AP Chem unit 8
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Acid
A compound that donates a proton (H+ ) in a reaction (according to bronsted-Lowry
Base
A compound that accepts a proton (H+) according to bronsted-Lowry
Strong Acid, Strong base
Strong acid dissociates completely.
Strong bases ionizes completely
Weak acid, Weak base
These will establish equilibrium (do not react completely)
% ionization
The extent to which an acid or base dissociates can be found by its percent ionization.
%ionization = [A-] / [HA] * 100
For a base % ionization = [HB+]/ [B] * 100
Always just it’s conjugate over the acid or base * 100
Water is _________. Meaning it can act as a acid or a base
Amphoteric
Common strong acids
HCl, HBr, HI, HNo3, HClo4, H2SO4
Common strong bases.
.Any Group 1 or 2 hydroxides:
LiOH NaOH KOH BaOH2 SrOH2
PH,
p anything equals?
Ph scale?
Value that can tell us concentration of Acid or base.
P (anything) = - log (anything)
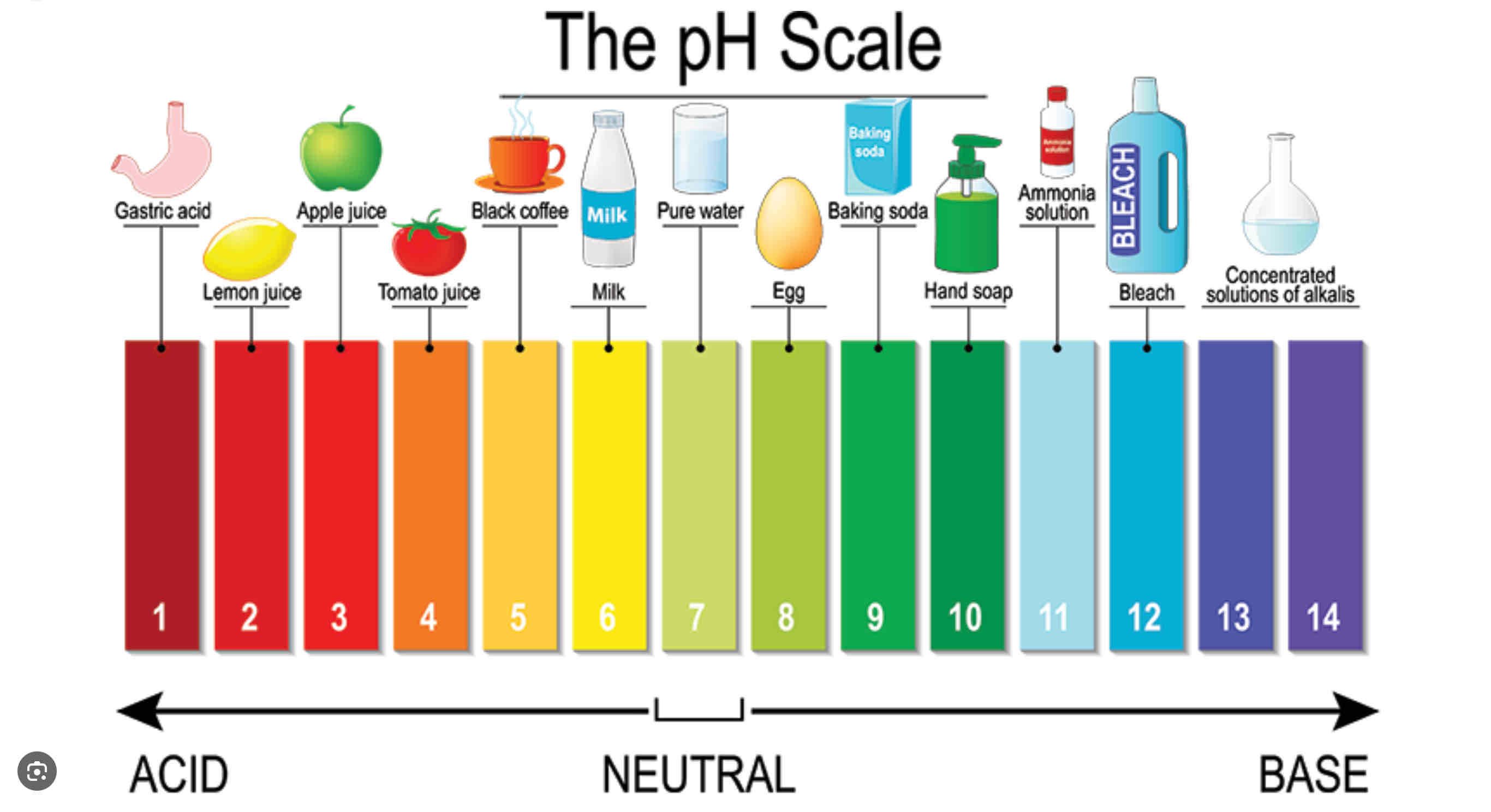
pH = ?
