive in the presence of oxygen - they carry out only aerobic respiration
Obligate anaerobes - organisms which can only survive in the absence of oxygen - they carry out only anaerobic respiration
Facultative anaerobes - organisms that can survive in the presence (do aerobic respiration) and absence (do anaerobic respiration) of oxygen
As respiration is key for animals to survive, what is crucial for plants?
Photosynthesis - it is the mode of nutrition for plants and algae
Heterotrophs vs autotrophs vs mixotrophs
Heterotrophs cannot make their own food, so they take it from other organisms (all animals)
Autotrophs make their own food (e.g., photosynthetic organisms)
Mixotrophs can behave both as heterotrophs and autotrophs —> these can be obligate (require both forms) or facultative (can switch between them)
What is holozoic nutrition?
Heterotrophs carry out holozoic nutrition, where they ingest food, internally digest it and absorb and assimilate the nutrients
What is saprotrophic nutrition?
Heterotrophs carry out saptrotrophic nutrition, where they externally digest foot (e.g., bacteria and fung - decomposers)
How do saprotrophs externally digest food?
By releasing enzymes which digest food, and then the saprotroph absorbs it
What are archaea?
They are one of the three domains of life and they are prokaryotes, which are metabolically diverse
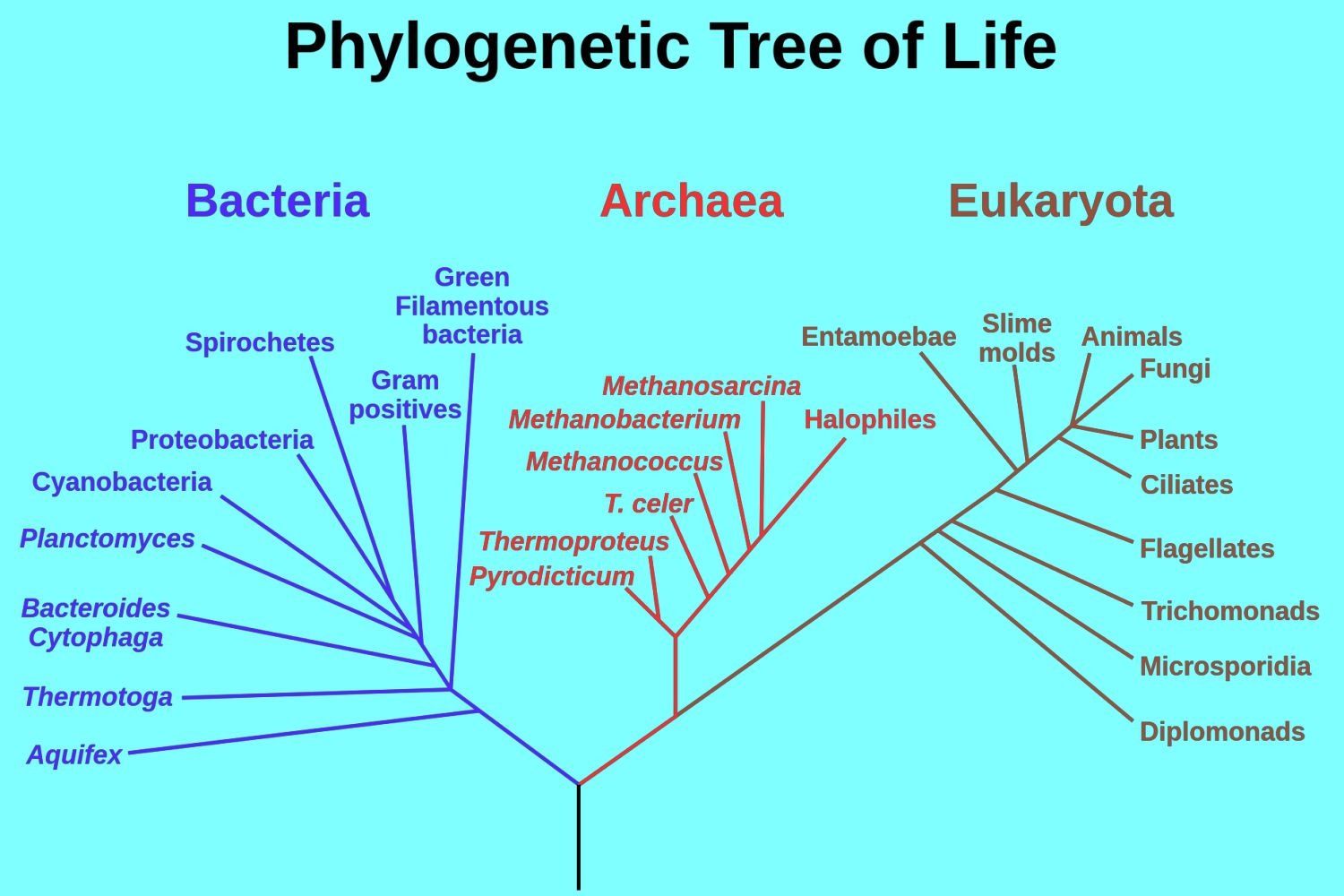
What are the different types of archaea based on how they produce ATP?
