COMPANA Lab-LE3
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
Mobility, Stabilization, Posture, Physiology, Protection, Temperature Regulation
What are the roles of the muscular system? (MSPPPTr)
Muscle Fibers
The muscular system is composed of specialized what specialized cells?
Contractability
What is the main quality of muscle fibers?
Sarcomere
It is the basic contractile unit of muscle fiber.
50%
The muscular system makes up roughly what percentage of a person’s body weight?
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth or Visceral
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal Muscle
Fibers: striated, tubular and multi-nucleated
Voluntary
Smooth Muscle
Fibers: non-striated, spindle-shaped, uninucleated
Involuntary
Usually covering wall of internal organs
Cardiac Muscle
Fibers: striated, branched, uninucleated
Involuntary
Has Intercalated Discs
Intercalated Discs
It’s responsible for synchronizing the contraction of the heart.
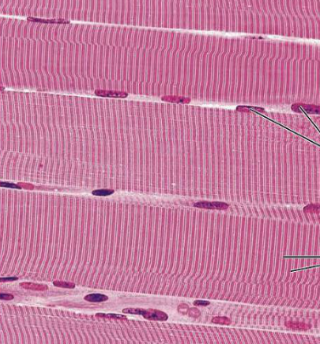
Skeletal Muscle
What type of muscle tissue is this?
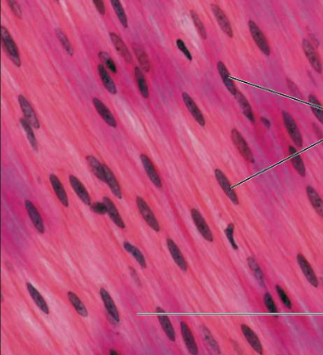
Smooth or Visceral Muscle
What type of muscle tissue is this?
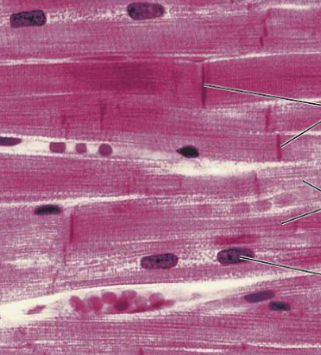
Cardiac Muscle
What type of muscle tissue is this?
Bone > tendon >deep fascia> epimysium > skeletal muscle > perimysium > fascicle > endomysium > muscle fiber > sarcolemma > myofibril > sarcomere
Enumerate the order in which how the a skeleton muscle is attached to a bone starting from the bone (Superficial-Deep).
Tendon
What is 1?
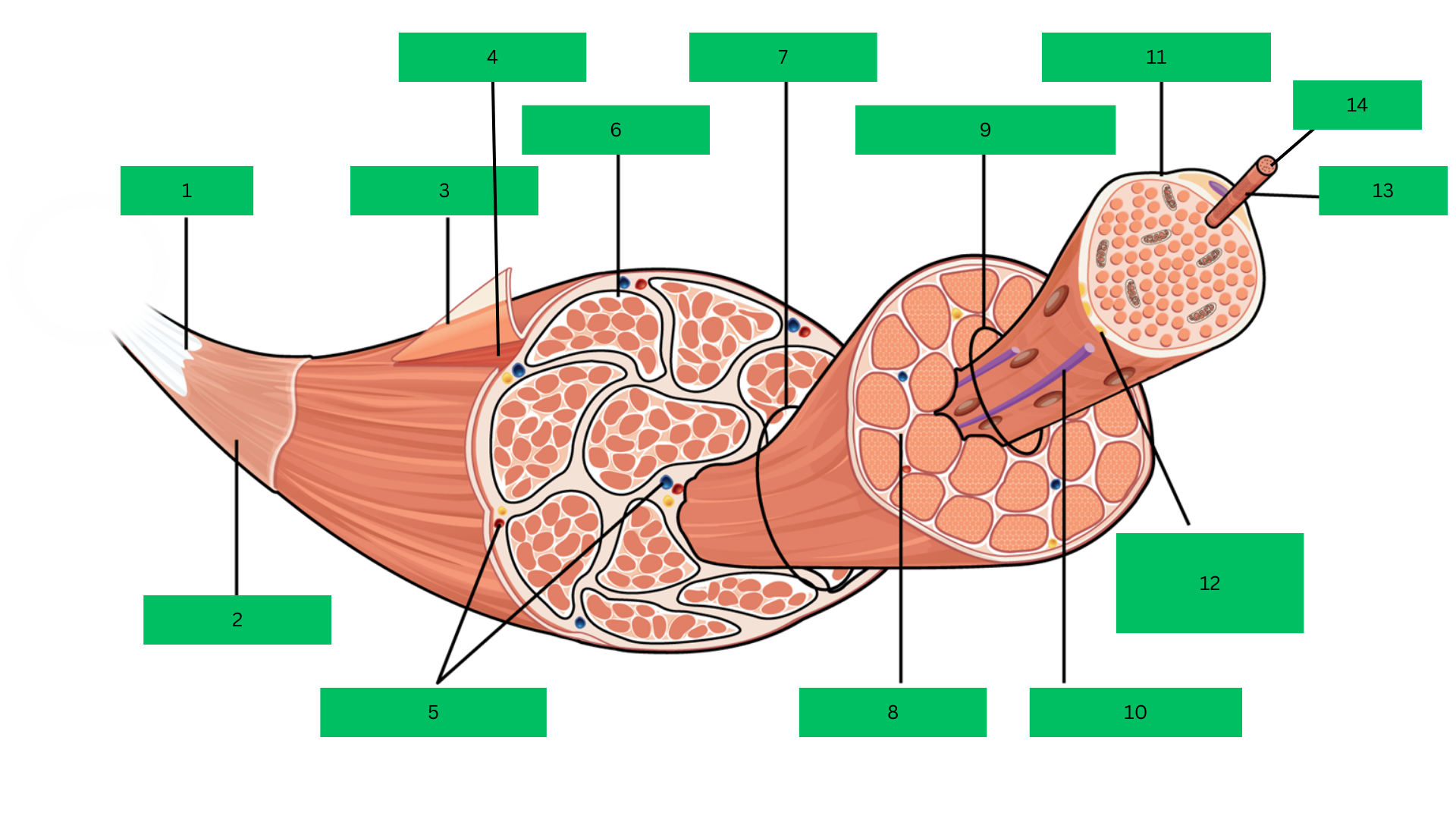
Deep Fascia
What is 2?