Anything in [] = concentration = moles/ L
-log [H+]
pOH=
-log [OH-]
pKa=
-log [Ka]
pKB
-log [KB]
pK w=
-log [kw]
How to convert from p(something) to concentration or to Constant? : ka kb kW etc..
If you are give the ph, simply put it as a negative exponent to ten to get concentration or constant
10^-ph = [H+]
10^-poh = [OH-]
10^ -pKa = Ka
Increasing Ph means ______ [H+]
Decreasing ph means______[H+]
Decreasing ;
Increasing
When there is High Ph, it is ________ for additional base to dissolve
Harder,
Because at high Ph there isn’t a high abundance in H+ ions make the solubility lower, because base need to react with acid to form water or else doesn’t dissolve.
Due to common ion
When there is abundance in H+ ions (low ph), the solubility of addition base would ______
Increase,
The H+ ions will react with the OH, decreasing concentration shift equilibrium to the right.
Many Hydroxide salts will _____ dissolve well in high PH
Many Acids salts will not _____ dissolve well in low Ph
This is due to common ion effect.
So acid dissolve well when there are things to neutralize not if things are already acidic
Same for base, dissolve well when things are acidic , not if already basic
For strong acids / bases, you can ______ find ____ from concentration.
strong acids goes to ________. No tendency for_______
Always; Ph
Completion; reverse
Weak acids / bases