Phototrophs - use light to produce ATP (different method to photosynthesis)
Chemolithotrophs - use inorganic compounds to produce ATP
Organotrophs - use organic compounds (such as carbohydrates and fatty acids) to produce ATP
Who are family hominidae?
The family of great apes, among which include modern humans (homo sapiens)
Why are the teeth different for some members of the family hominidae?
The teeth depend on whether they are herbivores or omnivores:
Some are herbivores, so they have large flat teeth and strong jaws for grinding seeds (ancestors such as homo floresciencis)
Some are omnivores, so they have sharp incisors for ripping through meat, as well as flat molars (Homo sapiens)
How does observing family hominidae skulls for their dentitions help scientists?
It help scientists predict the diet of the species, whether they were omnivore or herbivores
What adaptations have plants made to prevent being eaten by herbivores?
thorns
trichomes on stinging nettles that contain irritating chemicals
fibrous leaves that are stringy when eaten
release chemicals/toxins when eaten that cause burning sensation
What adaptations have herbivores made to eat grass?
flat molars for grinding grass - teeth continue growing and never wear down
Strong muscle and sharp edges in mouth to cut through cell walls
Some insects have evolved piercing mouthparts, such as slender tubes which they guide directly into the phloem to suck the nutrients
What adaptations have predators made to kill prey? (Physical, chemical, behavioural)
Physical:
sharp claws
sharp and strong teeth
speed
camouflage
Chemical:
some animals have venom in their tooth glands used to immobalize or kill prey
Behavioural:
Hunting in a pack
Waiting at the perfect time for ambush
What adaptations have prey made to avoid being killed by predators?
Physical:
speed
camouflage (some use mimicry)
protective covering - shells, spikes
Chemical:
produce toxic chemicals to discourage predators (often have bright colours)
Behavioural:
travelling in groups / moving in swarms
being active in a time where predators aren’t active
alarm calls - warn one another
How are autotroph canopy trees adapted for harvesting light?
they are tall and reach over other trees to avoid shade
they have a crown structure to maximize sunlight absorption
they have broad leaves - greater surface area
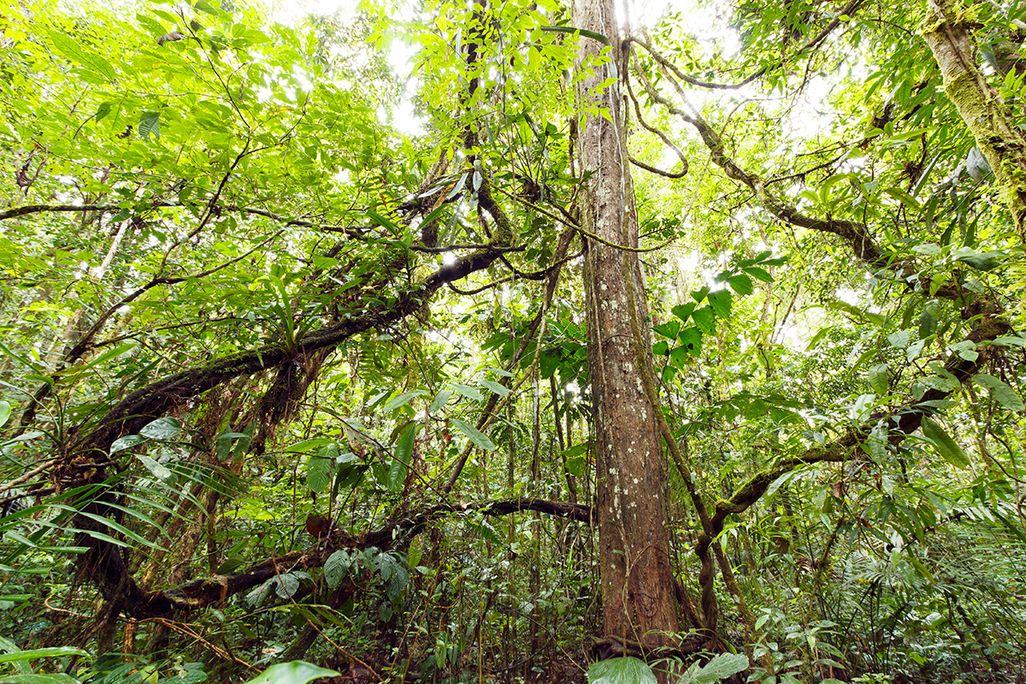
How are autotroph liana vines adapted for harvesting light?
