Final test review!! (Muscles)
1/261
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
262 Terms
Muscle tissue
Consists of all contractile tissues (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle)
Muscles
Can only pull; never push
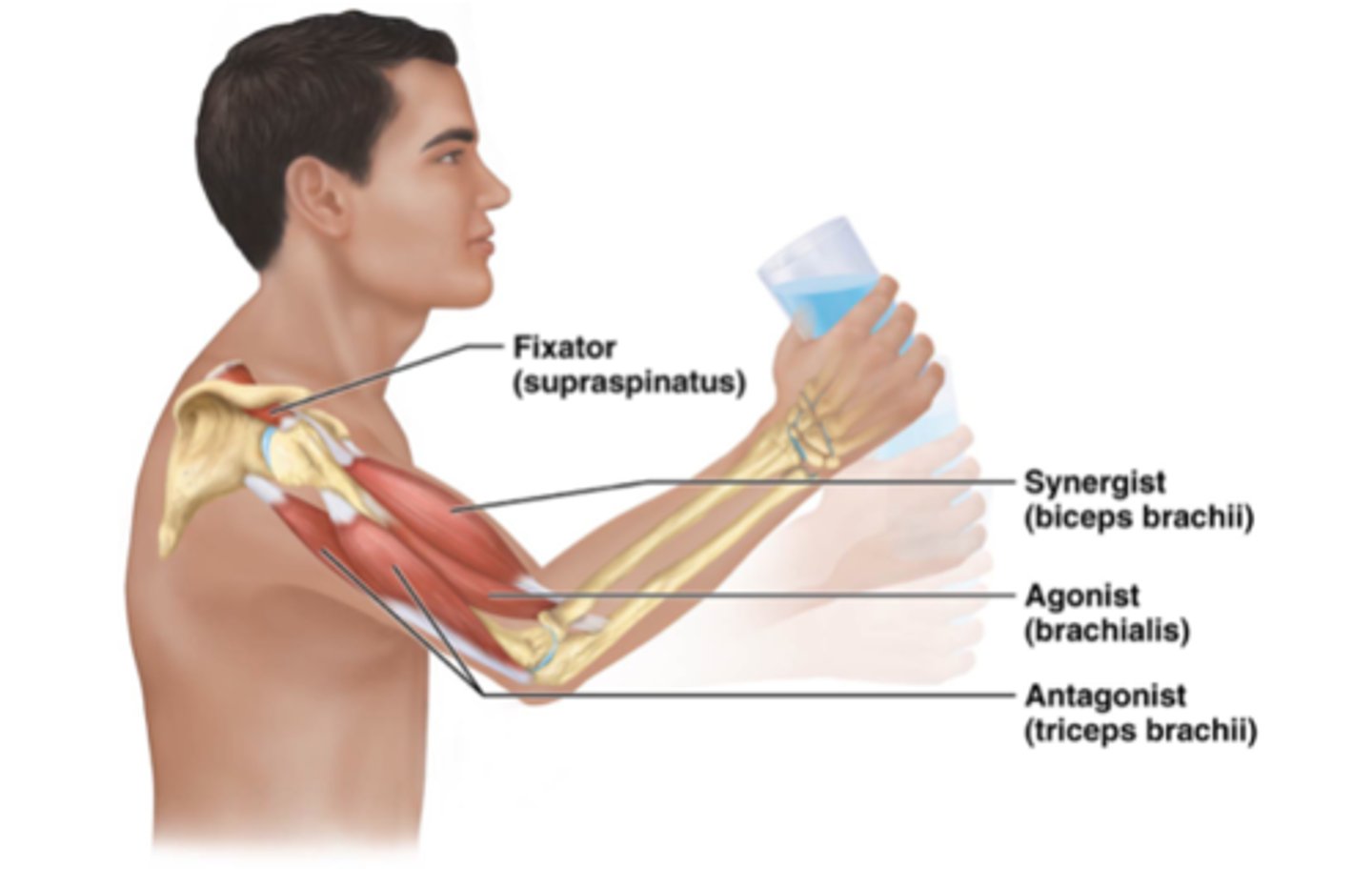
Prime mover (agonist)
Major responsibility for producing a specific movement
Antagonist
Opposes or reverses a particular movement
Prime mover and antagonist location
Located on opposite sides of the joint across which they act
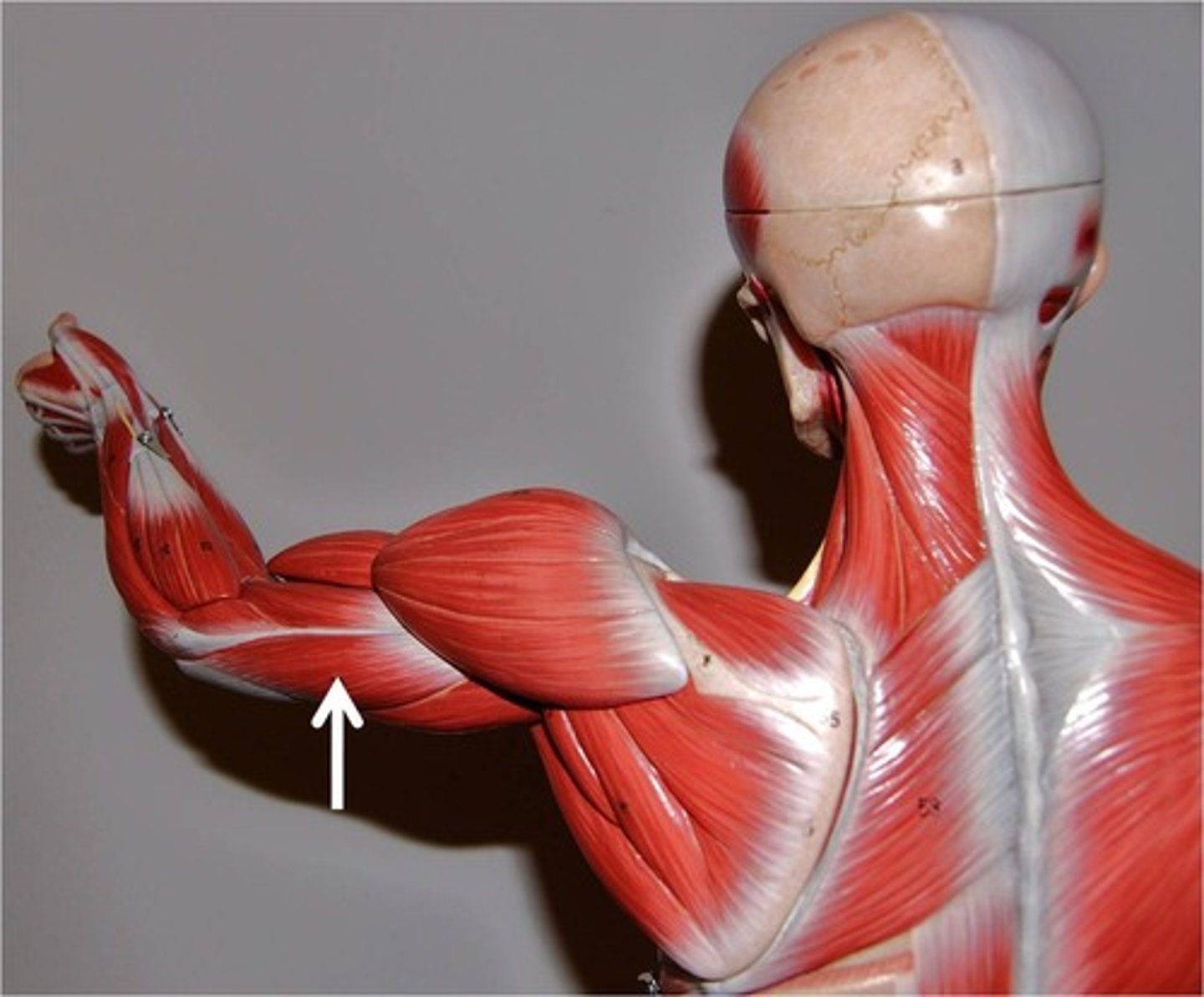
Synergist
Helps prime movers; adds extra force to same movement; reduces undesirable or unnecessary movement
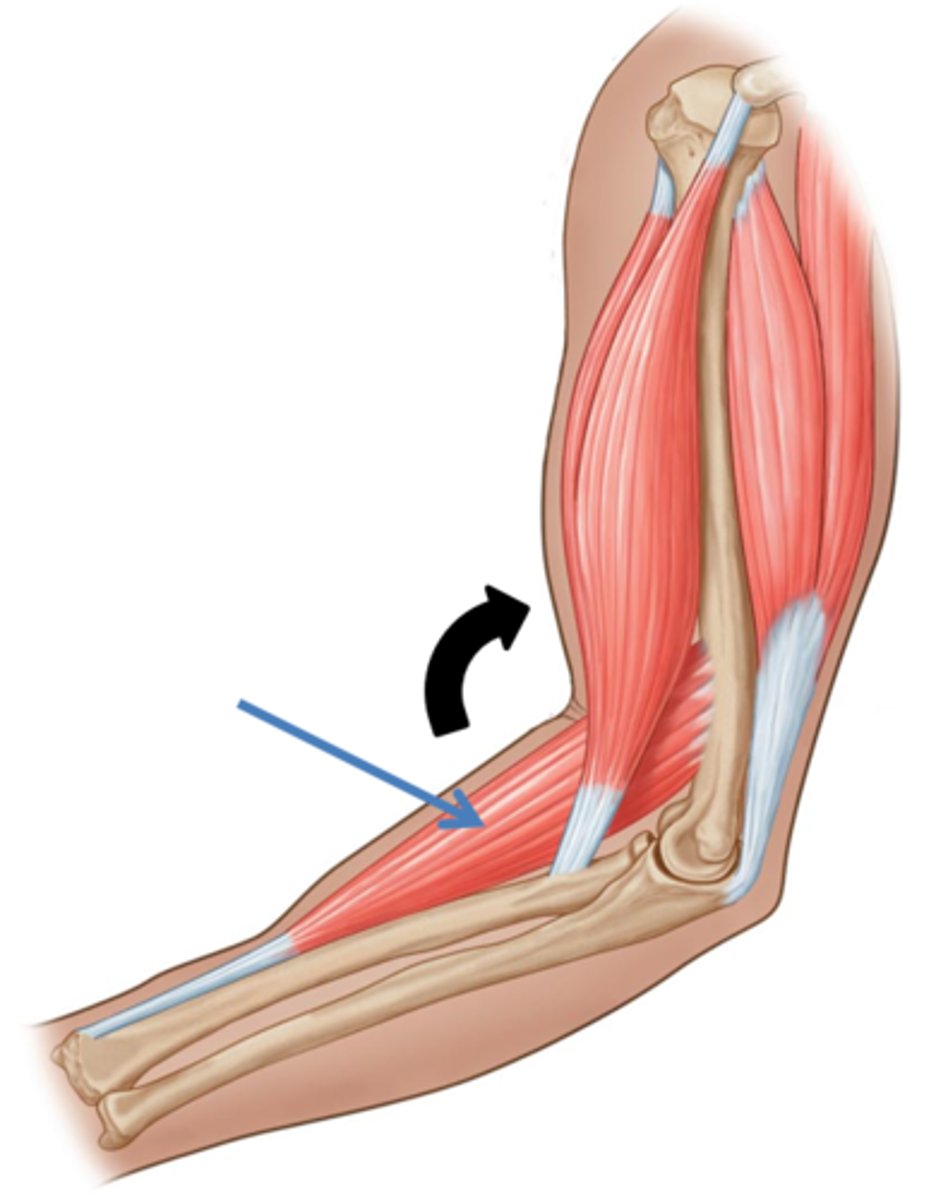
Fixators
Type of synergist that immobilizes bone or muscle's origin, giving the prime mover a stable base on which to act
Muscle location (naming criterion)
Named for the bone or body region associated (e.g., temporalis over temporal bone)
Muscle shape (naming criterion)
Named for distinctive shapes (e.g., deltoid = triangle)
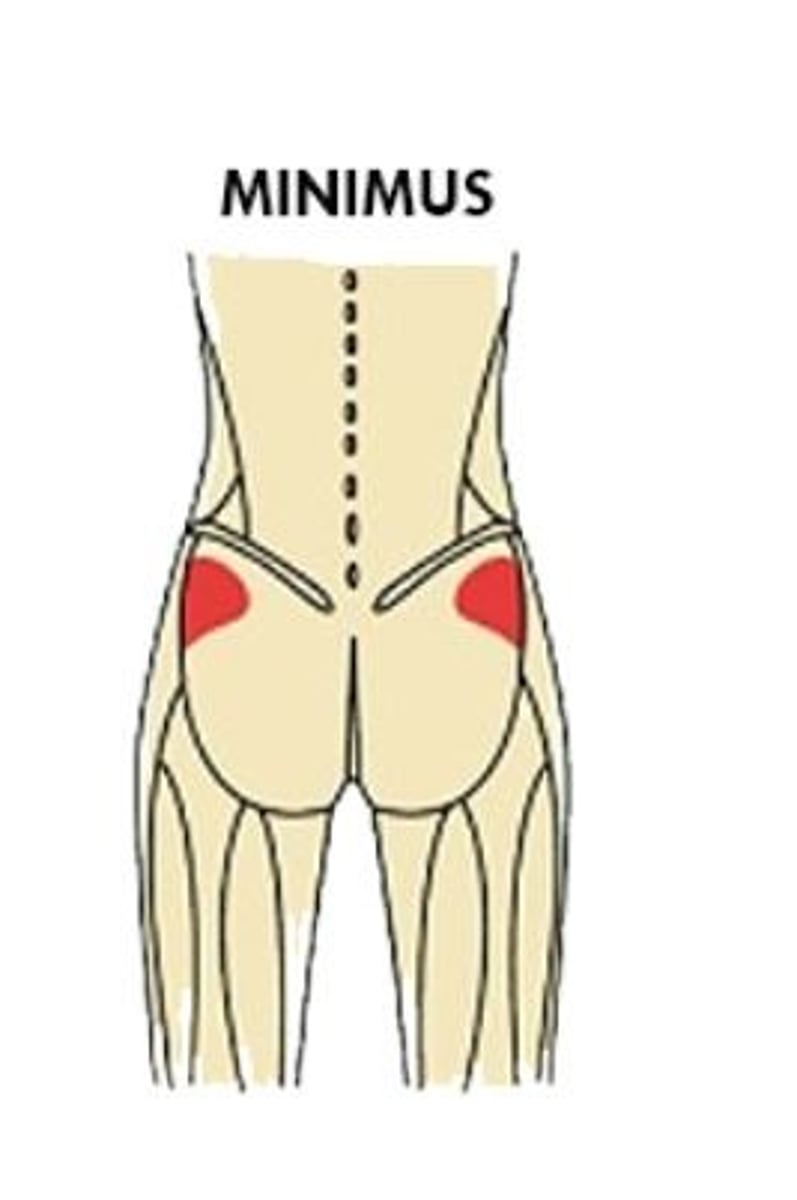
Muscle size (naming criterion)
Example: maximus (largest), minimus (smallest), longus (long)
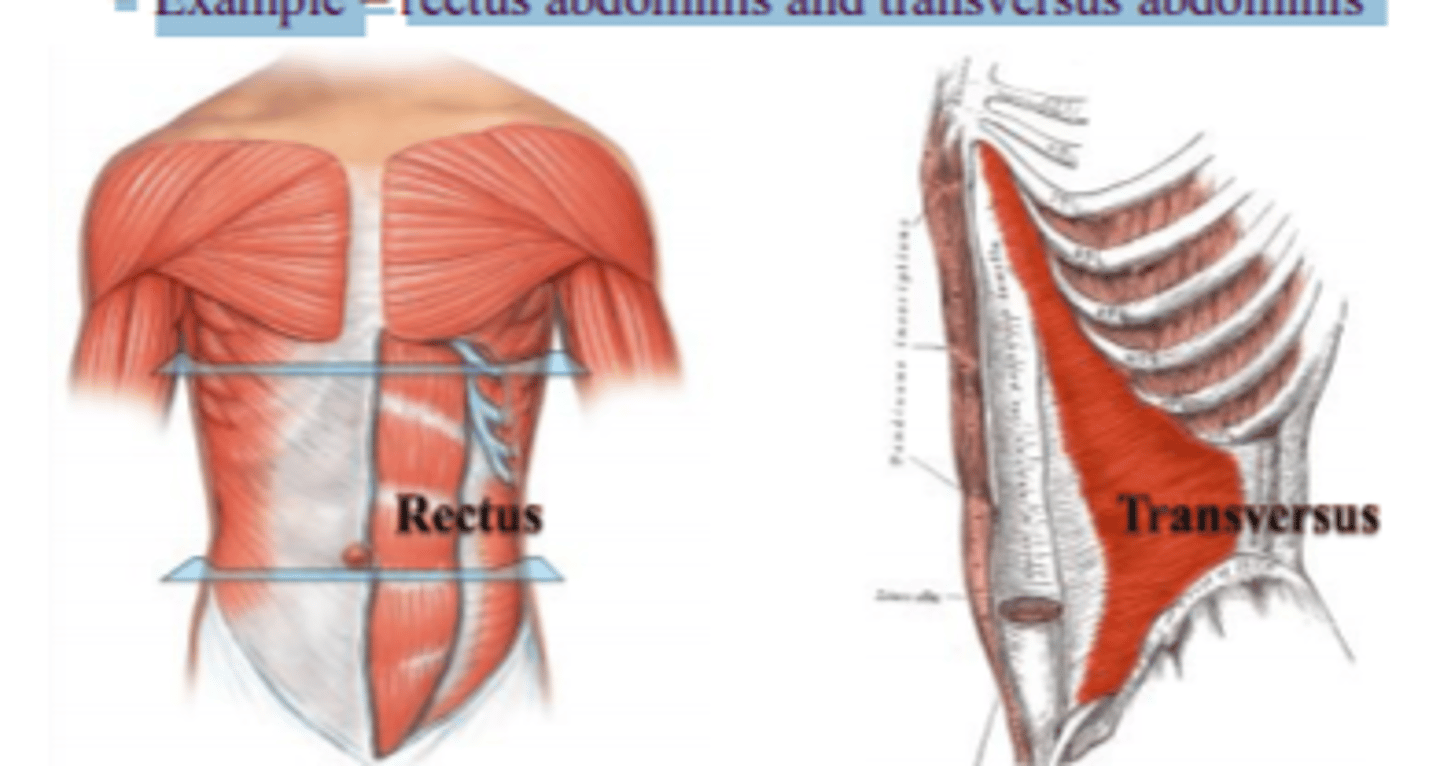
Direction of muscle fibers or fascicles (naming criterion)