Unlike strong, they do not dissociate all the way through, and most acid molecules remain as undissociated aqueous particles.
To solve for pH of these, sometimes Ice box is needed
X is always insignificant in weak acids
For weak acids / bases , x in ice box is?
Almost always insignificant compared to the initial concentration of the acid, so we just use the initial concentration in calculation
Acid dissociation constant
Ka = [H+] [A-]/ [HA]
Always product over reactant
![<p>Ka = [H+] [A-]/ [HA]</p><p>Always product over reactant </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c4f941ea-8fd8-4554-bfc6-f4cd3cc48da0.jpg)
Base dissociation constant
Kb= [HB+] [OH] / [B]
![<p>Kb= [HB+] [OH] / [B]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c21e1b45-da3f-400a-ad5e-e1e2c3540ff1.jpg)
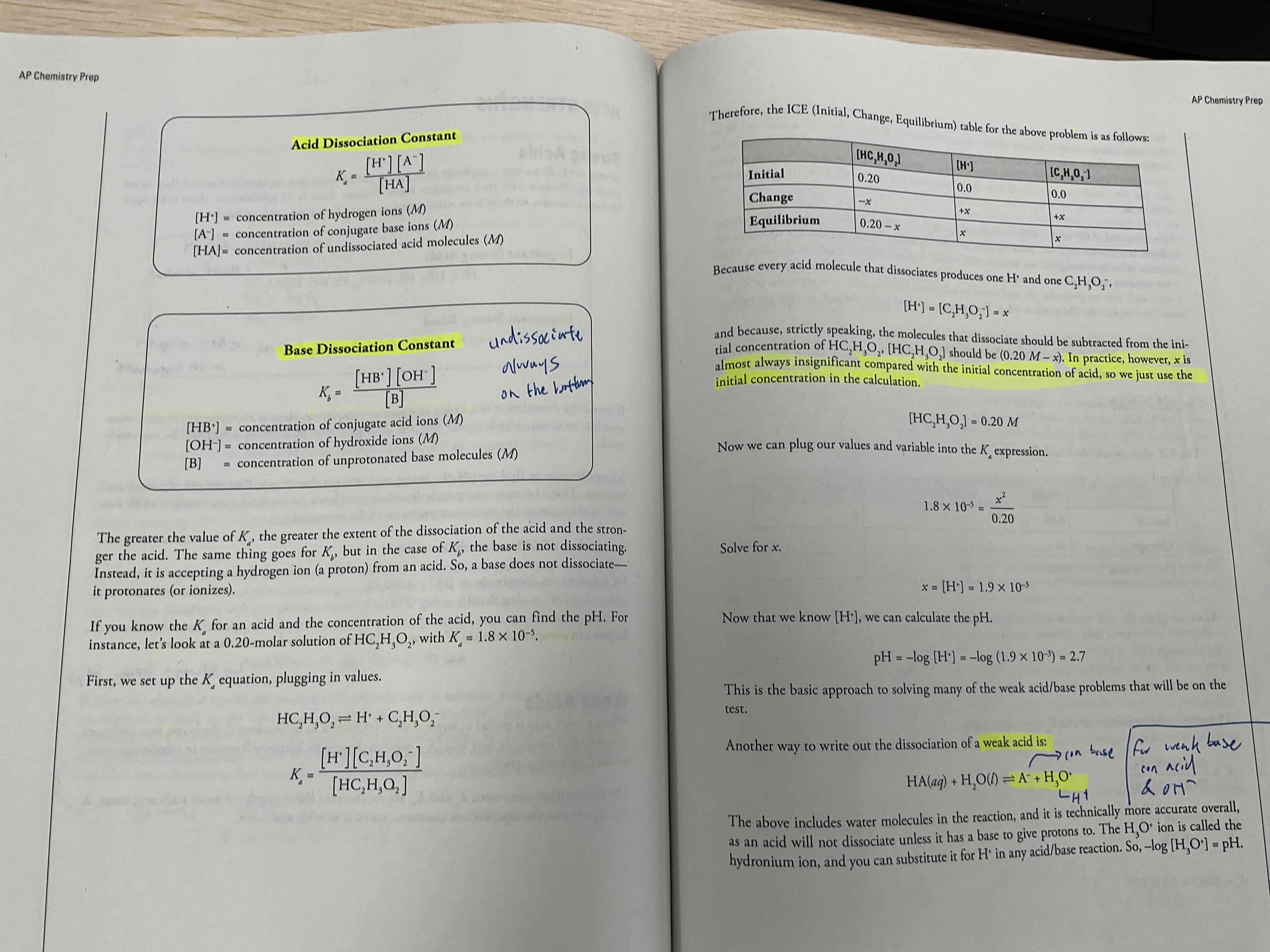
Equilibrium ICE problems
MAKE SURE YOU CAN DO THESE
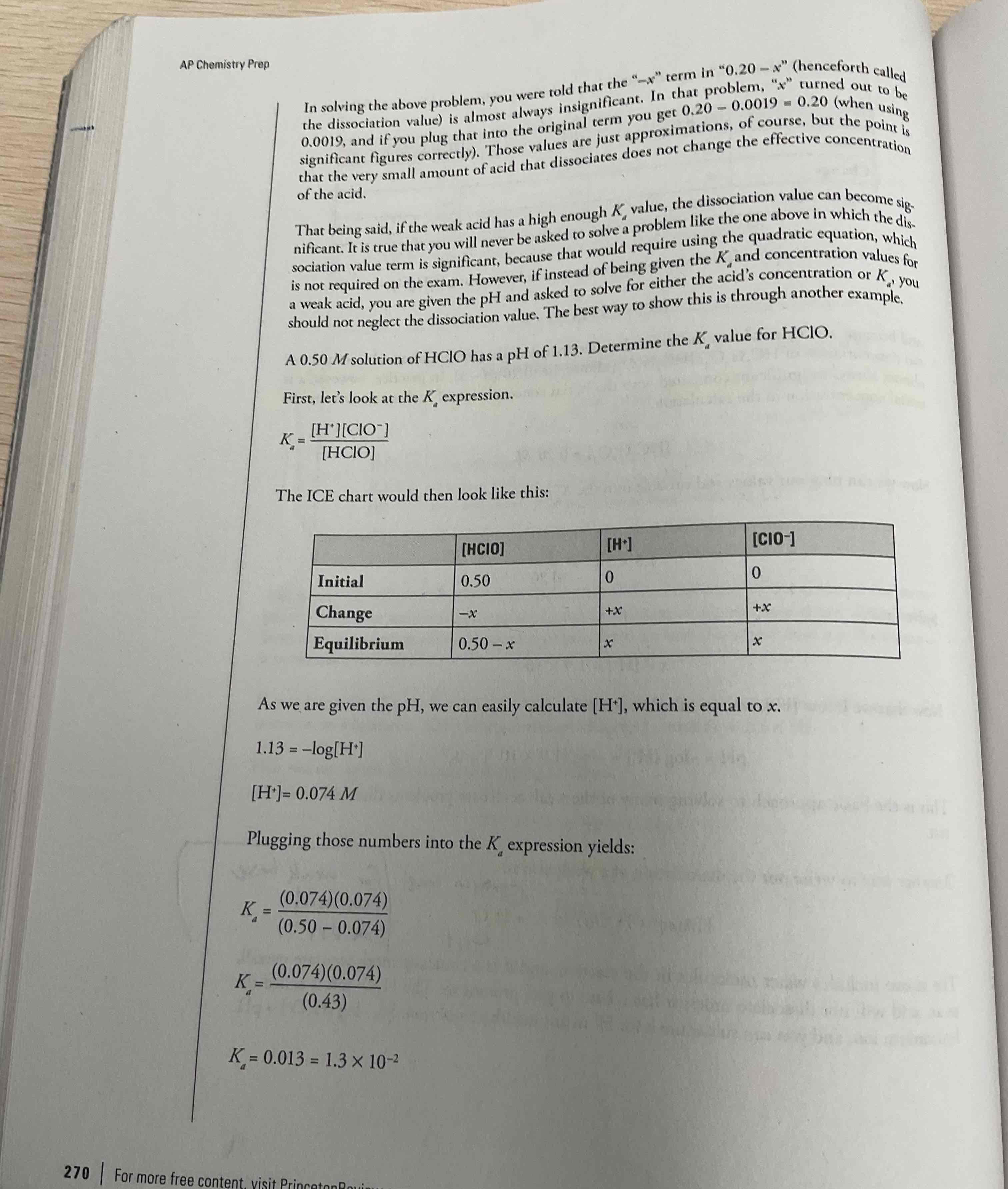
Percent dissociation (percent H break free)
Primary factor when it comes to determining acid strength depends on amount of H+ ions it can donate,
Electronegativity affects the dissociation, HIGH = LESS DISSOCIATION
EASIER FOR H TO BREAK FREE, the stronger the acid
Oxyacids ex: HCLO2,HCLO3 ,H2SO4, H2SO3
The overall all trend for oxyacids is the more oxygens that are attached to an oxyacid, the stronger it will be
Concentration’s relation with percent dissociation?