they climb up the trunks of trees, such as by twisting around it or hooking onto it, to reach sunlight
flexible and thin stems

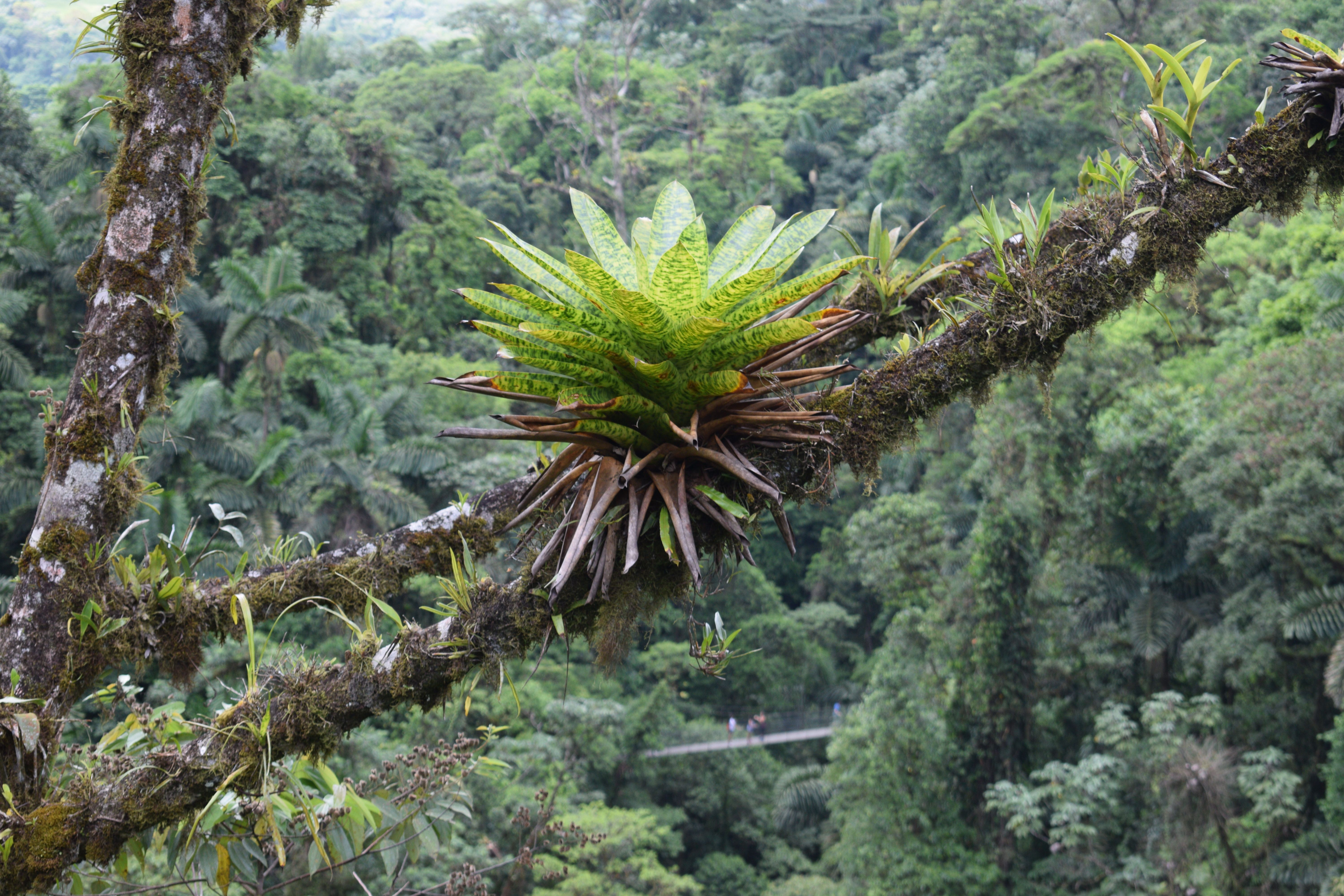
How are autotroph epiphytes adapted for harvesting light?
Epiphytes are plants that grow on other plants
grow on branches of canopy trees
broad flat leaves - maximize surface area
grow towards the light

How are shade tolerant plants adapted to live on the forest floor?
broad leaves to maximize SA
high concentration of chlorophyll
What is a fundamental niche?
It is a niche which an organism could potentially occupy if there were no competition from other species
What is a realized niche?
It is a niche which an organism currently occupies due to competition from other species
What is competitive exclusion?
It is that no two species can occupy the same niche, so one outcompetes and excludes the other species from the niche (usually the less adapted one). The excluded species is what causes them to occupy their realized niche