Example: rectus (fibers run straight), transversus (fibers run at right angles), oblique (fibers run at angles)
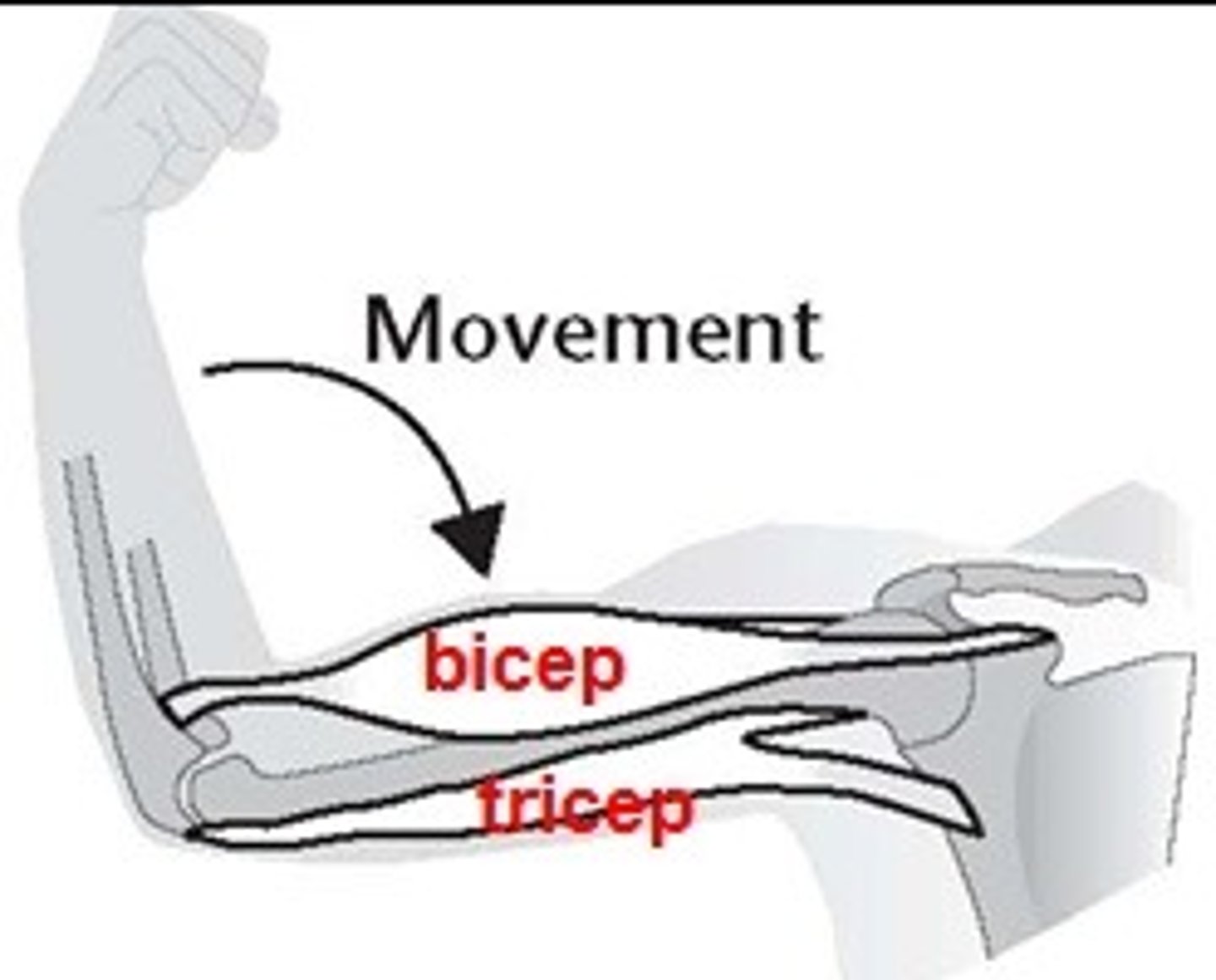
Number of origins (naming criterion)
Example: biceps (two origins), triceps (three origins)
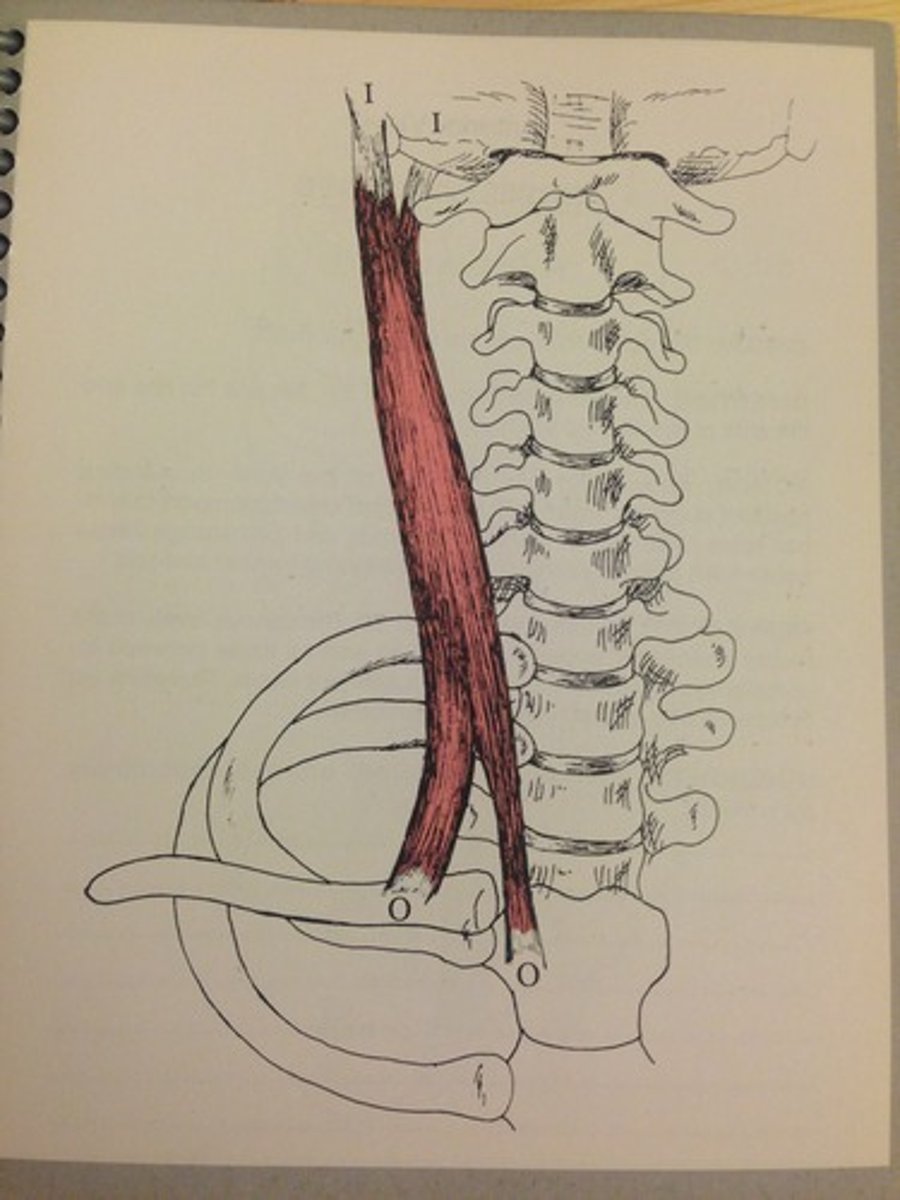
Location of attachments (naming criterion)
Named according to origin and insertion (origin named first) (e.g., sternocleidomastoid attaches to sternum and clavicle, inserts on mastoid process)
Muscle action (naming criterion)
Named for the action they produce (e.g., flexor or extensor)
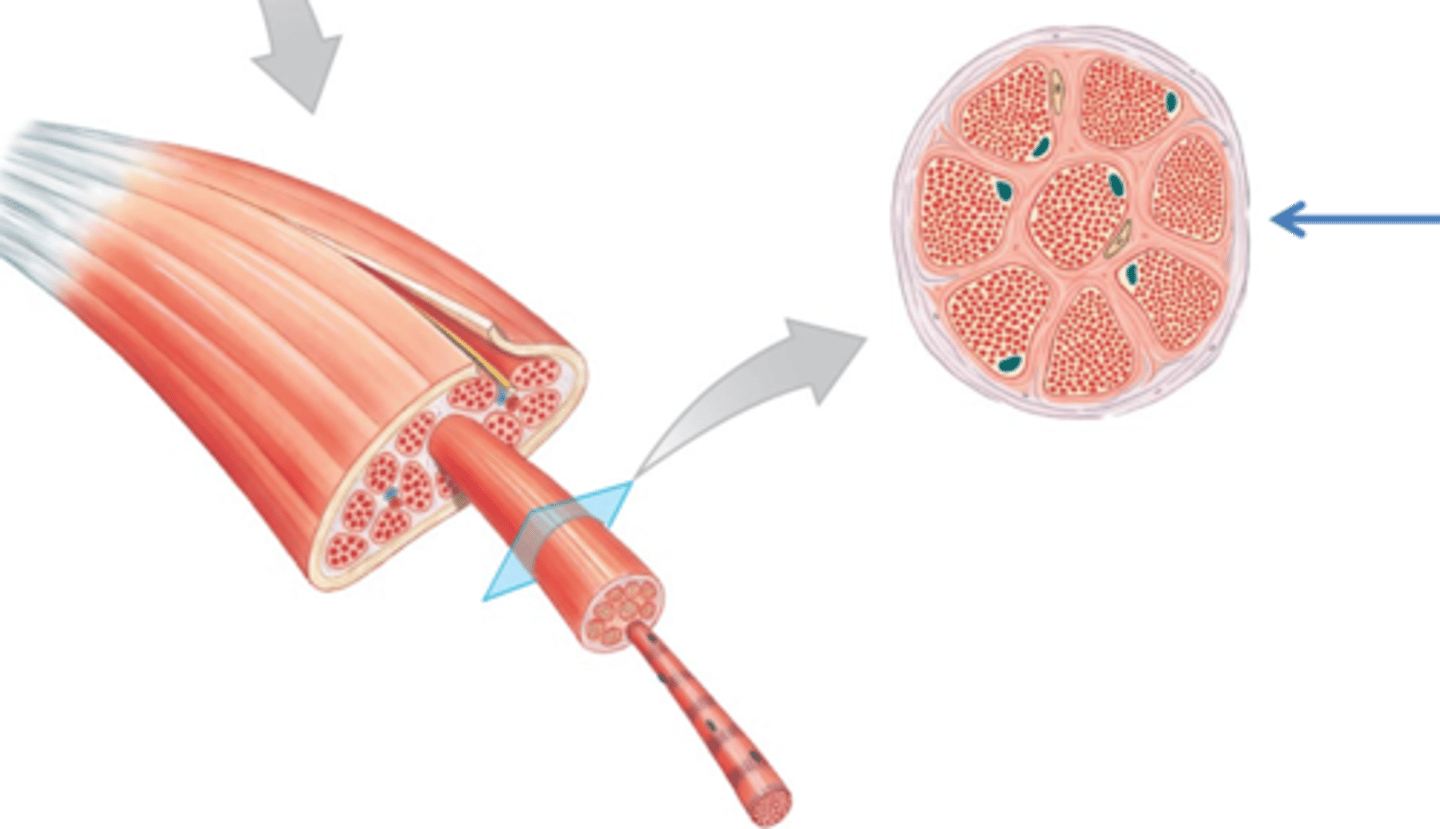
Fascicles
Bundles of muscle fibers that make up skeletal muscles
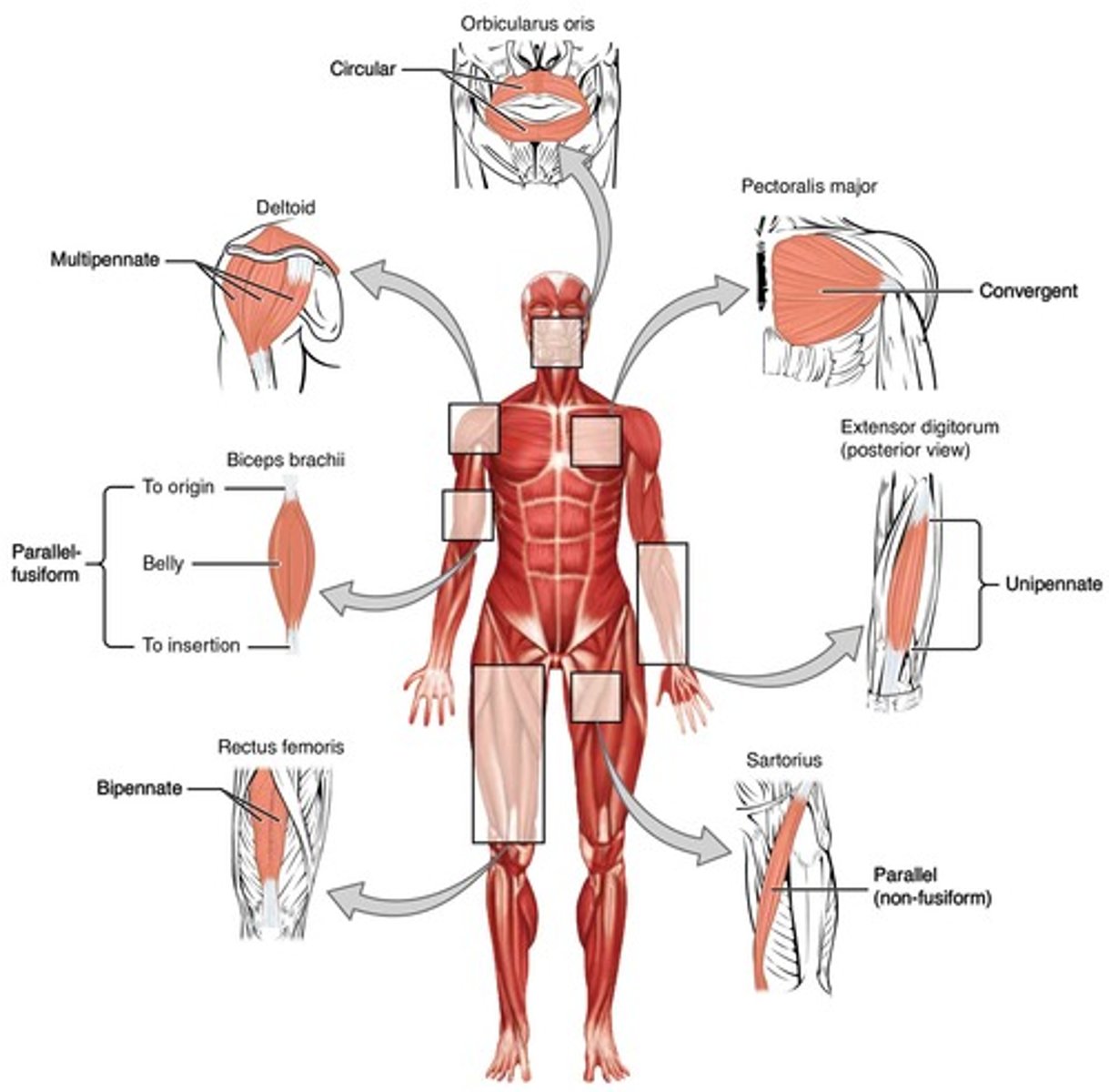
Common fascicle arrangements
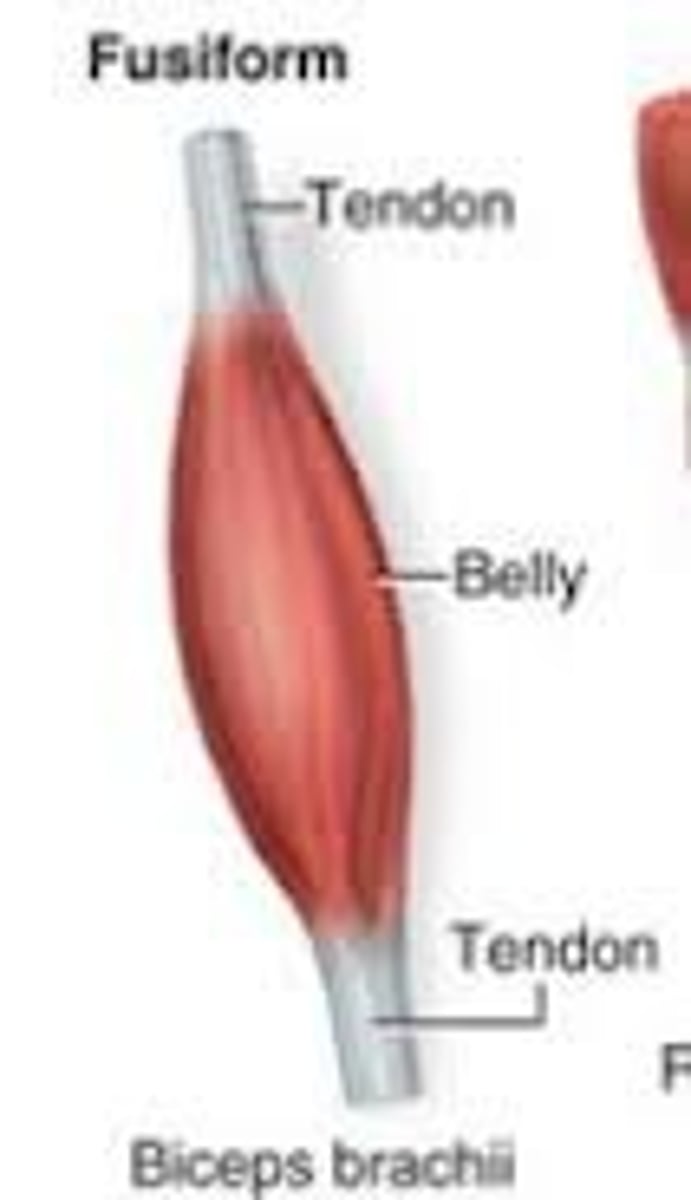
Circular, convergent, parallel, fusiform, and pennate
Fascicles determine
____ ____ the muscle's range of motion (movement when shortened) and muscle's power
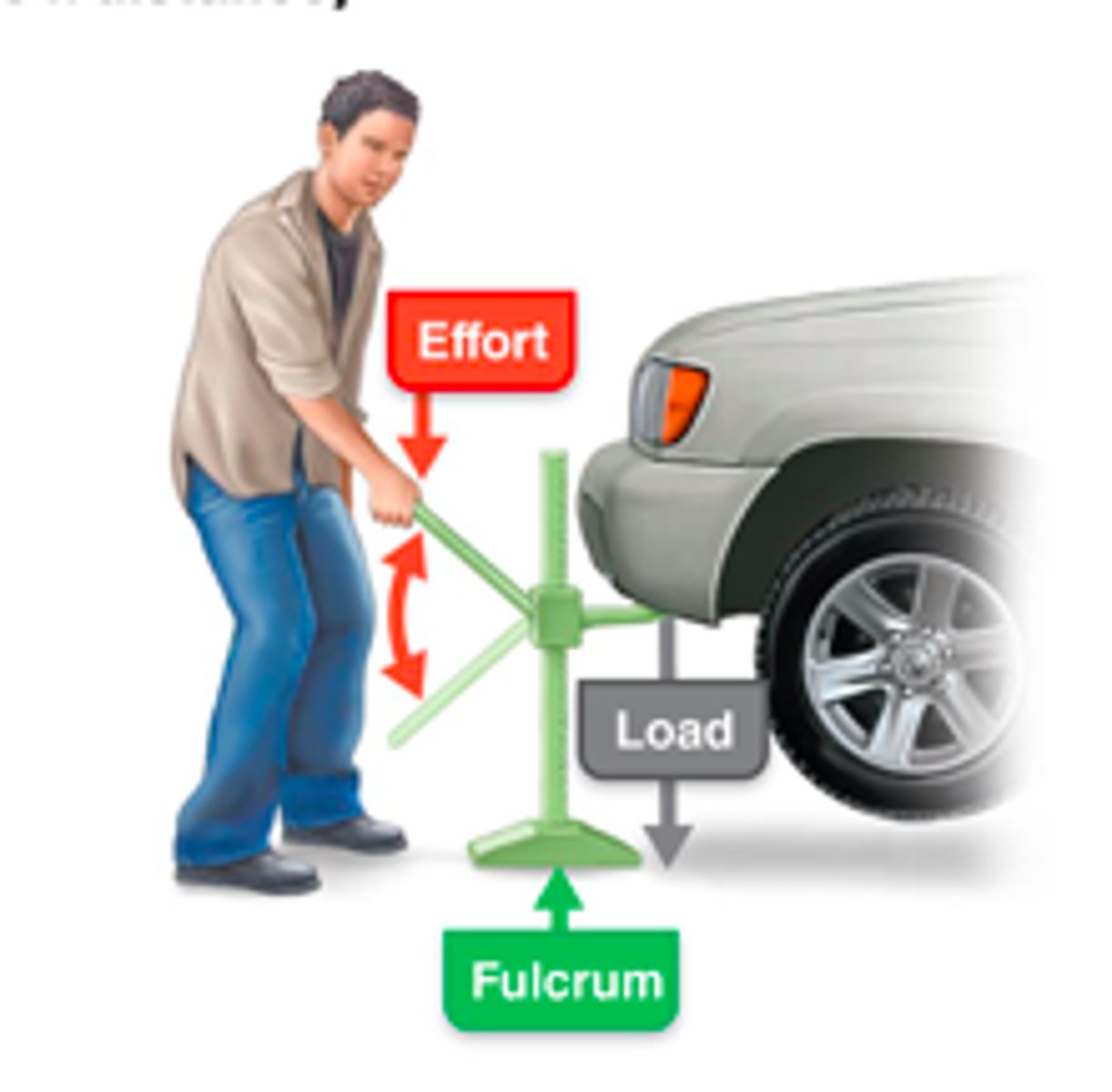
Lever system
Most skeletal muscles move using leverage
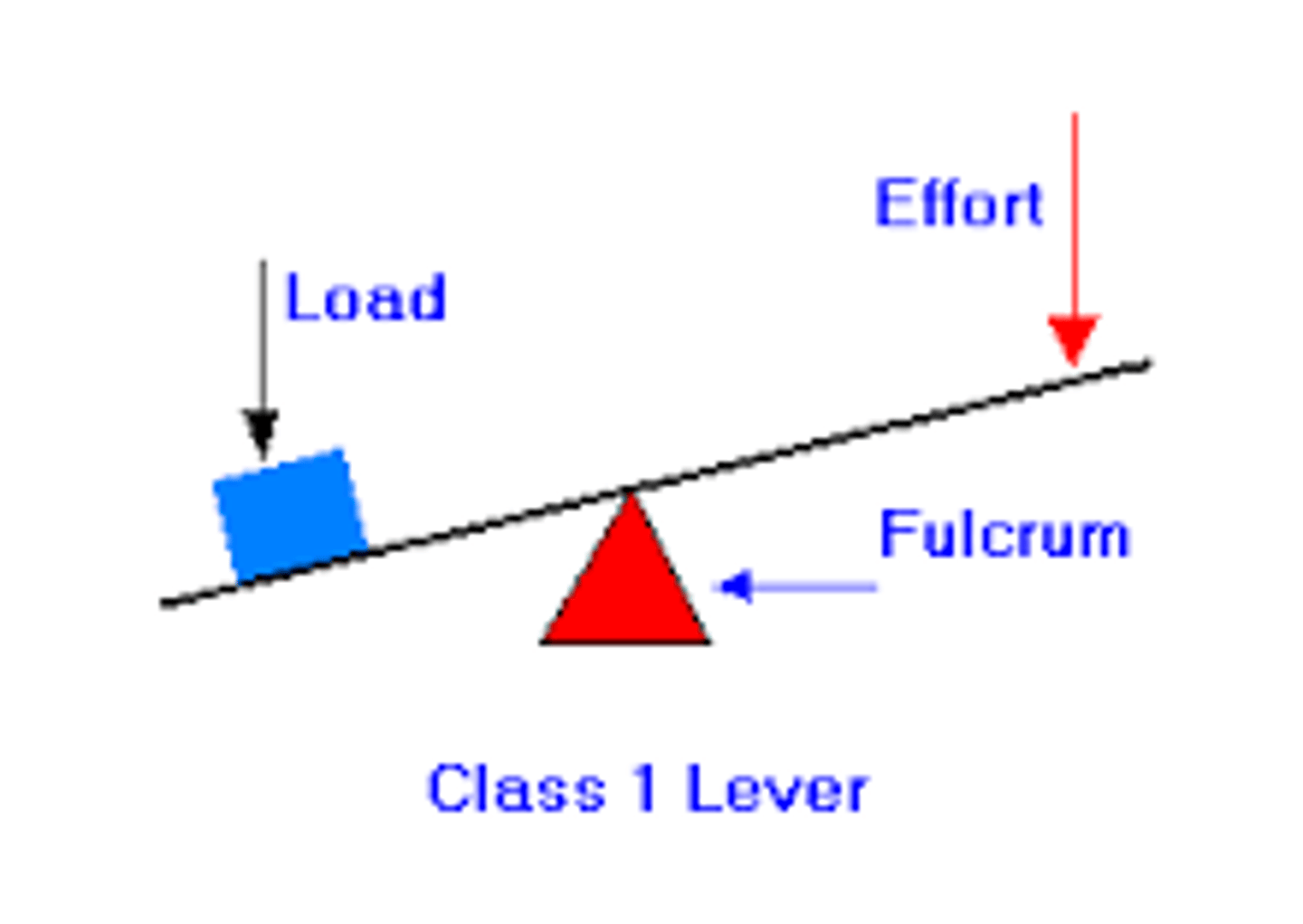
Lever
Rigid bar (bone) that moves on a fixed point called a fulcrum (joint)

Fulcrum
Fixed point on which the lever (bone) moves
Effort
Force supplied by muscle contraction
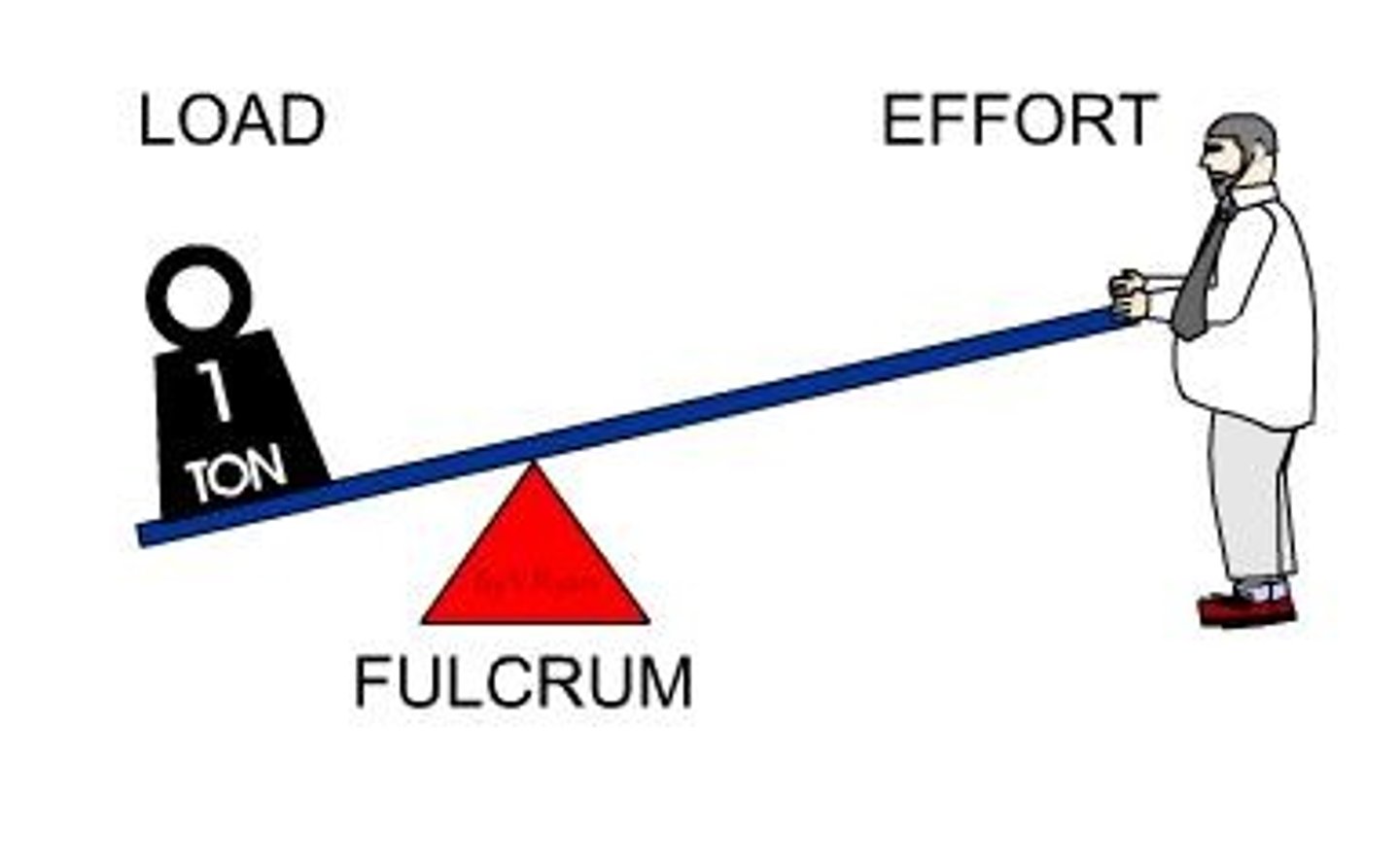
Load
Resistance (bone, tissue, or added weight)
