HESI Fundamentals Practice Test, Fundamentals HESI Exam, Fundamentals/Foundations/H.A. HESI, Hesi Fundamentals Practice Test, Nursing Fundamentals HESI Prep
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
64.A low-sodium, low-protein diet is prescribed for a 45-year-old client with renal insufficiency and hypertension, who gained 3 pounds in the last month. The nurse determines that the client has been noncompliant with the diet, based on which report from the 24-hour dietary recall? (Select all that apply.)
A. Snack of potato chips, and diet soda.
B. Lunch of tuna fish sandwich, carrot sticks, fresh fruit, and coffee.
C. Breakfast of eggs, bacon, toast, and coffee.
D. Dinner of vegetable lasagna, tossed salad, sherbet, and iced tea.
E. Bedtime snack of crackers and milk.
Potato chips (A) are high in sodium. Tuna (B) is high in protein. Bacon (C) and crackers (E) are high in sodium. Only (D) is a meal that is in compliance with a low sodium, low protein diet.
Correct Answer: A, B, C, E
65.What intervention should the nurse include in the plan of care for a client who is being treated with an Unna's paste boot for leg ulcers due to chronic venous insufficiency?
A. Check capillary refill of toes on lower extremity with Unna's paste boot.
B. Apply dressing to wound area before applying the Unna's paste boot.
C. Wrap the leg from the knee down towards the foot.
D. Remove the Unna's paste boot q8h to assess wound healing.
The Unna's paste boot becomes rigid after it dries, so it is important to check distally for adequate circulation (A). Kerlix is often wrapped around the outside of the boot and an ace bandage may be used to cover both, but no bandage should be put under it (B). The Unna's paste boot should be applied from the foot and wrapped towards the knee (C). The Unna's paste boot acts as a sterile dressing, and should not be removed q8h. Weekly removal is reasonable (D).
Correct Answer: A
66.A 75-year-old client who has a history of end stage renal failure and advanced lung cancer, recently had a stroke. Two days ago the healthcare provider discontinued the client's dialysis treatments, stating that death is inevitable, but the client is disoriented and will not sign a DNR directive. What is the priority nursing intervention?
A. Review the client's most recent laboratory reports.
B. Refer the client and family members for hospice care.
C. Notify the hospital ethics committee of the client situation.
D. Determine who is legally empowered to make decisions.
When death is impending, it is essential for the nurse to determine who is legally empowered to make decisions regarding the use of life-saving measures for the client (D). (A) will be abnormal and will worsen without dialysis, so are not of immediate concern. (B) may help improve the client's quality of life prior to death, but is of less immediacy than determining whether actions should be taken to save a client's life. If the nurse remains unable to determine who is empowered to make decisions in this situation, the nurse may choose to contact the ethics committee (C) for a resolution.
Correct Answer: D
67.The charge nurse assigns a nursing procedure to a new staff nurse who has not previously performed the procedure. What action is most important for the new staff nurse to take?
A. Review the steps in the procedure manual.
B. Ask another nurse to assist while implementing the procedure.
C. Follow the agency's policy and procedure.
D. Refuse to perform the task that is beyond the nurse's experience.
According to states' nurse practice acts, it is the responsibility of the nurse to function within the scope of competency (D), and in this case safe nursing practice constitutes refusal to perform the procedure because of a lack of experience. Although state mandates, agency policies, and continued education and experience identify tasks that are within the scope of nursing practice, nurses should first refuse to perform tasks that are beyond their proficiency, and then pursue opportunities to enhance their competency (A, B, and C).
Correct Answer: D
68.Before administering a client's medication, the nurse assesses a change in the client's condition and decides to withhold the medication until consulting with the healthcare provider. After consultation with the healthcare provider, the dose of the medication is changed and the nurse administers the newly prescribed dose an hour later than the originally scheduled time. What action should the nurse implement in response to this situation?