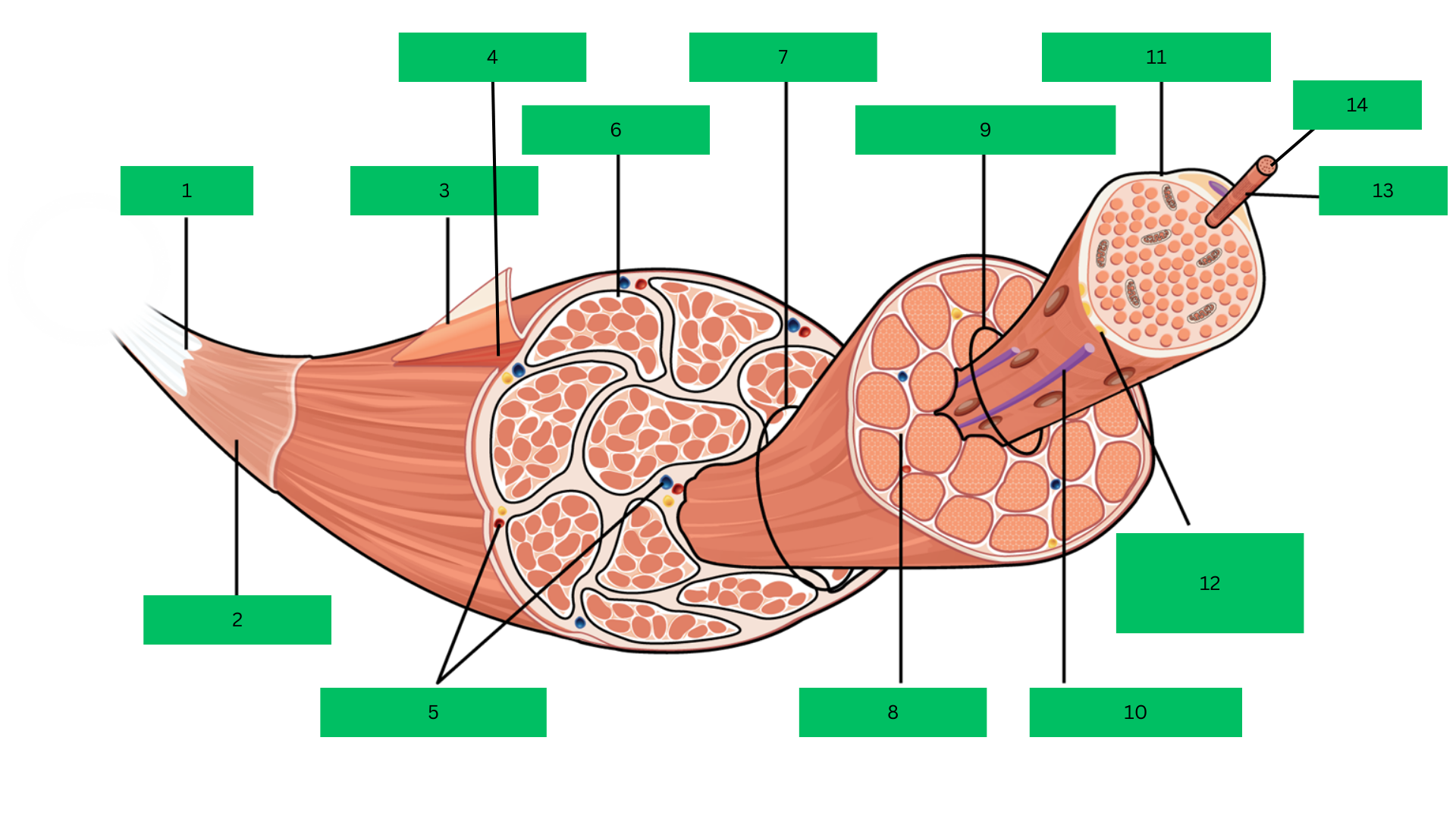
Epimysium
What is 3?
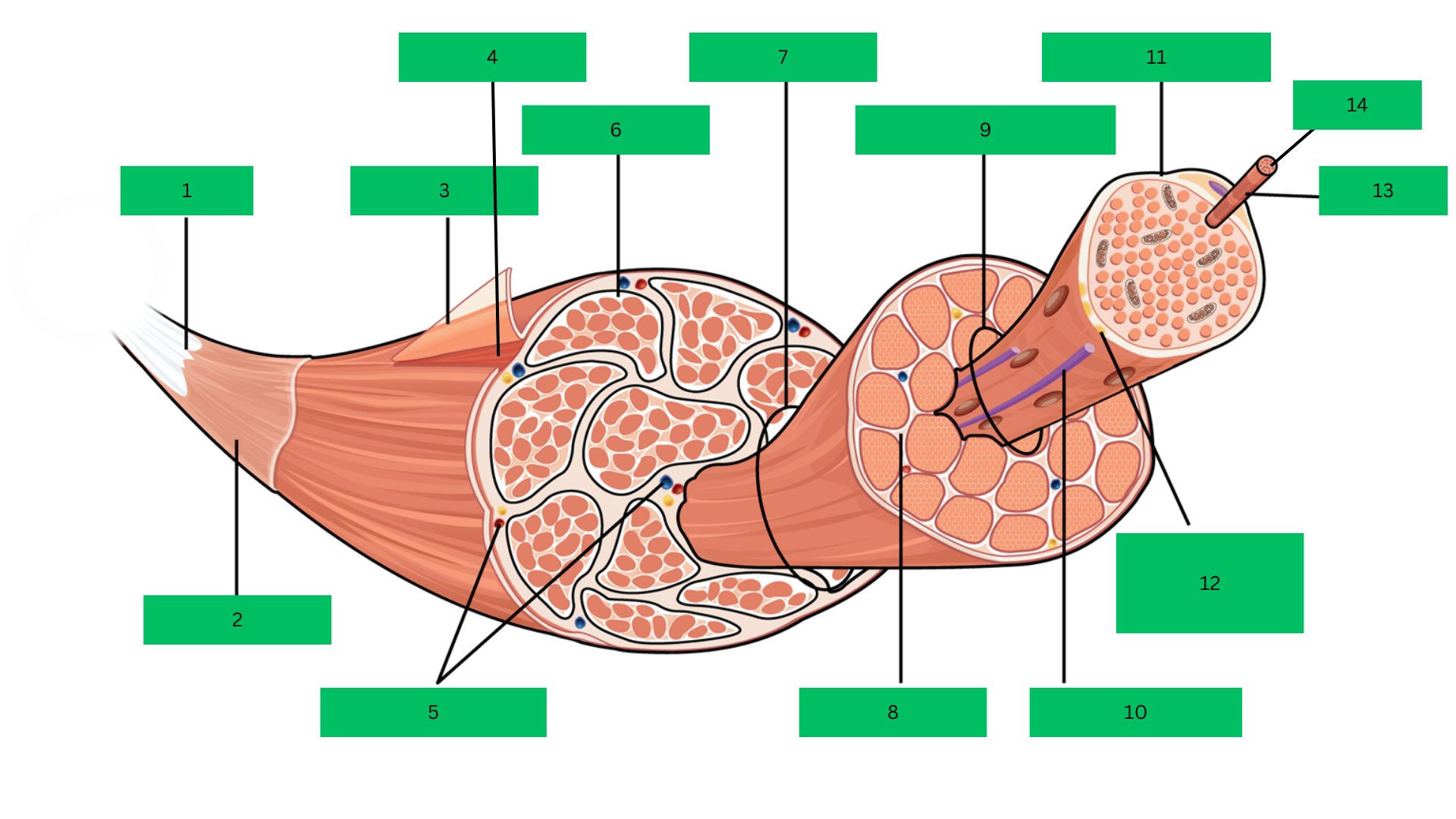
Skeletal Muscle
What is 4?