Mechanical advantage (power lever)
Load is close to fulcrum and effort applied far; slower but stronger; used when strength is a priority
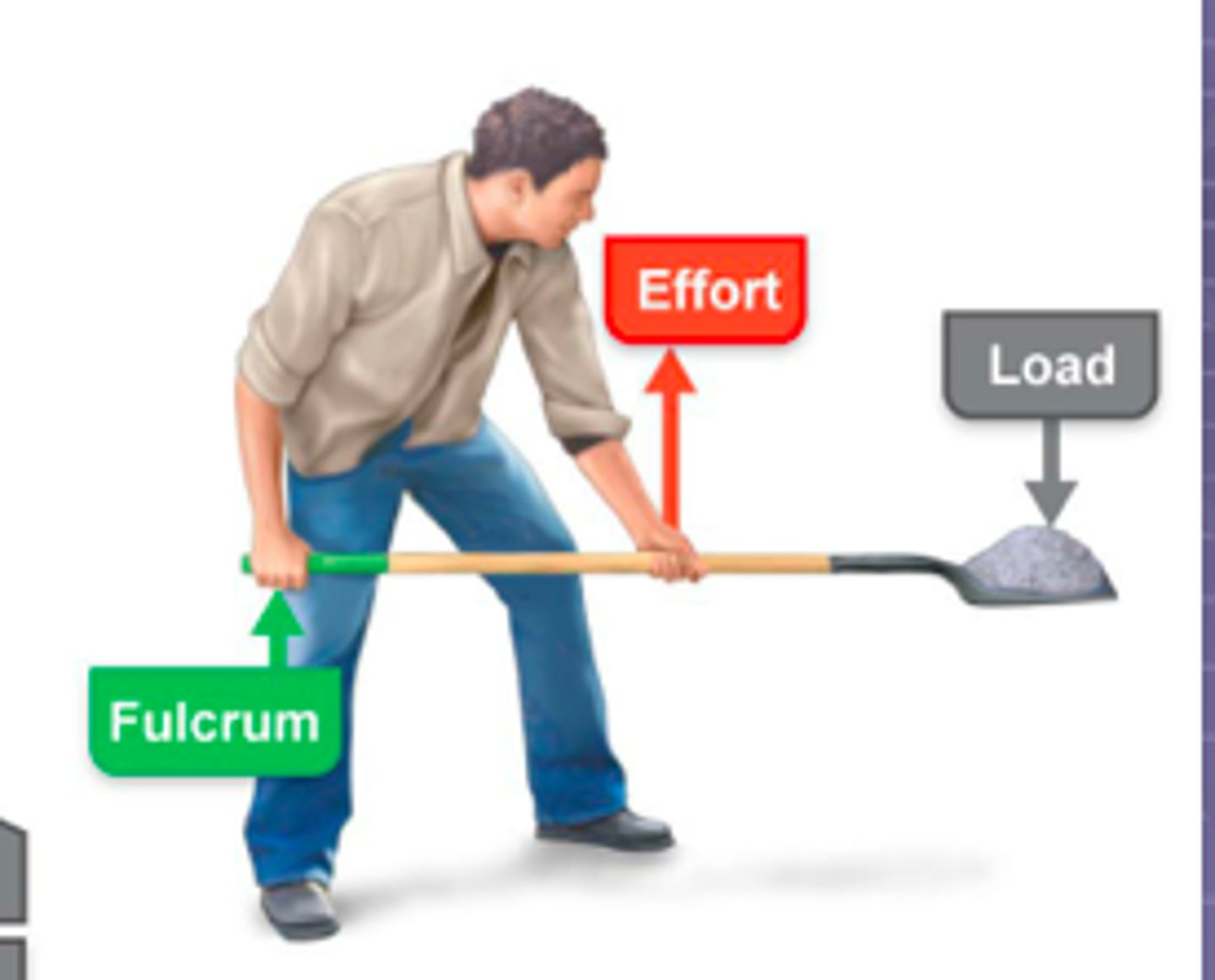
Mechanical disadvantage (speed lever)
Load is far from fulcrum and effort applied near; less force, but more speed and range of motion
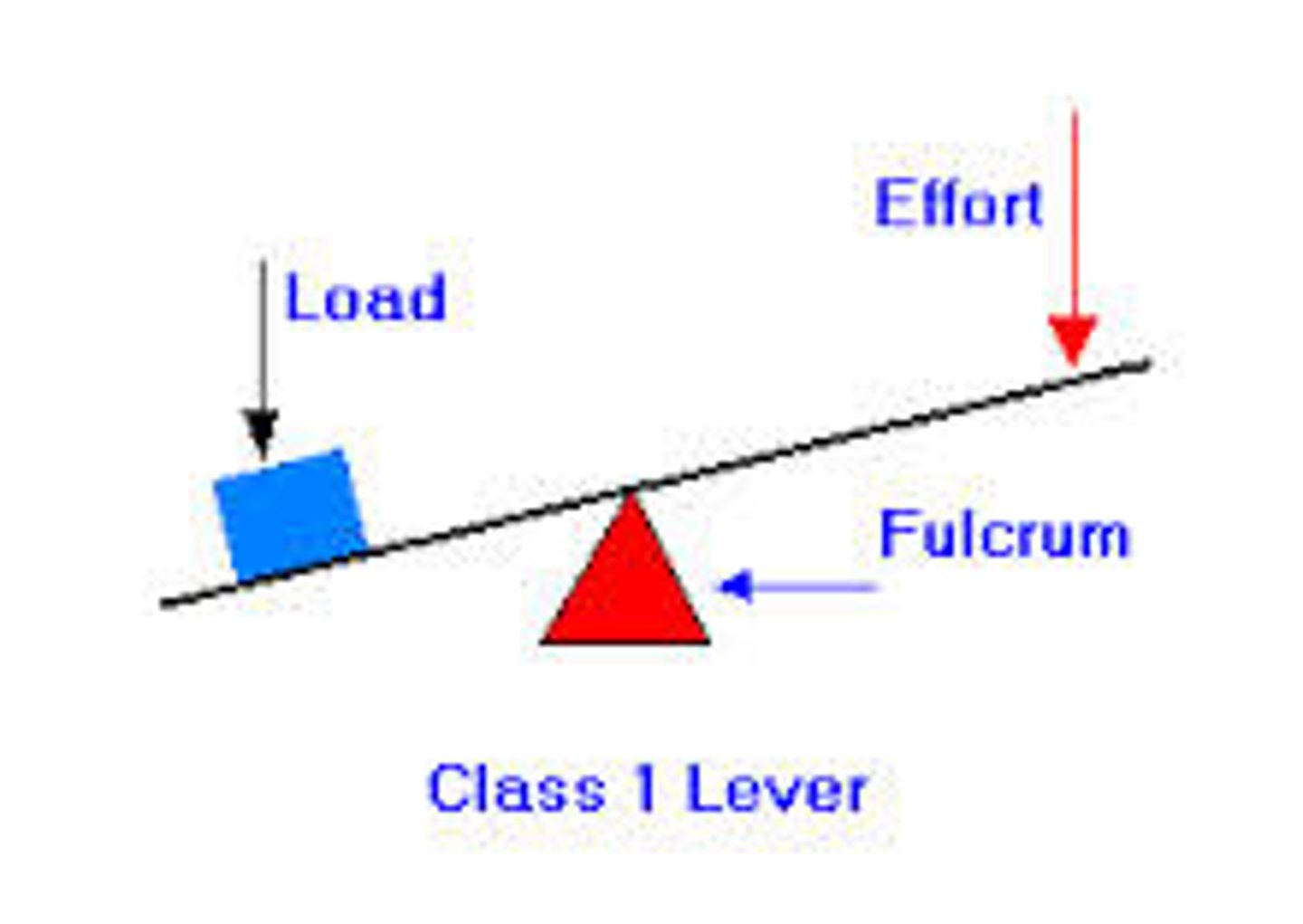
First-class lever
Fulcrum is between load and effort (example: seesaw, scissors)
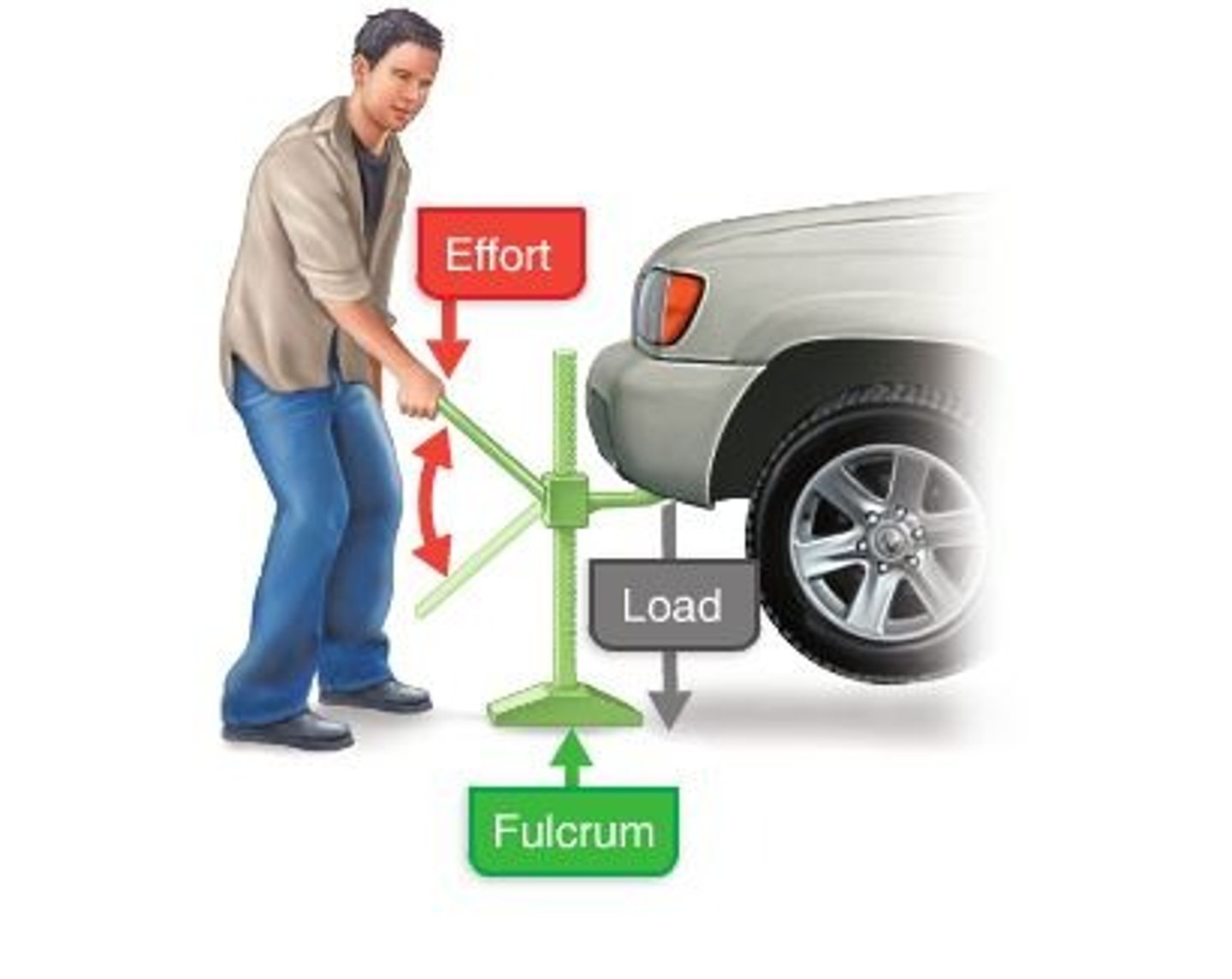
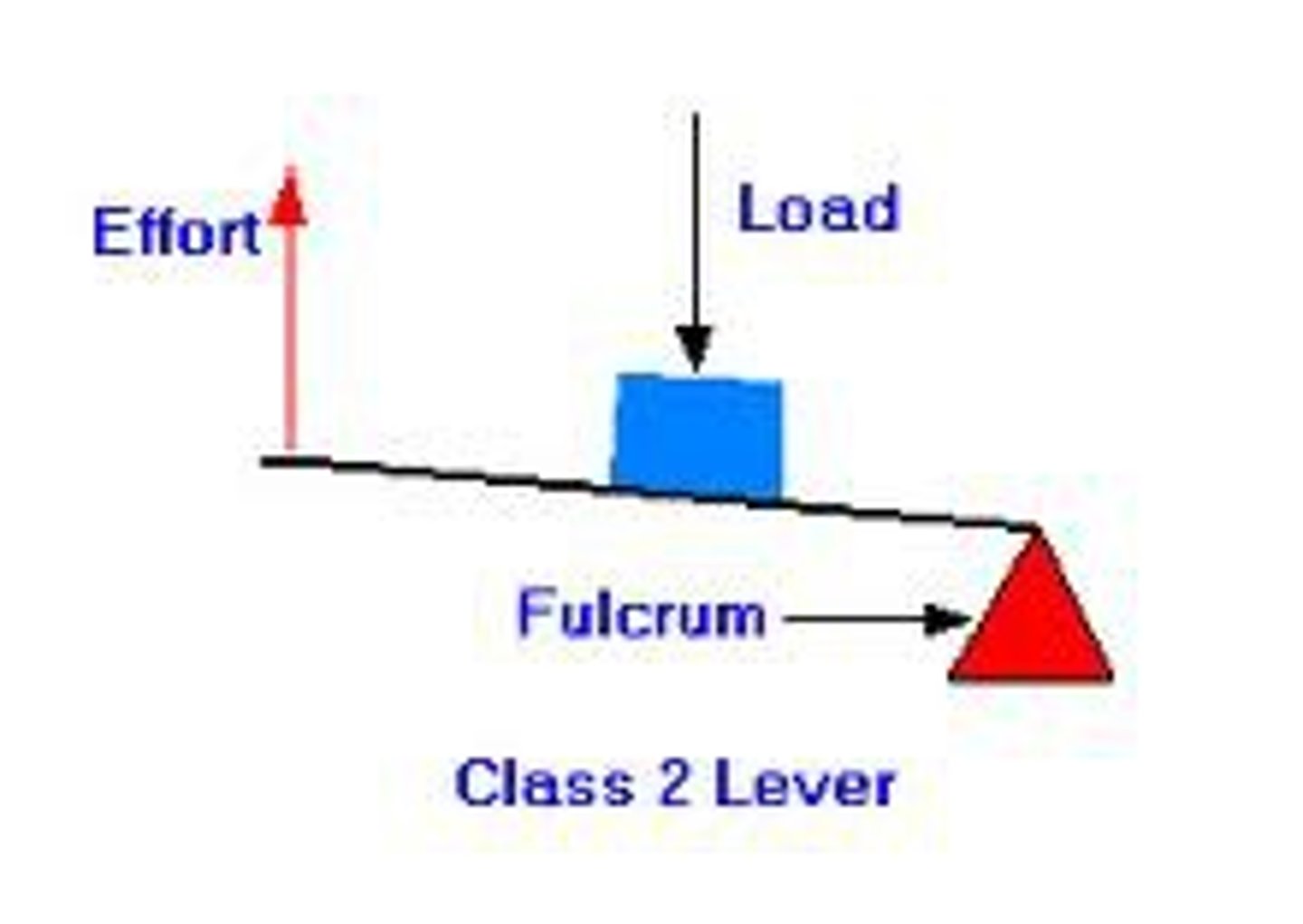
Second-class lever
Load is between fulcrum and effort (example: wheelbarrow, standing on toes)
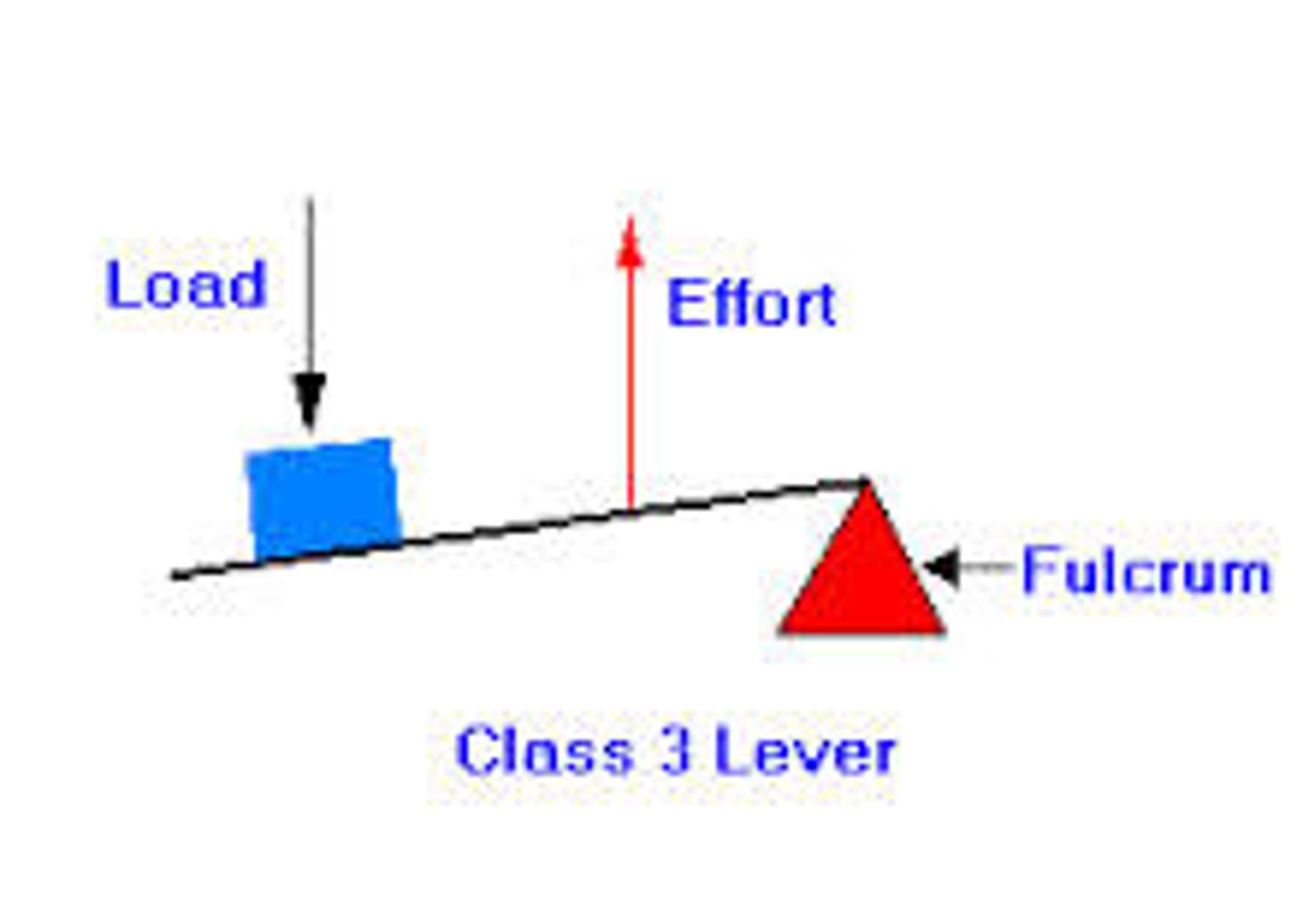
Third-class lever
Effort is between fulcrum and load (example: tweezers, most skeletal muscles)
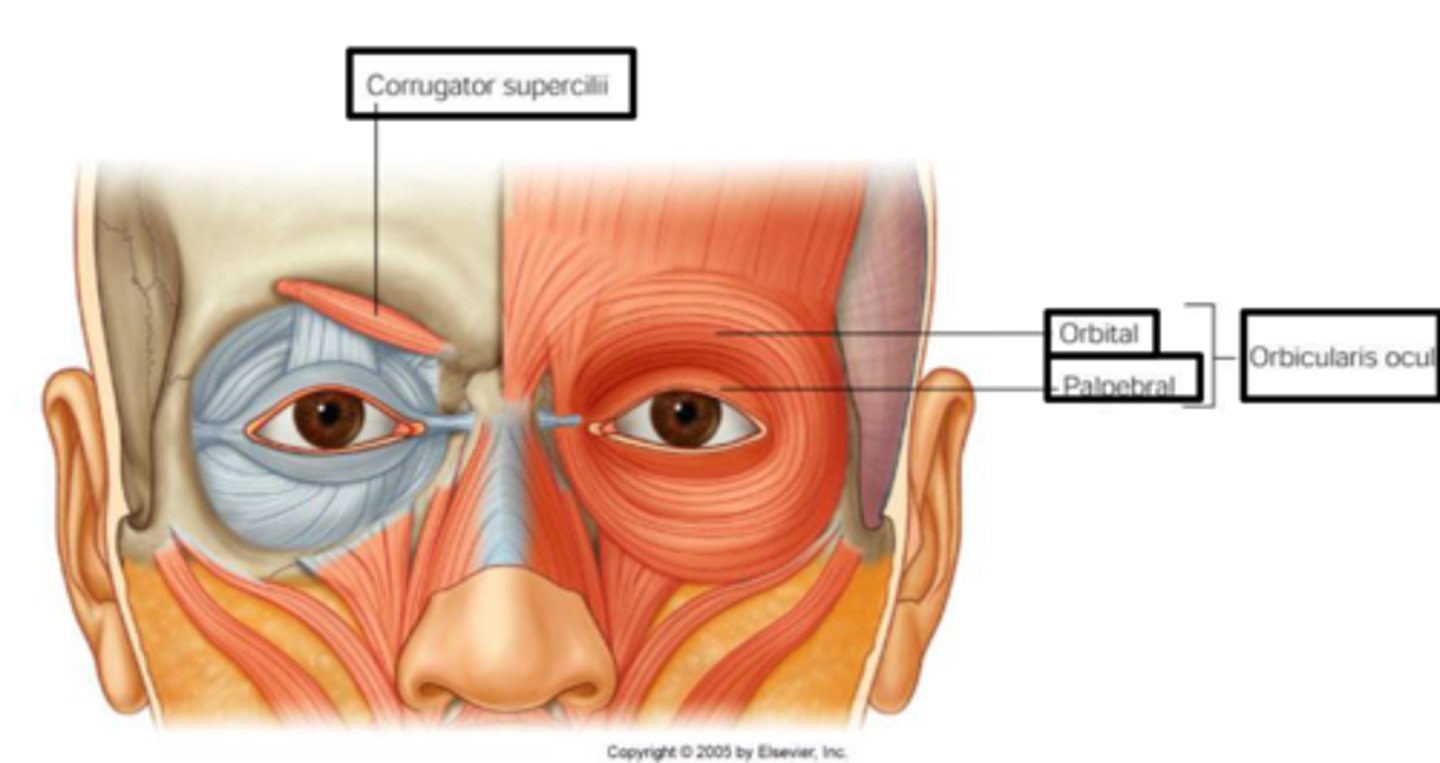
Facial expression muscles
Insert into skin, not bone; important for nonverbal communication; all innervated by cranial nerve VII (facial nerve)
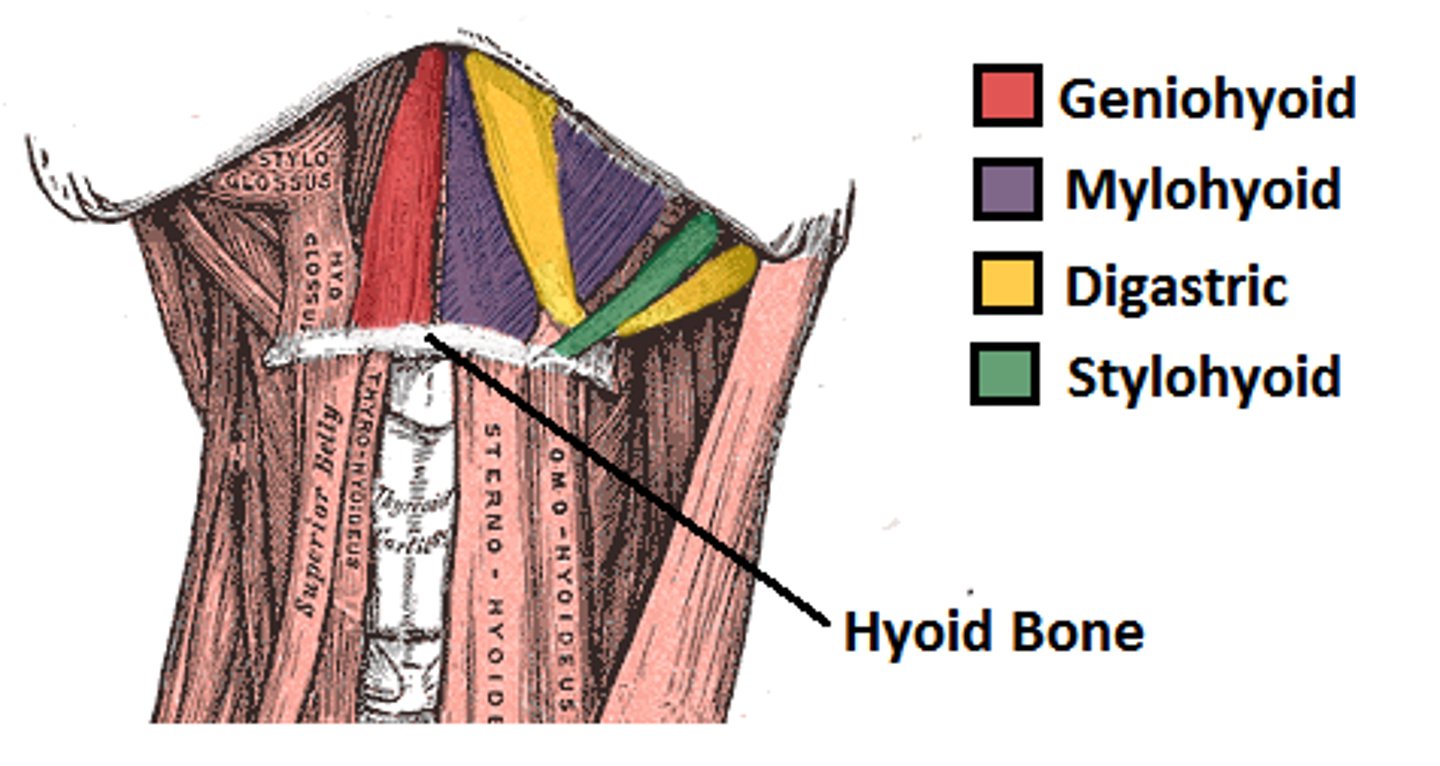
Suprahyoid muscles
Four deep muscles involved in swallowing; move hyoid bone and larynx; form floor of oral cavity; anchor tongue; elevate hyoid bone
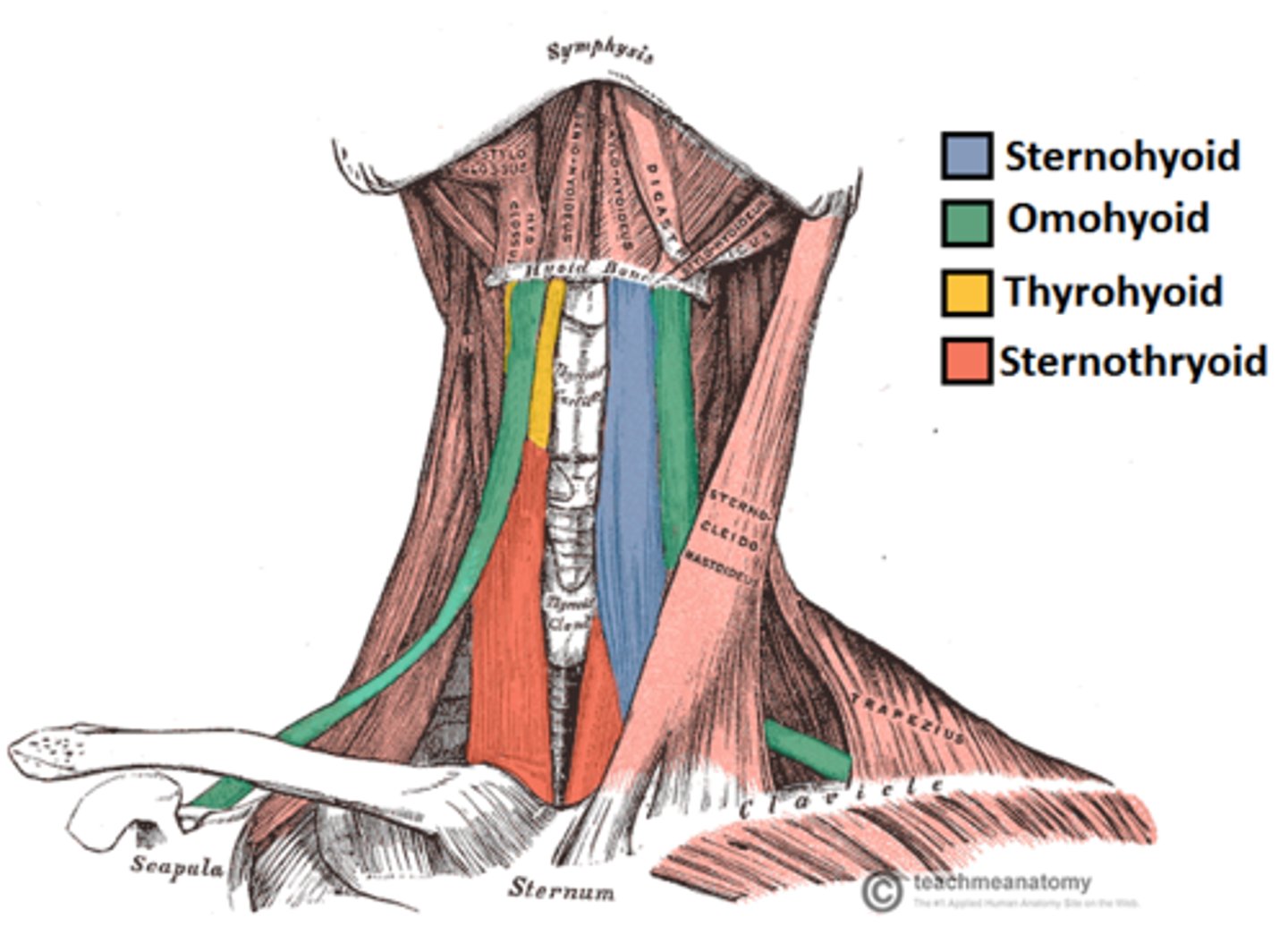
Infrahyoid muscles
Four straplike muscles; depress hyoid bone and larynx during swallowing and speaking
Inspiration (inhaling)