A. Notify the charge nurse that a medication error occurred.
B. Submit a medication variance report to the supervisor.
C. Document the events that occurred in the nurses' notes.
D. Discard the original medication administration record.
The nurse took the correct action and should document the events that occurred in the nurses' notes (C). (A) did not occur and (B) is not indicated. The medication administration record is part of the client's medical record and should be placed in the chart, (D) when no longer current.
Correct Answer: C
69.On the third postoperative day following thoracic surgery, a client reports feeling constipated. Which intervention should the nurse implement to promote bowel elimination?
A. Remind the client to turn every two hours while lying in bed.
B. Provide warm prune juice before the client goes to bed at night.
C. Teach the client to splint the incision while walking to the bathroom.
D. Administer an analgesic before the client attempts to defecate.
Prune juice is a natural laxative that stimulates peristalsis, and warming the prune juice (B) facilitates peristalsis. (A) is also helpful in promoting peristalsis but is less likely to relieve the client's constipation. (C) reduces discomfort during ambulation, but will not help relieve the client's constipation. Defecation is not painful following most surgeries, and many analgesics used postoperatively cause constipation, so (D) is contraindicated.
Correct Answer: B
70.The home health nurse visits an elderly client who lives at home with her husband. The client is experiencing frequent episodes of diarrhea and bowel incontinence. Which problem, for which the client is at risk, has the greatest priority when planning the client's care?
A. Disturbed sleep pattern.
B. Caregiver role strain.
C. Impaired skin integrity.
D. Fluid volume imbalance.
Diarrhea can lead to fluid volume loss, which is potentially life-threatening, so the highest priority is to prevent a fluid volume imbalance (D). Diarrhea and bowel incontinence can also lead to (A, B, and C), but these are of less potential harm than a fluid volume deficit.
Correct Answer: D
71.After a client has been premedicated for surgery with an opioid analgesic, the nurse discovers that the operative permit has not been signed. What action should the nurse implement?
A. Notify the surgeon that the consent form has not been signed.
B. Read the consent form to the client before witnessing the client's signature.
C. Determine if the client's spouse is willing to sign the consent form.
D. Administer an opioid antagonist prior to obtaining the client's signature.
Once a client has been premedicated for surgery with any type of sedative, legal informed consent is not possible, so the nurse must notify the surgeon (A). (B, C, and D) are not legally viable options for ensuring informed consent.
Correct Answer: A
72.A client who has been on bedrest for several days now has a prescription to progress activity as tolerated. When the nurse assists the client out of bed for the first time, the client becomes dizzy. What action should the nurse implement?
A. Encourage the client to take several slow, deep breaths while ambulating.
B. Help the client to remain standing by the bedside until the dizziness is relieved.
C. Instruct the client to remain on bedrest until the healthcare provider is contacted.
D. Advise the client to sit on the side of the bed for a few minutes before standing again.
The nurse should implement (D), because orthostatic hypotension is a common result of immobilization, causing the client to feel dizzy when first getting out of bed following a period of bedrest. To prevent this problem, it is helpful to have the body acclimate to a standing position by sitting upright for a short period (D) before rising to a standing position. (A) is unlikely to alleviate the dizziness. (B) may result in a loss of consciousness. (C) is not indicated and will increase the potential for complications associated with prolonged immobility.
Correct Answer: D
74.A client is admitted to the hospital with intractable pain. What instruction should the nurse provide the unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) who is preparing to assist this client with a bed bath?
A. Take measures to promote as much comfort as possible.
B. Report any signs of drug addiction to the nurse immediately.
C. Wait until the client's pain is gone before assisting with personal care.
D. This client's pain will be difficult to manage, since the cause is unknown.
Intractable pain is highly resistant to pain relief measures, so it is important to promote comfort (A) during all activities. A client with intractable pain may develop drug tolerance and dependence, but (B) is inappropriate for a UAP. Since intractable pain is resistant to relief measures, (C) may not be possible. Psychogenic pain (D) is a painful sensation that is perceived but has no known cause.
Correct Answer: A
75.A male client arrives at the outpatient surgery center for a scheduled needle aspiration of the knee. He tells the nurse that he has already given verbal consent for the procedure to the healthcare provider. What action should the nurse implement?