The lower the concentration is for an acid the higher the percent dissociation.
Because over abundance of water molecules makes it easier for acid to find water to donate to, and it hinders the reverse reaction, because H3O+ and conjugate base are more spread out in a dilute solution (low concentration).
Greater concentration lead to greater conjugate base
Are all hydrogen in acid dissociable?
No, because only the hydrogens that are attached to elements with very big electronegativity differences can dissociate., Ex: oxygen. not like carbon with similar diff
Can Ph effect solubility?
Yes, due to common ion effect, high ph substance have hard time dissolving in high pH, low ph substance have hard time dissolving in low ph
Polypro tic Acids Ex: H2So4, H3 Po4
Acids that can give up more than 1 hydrogen in solution.
They give up first easily than future electrons
The equilibrium Constant of water
Kw= 1.0 × 10^-14 at 25 C
This can be useful because Ka * Kb = Kw,
You can manipulate using ka to fin kb, or kb to find ka,
KW divide by either = the other k
pH + pOH=
14
pKa + pKb = ?
14
pKa, or pKb = what at half way point?
Ph at halfway point
Since kb, kw, ka are equilibrium constants, a change in temperature will?
Change their value, any equilibrium constant will experience a change in value if the temperature does.
Neutralization reactions:
Strong Acid + Strong base =?