One of the two phases of breathing (1st)
Expiration (exhaling)
One of the two phases of breathing (2nd)
Inspiratory muscles
Diaphragm and external intercostals; their contraction enlarges the rib cage
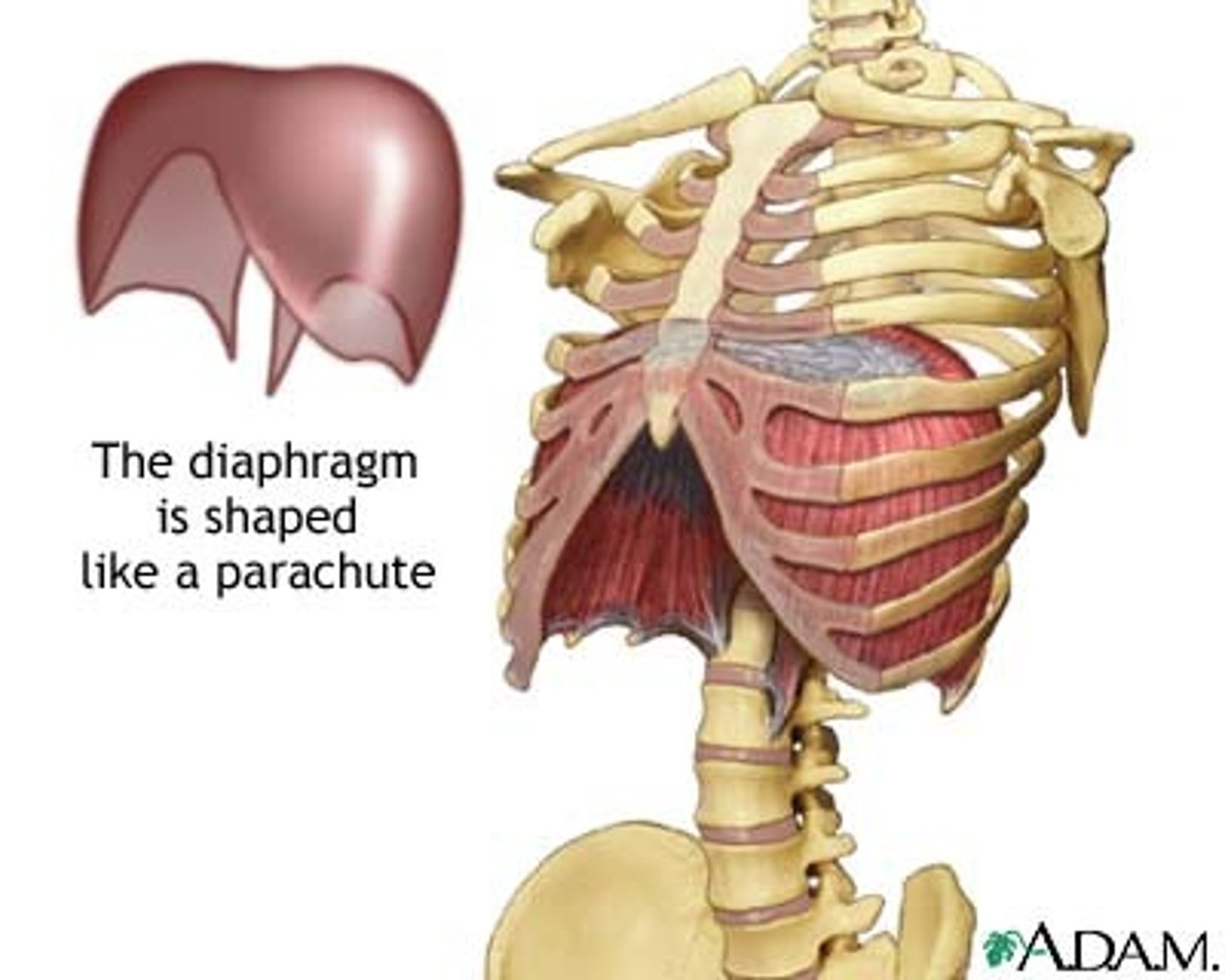
Diaphragm
Divides thoracic and abdominal cavities
Expiration mechanism
Caused by relaxation of inspiratory muscles and contraction of internal intercostals; decreases rib cage size
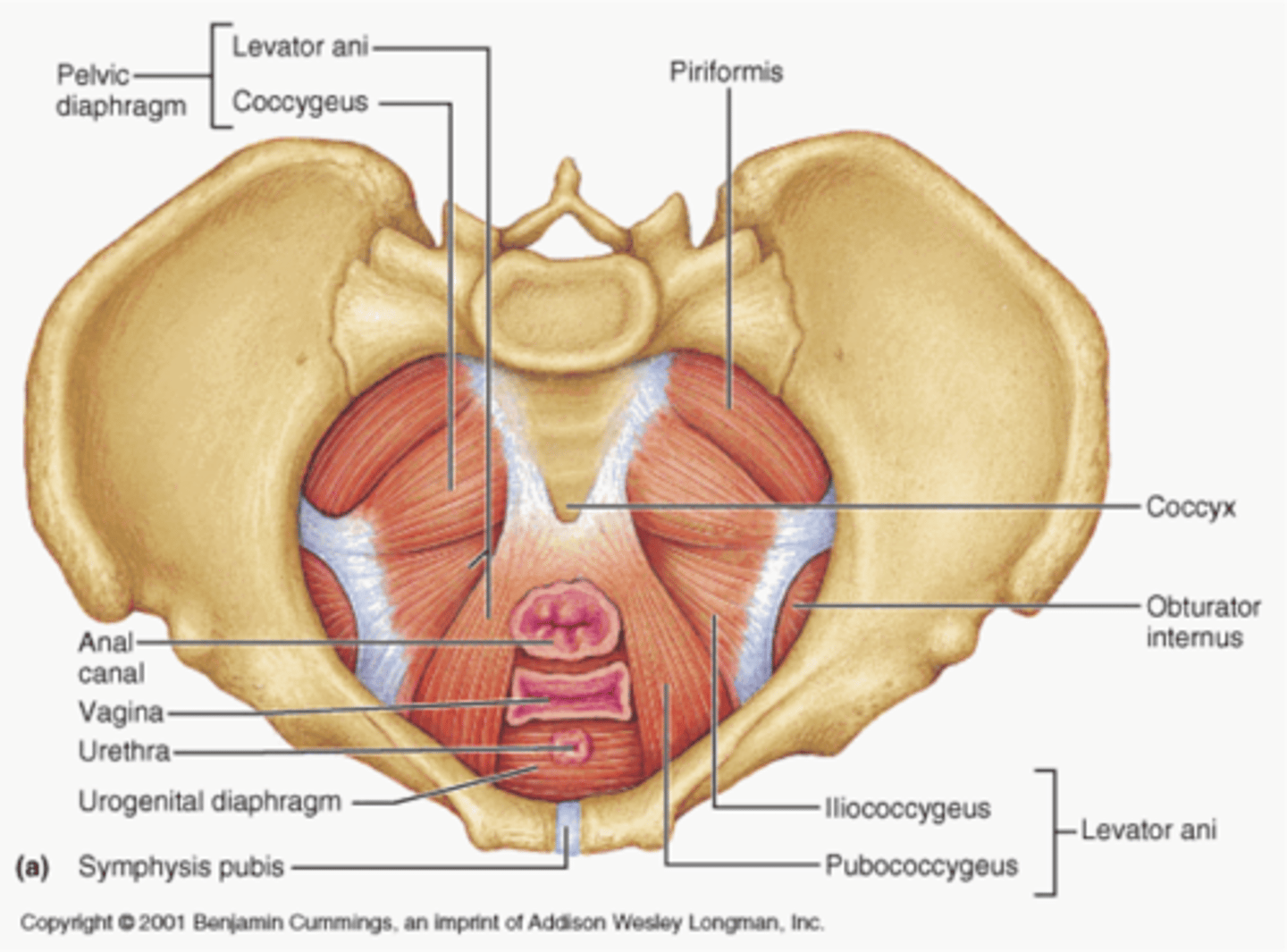
Muscles of the pelvic diaphragm
Levator ani and coccygeus; support pelvic organs, resist pressure, lift pelvic floor to release feces
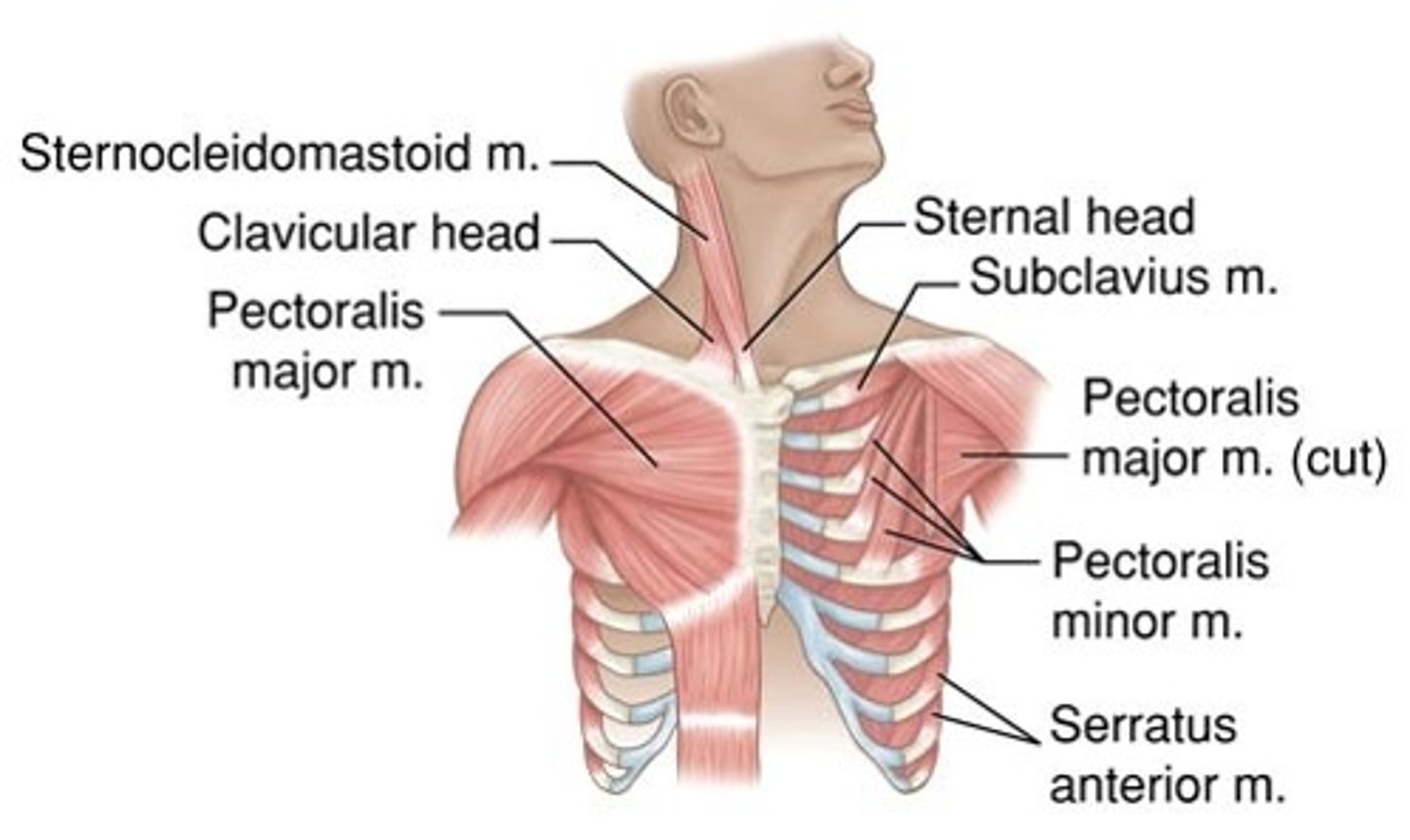
Extrinsic shoulder muscles
Fix the scapula and move it to increase range of arm movements; perform elevation, depression, rotation, protraction, and retraction
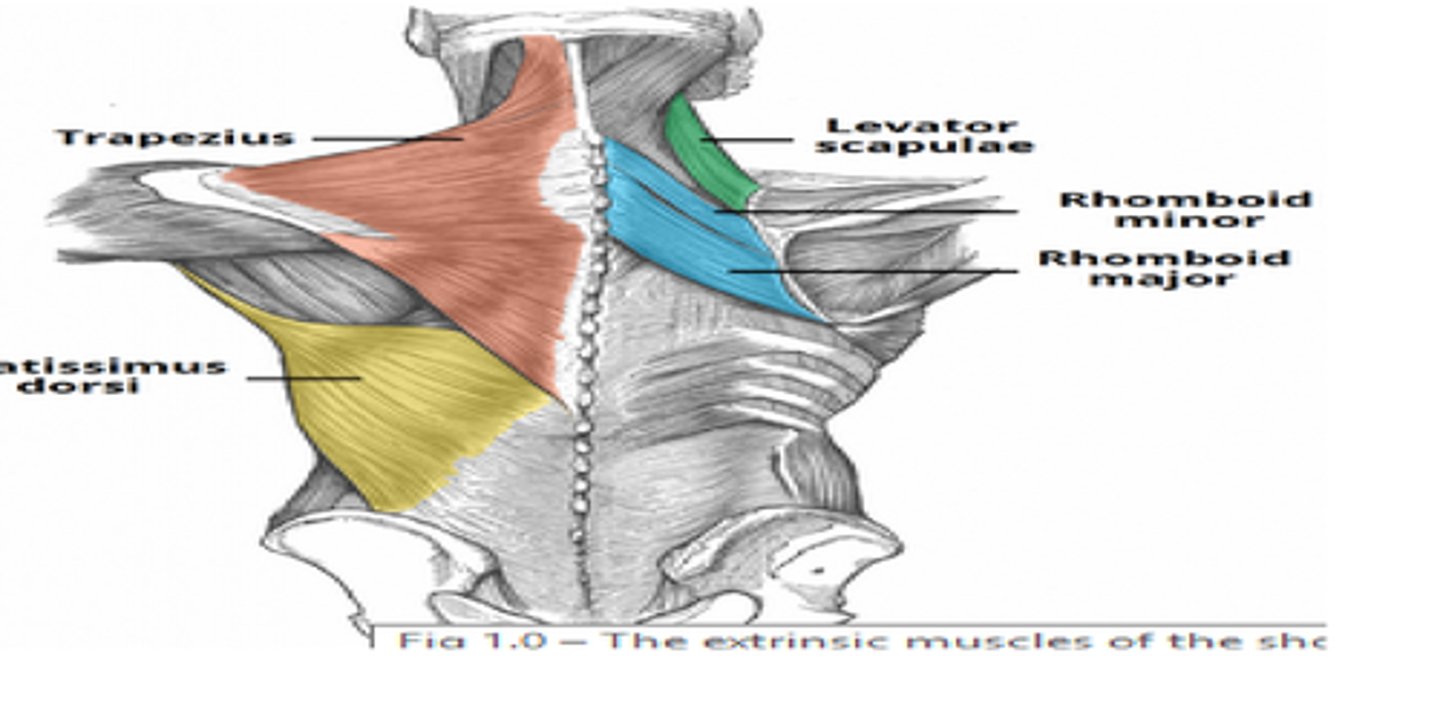
Nine muscles crossing shoulder joint
Insert on and move the humerus; originate from scapula or axial skeleton; perform flexion, extension, and adduction
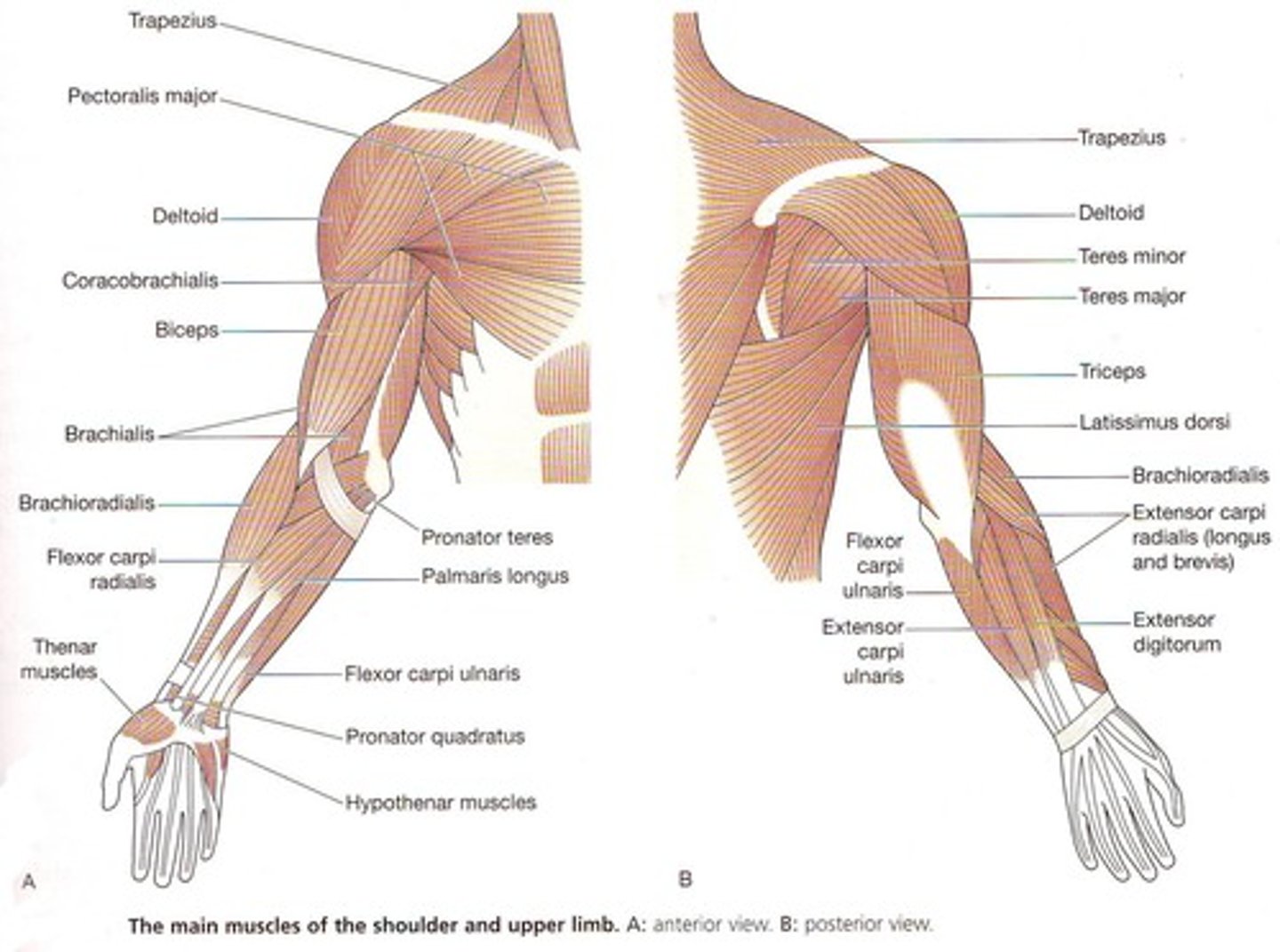
Three prime movers of the arm (shoulder joint)
Pectoralis major, Latissimus dorsi, and Deltoid
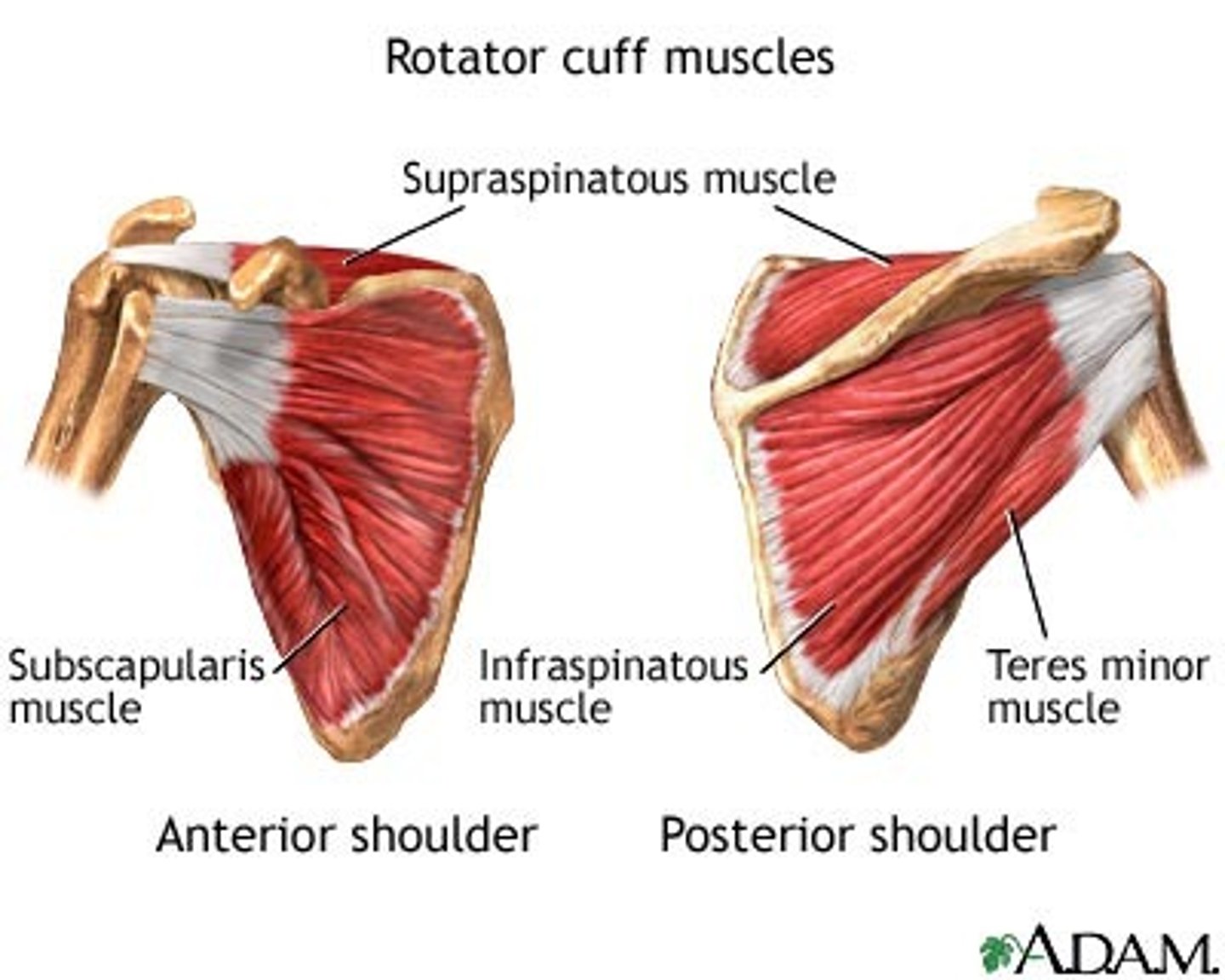
Rotator cuff muscles
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor, and Subscapularis; stabilize shoulder joint and prevent dislocation