A. Witness the client's signature on the consent form.
B. Verify the client's consent with the healthcare provider.
C. Notify the healthcare provider that the client is ready for the procedure.
D. Document that the client has given consent for the needle aspiration.
Written informed consent is required prior to any invasive procedure. The healthcare provider must explain the procedure to the client, but the nurse can witness the client's signature on a consent form (A). (B) is not necessary since written consent must be obtained. (C) is not correct because written consent has not been obtained. (D) must occur after written consent is obtained.
Correct Answer: A
76.In assessing a client's femoral pulse, the nurse must use deep palpation to feel the pulsation while the client is in a supine position. What action should the nurse implement?
A. Elevate the head of the bed and attempt to palpate the site again.
B. Document the presence and volume of the pulse palpated.
C. Use a thigh cuff to measure the blood pressure in the leg.
D. Record the presence of pitting edema in the inguinal area.
Deep palpation may be required to palpate the femoral pulse; and, when palpated, the nurse should document the presence and volume of the pulse (B). The site is best palpated with the client supine; elevation of the head of the bed requires even deeper palpation (A). The use of deep palpation to feel the femoral pulse does not indicate a problem requiring further assessment, such as (C), and does not reflect the presence of edema (D).
Correct Answer: B
77.A nurse is preparing to insert a rectal suppository and observes a small amount of rectal bleeding. What action should the nurse implement?
A. Administer the medication as scheduled after assessing the client's vital signs.
B. Ask the pharmacist to send an alternate form of the prescribed medication to the unit.
C. Withhold the administration of the suppository until contacting the healthcare provider.
D. Insert the suppository very gently being careful not to further injure the rectal mucosa.
The presence of rectal bleeding is generally a contraindication for the insertion of a rectal suppository, so the nurse should withhold the medication and notify the healthcare provider (C). (A and D) may cause increased rectal bleeding. Prior to asking the pharmacist for another form of the medication, the nurse must have a new prescription from the healthcare provider (B).
Correct Answer: C
78.The nurse is preparing to irrigate a client's indwelling urinary catheter using an open technique. What action should the nurse take after applying gloves?
A. Empty the client's urinary drainage bag.
B. Draw up the irrigating solution into the syringe.
C. Secure the client's catheter to the drainage tubing.
D. Use aseptic technique to instill the irrigating solution.
To irrigate an indwelling urinary catheter, the nurse should first apply gloves, then draw up the irrigating solution into the syringe (B). The syringe is then attached to the catheter and the fluid instilled, using aseptic technique (D). Once the irrigating solution is instilled, the client's catheter should be secured to the drainage tubing (C). The urinary drainage bag can be emptied (A) whenever intake and output measurement is indicated, and the instilled irrigating fluid can be subtracted from the output at that time.
Correct Answer: B
79.When assessing a client with an indwelling urinary catheter, which observation requires the most immediate intervention by the nurse?
A. The drainage tubing is secured over the siderail.
B. The clamp on the urinary drainage bag is open.
C. There are no dependent loops in the drainage tubing.
D. The urinary drainage bag is attached to the bed frame.
Maintaining a closed urinary drainage system is important to prevent infection, so the most immediate priority is to close the clamp (B) to reduce the risk for ascending microorganisms. If the drainage tubing is secured over the siderail (A), urine will not be able to flow out of the bladder, so the nurse should next reposition the tubing. (C and D) indicate correct care of the urinary drainage system, so documentation of an intact system is the last intervention needed.
Correct Answer: B
80.While preparing to insert a rectal suppository in a male adult client, the nurse observes that the client is holding his breath while bearing down. What action should the nurse implement?
A. Advise the client to continue to bear down without holding his breath.
B. Gently insert the lubricated suppository four inches into the rectum.
C. Perform a digital exam to determine if a fecal impaction is present.
D. Instruct the client to take slow deep breaths and stop bearing down.
During administration of a rectal suppository, the client is asked to take slow deep breaths through the mouth to relax the anal sphincter (D). Bearing down (A) will push the suppository out of the rectum, so the suppository should not be inserted while the client is bearing down (B). Further data is needed before performing an invasive digital exam to check for fecal impaction (C).