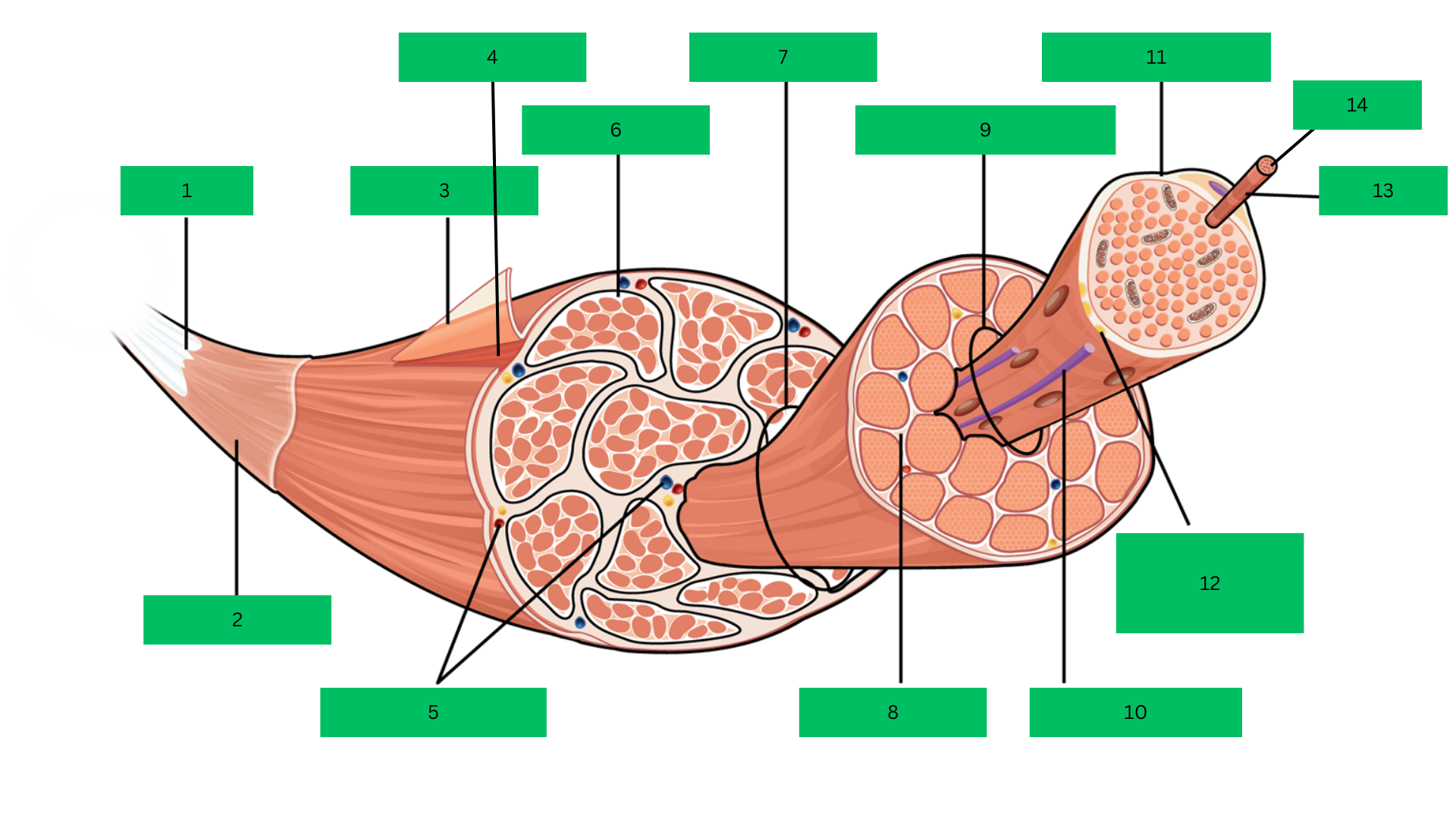
Blood Vessels
What are 5?
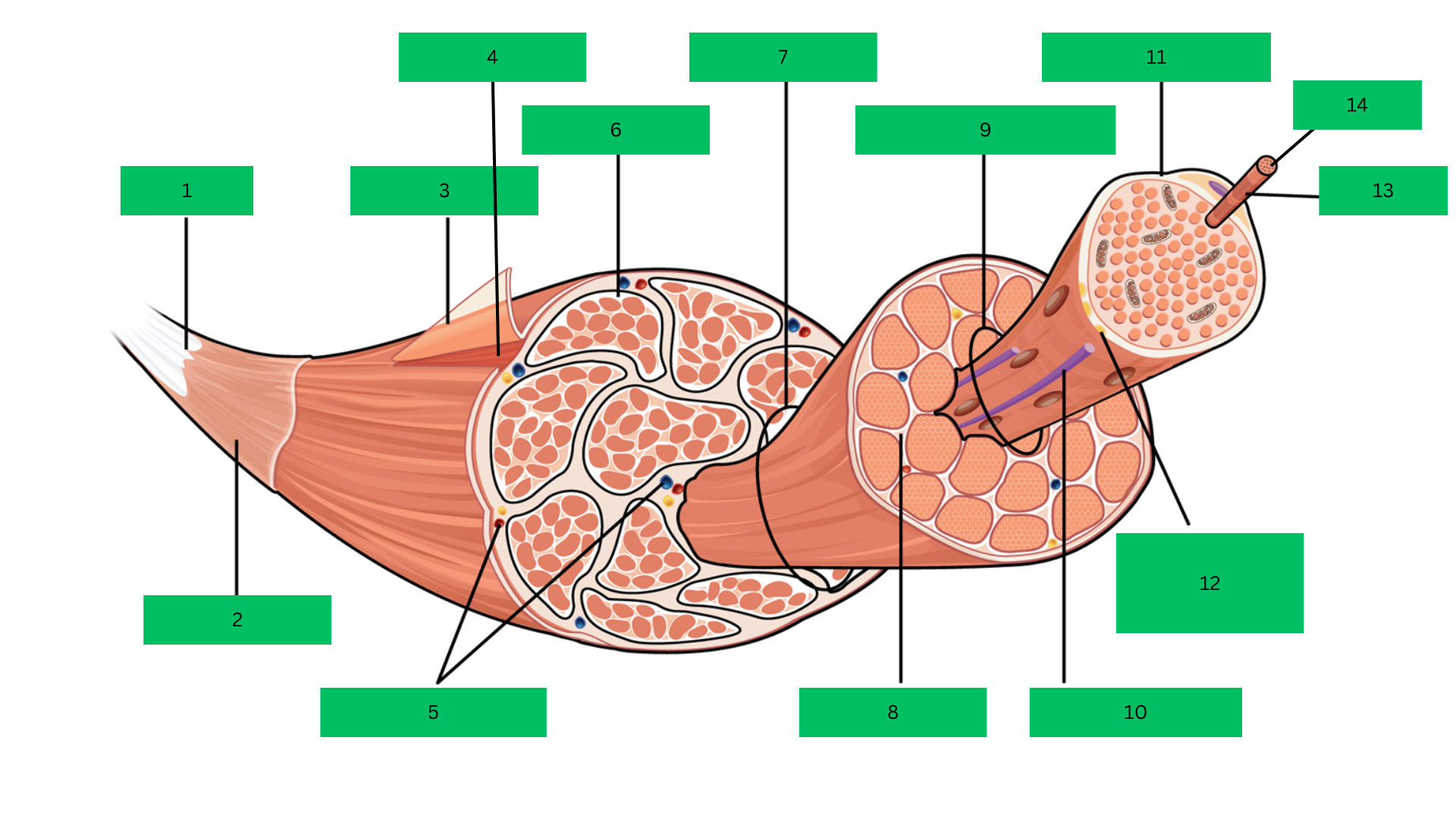
Perimysium
What is 6?