Coracobrachialis and teres major
Synergists to the prime movers of the arm
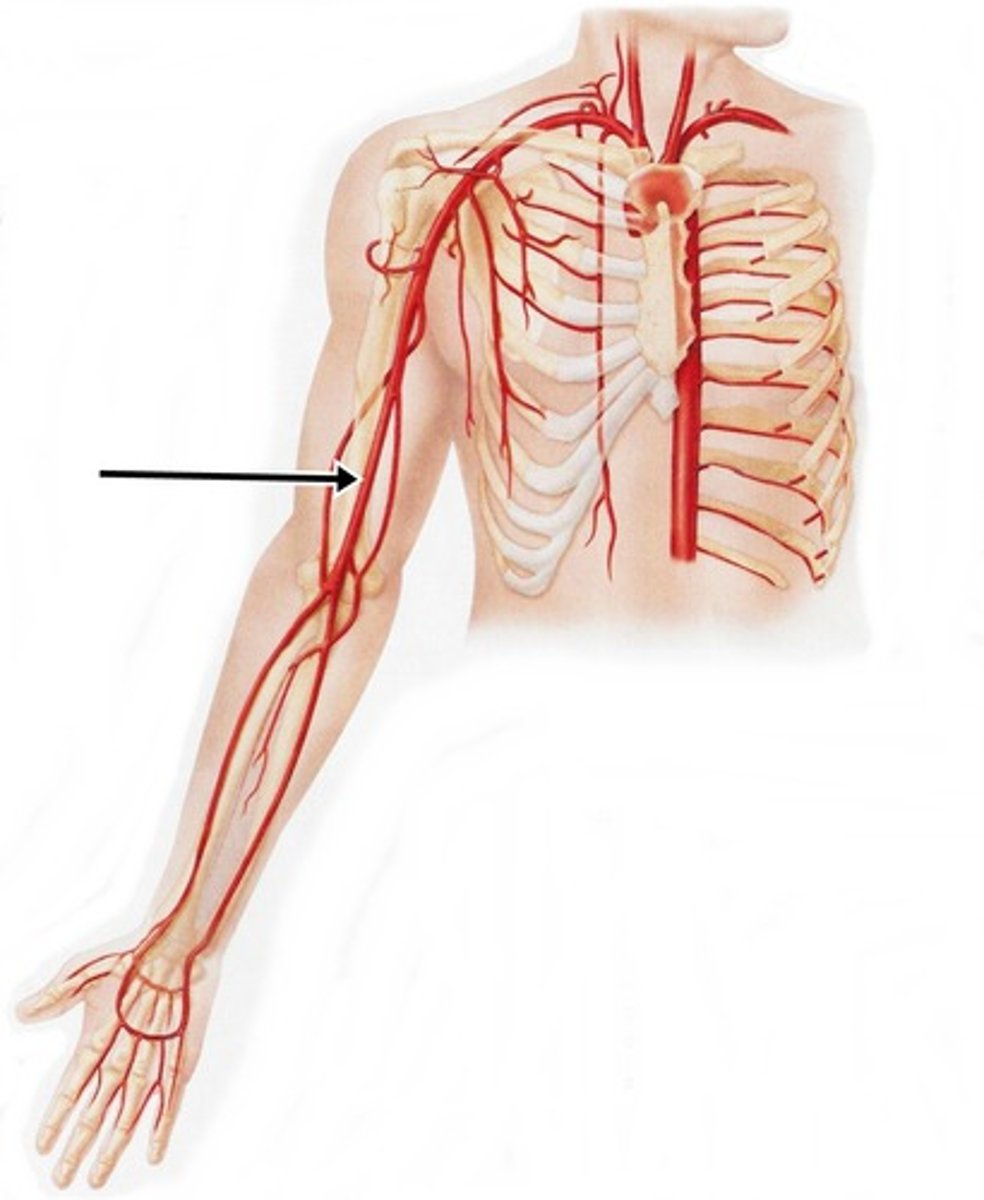
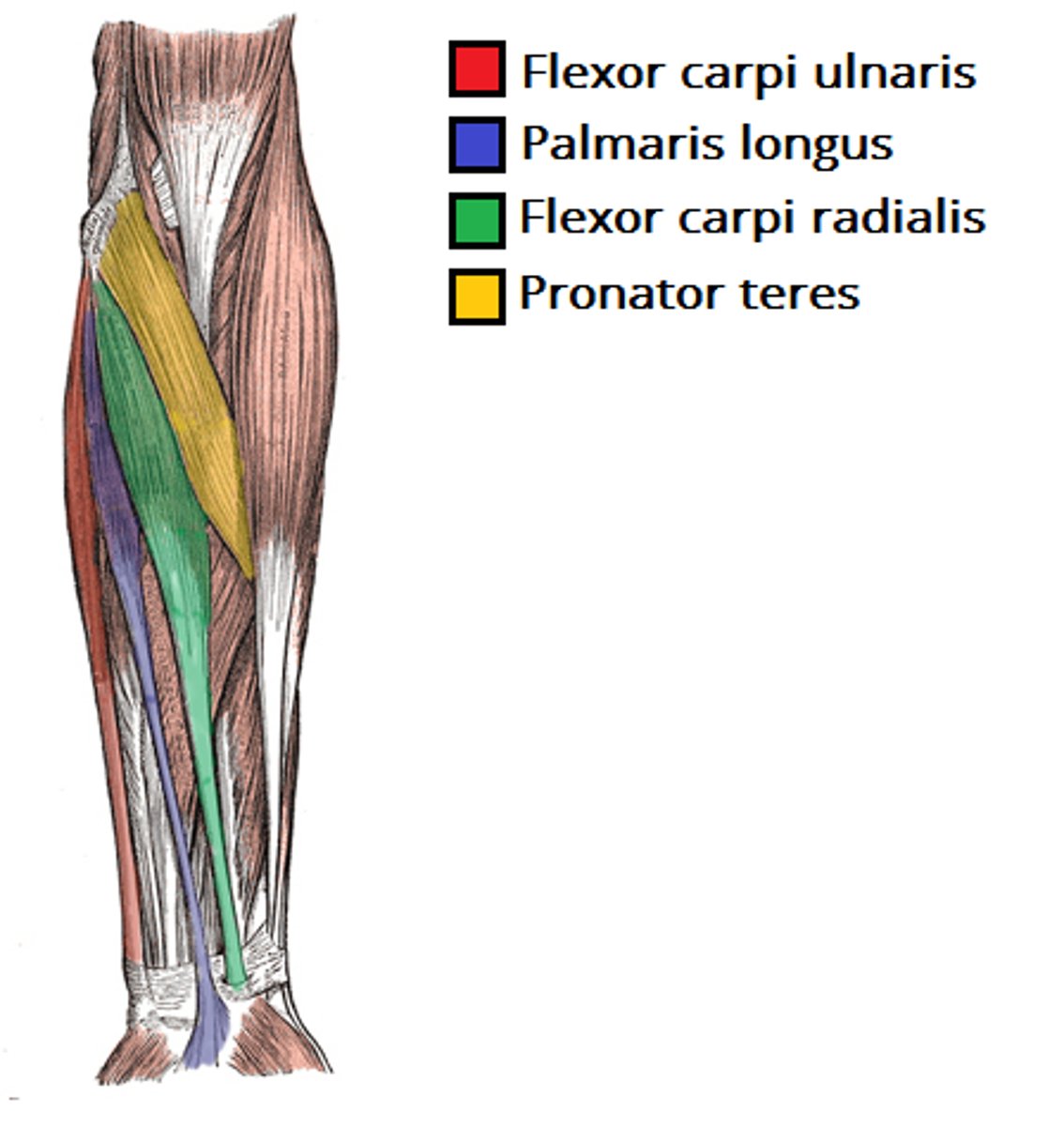
Anterior forearm muscles
Mostly flexors; insert via flexor retinaculum
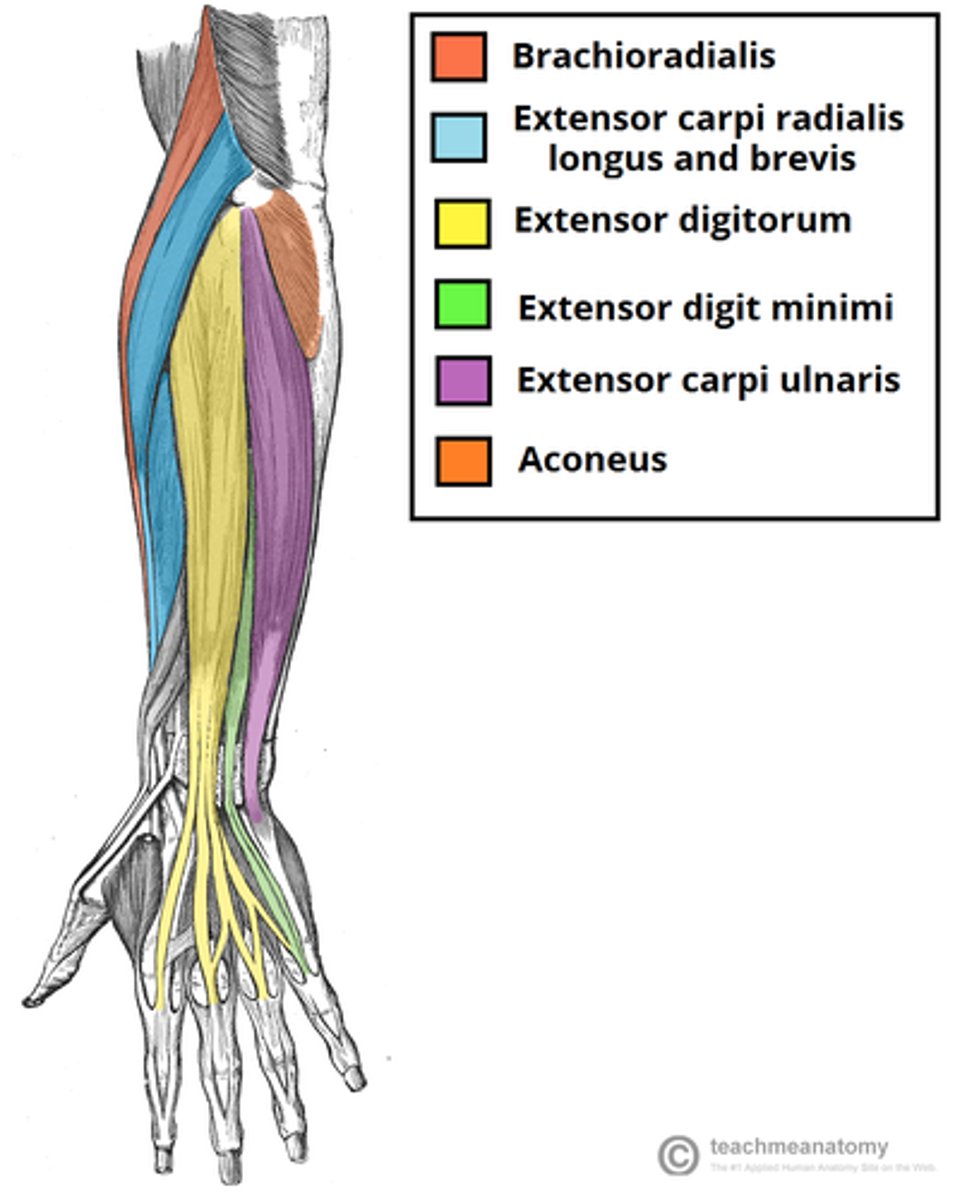
Posterior forearm muscles
Mostly extensors; insert via extensor retinaculum
Pronator teres and pronator quadratus
Muscles that pronate the forearm
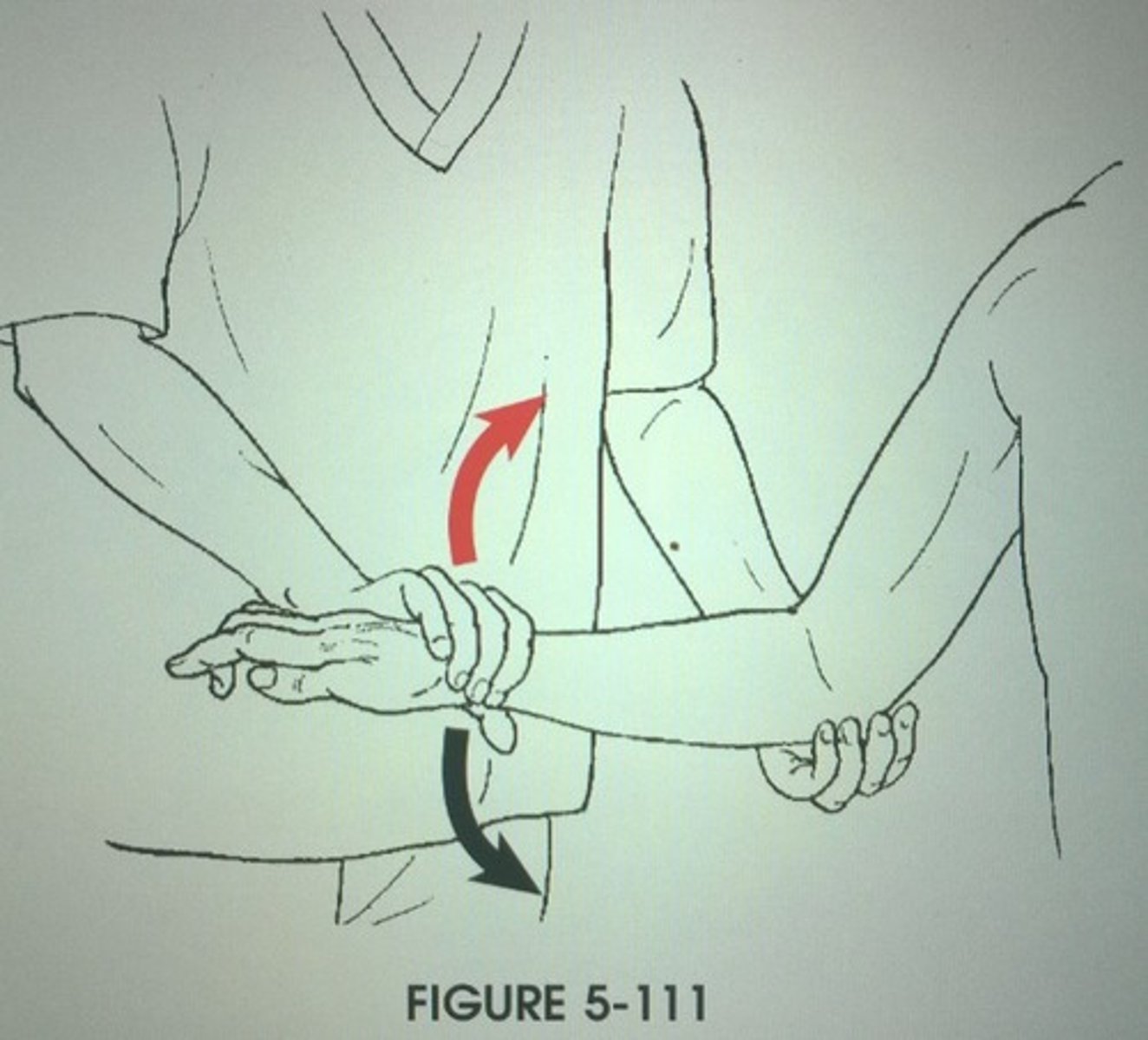
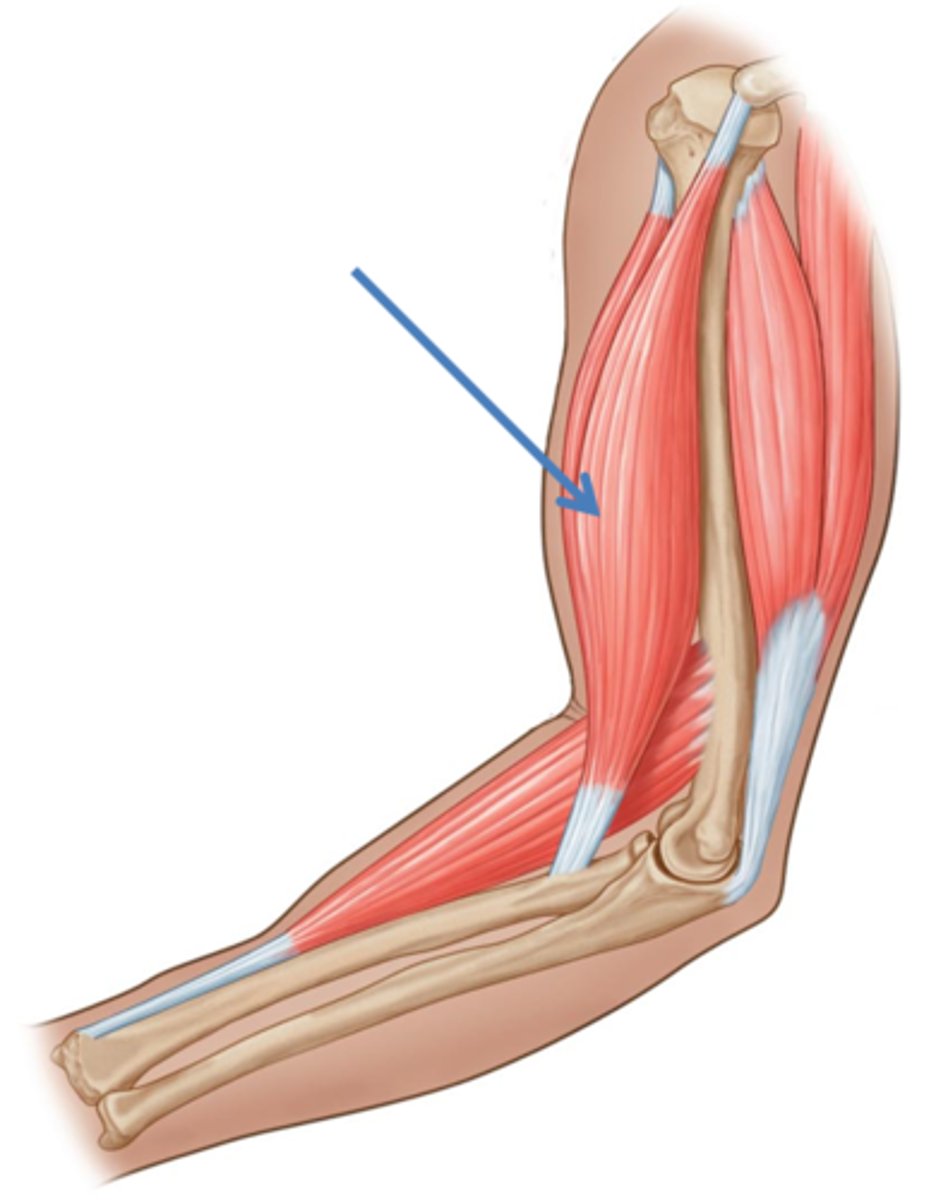
Supinator
Synergist with biceps brachii in forearm supination
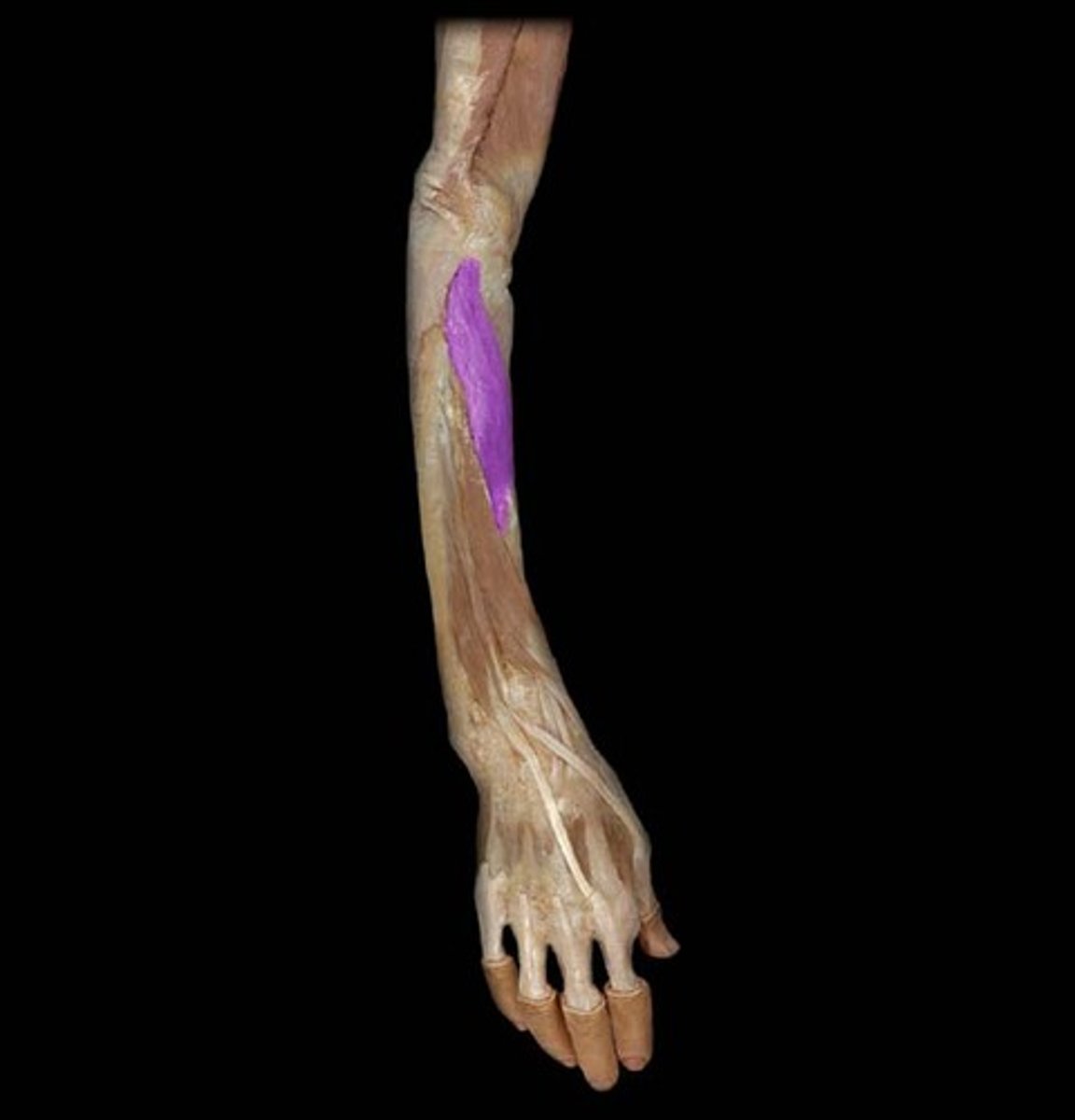
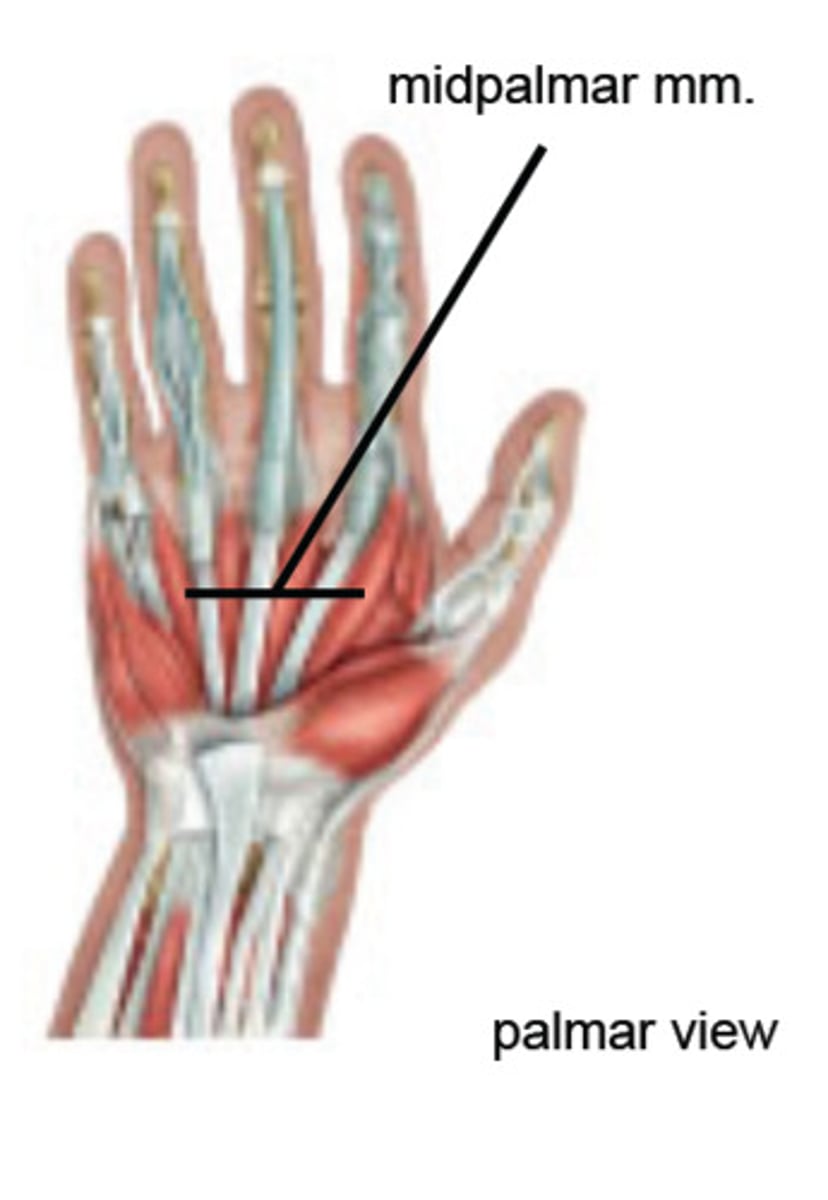
Intrinsic muscles of the hand
Cause fine finger movements; include Thenar eminence, Hypothenar eminence, and Midpalmar muscles
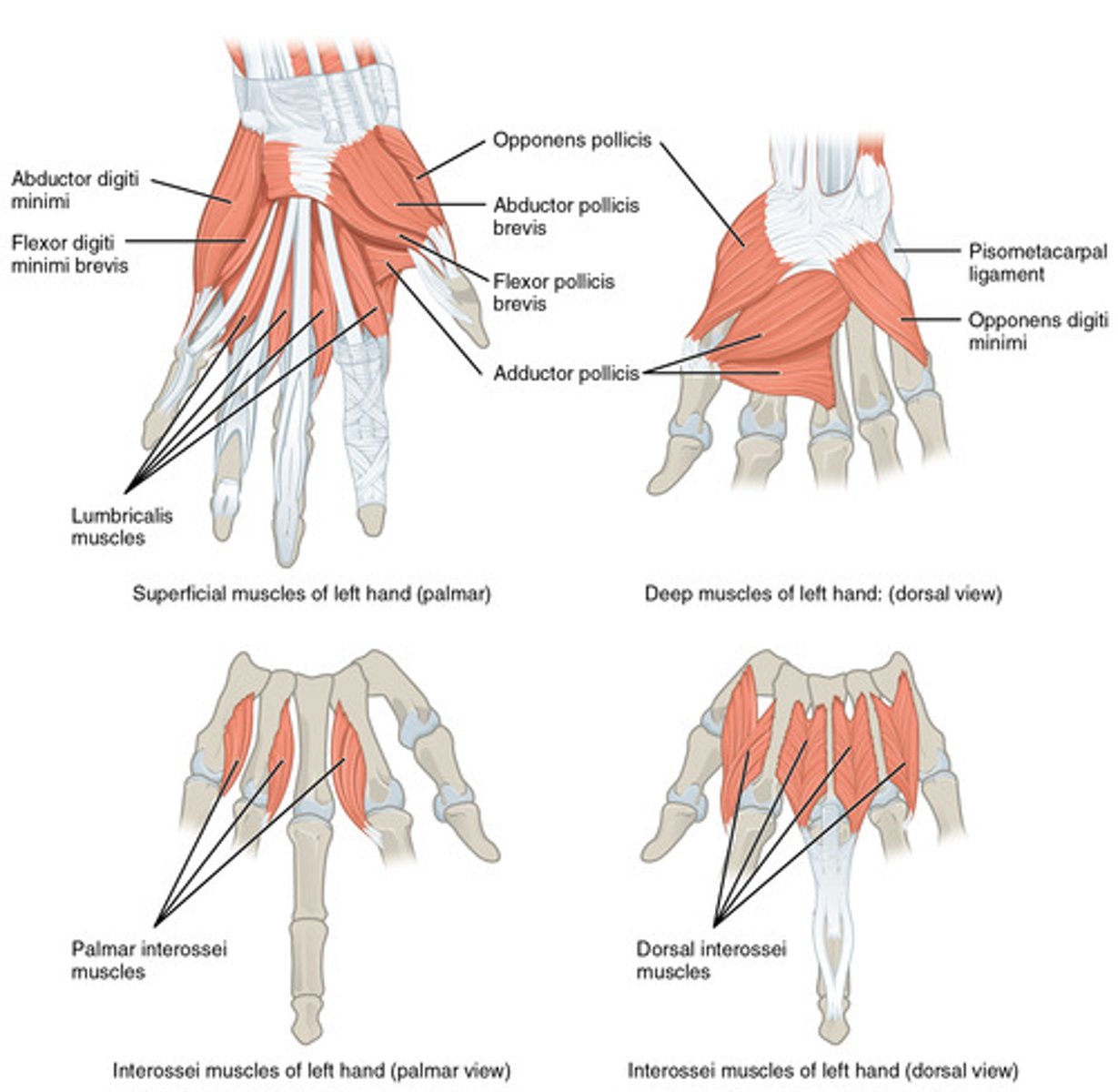
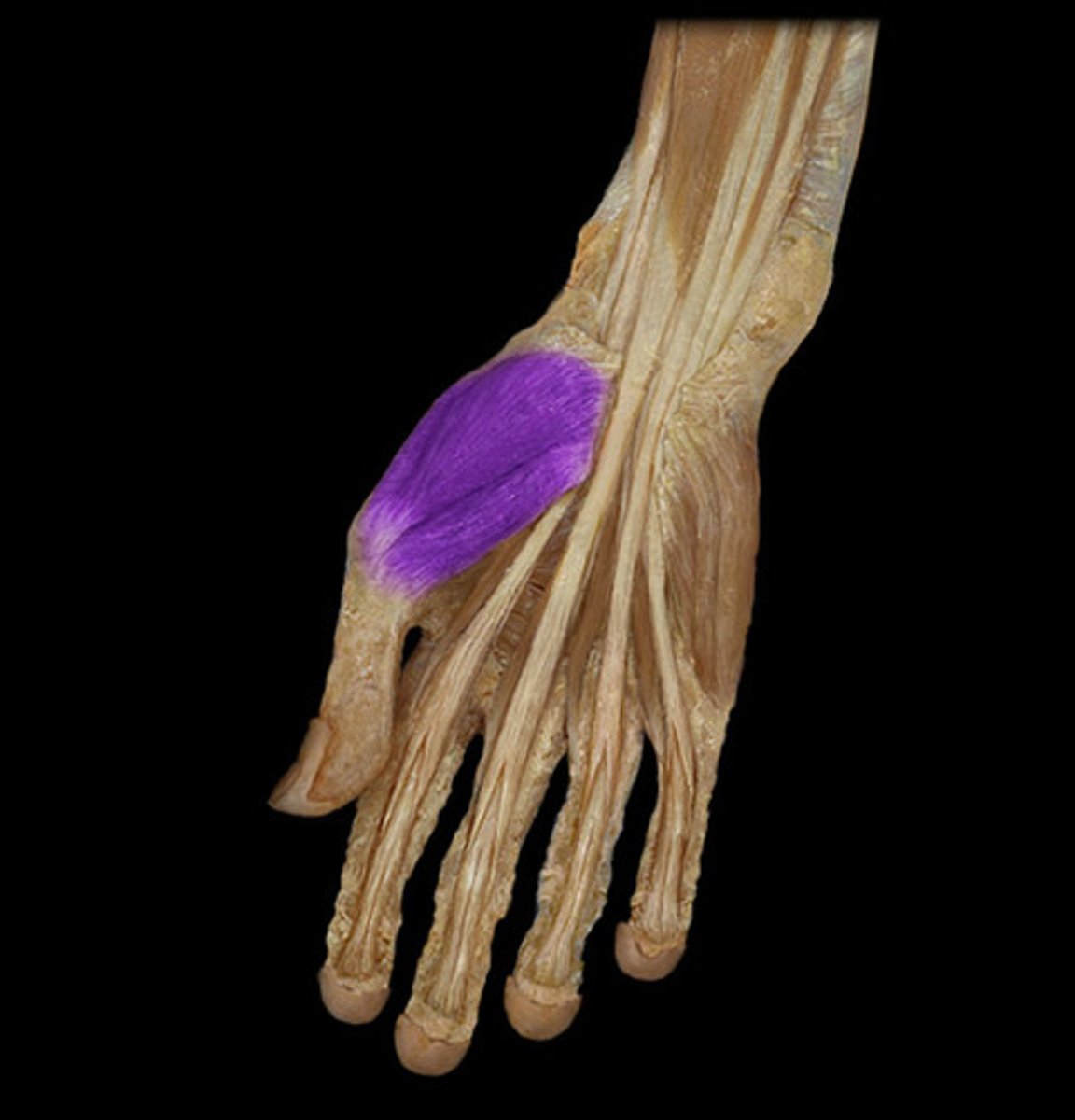
Thenar eminence
Ball of thumb; includes flexor, abductor, and opponens muscles
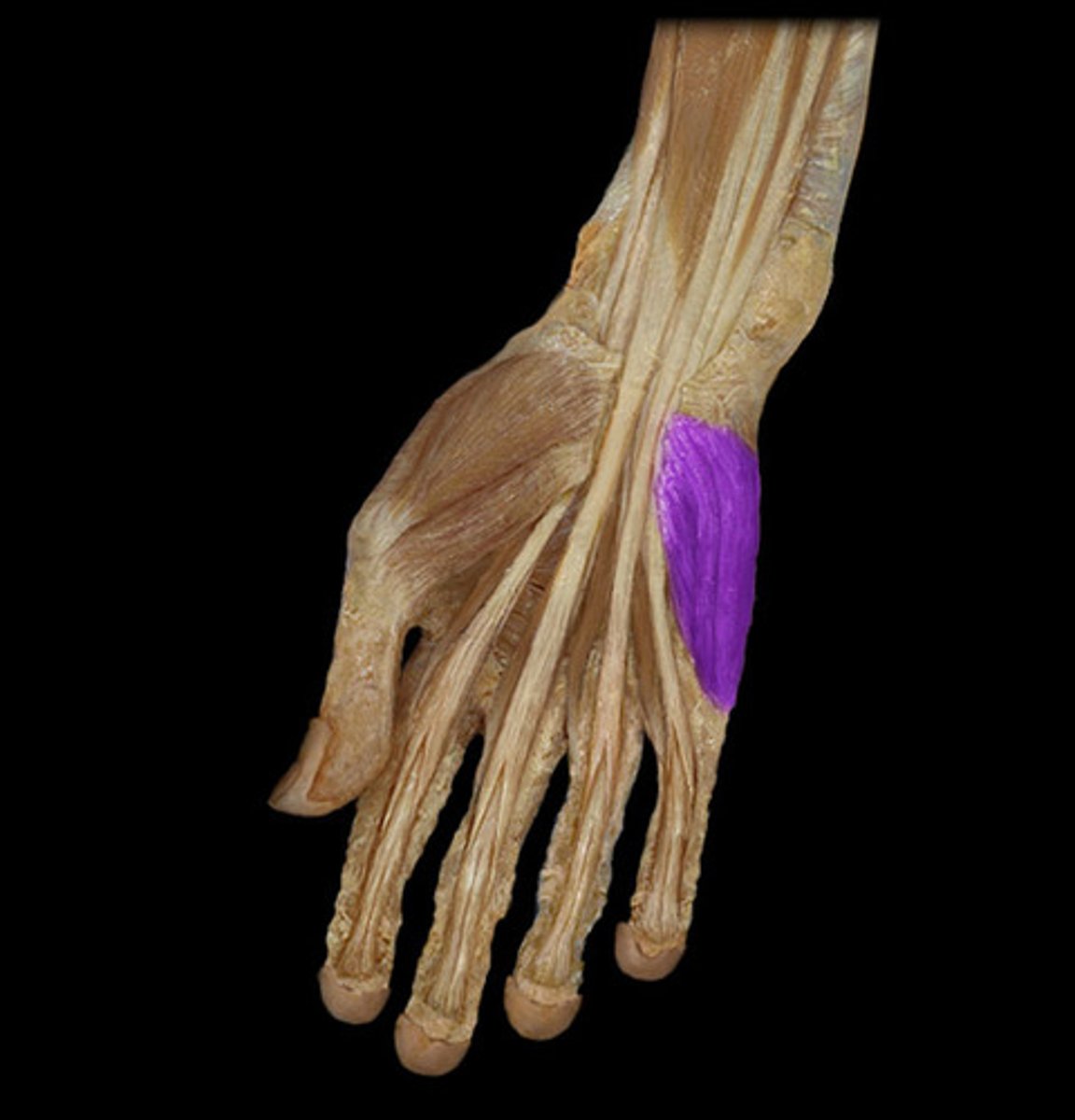
Hypothenar eminence
Ball of the little finger; includes flexor, abductor, and opponens muscles
Lumbricals and interossei
Midpalmar muscles ; extend fingers
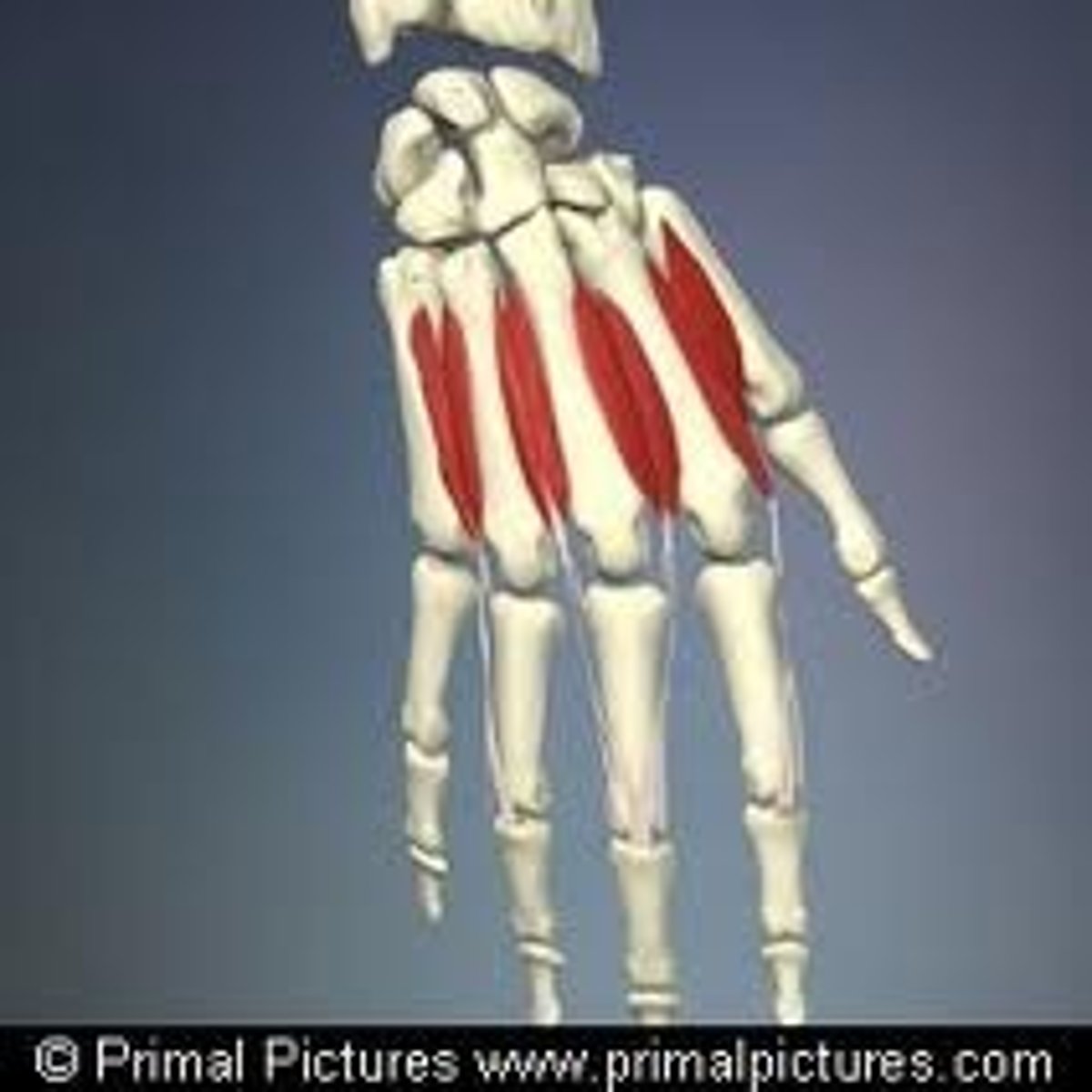
Interossei muscles
Abduct and adduct fingers
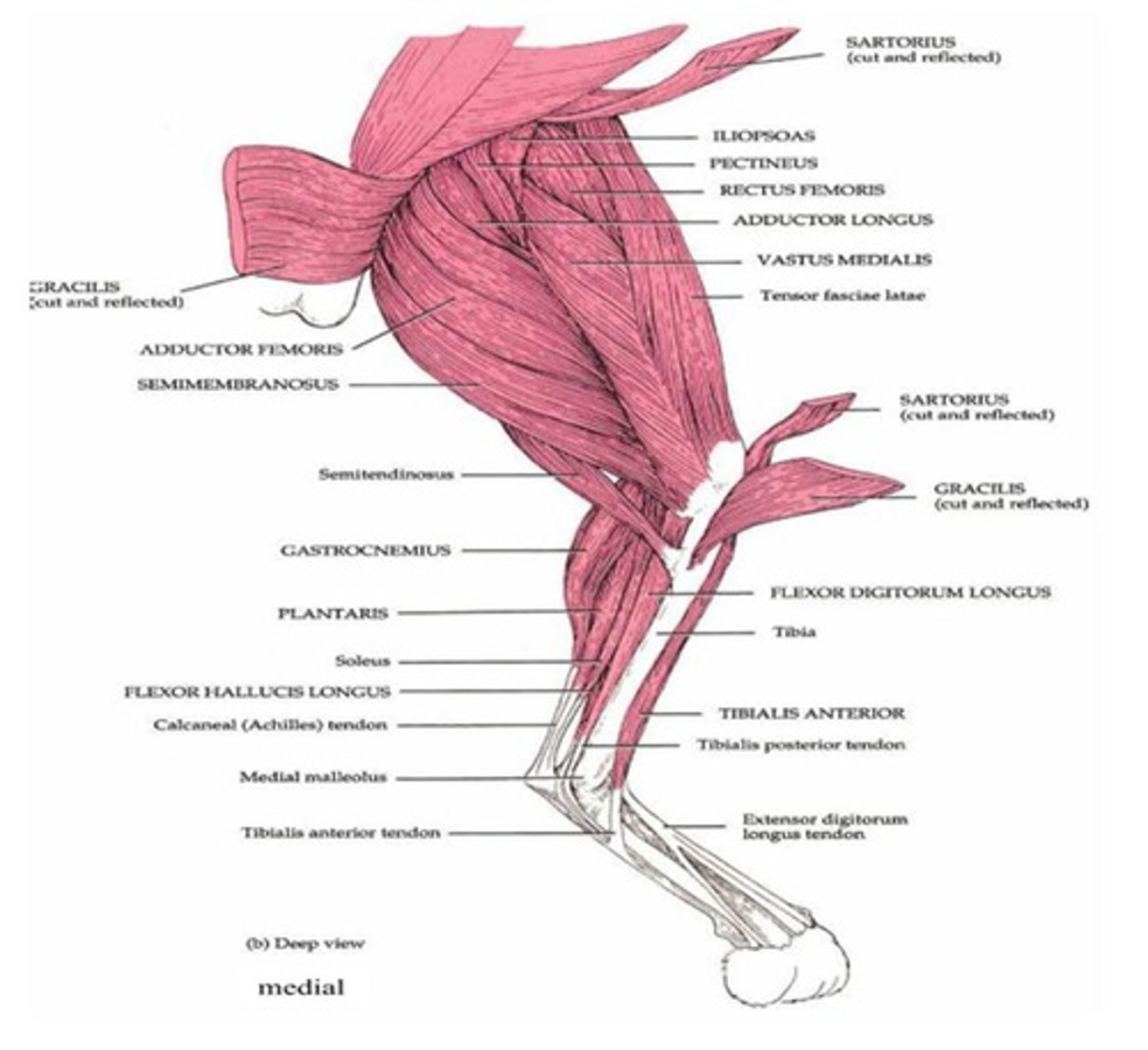
Thigh muscle groups
Divided into anterior, medial, and posterior compartments