Correct Answer: D
82.While the nurse is administering a bolus feeding to a client via nasogastric tube, the client begins to vomit. What action should the nurse implement first?
A. Discontinue the administration of the bolus feeding.
B. Auscultate the client's breath sounds bilaterally.
C. Elevate the head of the bed to a high Fowler's position.
D. Administer a PRN dose of a prescribed antiemetic.
When a client receiving a tube feeding begins to vomit, the nurse should first stop the feeding (A) to prevent further vomiting. (C) should then be implemented to reduce the risk of aspiration. After that, (B and D) can be implemented as indicated.
Correct Answer: A
84.Which client care requires the nurse to wear barrier gloves as required by the protocol for Standard Precautions?
A. Removing the empty food tray from a client with a urinary catheter.
B. Washing and combing the hair of a client with a fractured leg in traction.
C. Administering oral medications to a cooperative client with a wound infection.
D. Emptying the urinary catheter drainage bag for a client with Alzheimer's disease.
Possible contact with body secretions, excretions, or broken skin is an indication for wearing barrier (nonsterile) gloves. Emptying a urine drainage bag requires the use of gloves (D). (A, B, and C) do not require gloves.
Correct Answer: D
85.What action should the nurse implement when adding sterile liquids to a sterile field?
A. Use an outdated sterile liquid if the bottle is sealed and has not been opened.
B. Consider the sterile field contaminated if it becomes wet during the procedure.
C. Remove the container cap and lay it with the inside facing down on the sterile field.
D. Hold the container high and pour the solution into a receptacle at the back of the sterile field.
Wet or damp areas on a sterile field allow organisms to wick from the table surface and permeate into the sterile area, so the field is considered contaminated if it becomes wet (B). Outdated liquids may be contaminated and should be discarded, not used (A). The container's cap should be removed, placed facing up, and off the sterile field, not (C). To prevent contamination of the sterile field, liquids should be held close (6 inches) to the receptacle when pouring to prevent splashing, and the receptacle should be placed near the front edge to avoid reaching over or across the sterile field (D).
Correct Answer: B
86.A healthcare provider is performing a sterile procedure at a client's bedside. Near the end of the procedure, the nurse observes the healthcare provider contaminate a sterile glove and the sterile field. What is the best action for the nurse to implement?
A. Report the healthcare provider for the violation in aseptic technique.
B. Allow the completion of the procedure.
C. Ask if the glove and sterile field are contaminated.
D. Identify the break in surgical asepsis and provide another set of sterile supplies.
Any possible break in surgical asepsis that is identified when others are unaware should be considered contaminated and new sterile supplies added to maintain the sterile field (D). Reporting the healthcare provider is not indicated (A). When sterility is suspect during aseptic technique, it should not be questioned (C) but all members of the team should move forward with reestablishing a sterile field. Allowing the procedure to progress under unsterile conditions (B) places the client at risk for infection and is an act of omission (negligence) by the nurse and other healthcare team members.
Correct Answer: D
87.An older client who is able to stand but not to ambulate receives a prescription to be mobilized into a chair as tolerated during each day. What is the best action for the nurse to implement when assisting the client from the bed to the chair?
A. Use a mechanical lift to transfer from the bed to a chair.
B. Place a roller board under the client who is sitting on the side of the bed and slide the client to the chair.
C. Lift the client out of bed to the chair with another staff member using a coordinated effort on the count of three.
D. Place a transfer belt around the client, assist to stand, and pivot to a chair that is placed at a right angle to the bed.
A client who can stand can safely be assisted to pivot and transfer with the use of a transfer belt (D). A mechanical lift (A) is usually used for a client who is obese, unable to be weight-bearing, and who is unable to assist. Roller boards (B) placed under a sheet are used to facilitate the transfer of a recumbent client who is being transferred to and from a stretcher. Lifting a client (C) out of bed places the client and nurses at risk for injury and should only be implemented by skilled lift teams.
