PChem U1
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Mixture
Contains two or more pure substances; can be homogeneous or heterogeneous
Homogeneous
In chemistry, homogeneous refers to a substance or mixture that has a uniform composition throughout. This means that any sample taken from a homogeneous mixture will have the same characteristics and properties, regardless of where it is taken from..
Heterogeneous
In chemistry, "heterogeneous" refers to a mixture that is composed of different constituents or dissimilar components. This means that the composition of a heterogeneous mixture is non-uniform, varying from one location to another within the mixture.
Extensive Properties
Properties that depend on the amount of substance (mass, length)
Intensive Properties
Properties that do not depend on the amount of substance (such as boiling point, density).
Phase Change
The transition of a substance from one state of matter to another, such as solid to liquid or liquid to gas, often involving energy changes.
Kelvin Equation
K = C + 273.15
Sublimation
The process by which a solid turns directly into a gas without passing through the liquid phase
Deposition
The process by which a gas turns directly into a solid
Condensation
Gas —> Liquid
Vaporization
Liquid —> Gas
Melting
Solid —> Liquid
Freezing
Liquid —> Solid
Viscosity
the resistance of a fluid to flow or change shape
Critical Point
the point at which two phases of a substance initially become indistinguishable from one another. The critical point is the end point of a phase equilibrium curve, defined by a critical pressure Tp and critical temperature Pc. At this point, there is no phase boundary.
Supercritical Fluid
Substance that exhibits properties of both liquids and gases
Triple Point
the unique temperature and pressure at which a substance can exist simultaneously in solid, liquid, and gas phases in thermodynamic equilibrium.
atm
atmospheric pressure
Volatile
easily evaporated
more evaporation =
= more pressure and lower boiling point
Volatility
A measure of how easily a liquid changes to a gas (evaporation)
Work =
= Force x Distance
Unit for energy
joules
Unit for pressure
Pascals (Pa)
760 mm Hg (Mercury) =
= 1 atm
Boiling of a liquid occurs when
occurs when its vapor pressure equals the atmospheric pressure
kilojoules (kJ) to joules (J)
1 kJ = 1000 J
kilocalories (kcals) to kilojoules (kJ)
1 kcal = 4.184 kJ
calories to joules
1 cal = 4.184 J
Pressure =
= Force/Area
Temperature is a measurement of
average kinetic energy per particle
Latent heat
Energy released or absorbed during a phase transition due to changes in the potential energy of the system.
Pressure is the
number of collisions
Ideal gas law
PV = kbNT
R =
= 0.0821 L x atm/(K x mol)
kb
= Boltzmann constant
∝
direct proportionality
Kinetic energy is due to particle ____
motion
potential energy is due to particle ____
interactions
As particles move away from each other, potential energy ______
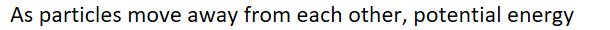
INCREASES
As particles move closer to each other, potential energy ______
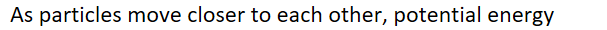
DECREASES
KE =
= ½ mv2
Ionic Bond
Transfer of valence electrons (metals and nonmetals)
Covalent Bond
Sharing of electrons (nonmetals)
ions
charged particles
cations
positively charged ions
anions
negatively charged ions
Avogadro’s Number
6.022 × 1023 particles
Molar mass
mass of one mole of particles of any substance (g/mol)
mass of a volume of a liquid
M = V x d (density)
Consentration
Amount of a substance per unit volume of a mixture.
Elementary substance
composed of identical particles made of free or bonded atoms of the same type
Chemical compound
composed of identical particles made of bonded atoms of two or more different types
Molecular compound (covalent)
They are made up of molecules
Ionic compound
made up of ions arranged in lattice networks (no molecules)
Density =
Mass/Volume
Ions
When # of protons does NOT equal # of electrons
Isotopes
Same # of protons, but different # of neutrons