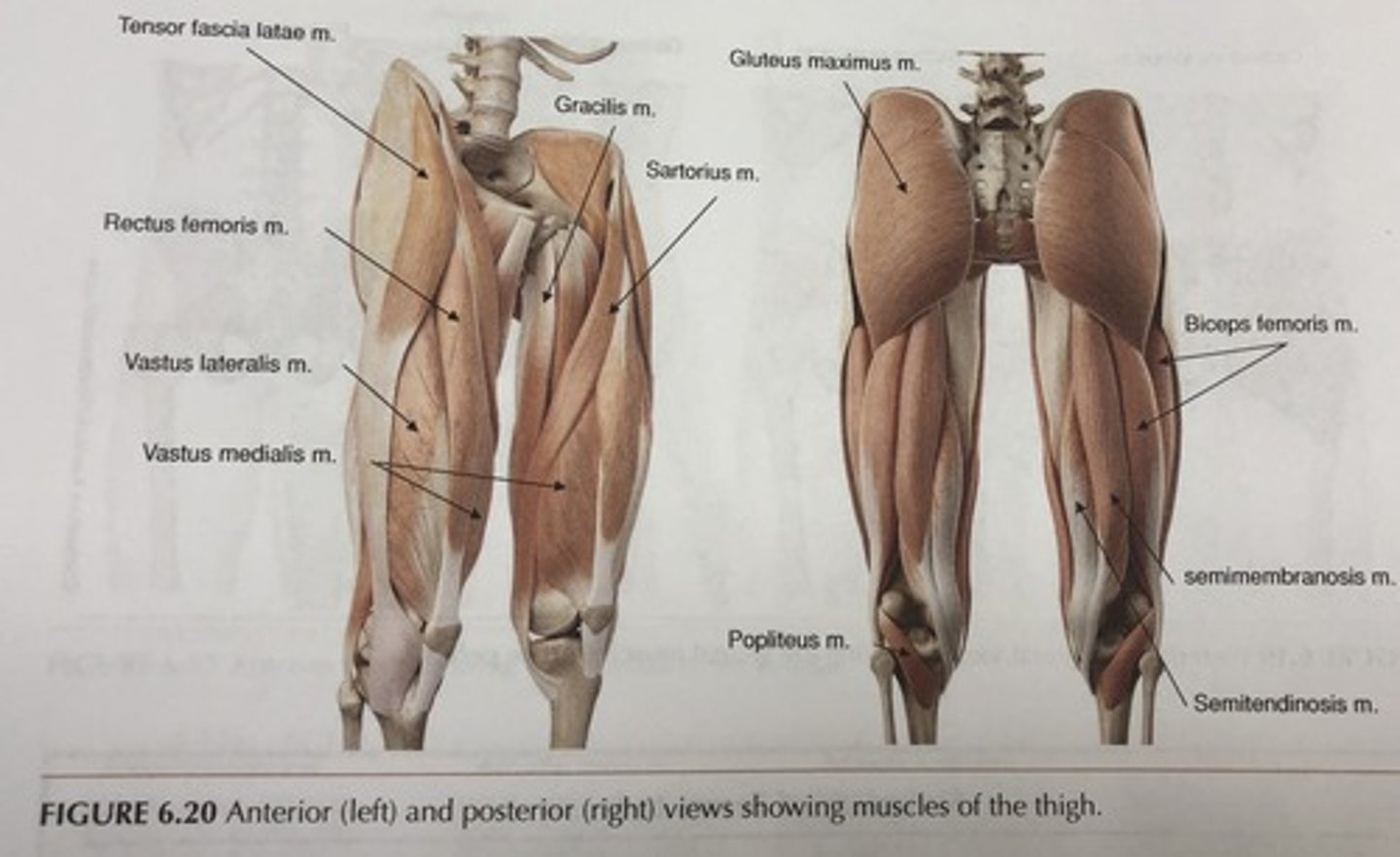
Most anterior thigh muscles
Flex femur at hip and extend leg at knee (foreswing of walking)
Most posterior thigh muscles
Extend thigh and flex leg (backswing of walking)
Medial thigh muscles
Adduct thigh
Fascia lata
Fibrous connective tissue that encloses all three thigh muscle groups
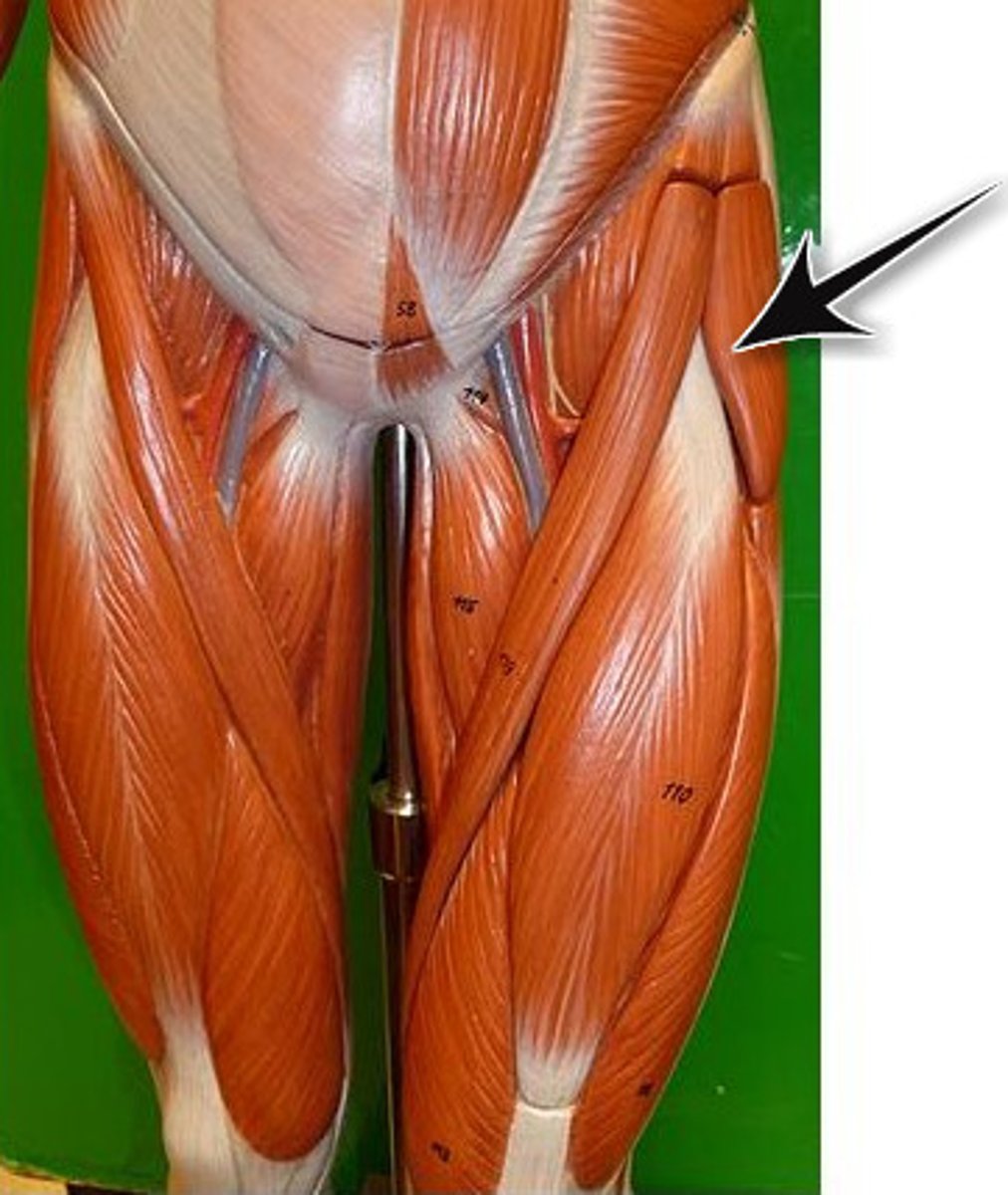
Thigh flexors
Pass in front of hip joint; include Iliopsoas, Tensor fasciae latae, and Rectus femoris; assisted by medial adductors and sartorius
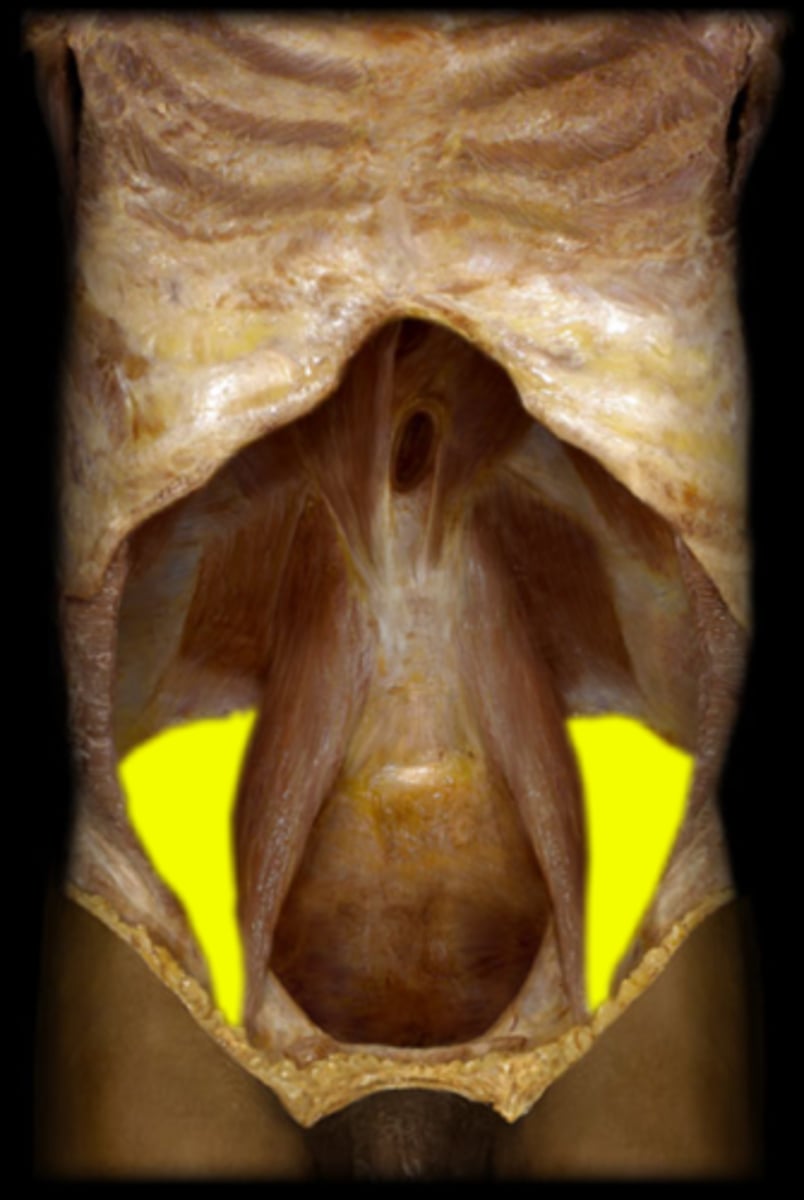
Iliopsoas (iliacus and psoas major)
Prime mover of hip flexion
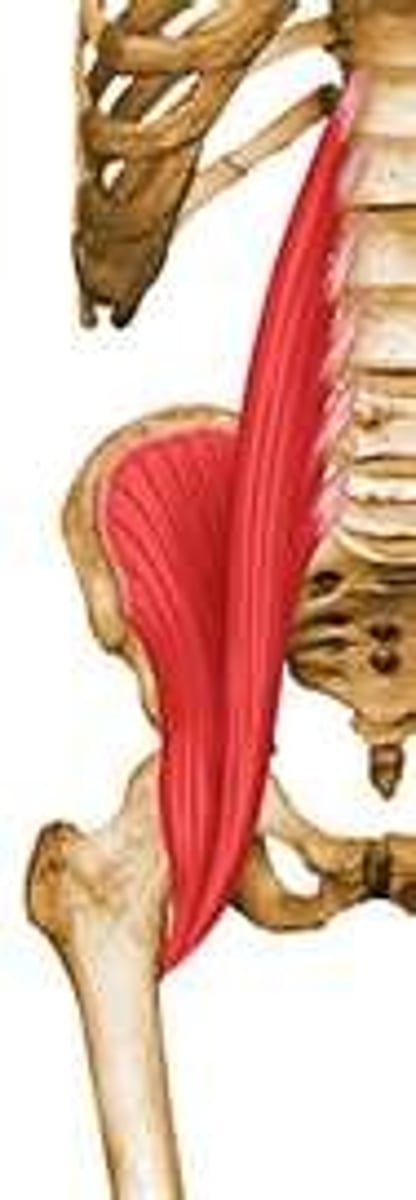
Thigh extensors
Hamstring muscles are the prime movers of thigh extension
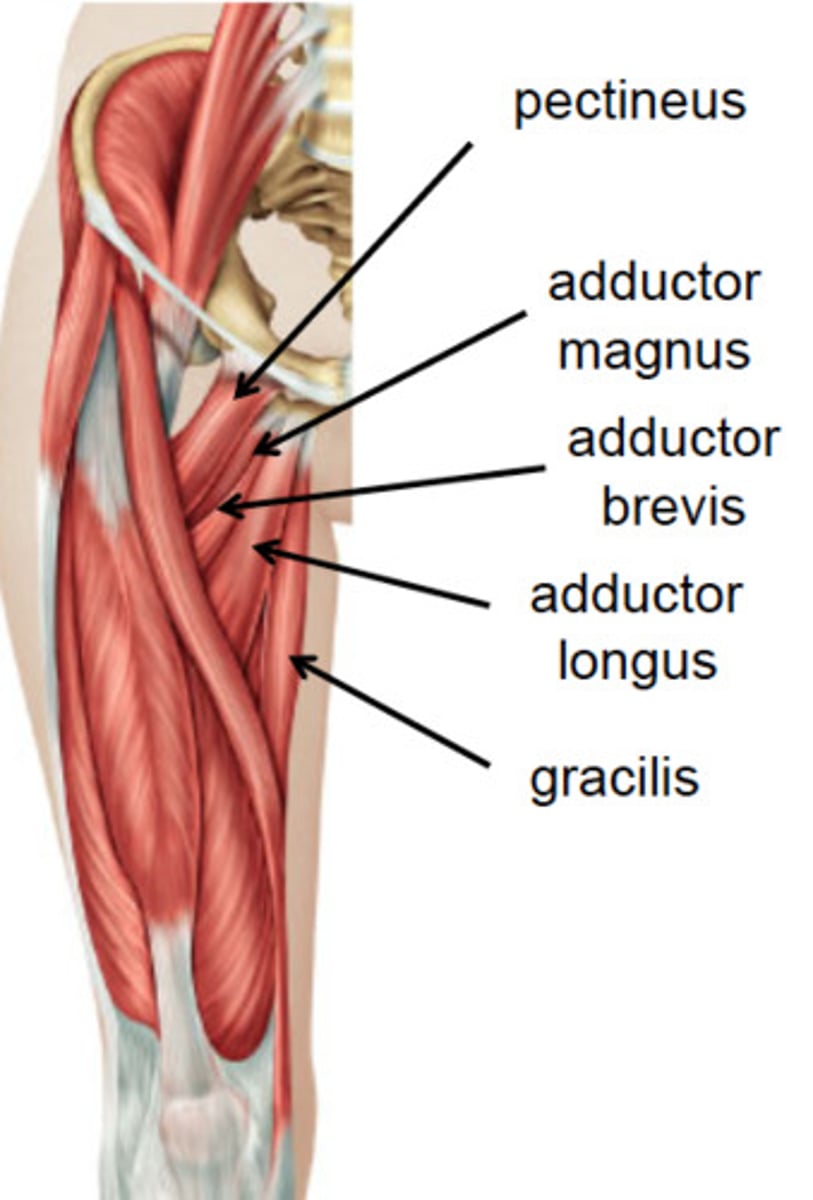
Adductors (medial thigh muscles)
Medially rotate the thigh and press thighs together
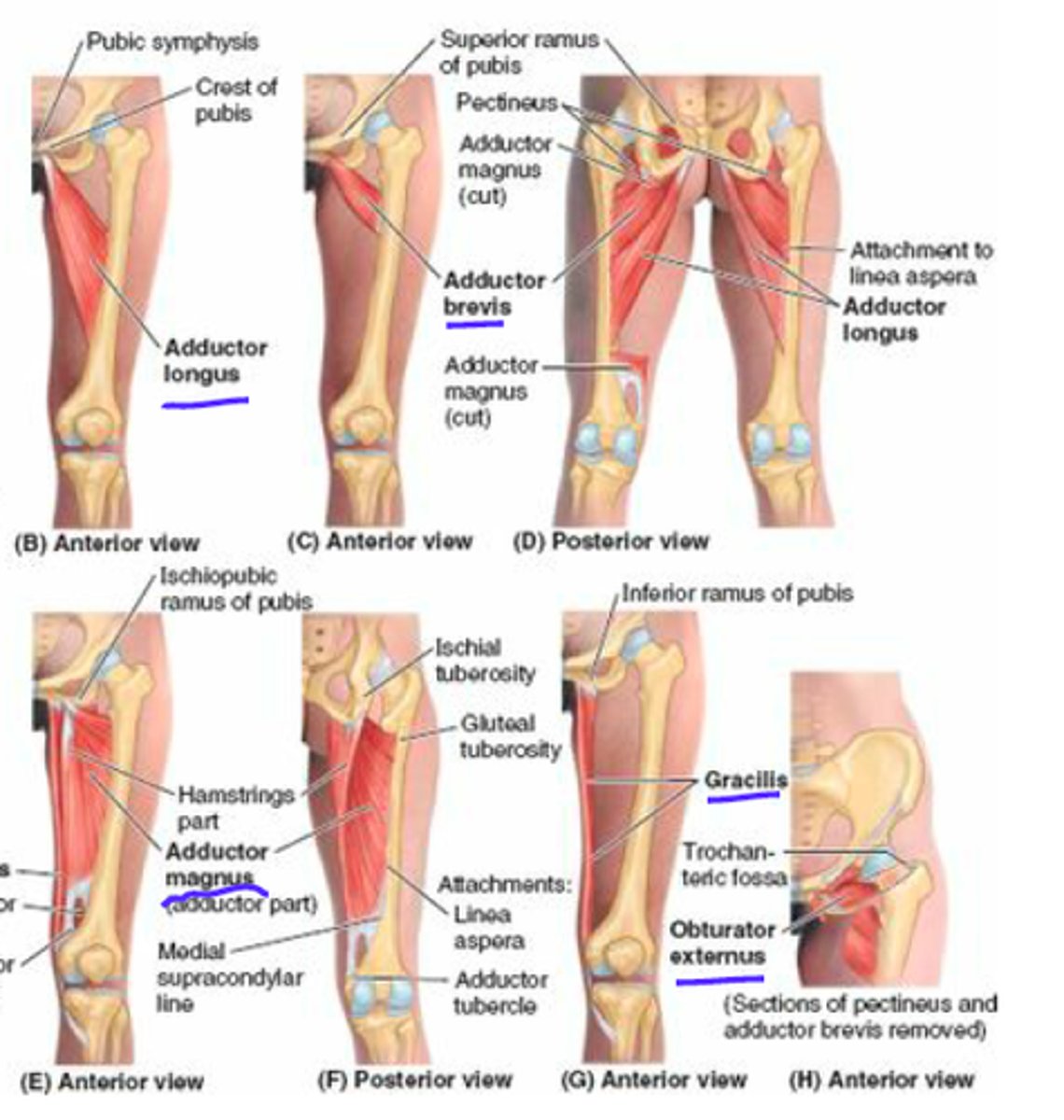
Adductor muscles
Adductor magnus, Adductor longus, Adductor brevis, Pectineus, and Gracilis
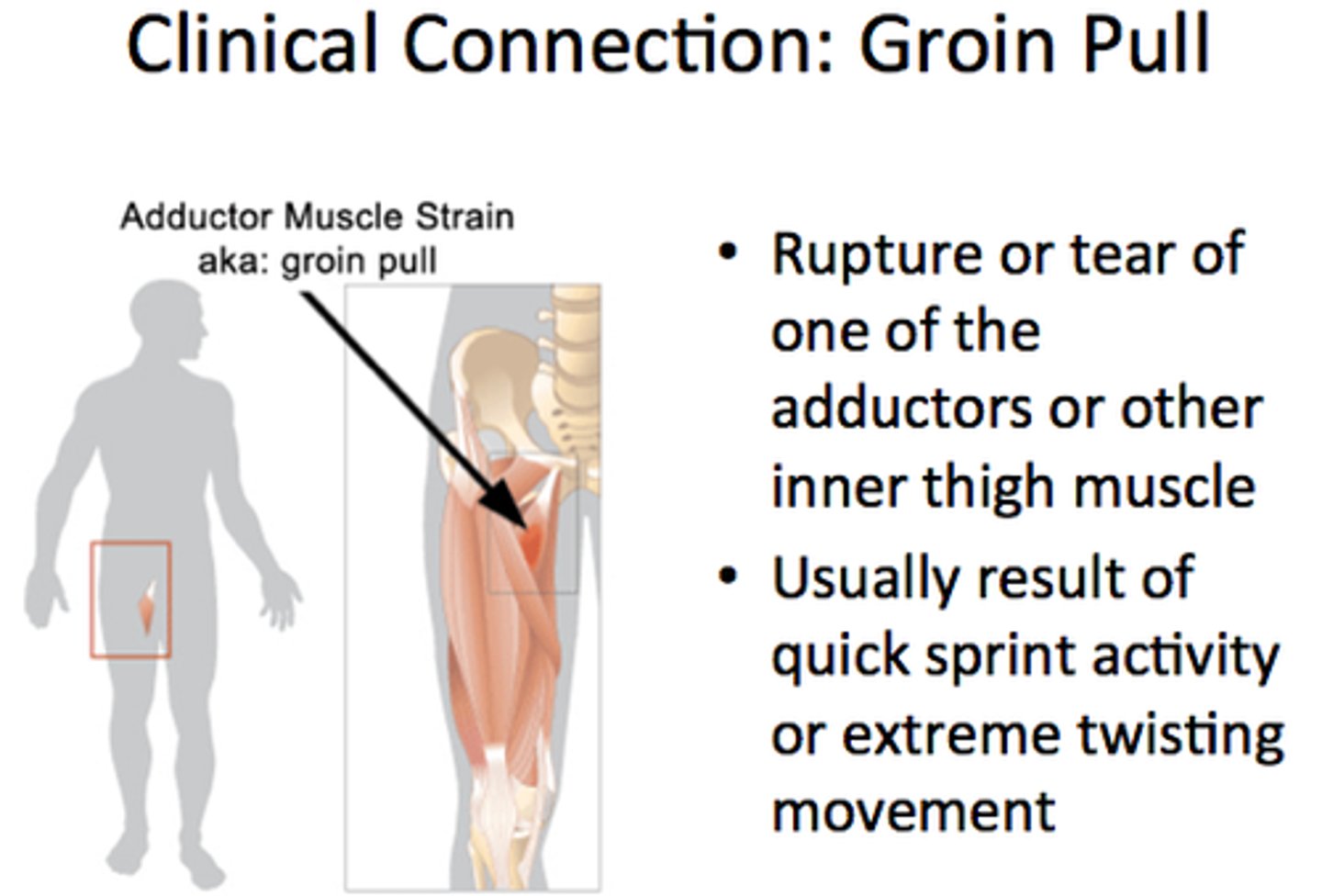
Pulled groin
Overstretched or torn thigh adductor muscles
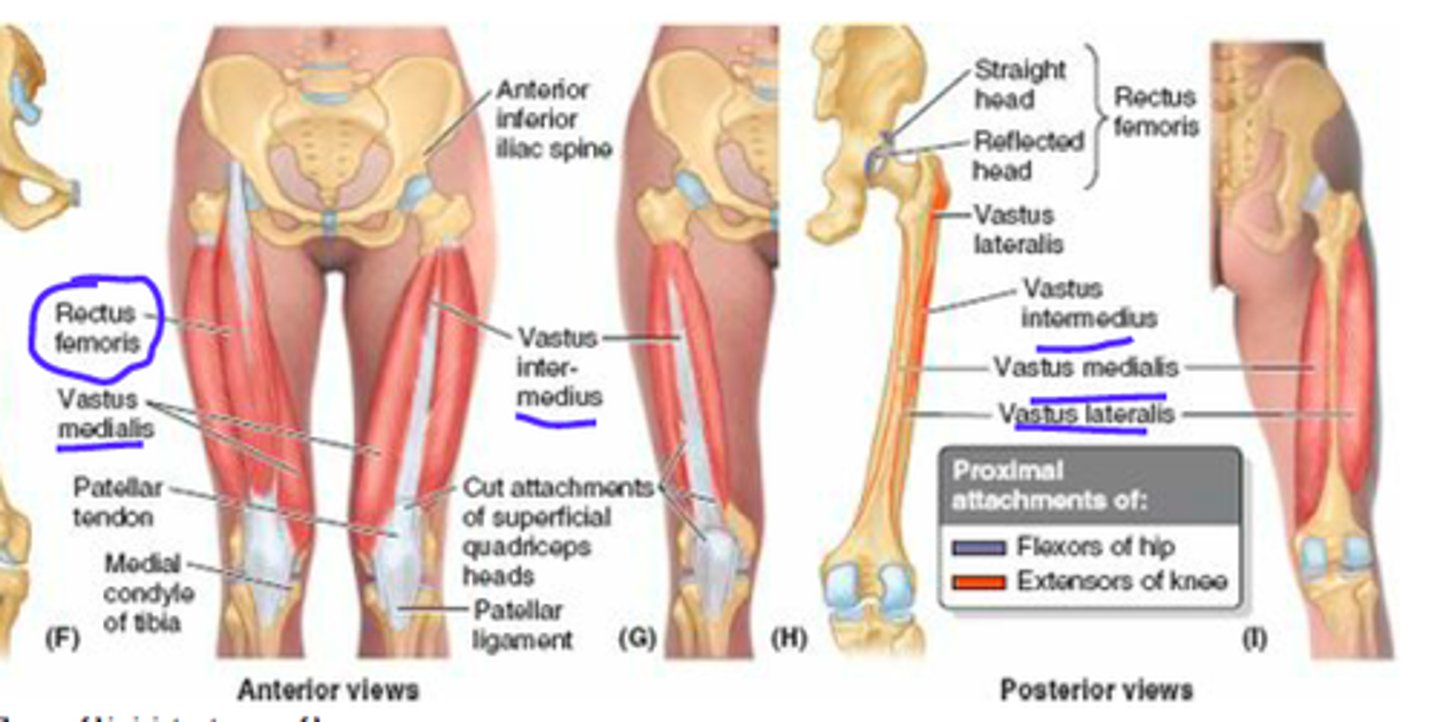
Quadriceps femoris
Four-headed muscle; powerful knee extensor
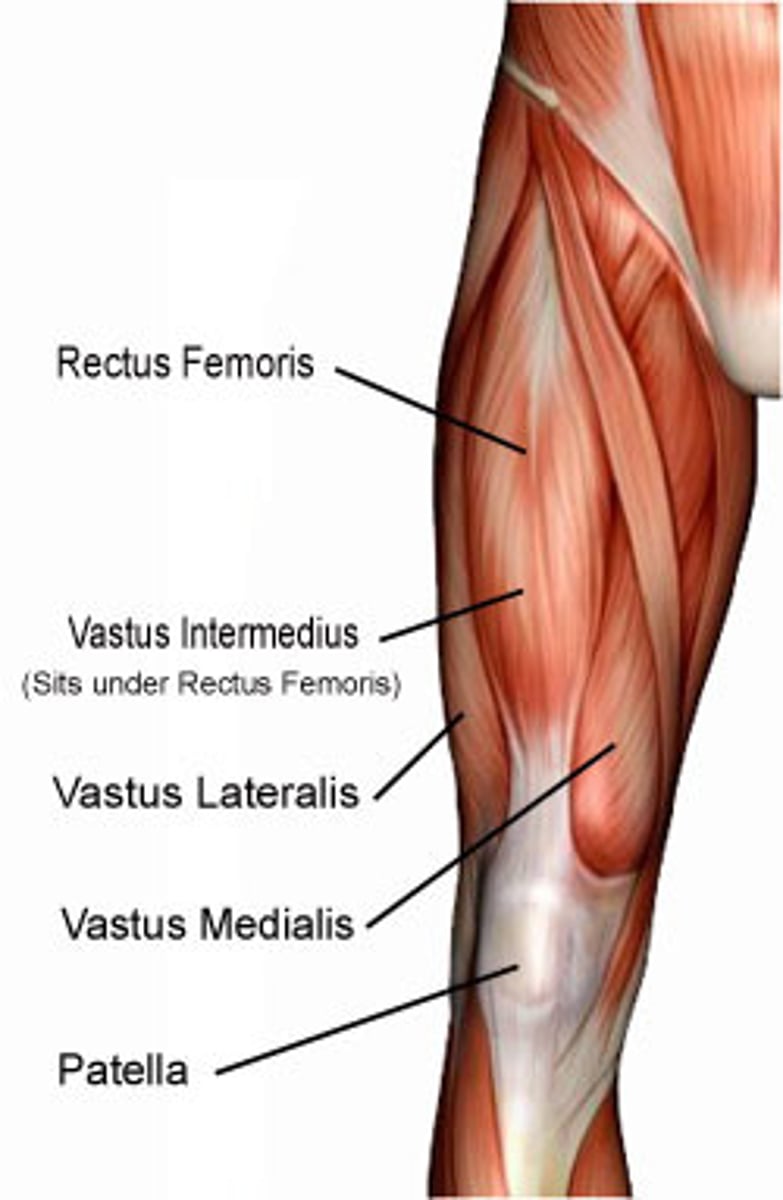
Quadriceps femoris insertion