Correct Answer: D
88.What action should the nurse implement to prevent the formation of a sacral ulcer for a client who is immobile?
A. Maintain in a lateral position using protective wrist and vest devices.
B. Position prone with a small pillow below the diaphragm.
C. Raise the head and knee gatch when lying in a supine position.
D. Transfer into a wheelchair close to the nurse's station for observation.
The prone position (B) using a small pillow below the diaphragm maintains alignment and provides the best pressure relief over the sacral bony prominence. Using protective (restraining) devices (A) is not indicated. Raising the head and bed gatch (C) may reduce shearing forces due to sliding down in bed, but it interferes with venous return from the legs and places pressure on the sacrum, predisposing to ulcer formation. Sitting in a wheelchair (D) places the body weight over the ischial tuberosities and predisposes to a potential pressure point.
Correct Answer: B
89.What action is most important for the nurse to implement when placing a client in the Sim's position?
A. Raise the bed to a waist-high working level.
B. Elevate the head of the bed 45 degrees.
C. Place a pillow behind the client's back.
D. Bring the client to one edge of the bed.
A waist-high bed height (A) is a comfortable and safe working height to maintain the nurse's proper body mechanics and prevent back injury. The head should be flat for a Sim's side-lying position, not raised (B). (C) is implemented after the client is positioned laterally. (D) brings the client closer to the nurse when being turned.
Correct Answer: A
90.The nurse is providing passive range of motion (ROM) exercises to the hip and knee for a client who is unconscious. After supporting the client's knee with one hand, what action should the nurse take next?
A. Raise the bed to a comfortable working level.
B. Bend the client's knee.
C. Move the knee toward the chest as far as it will go.
D. Cradle the client's heel.
Passive ROM exercise for the hip and knee is provided by supporting the joints of the knee and ankle (D) and gently moving the limb in a slow, smooth, firm but gentle manner. (A) should be done before the exercises are begun to prevent injury to the nurse and client. (B) is carried out after both joints are supported. After the knee is bent, then the knee is moved toward the chest to the point of resistance (C) two or three times.
Correct Answer: D
91.The nurse is caring for a client who is weak from inactivity because of a 2-week hospitalization. In planning care for the client, the nurse should include which range of motion (ROM) exercises?
A. Passive ROM exercises to all joints on all extremities four times a day.
B. Active ROM exercises to both arms and legs two or three times a day.
C. Active ROM exercises with weights twice a day with 20 repetitions each.
D. Passive ROM exercises to the point of resistance and slightly beyond.
Active, rather than passive, ROM is best to restore strength and (B) is an effective schedule. Passive ROM 4 times a day (A) is not as beneficial for the client as (B). With weights (C), the client may fatigue quickly and develop muscle soreness. ROM is not performed beyond the point of resistance or pain (D) because of the risk of damage to underlying structures.
Correct Answer: B
What does PASS stand for?
Pull the pin
Aim for the base of the flames
Squeeze handle
Sweep
What does RACE stand for?
Rescue the patient
Activate alarm
Confine or contain
Extinguish
Why should you think carefully before giving an antipyretic?
Because fever up to a certain point is beneficial
Dorsal recumbent position
Supine with knees flexed; used to promote relaxation of abdominal muscles
Lithotomy position
Dorsal recumbent position with feet in stirrups
Sims' position
Flexion of the hip and knees in a side-lying position; used to examine the rectal area and if a female is unable to assume the lithotomy position
Prone position
Lying on stomach
Fowler's and semi-Fowler's position
Laying on back with head of bed elevated 60 degrees for Fowler's and 30-45 degrees for semi-Fowler's
Chain of infection (6 links)
1) Infectious agent
2) Reservoir
3) Portal of exit
4) Mode of transmission
5) Portal of entry
6) Susceptible host
5 stages of infection
Incubation, prodromal, illness, decline, convalescence
Asepsis
Absence of contamination (clean)
Contact precautions
-Most common form of transmission
-Use gown and gloves
-Remove PPE and wash hands BEFORE leaving room
Droplet precautions
-Wear gown, mask, gloves
-Remove gloves first, then gown and mask
Airborne precautions
-Includes TB, varicella (chickenpox), SARS (pneumonia), and rubeola (measles)
-Wear gown, N-95 mask, gloves
-Remove mask OUTSIDE the room after closing the door
Protective, or reverse isolation
-Immunosuppressed patients (low WBC counts, chemotherapy, large open wounds)
-Make sure equipment is disinfected BEFORE it is taken into the room
What is the most common incident reported in hospitals?