Dissociated completely
Always RESULTS in creation of water H2O

Strong Acid + weak base
Conjugate acid of the weak base will be produced
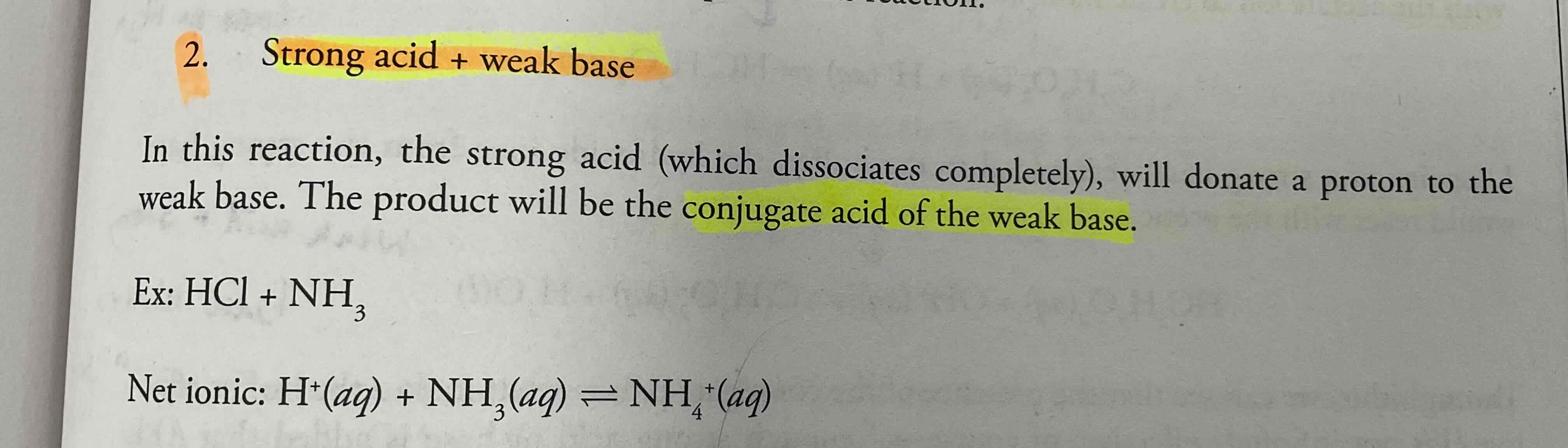
Weak acid + strong base = ?
Conjugate base of the weak acid and water
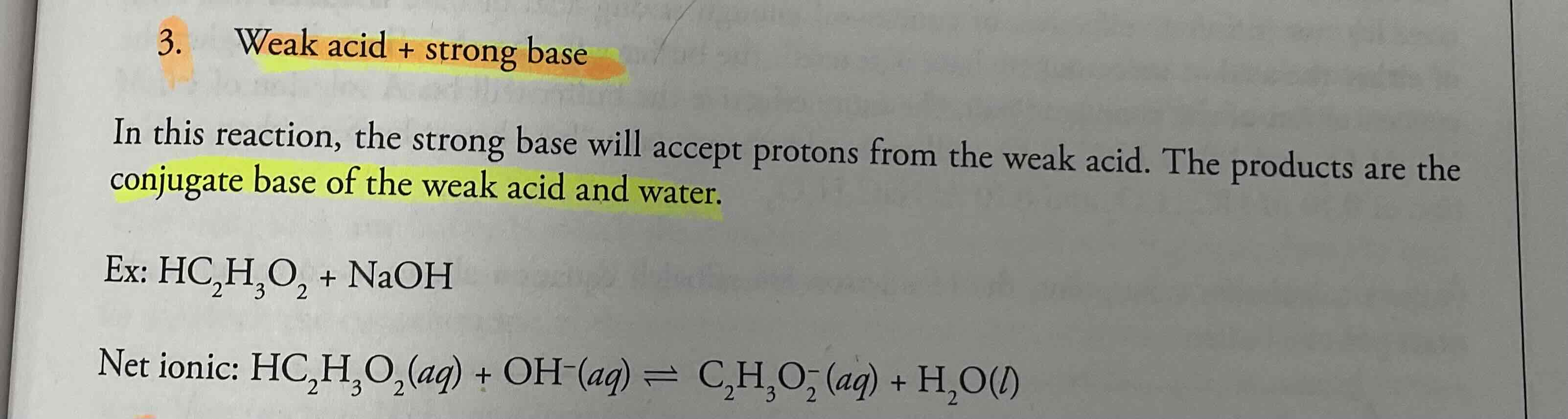
Weak acid + weak base = ?
Simple proton transfer reaction, in which the acid gives protons to the base.