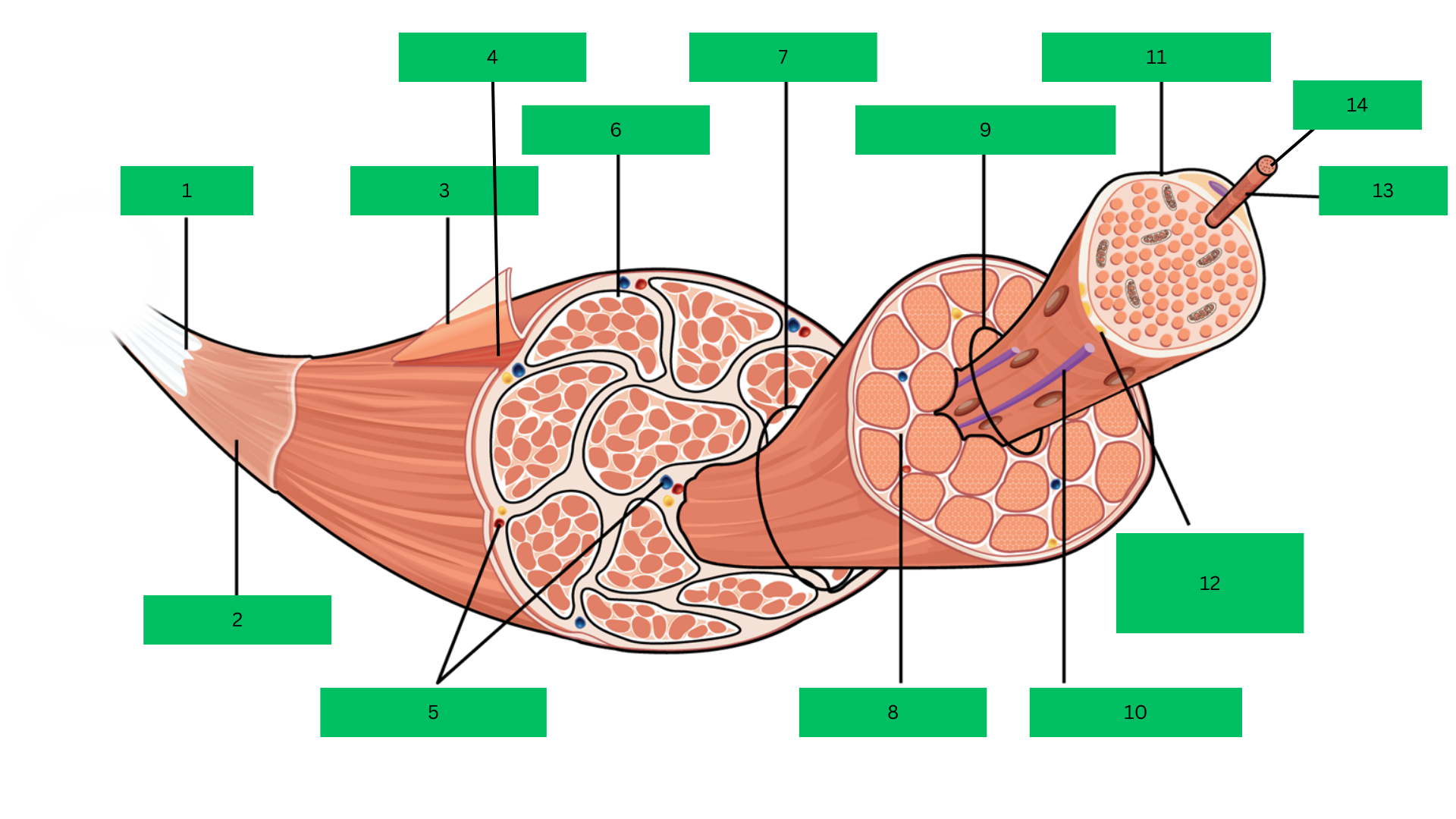
Fascicle
What is 7?
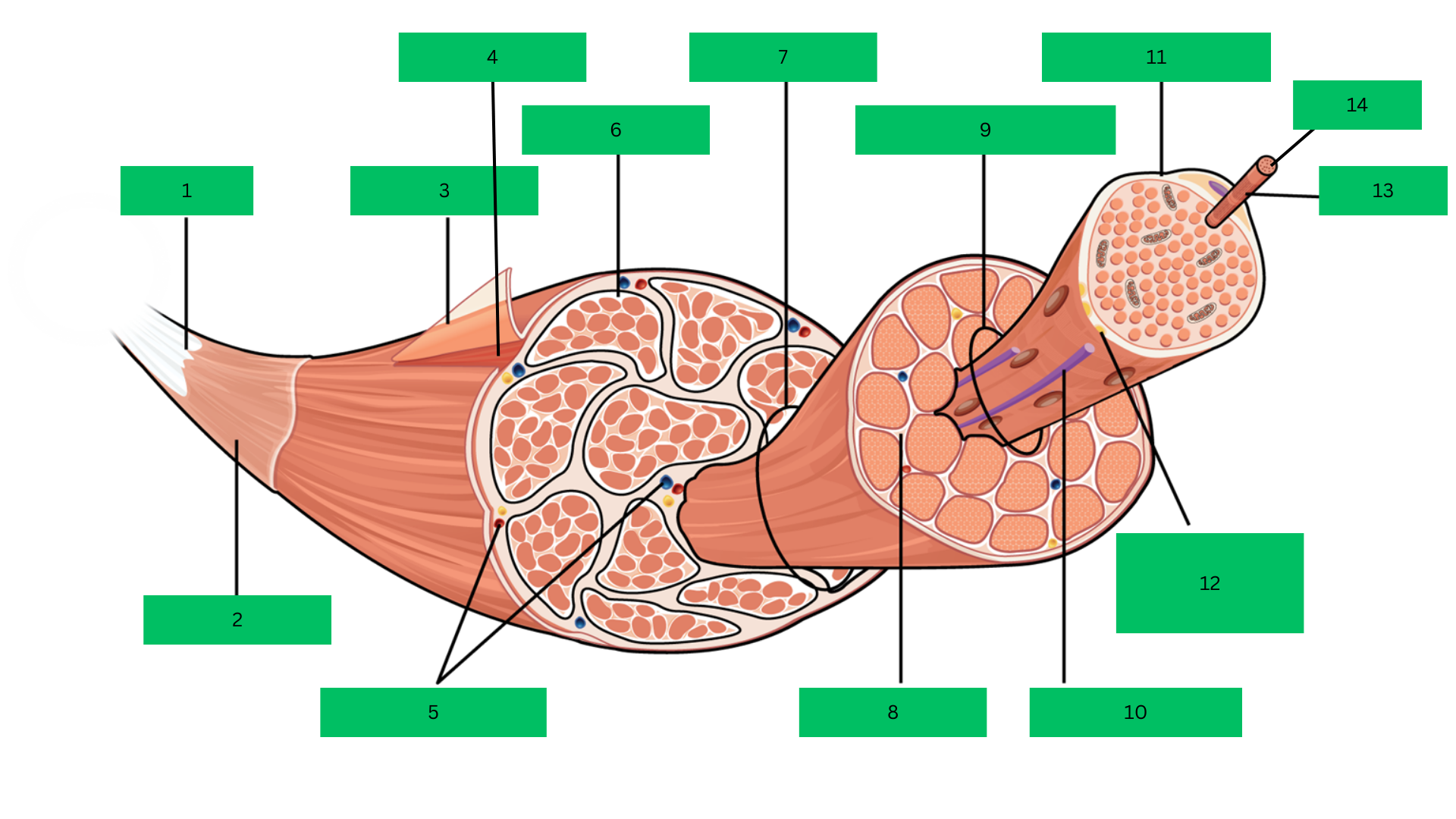
Endomysium
What is 8?