Insert into quadriceps tendon → patella → patellar ligament → tibial tuberosity
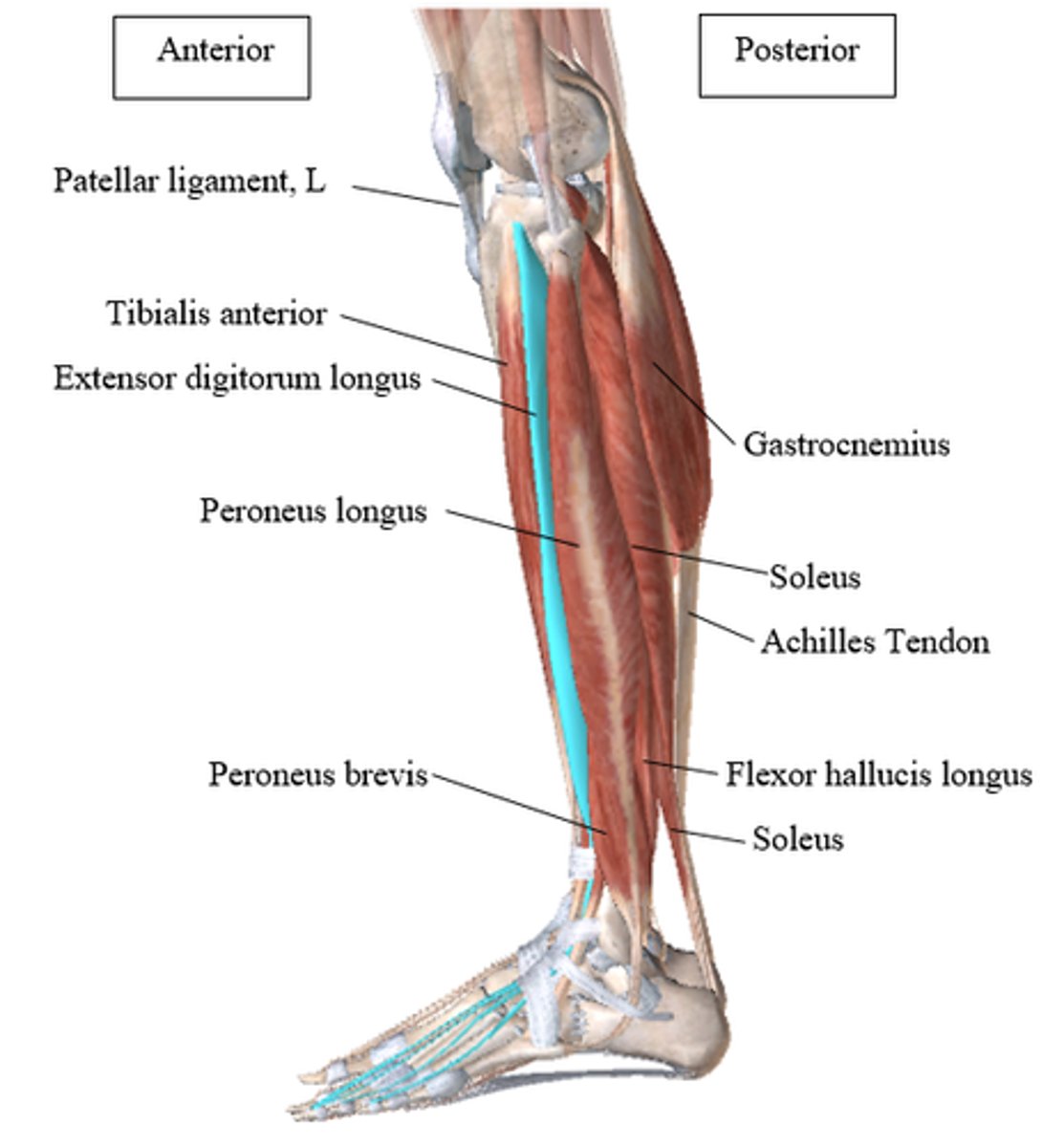
Anterior compartment of the leg
Muscles that dorsiflex the ankle
Lateral compartment of the leg
Muscles that plantar flex and evert the foot
Posterior compartment of the leg
Muscles that plantar flex the ankle; all innervated by the tibial nerve; divided into superficial and deep groups
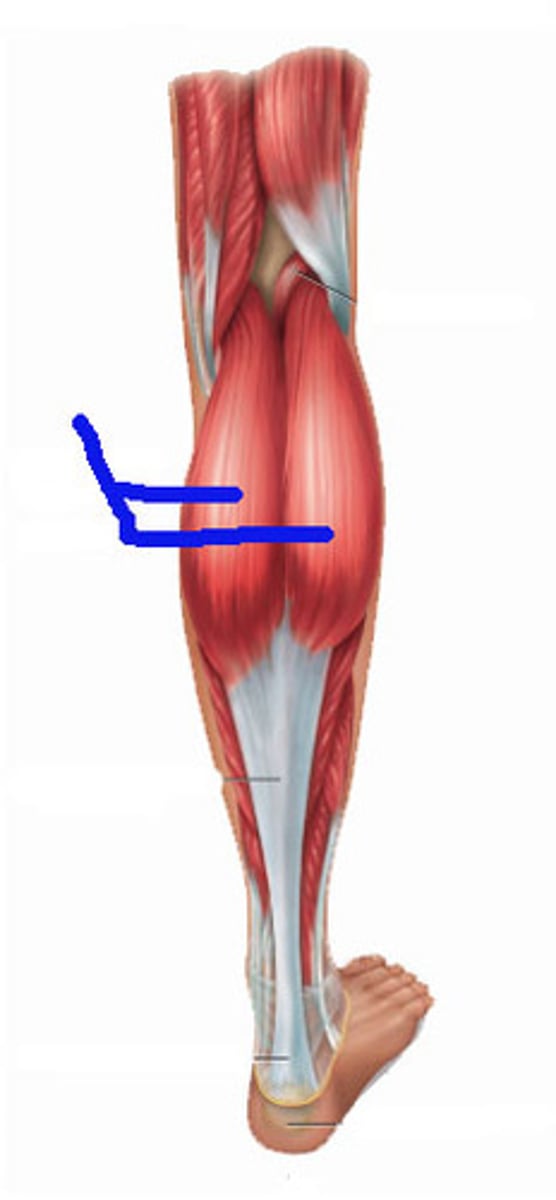
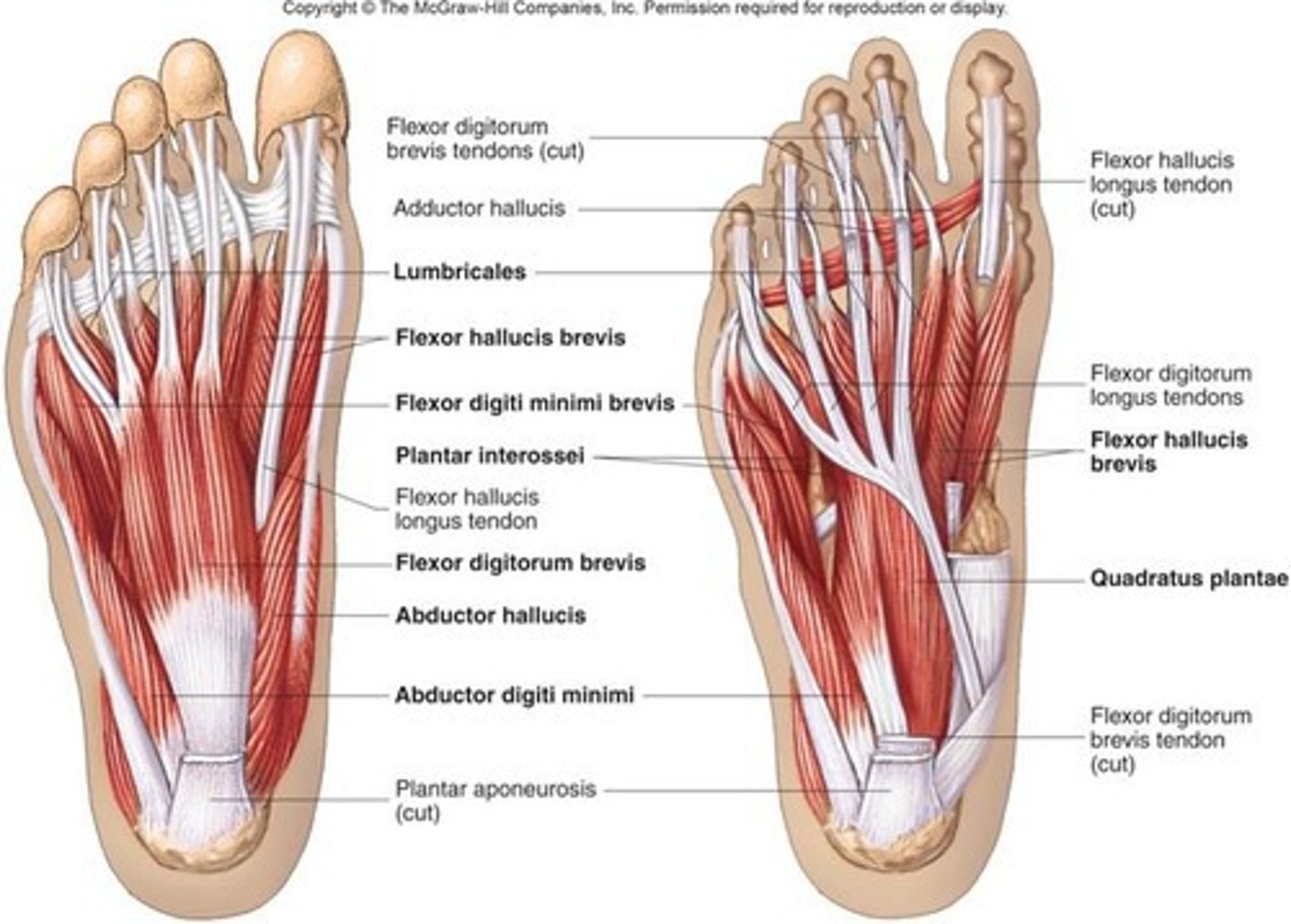
Intrinsic muscles of the foot
Responsible for toe movement and arch support; consist of four plantar layers (superficial to deepest)
minimus
smallest
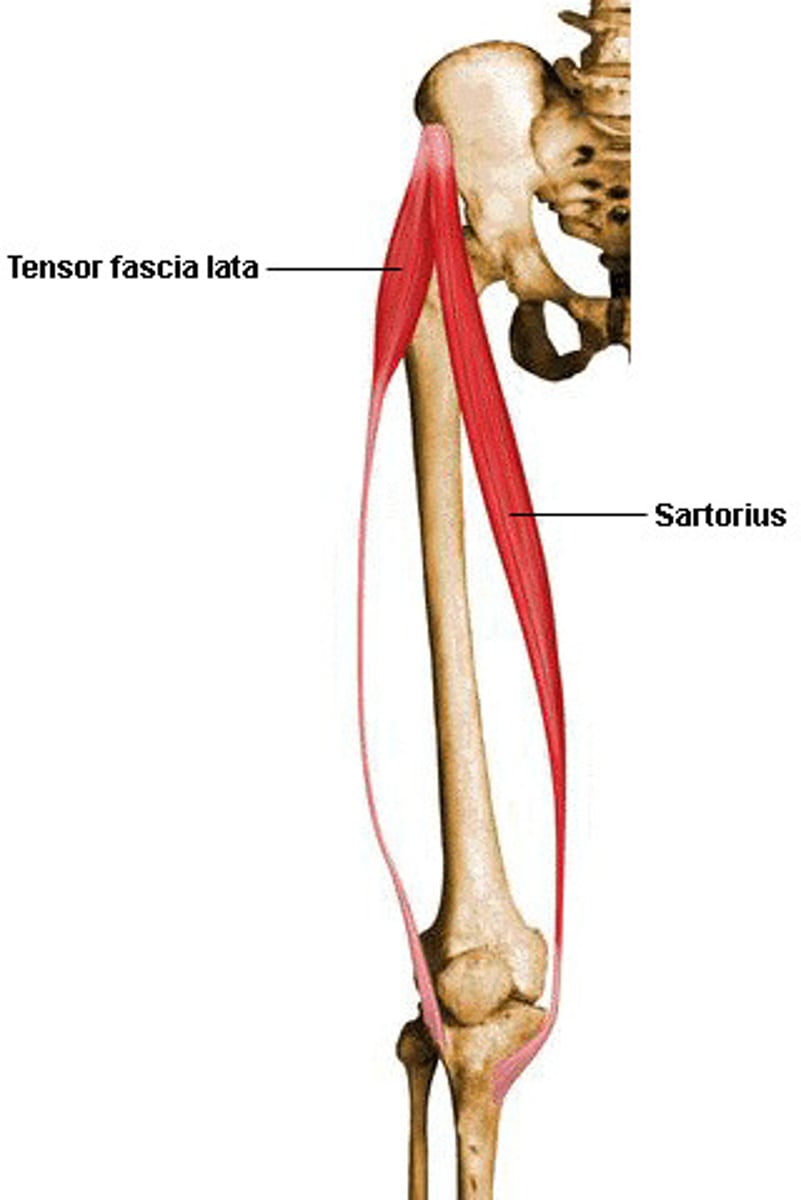
Tensor fascia lata
a muscle that stretches a part + bandage + side
Quadriceps femoris
four + heads + thigh
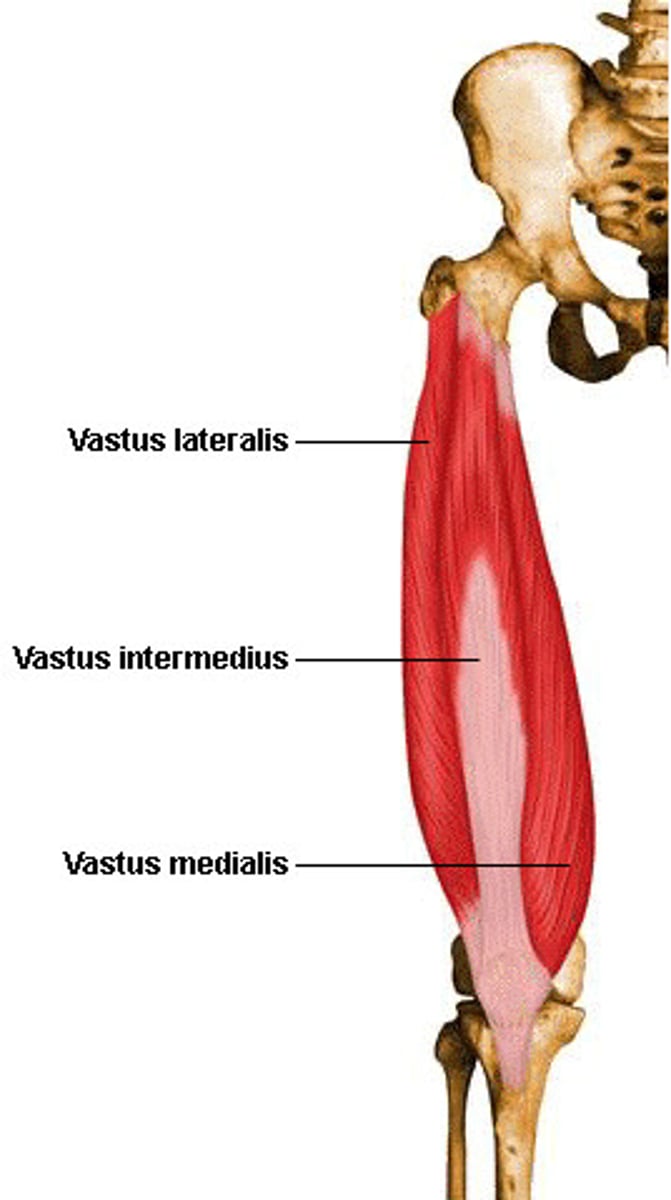
Vastus
large
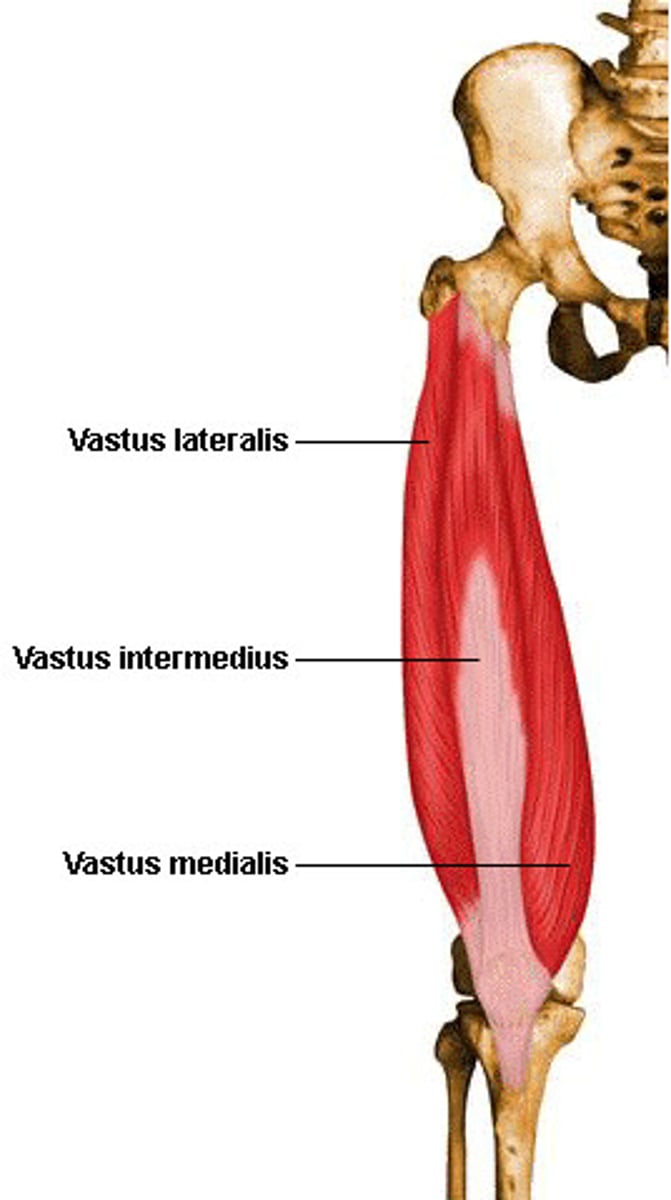
lateralis
side
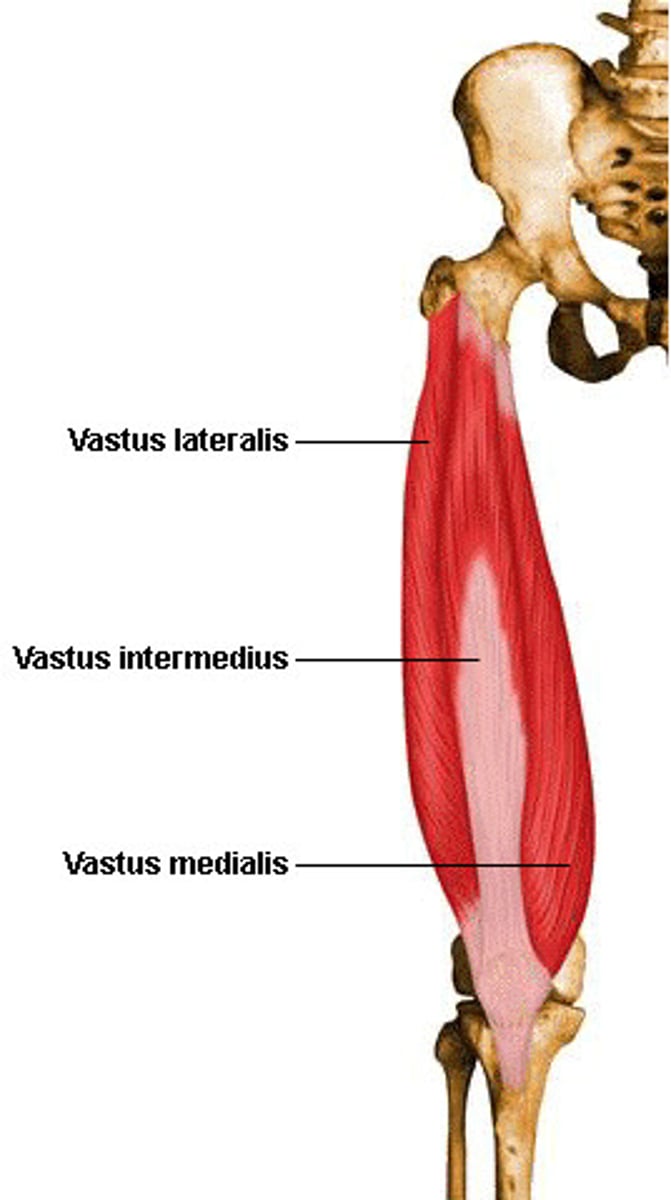
medialis
middle
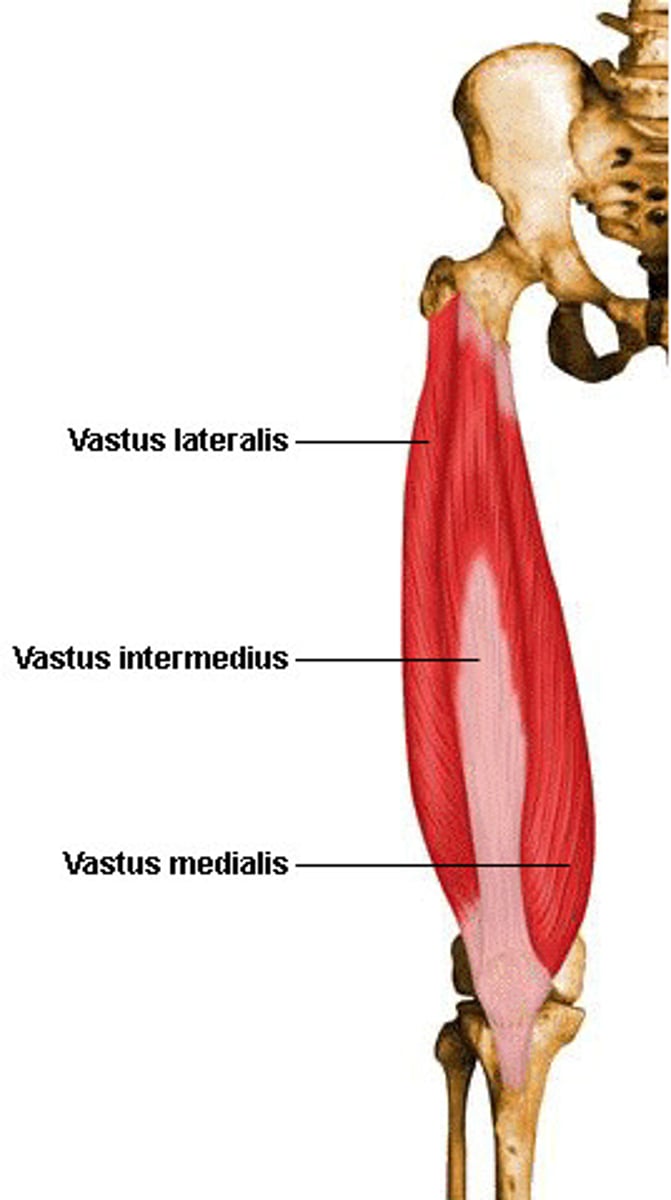
intermedius
in between
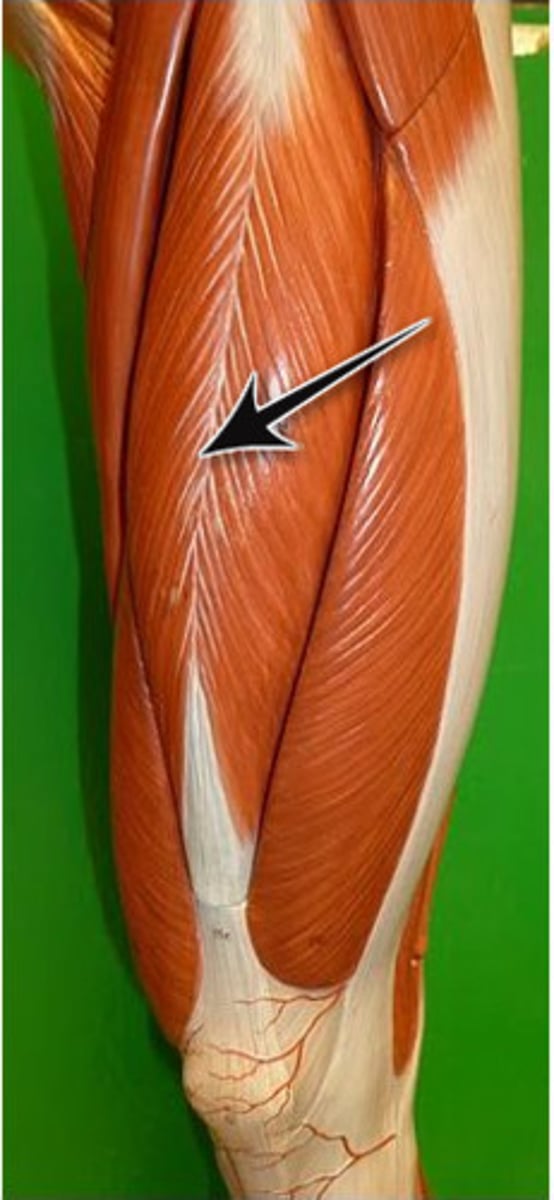
Rectus femoris
straight + thigh
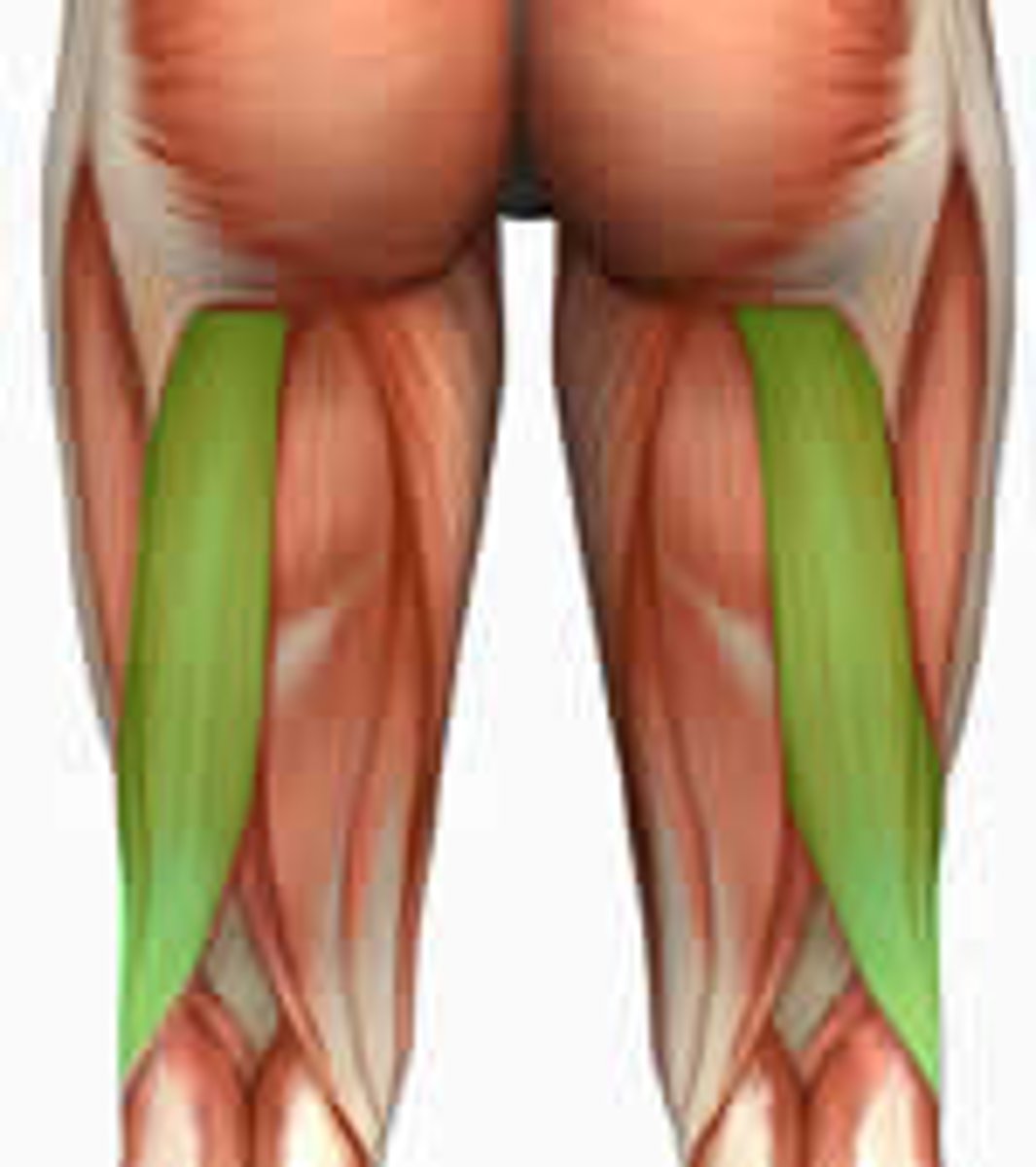
Biceps femoris
two + heads + thigh
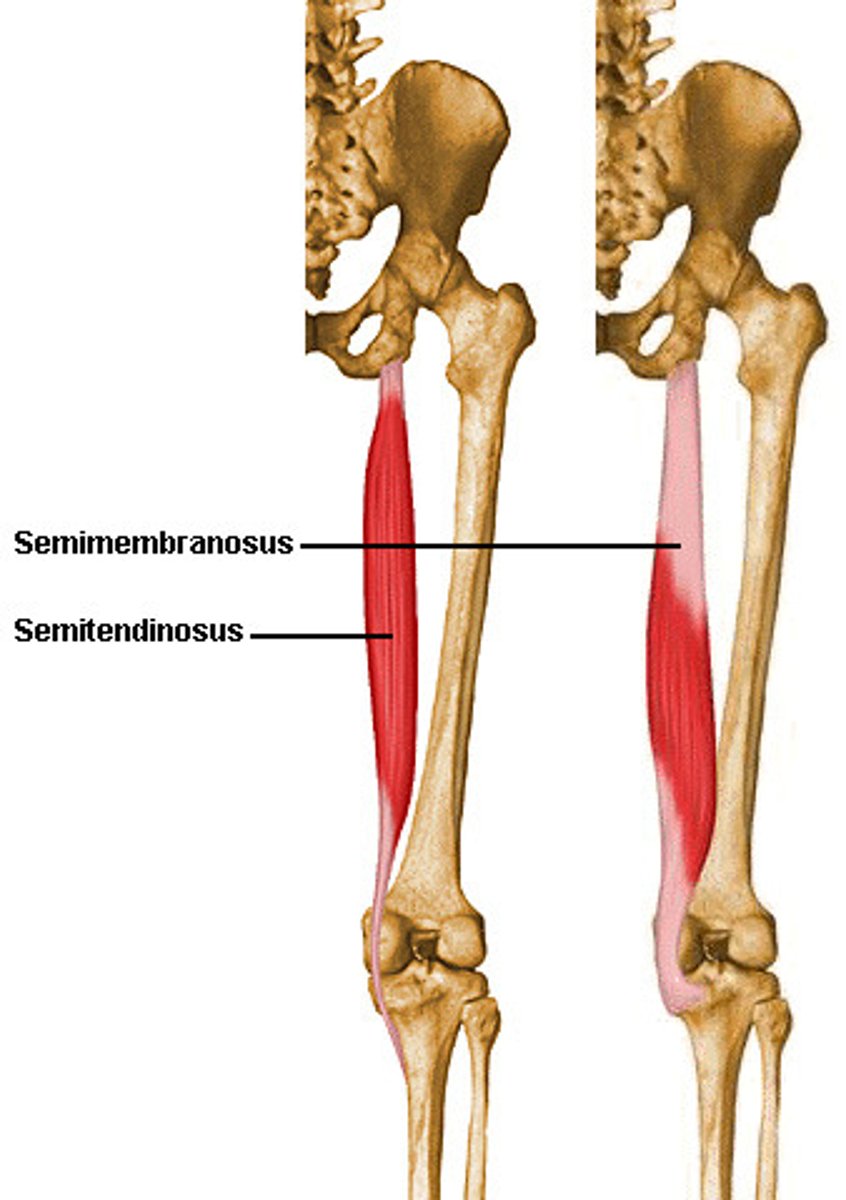
Semitendinosus
half tendon
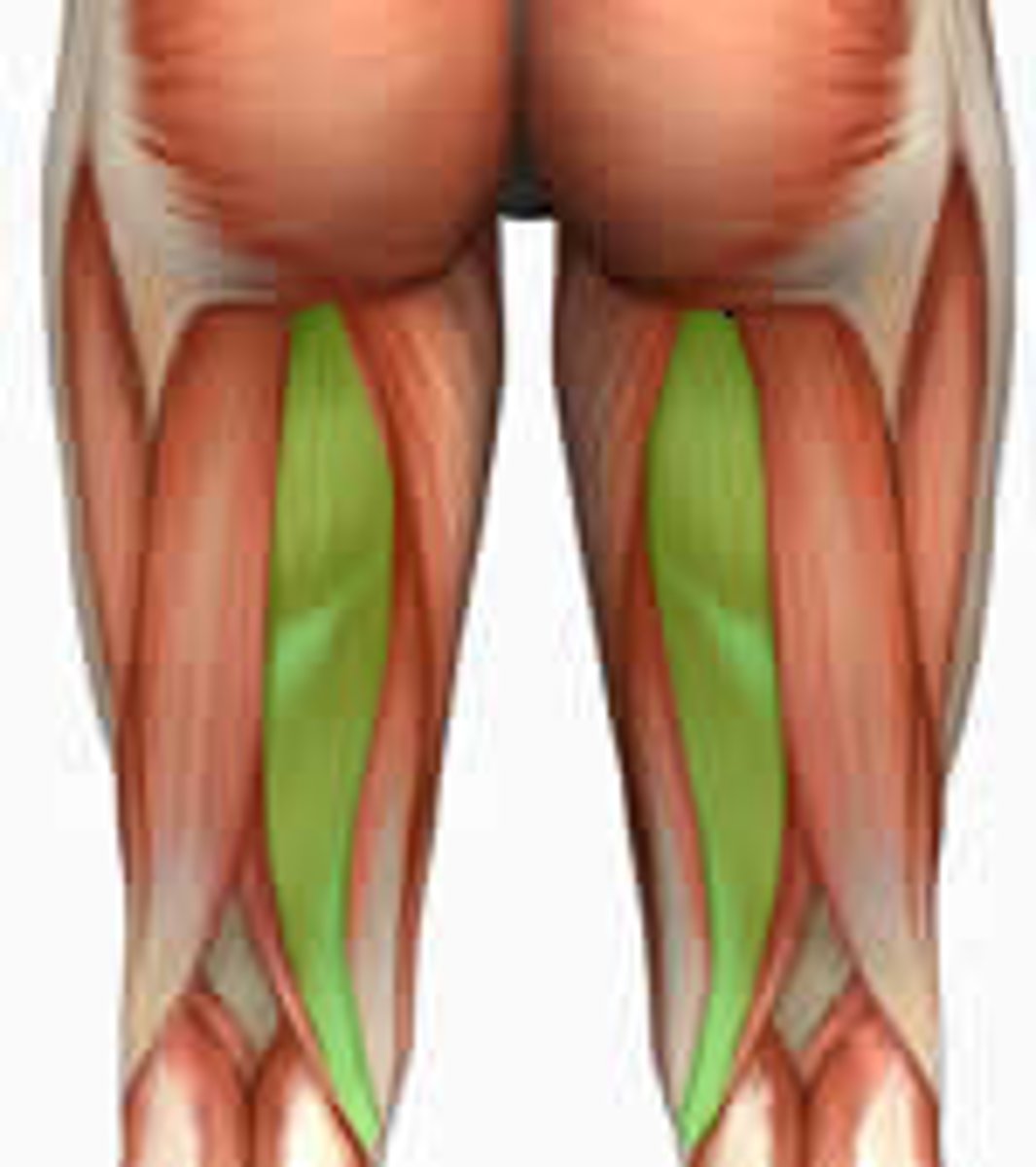
Semimembranosus
half membrane