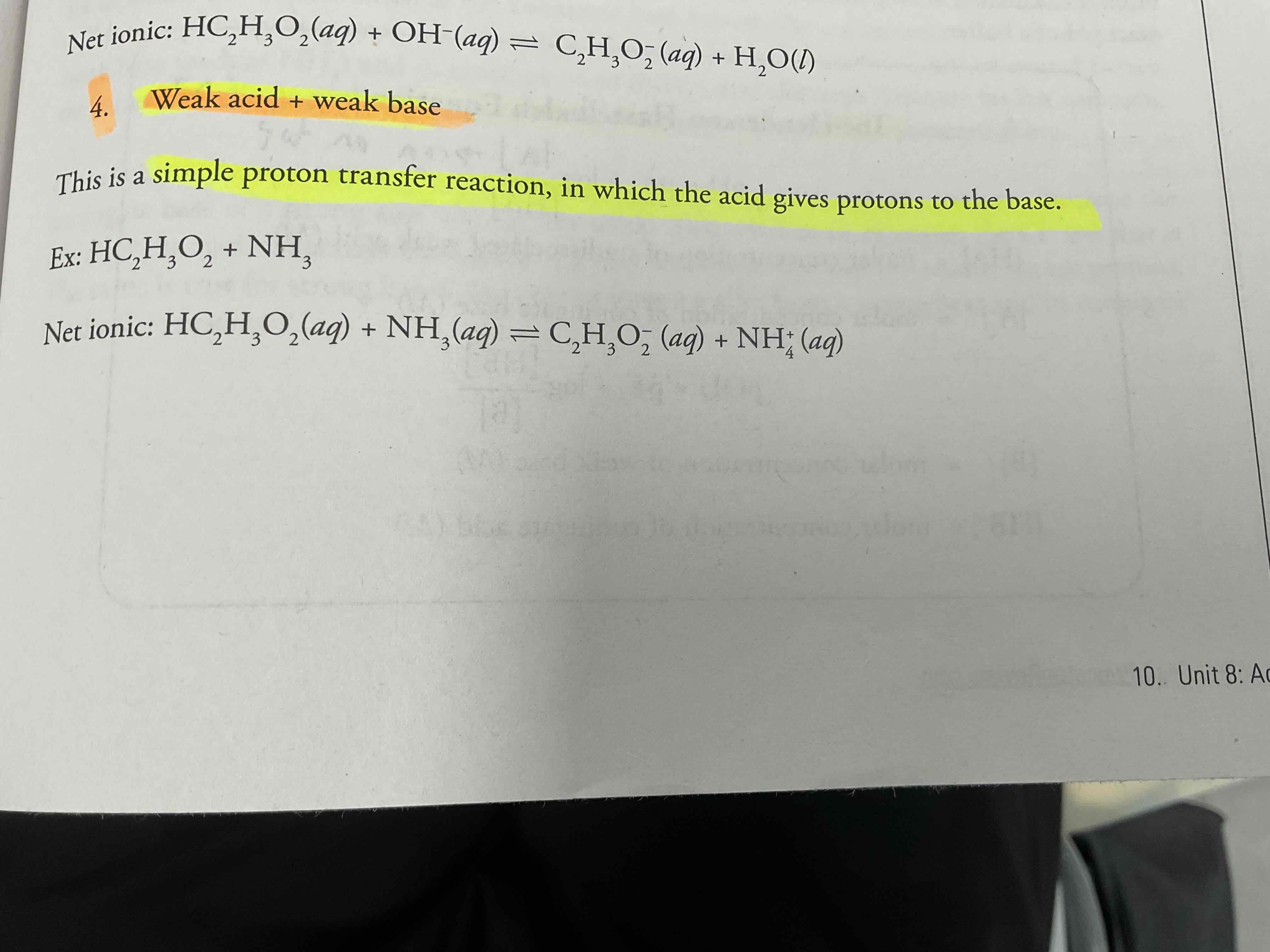
Buffer
A solution with very stable pH, that will fight stress (addition of acid or base will not greatly effect ph)
Created by adding weak acid or base WITH IT’S Conjugate


Henderson Hasselbalch equation (given) , what is it used for?
Allows us to calculate the exact Ph of a buffer

Indicators
Are weak acids which change colors in certain pH ranges due to Le Chateliers,
We use Hon to indicate an indicator. It should have range of + or - 1 to be EFFECTIVE RANGE
Larger Ka indicates?
A strong acid because more will dissociate
Larger Kb indicates
A stronger base, because high dissociation level

Equivalence point
Titration when exactly enough base has been added to neutralize all the acid (into conjugate base, only [A-]) that was initially present. pH can be 7 if both are strong, but will vary due to concentration or one is weak.
Half- way point
Enough base has been added to convert exactly half of the acid into conjugate base; here the conversation of acid is equal to the concentration of conjugate base ([HA]=[A-]), At this point ka = H +, so pKa = pH, explained in the picture
![<p>Enough base has been added to convert exactly half of the acid into conjugate base; here the conversation of acid is equal to the concentration of conjugate base ([HA]=[A-]), At this point ka = H +, so pKa = pH, explained in the picture</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/24548015-ec51-4002-a0eb-4853b0f1e77c.jpg)
The greater the concentration of the buffer the ?
more effective it is