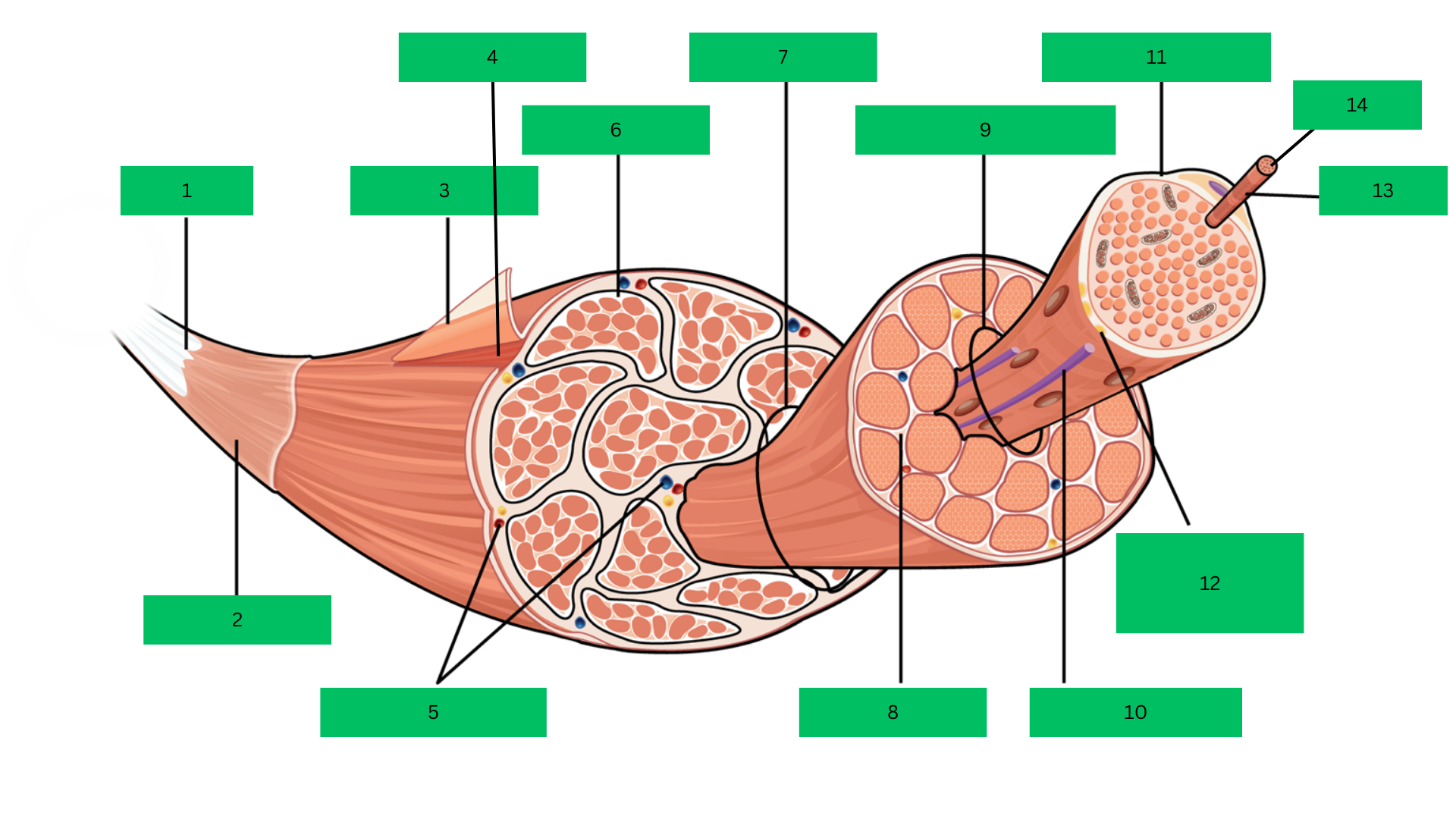
Muscle Fiber
What is 9?
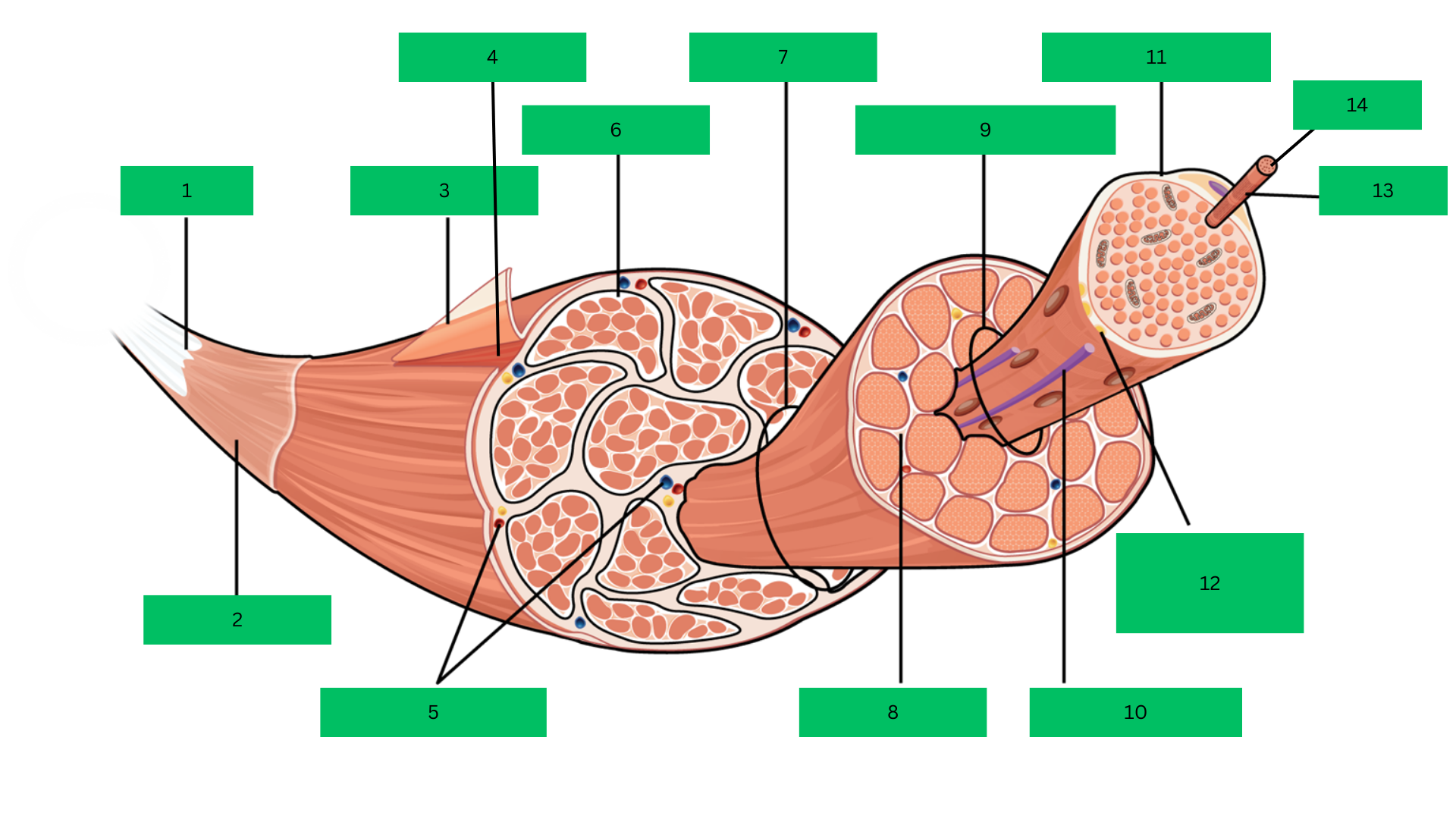
Blood capillary
What is 10?