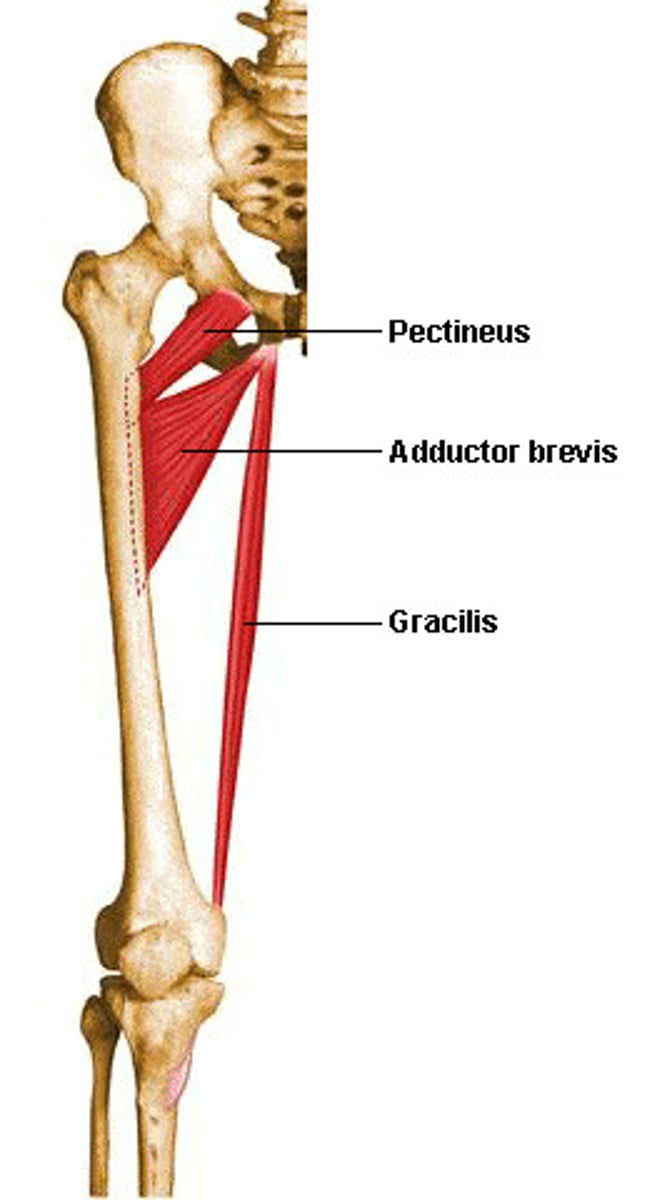
Gracilis
slender, thin
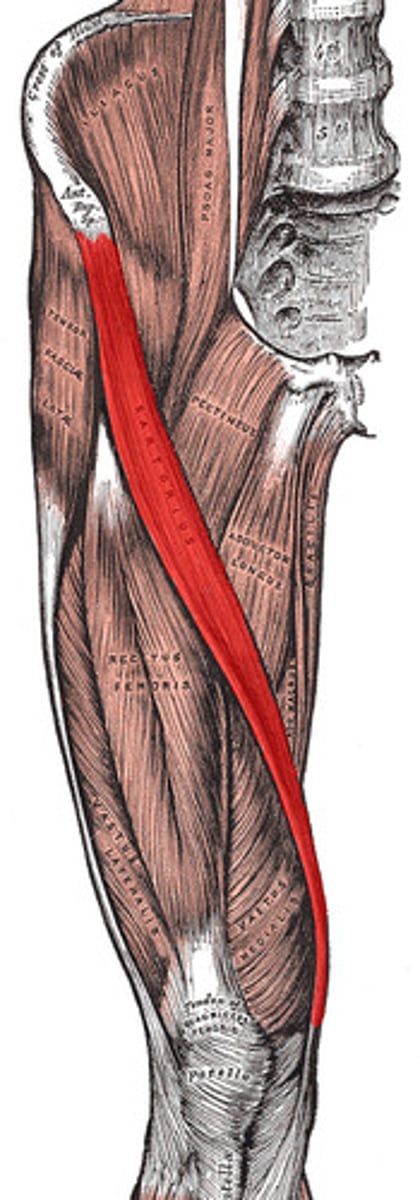
Sartorius
to mend or patch; tailor's muscle
Adductor femoris
to lead to
longus (Adductor femoris)
long
brevis (Adductor femoris)
short
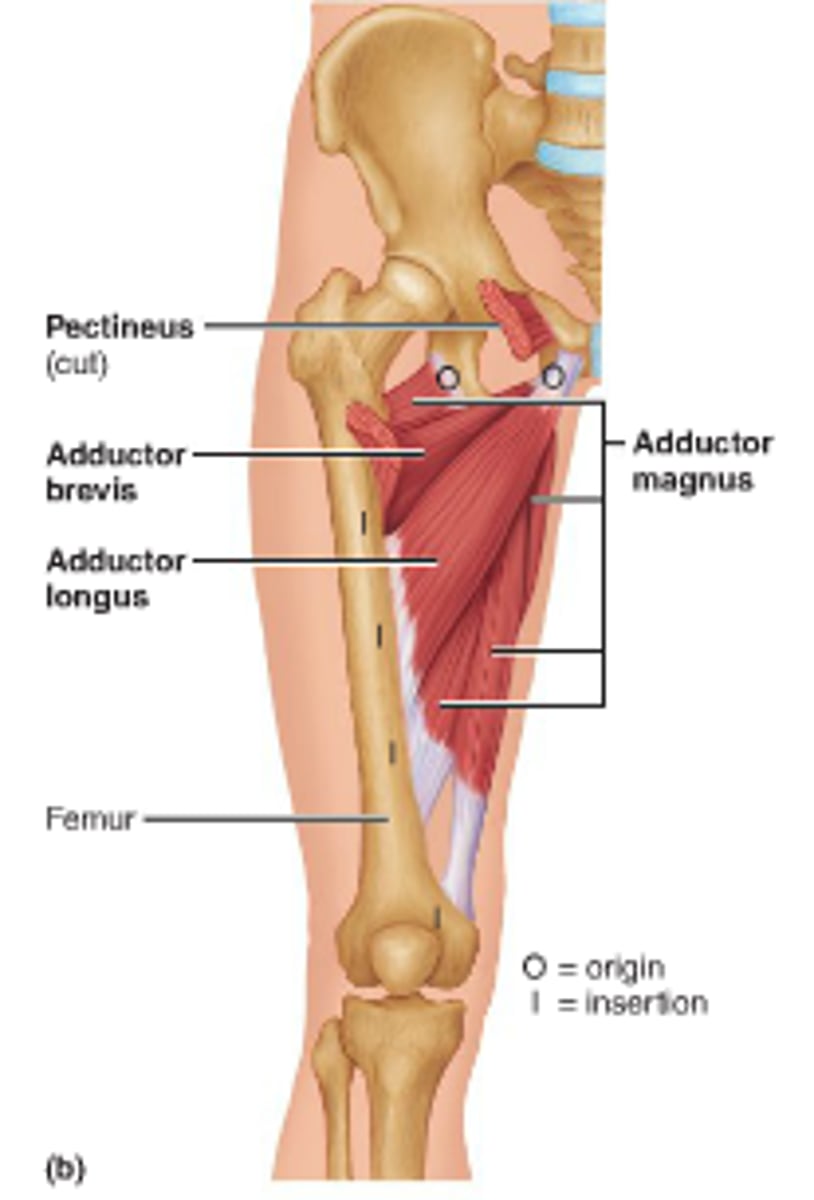
magnus (Adductor femoris)
big
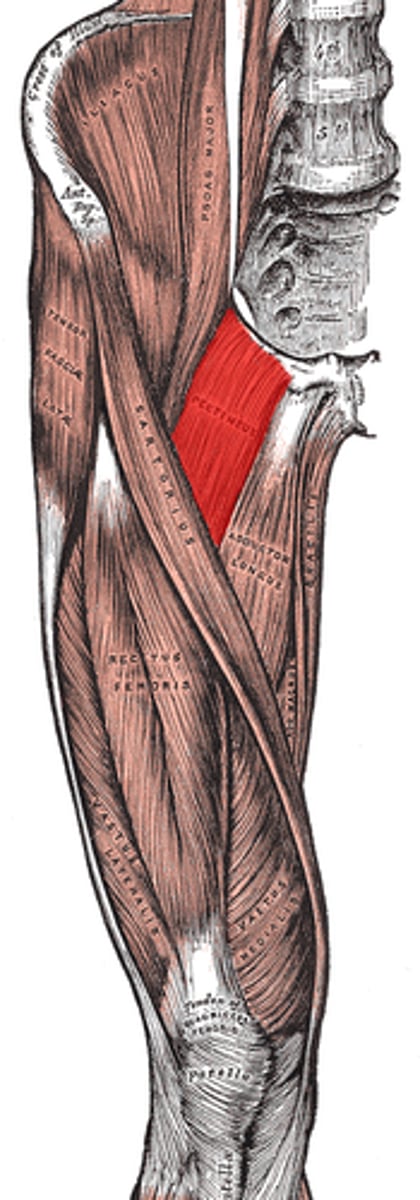
Pectineus
honey-comb
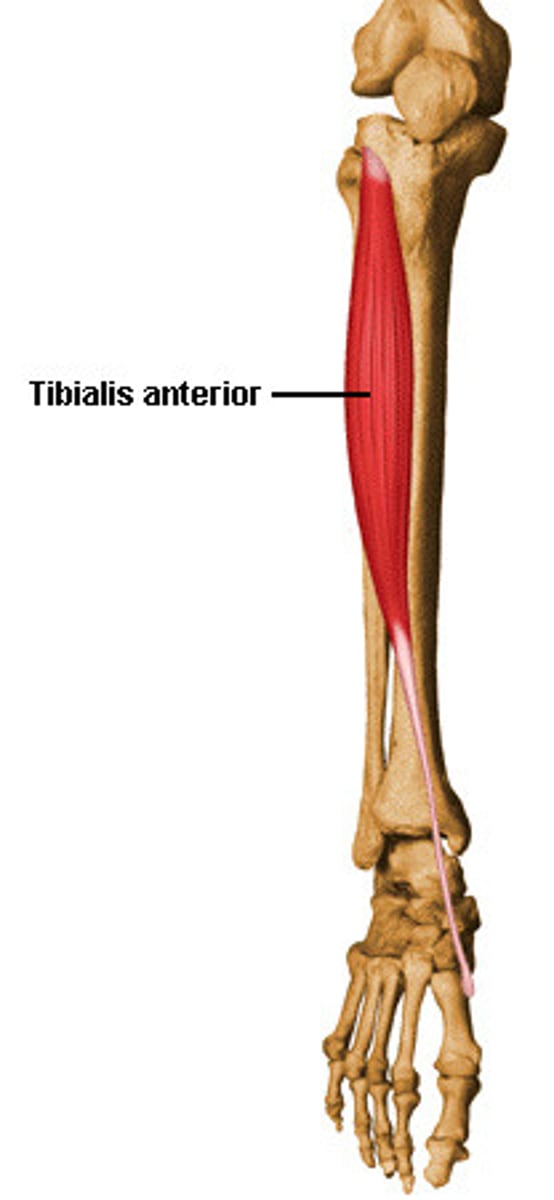
Tibialis anterior
shin + front
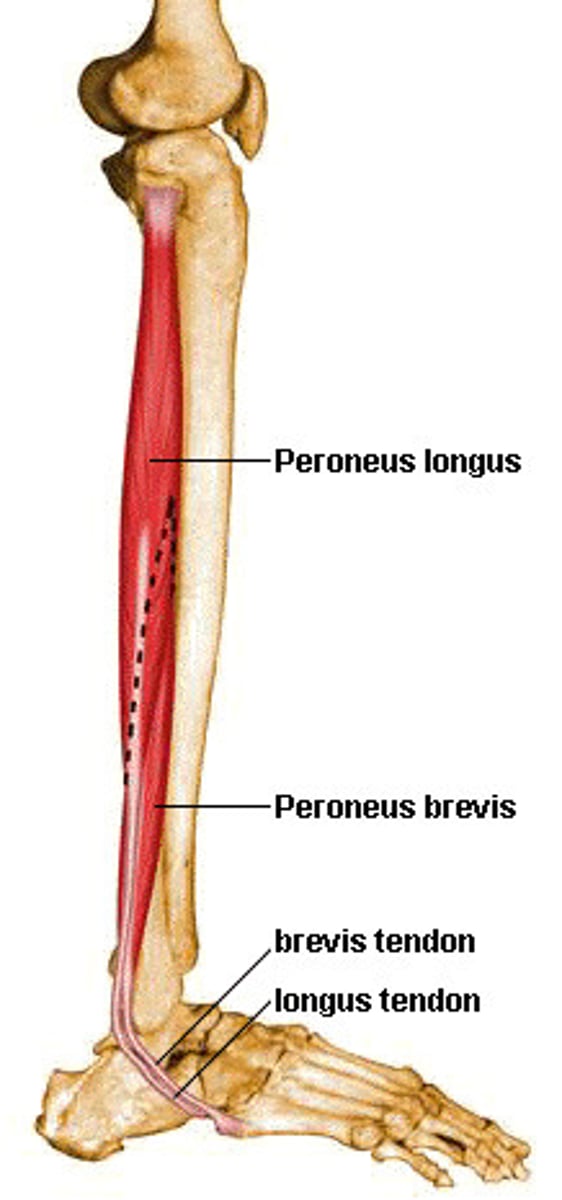
Peroneus longus
fibula + long
Extensor digitorum (Lower leg)
extend + fingers
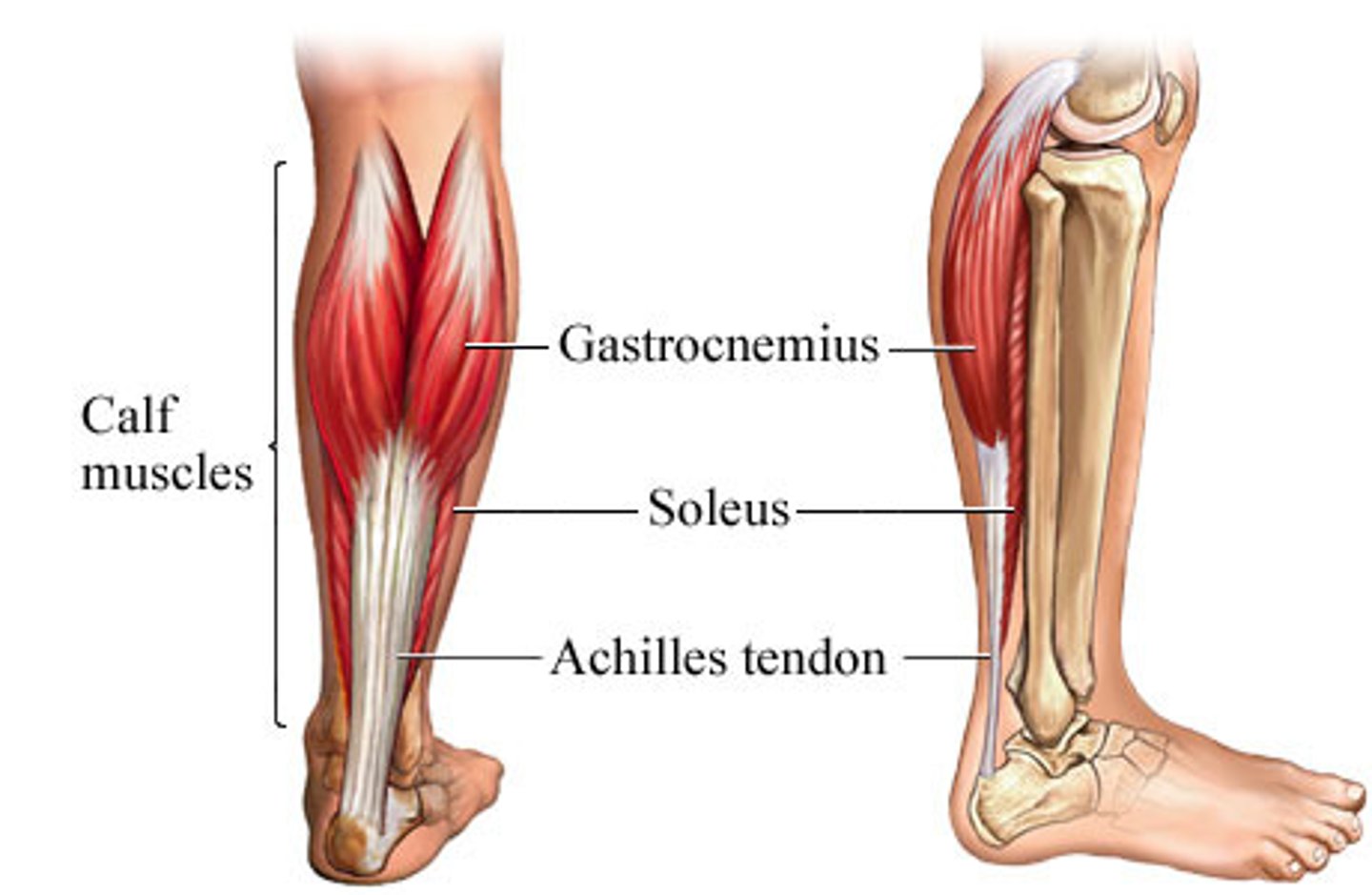
Gastrocnemius
belly + leg
Soleus
alone
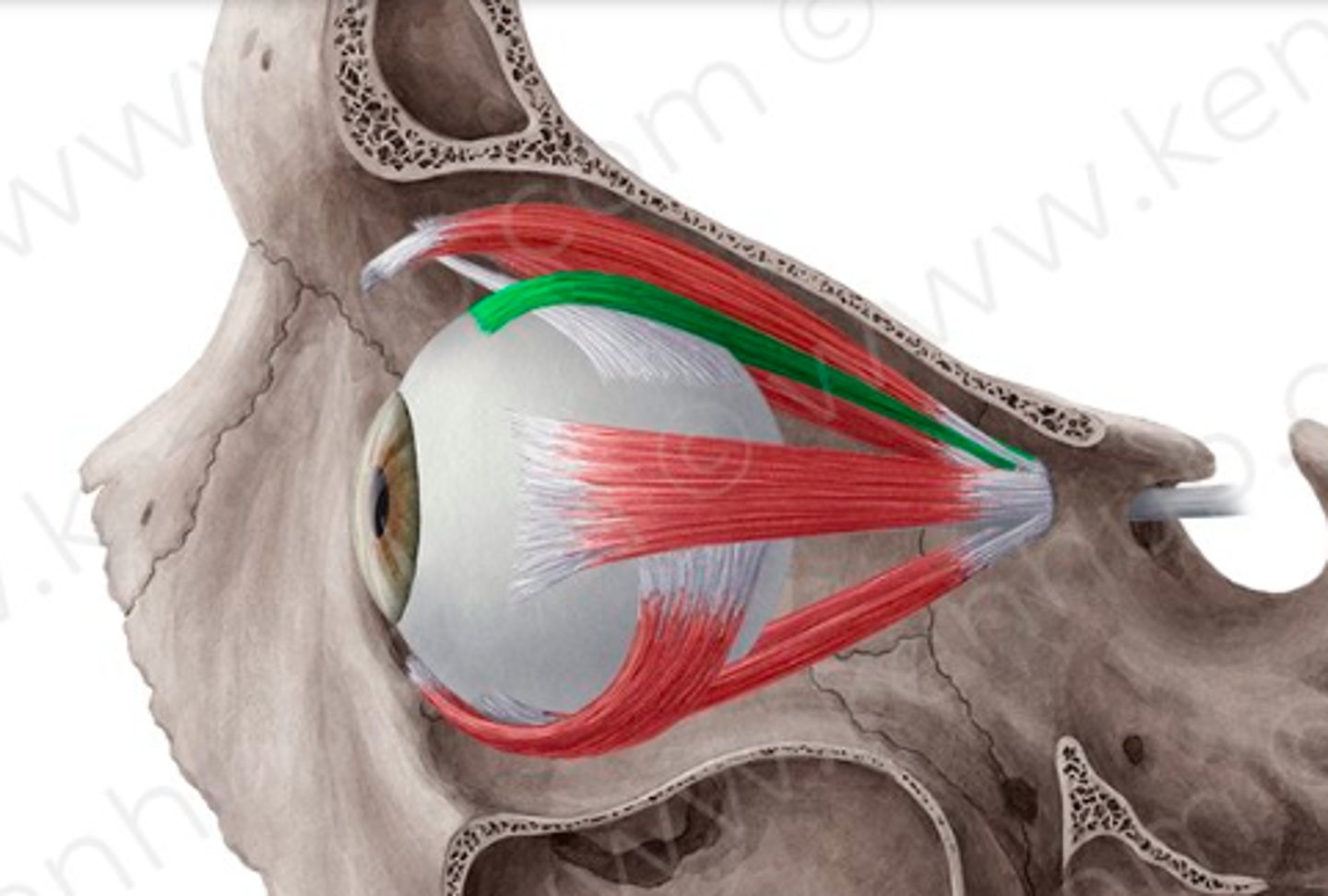
Rectus superior
above
Rectus inferior
below
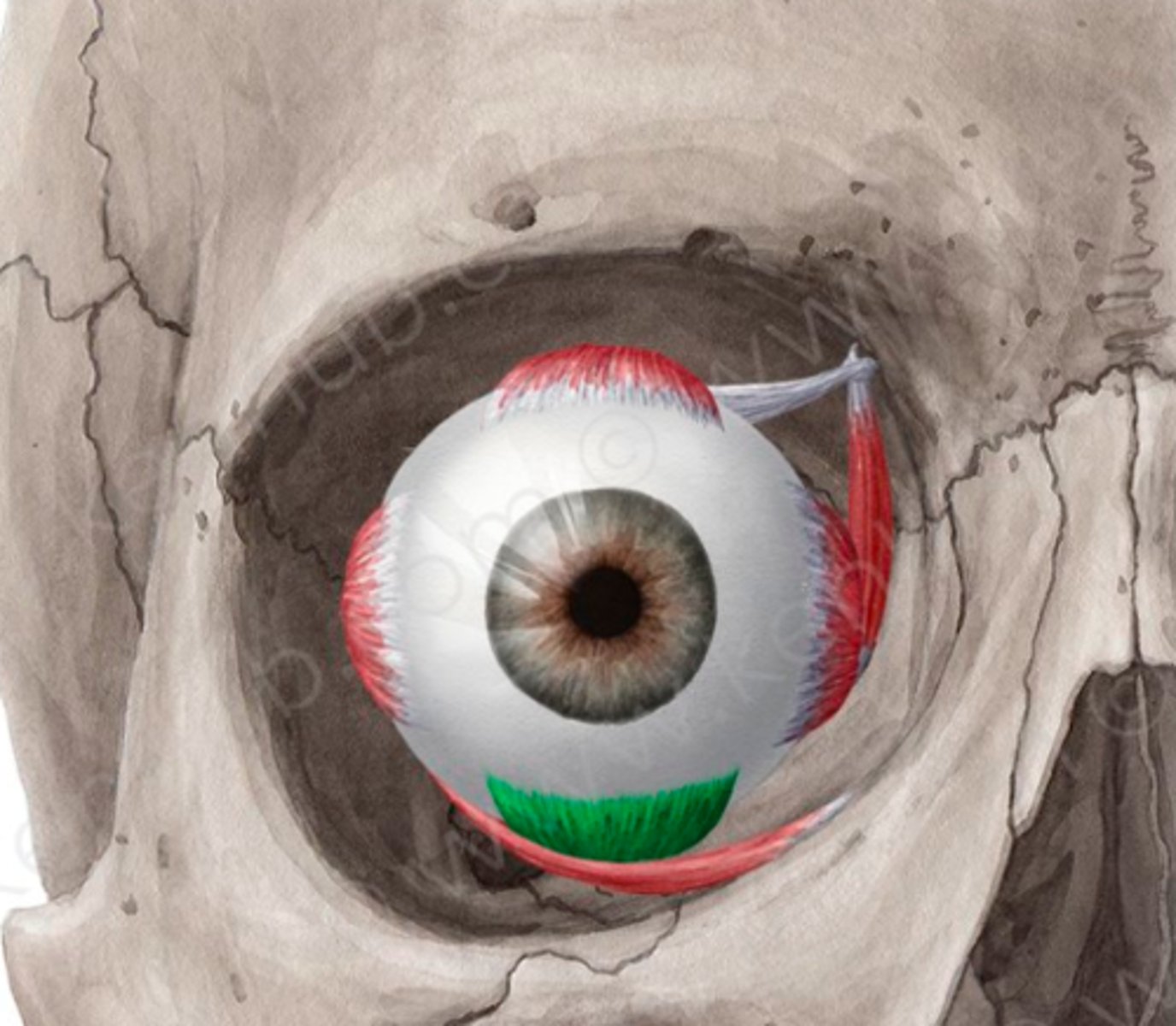
Rectus medial
middle
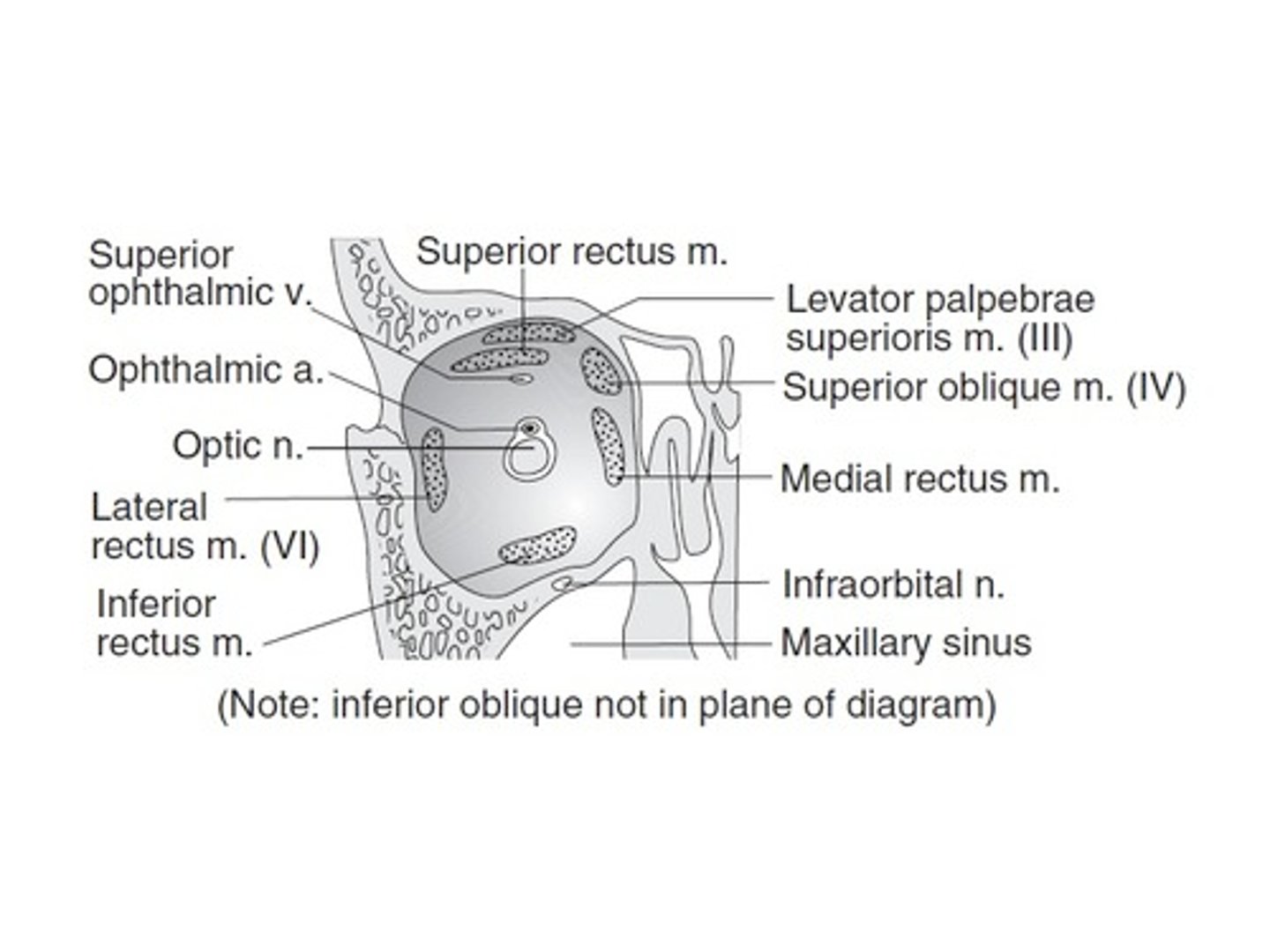
Rectus lateral
side
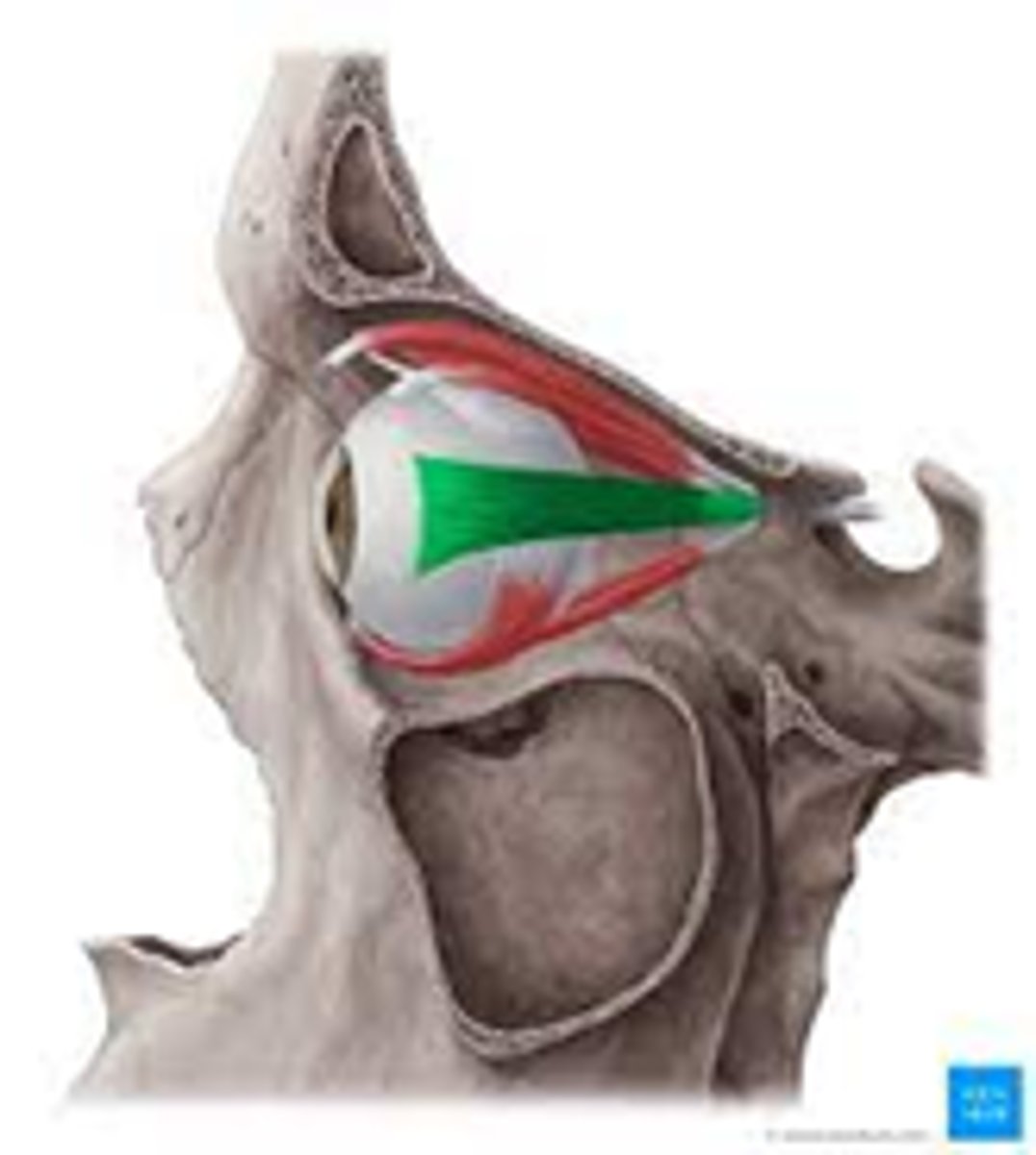
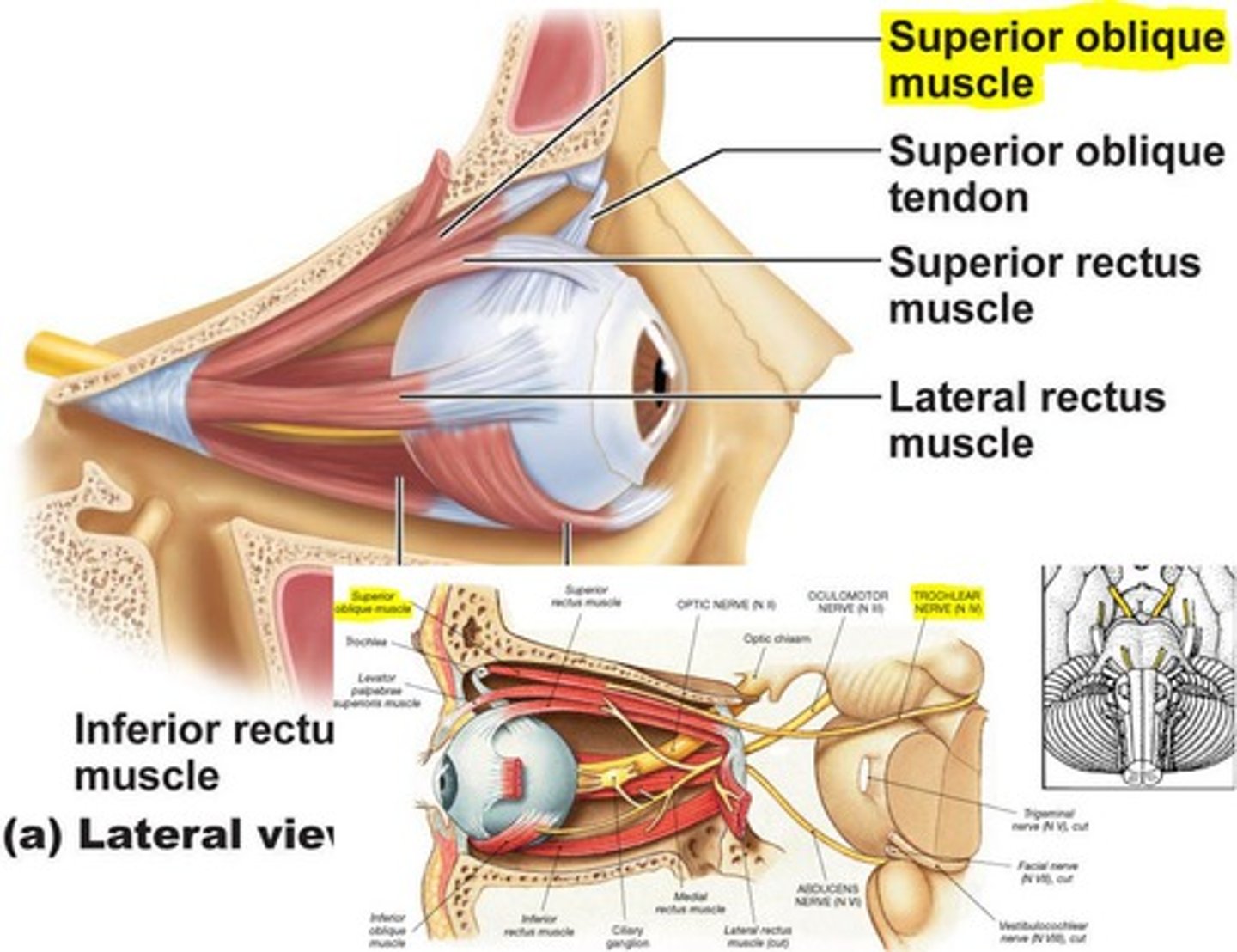
Oblique superior
above
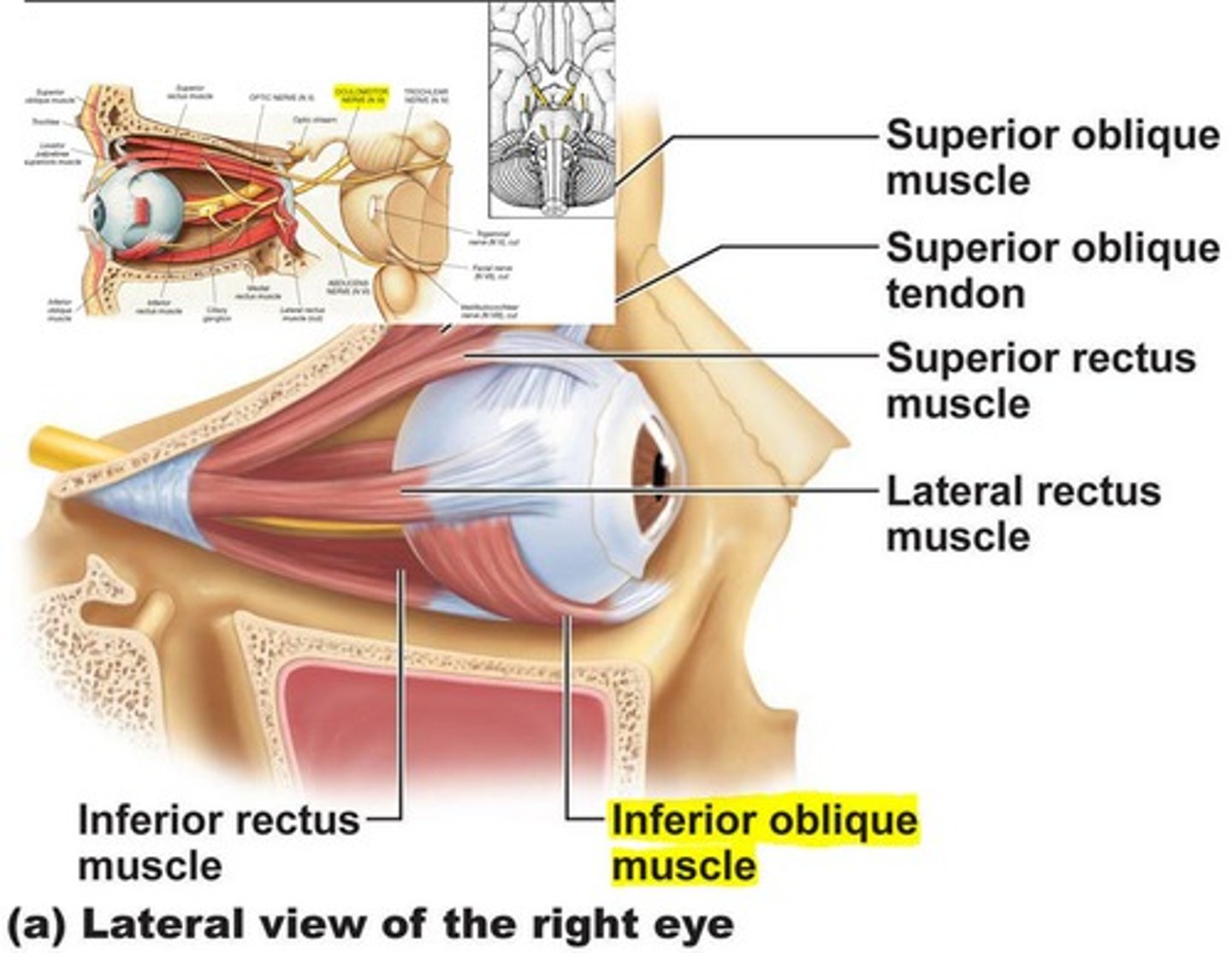
Oblique inferior eye
below
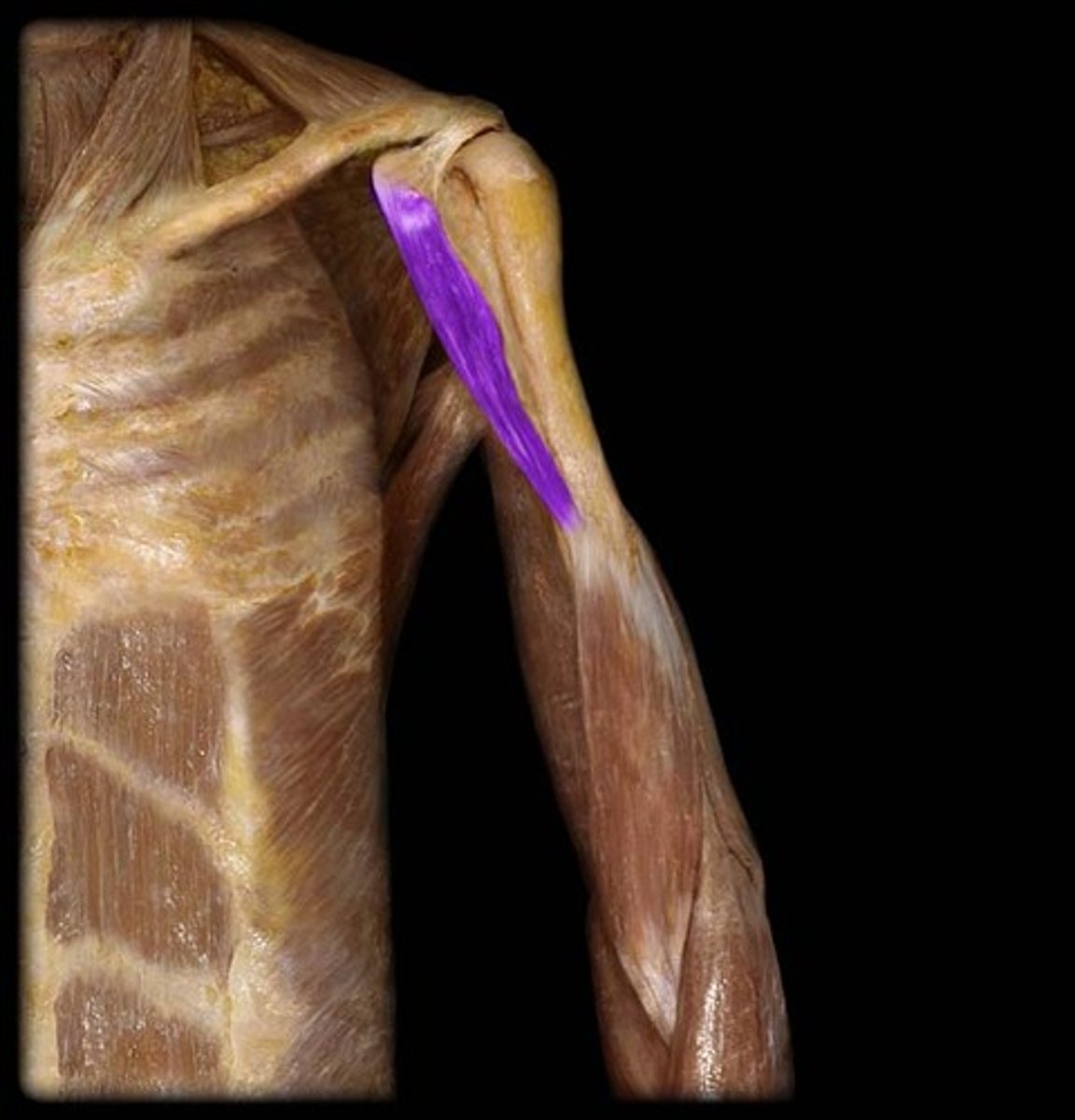
Coracobrachialis
raven's beak + upper arm
Epitrochlearis
upon + pulley
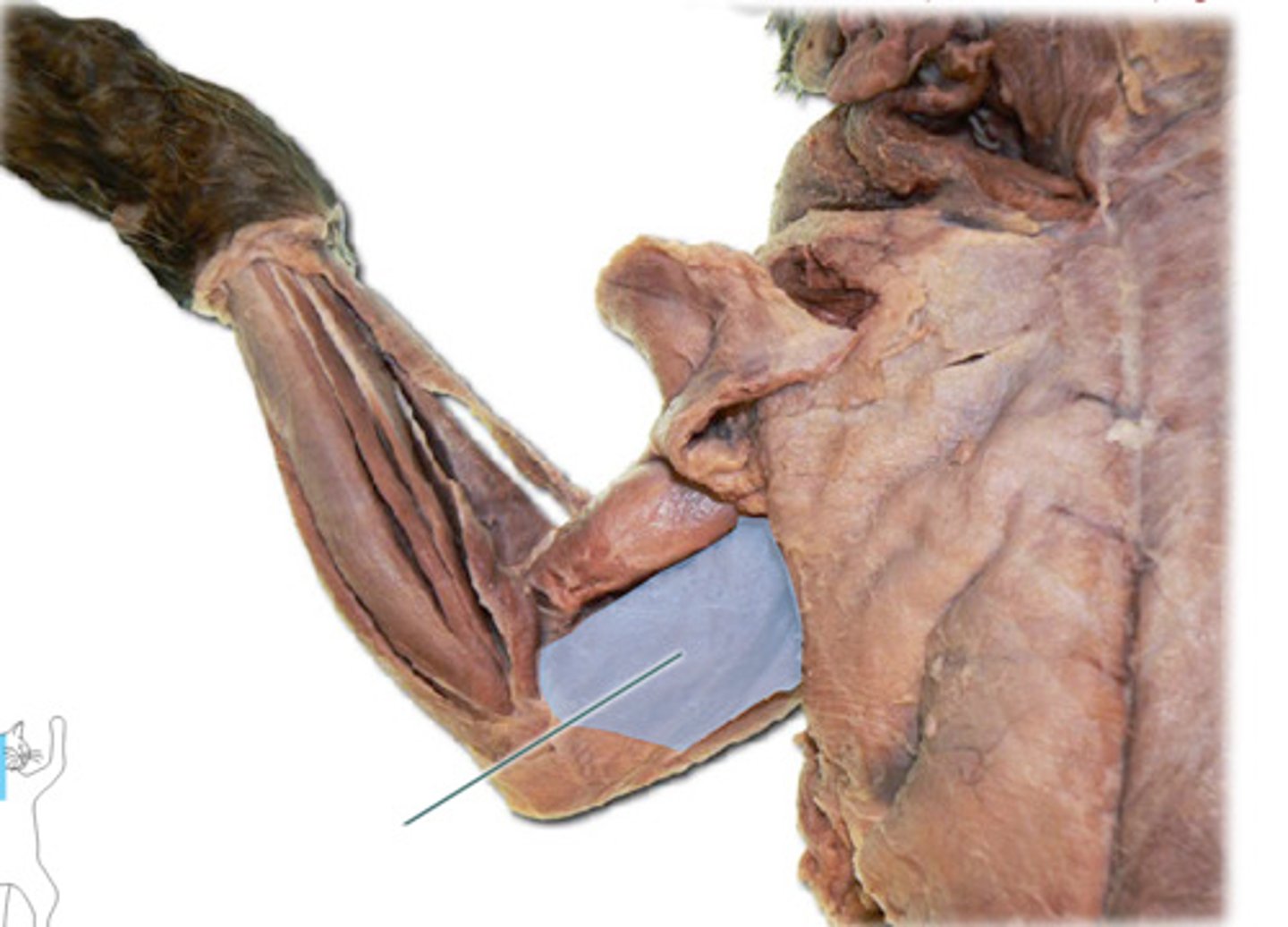
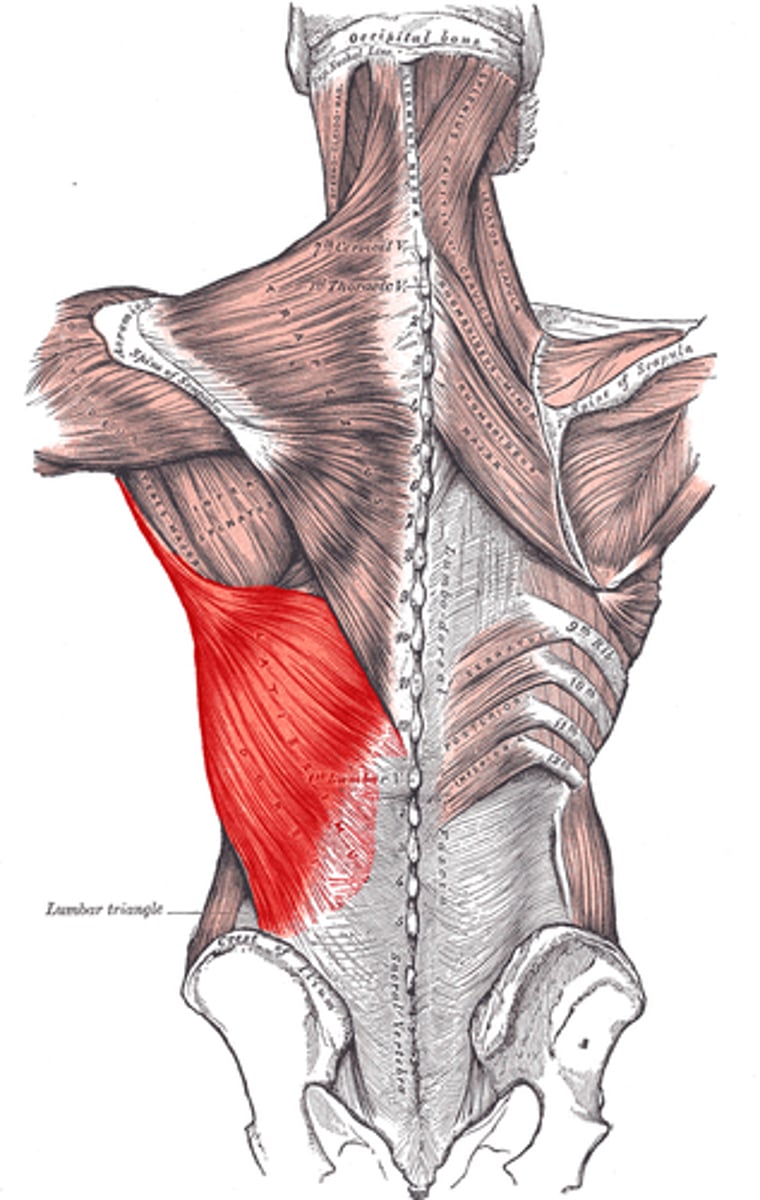
Latissimus dorsi
side + back
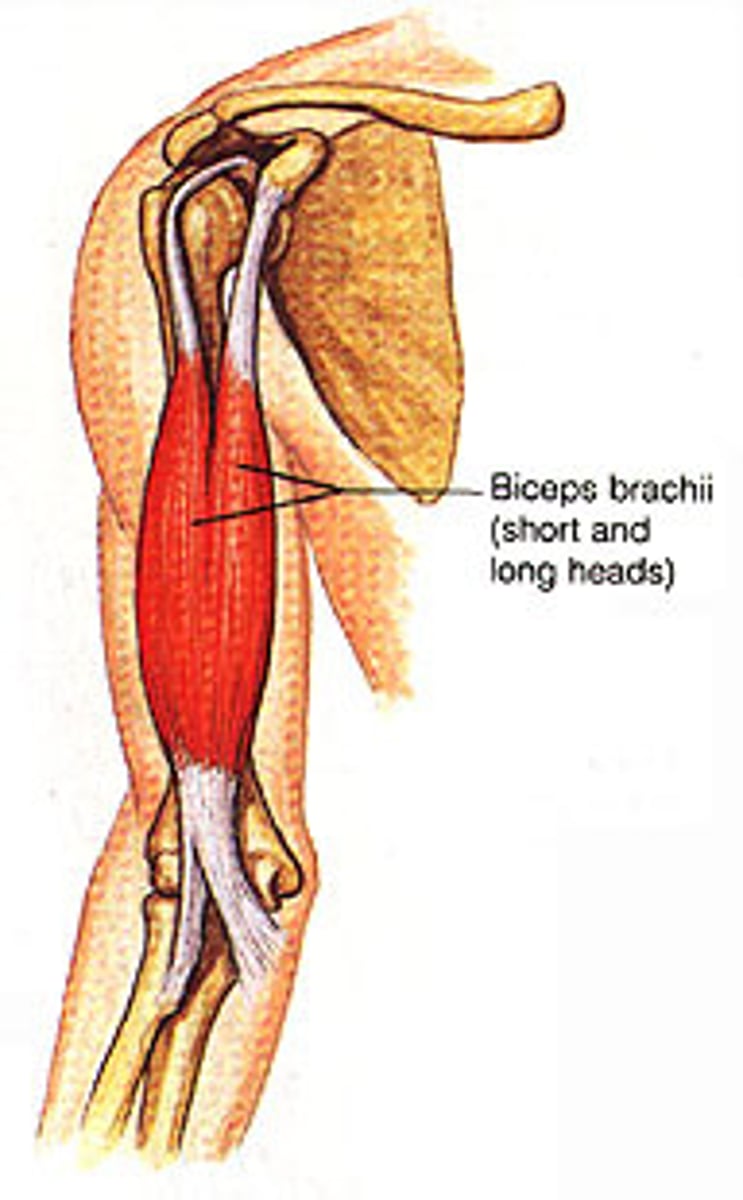
Biceps brachii
two + head + arm