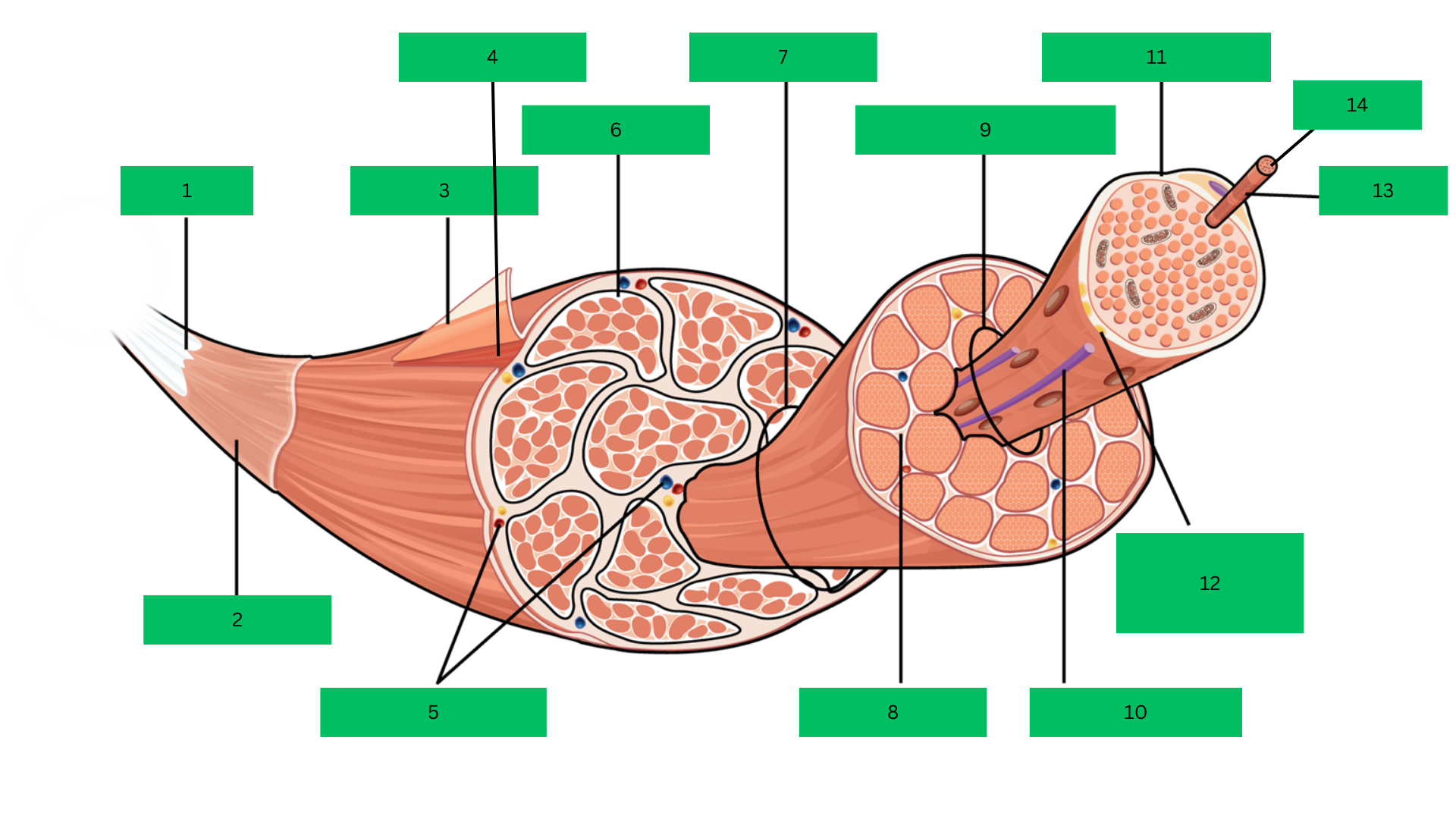
Sarcolemma
What is 11?
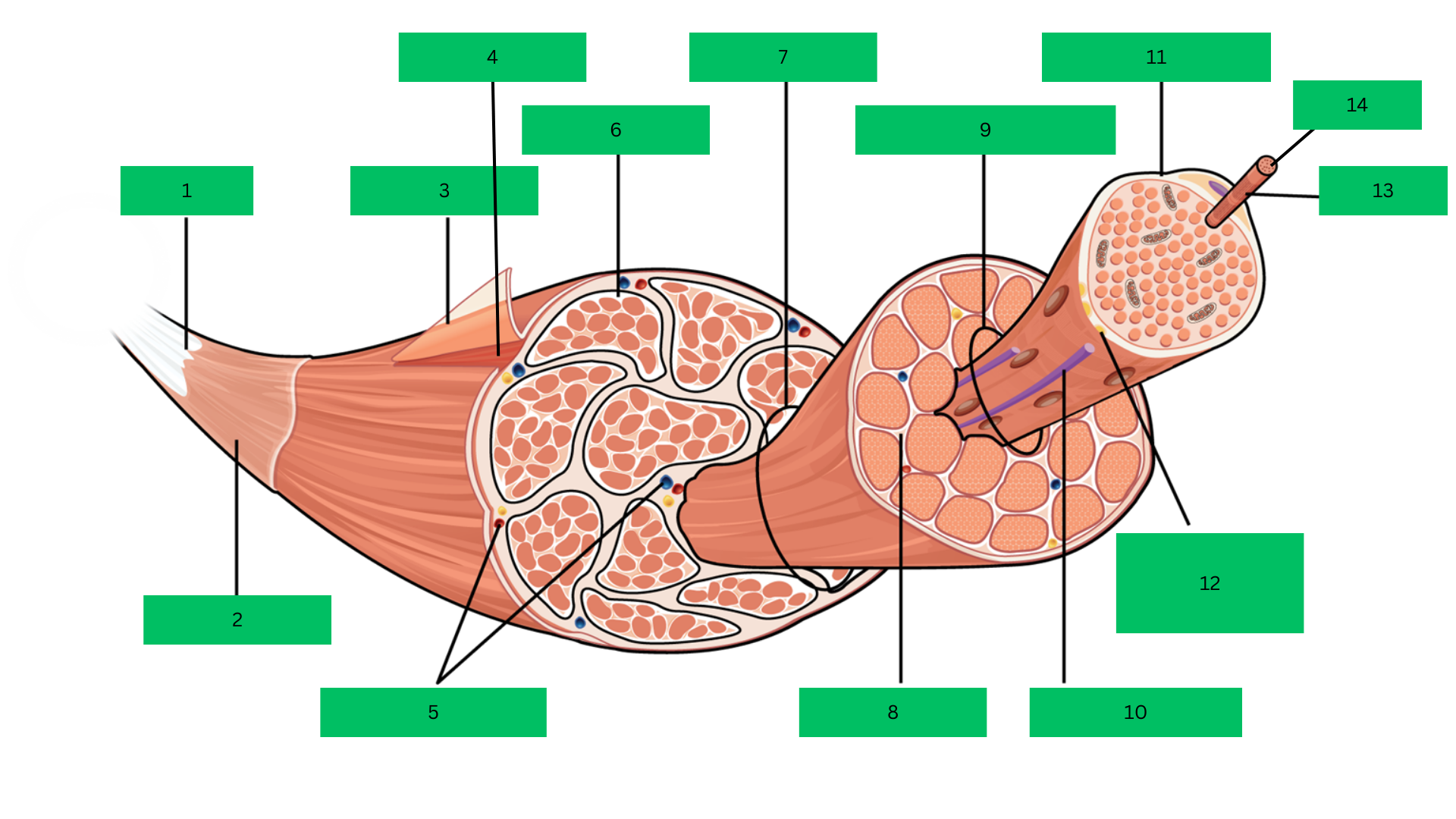
Motor Neuron
What is 12?
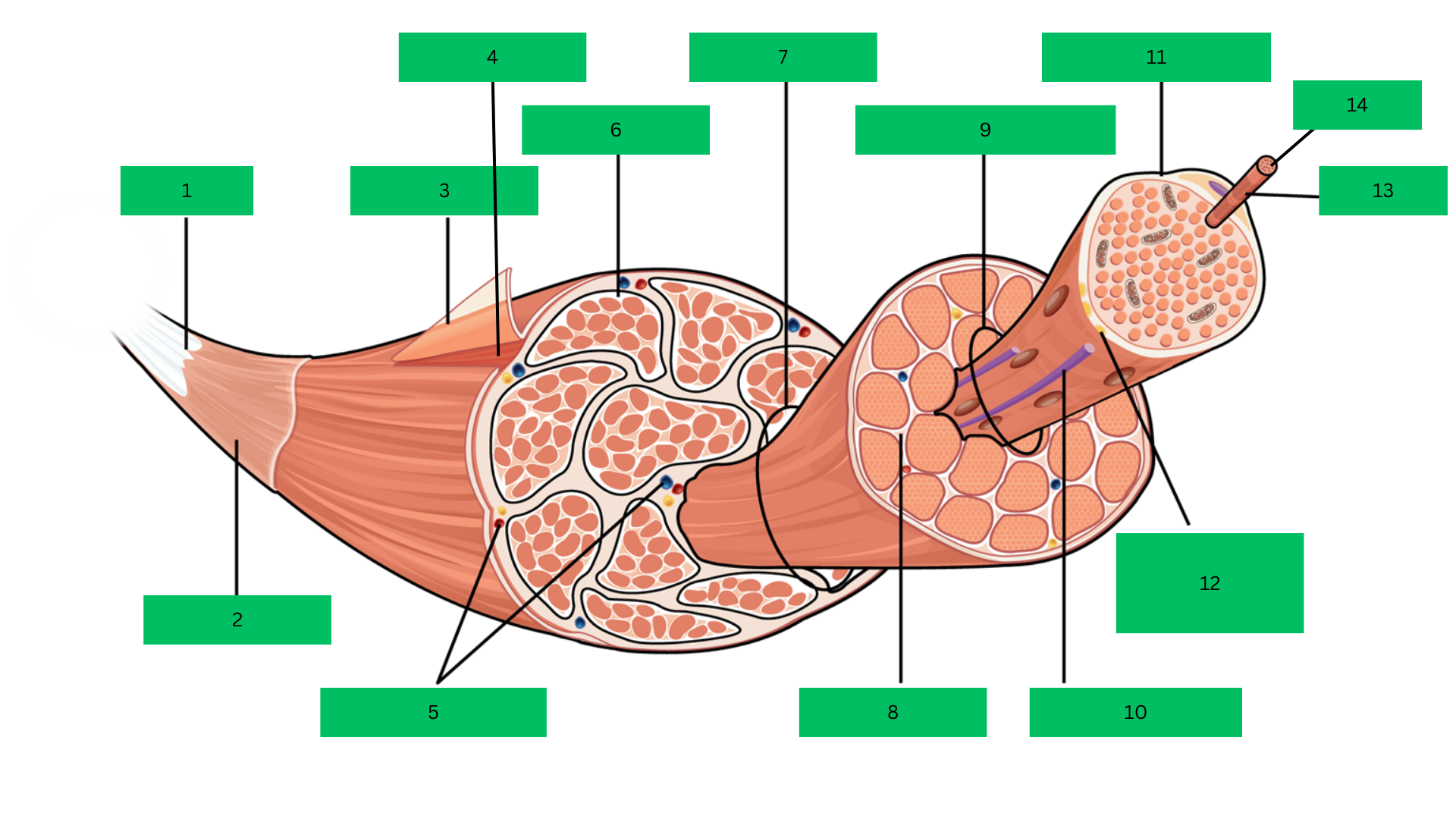
Myofibril
What is 13?
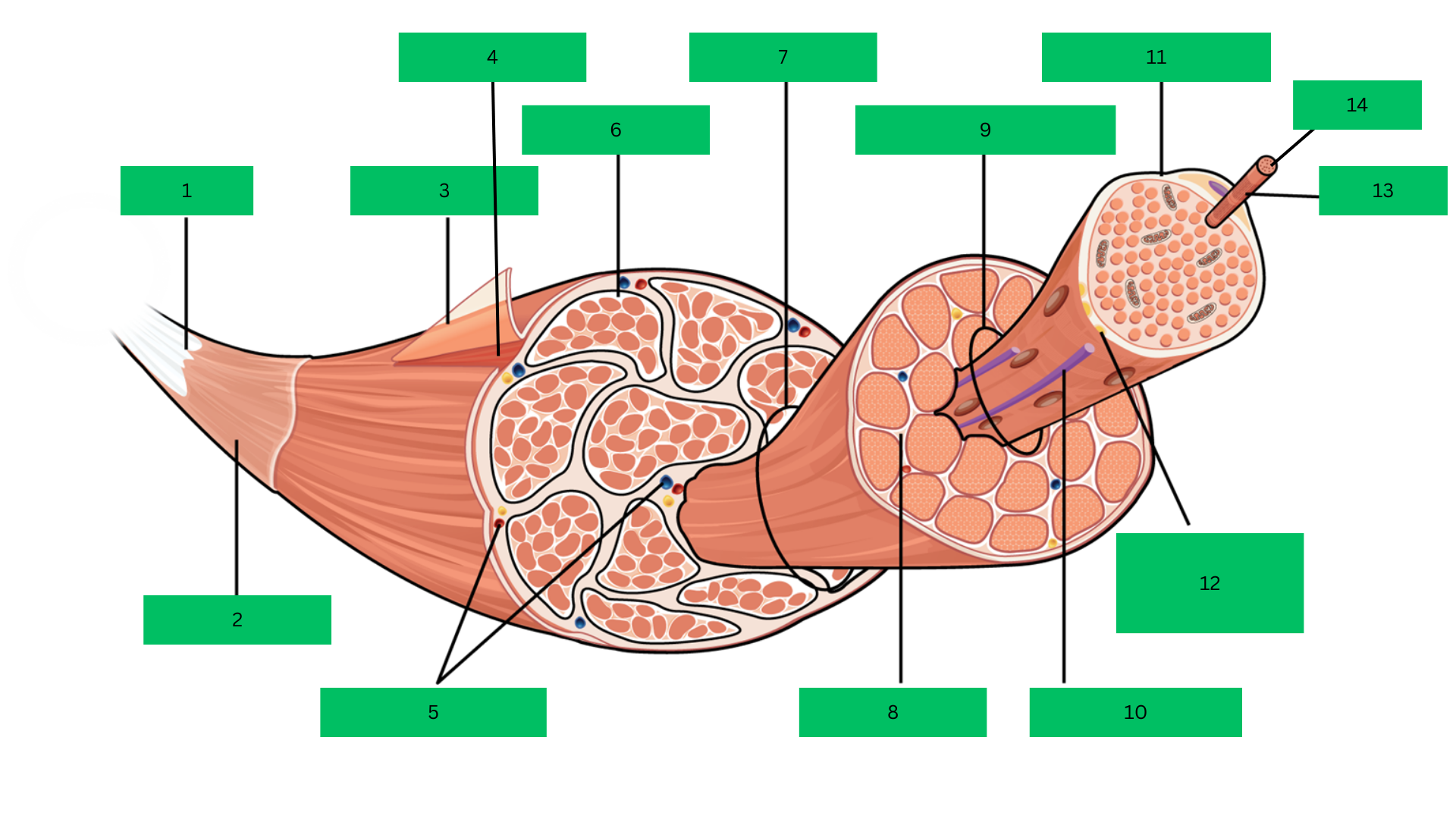
Sarcomere
What is 14?
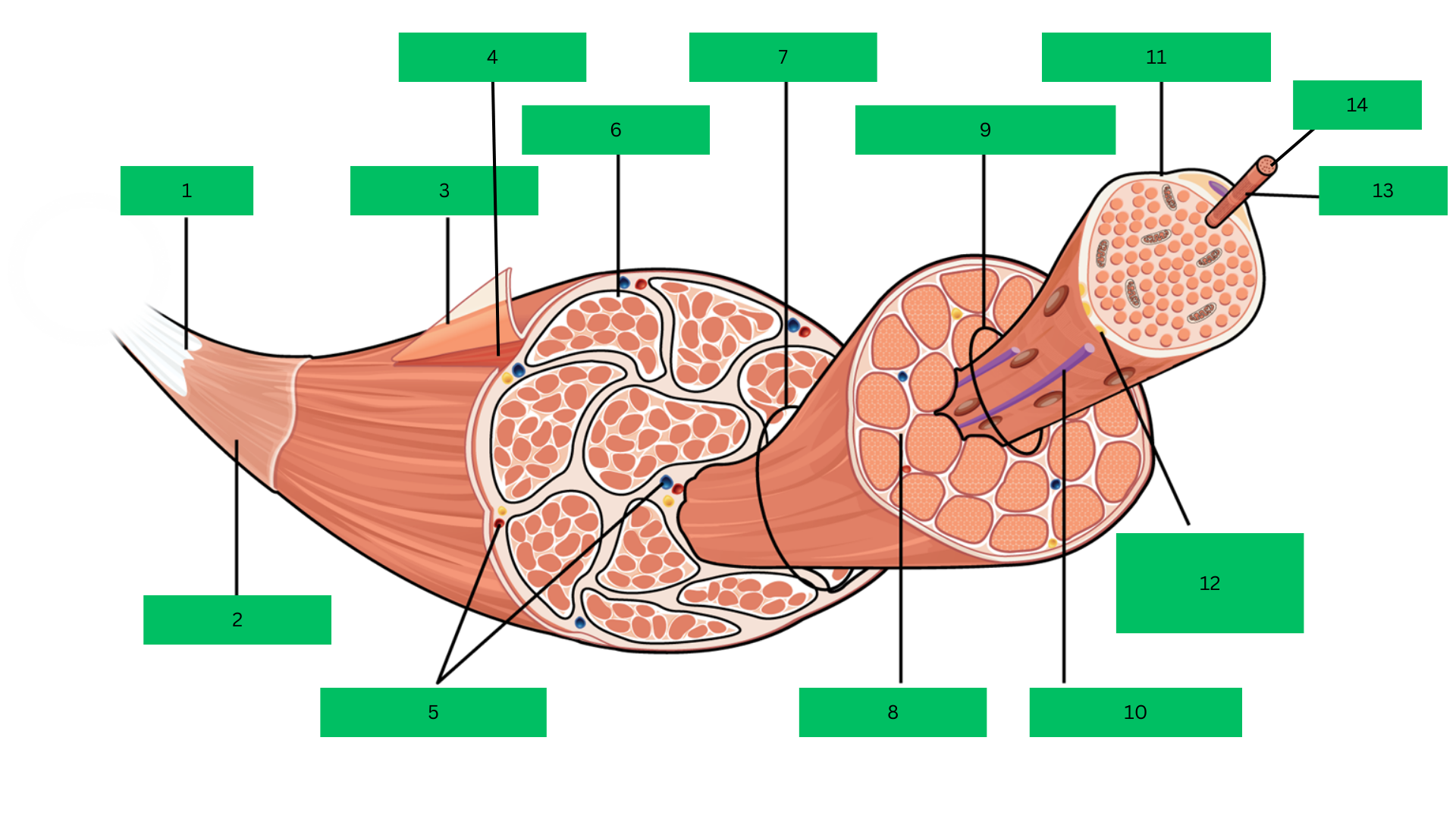
Epimysium
Outermost dense connective tissue layer that surrounds the
entire skeletal muscle, providing structural integrity and reducing friction.
Skeletal Muscle
A complete organ composed of bundles of muscle
fibers, responsible for voluntary movements.
Perimysium
Connective tissue that wraps around bundles of muscle
fibers (fascicles) within the muscle.
Fascicle
A bundle of muscle fibers within a skeletal muscle, surrounded
by the perimysium.
Endomysium
Thin connective tissue layer that surrounds each individual
muscle fiber within a fascicle.
Muscle Fiber
A single muscle cell, long and cylindrical, responsible for
contraction.
Sarcolemma
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber that encases each
cell and transmits action potentials.
Myofibril
Rod-like structures within muscle fibers, composed of
repeating units called sarcomeres, responsible for muscle contraction.
Sarcomere
The smallest functional unit of a myofibril, consisting of actin
and myosin filaments, which contracts to produce force.
Connective tissues sheaths
Layers that provide support, protection, and organization to the muscle
at different levels (whole muscle, fascicles, and individual fibers)
Fascia
Connective tissue that surrounds and separates muscles
Aponeurosis
A type of fascia that is flat and sheet-like attaching muscles to muscles or
muscles to bones
Tendon
fibrous tissue that connects muscles to bones
Thick, dense
outer layer
covering the
entire muscle
Describe the appearance of the epimysium.
Provides
structural
support,
protection,
reduces friction
Describe the function of the epimysium.
Intermediate
thickness,
surrounds
fascicles
Describe the appearance of the perimysium.
Groups fibers
into fascicles,
carries vessels
Describe the function of the perimysium.
Thin, delicate
layer around
muscle fibers
Describe the appearance of the endomysium.
Supports,
facilitates
nutrient
exchange
Describe the function of the endomysium.
Thin, fibrous
connective
tissue around
muscles and
groups
Describe the appearance of the fascia.
Separates and
protects
muscles,
supports
vessels and
nerves
Describe the function of the fascia.
Flat, sheet-like,
shiny, and
fibrous
Describe the appearance of the aponeurosis.
Transmits force
across a broad
area, connects
muscles to
bones or other
muscles
Describe the function of the aponeurosis.
Thick, rope-
like, dense
regular
connective
tissue
Describe the appearance of a tendon.
Attaches
muscles to
bones,
transmits force
for movement
Describe the function of a tendon.
Point where a muscle attaches to a stationary
bone or structure.
What is the definition of the muscle origin?
Point where a muscle attaches to a movable
bone or structure.
What is the definition of the muscle insertion?
Typically proximal
What is the general location of a muscle origin?
Typically distal
What is the general location of a muscle insertion?
relatively stable
Describe the stability of the muscle origin during movement.
moves and is responsible for the
actual movement
Describe the stability of the muscle insertion during movement.
Supraglenoid tubercle of scapula
What is the origin of the long head of the Biceps brachii?
Coracoid process of scapula
What is the origin of the short head of the Biceps brachii?
Radial tuberosity of radius via bicipital tendon
What is the insertion of the Biceps brachii?
Flexes forearm at the elbow joint; supinates forearm
What is the action of the Biceps brachii?
Pubic symphysis and pubic crest
What is the point of origin of the Rectus abdominis?
Xiphoid process and costal cartilages of ribs 5-7
What is the insertion of the Rectus abdominis?
Flexes the vertebral column, compresses abdominal contents
What is the action of the Rectus abdominis?
Ilium, sacrum, and coccyx
What is the origin of the Gluteus maximus?
Gluteal tuberosity of femur, iliotibial tract
What is the insertion of the Gluteus maximus?
Extends and laterally rotates the thigh at the hip
What is the action of the Gluteus maximus?
Maximus/magnus
Code for largest muscle
Minimus
Code for smallest muscle
Medius
Code for the muscle that “medium” in size
Major
Code for the larger muscle
Minor
Code for the smaller muscle
Brevis
Code for the shorter muscle
Longus
Code for the longest muscle
Vastus
Code for muscles that are great or huge in surface area.
Trapezius
Code for muscles shaped like a trapezoid
Deltoid
Code for muscles shaped like a triangle. Commonly sits on top of the shoulder.
Serratus
Code for saw-shaped muscles.
Platysma
Code for flat-shaped muscles.
Rhomboid
Code for diamond-shaped muscles
Quadratus
Code for square/four-sded muscles.
Teres
Code for round or cylindrical-shaped muscles.
Rectus
Code for a straight/errect muscle that is parallel to the midline.
Transversus
Code for when the muscle is perpendicular to the midline.
Oblique
Code for when the muscle is slanted or diagonal to the midline
Orbicularis, sphincter
a name given to ringlike muscles that encircle or may form a constricting passage
Flexor
decrease the angle at a joint
Extensors
muscles that counter flexors and increase the angle at a joint
Pronator
turn limbs so that they face downwards or backward
Supinator
counters pronators turn limbs so they face upwards or forward
Levator
lifts a structure up
Depressor
lowers a structure
Adductor
moves towards the midline
Abductor
moves away from the midline
Rotator
rotates one structure relative to another
Pollicis
refers to thumb
Biceps
Code for muscles that have 2 points origin