Falls
Release restraints at least every ____ hours.
2
When giving a bed bath, wash from _____ to _____.
Distal to proximal (upward motion to increase circulation)
What do you do first if you commit a medication error?
Check the patient (take VS)
3 checks of safe medication administration
1) Before you pour, mix, or draw up a medication
2) After you prepare the medication
3) At the bedside
Rights of medication
1) Right drug
2) Right patient
3) Right dose
4) Right route
5) Right time
6) Right documentation
Others:
7) Right reason
8) Right to know
9) Right to refuse
What is the preferred IM site for infants?
Vastus lateralis muscle
What is the site of choice for IM injections?
-Ventrogluteal muscle
-Landmarks are the greater trochanter, anterior superior iliac spine, and iliac crest
What supplements do pregnant women need to take?
Folic acid, iron, calcium (vitamin D)
Normal creatinine levels
0.5-1.2 mg/dL
Low levels of _____ are associated with malnutrition.
Albumin
Paralytic ileus
Cessation of bowel peristalsis
Digital removal can stimulate the _____ nerve, so stop the procedure if the patient accumulates bradycardia.
Vagus
Normal urine output
50-60 mL/hr or 1500 mL/day
Urine output indicating renal failure
<30 mL/hr
Specific gravity
Measure of dissolved solutes in a solution; an increase in fluid intake dilutes and makes urine lighter as it approaches 1.000; low fluid intake or fluid loss (diarrhea or vomiting) darkens urine and makes the specific gravity rise
Normal specific gravity range
1.002 to 1.028
For men, if the catheter will remain in place long-term, secure tubing to the ______ to prevent damage to penile-scrotal juncture.
Abdomen
What happens when someone has pain?
1) Transduction
2) Transmission
3) Perception
4) Modulation
NSAIDS decrease _______ response.
Prostaglandin (activate nociceptors so trigger pain)
What do you perceive pain?
Frontal cortex
Sedation rating scale
1=awake and alert
2=slightly drowsy, easily aroused
3=frequently drowsy, arousable by voice
4=arousable by shaking*
5=somnolent, not arousable*
*Stimulate patient and notify physician
Orthopneic position
For shortness of breath; leaning forward over a table with a pillow
What orders would you expect if a patient had low H&H?
Oxygen and PRBCs (packed red blood cells)
What breathing is noted with diabetic ketoacidosis?
Kussmaul's (trying to get rid of CO2)
Which mask can deliver 100% oxygen?
Non-rebreather
In emergencies, turn oxygen all the way up to ______ liters.
15
Early Signs of Hypoxia
-anxiety,
-restlessness
-inability to concentrate
-increases in heart rate
-increased respiratory rate and blood pressure
-cardiac dysrhythmias
Signs of Hypocalcemia
-paresthesias followed by numbness
-hyperactive deep tendon reflexes
-a positive Trousseau's or Chvostek's sign
-neuromuscular excitability
-muscle cramps
-twitching
-tetany
-seizures, irritability, and anxiety
-increased gastric motility, hyperactive bowel sounds, abdominal cramping, and diarrhea.

Trousseau Sign
Trousseau sign of latent tetany is a medical sign observed in patients with low calcium.
To elicit the sign, a blood pressure cuff is placed around the arm and inflated to a pressure greater than the systolic blood pressure and held in place for 3 minutes. This will occlude the brachial artery. In the absence of blood flow, the patient's hypocalcemia and subsequent neuromuscular irritability will induce spasm of the muscles of the hand and forearm.
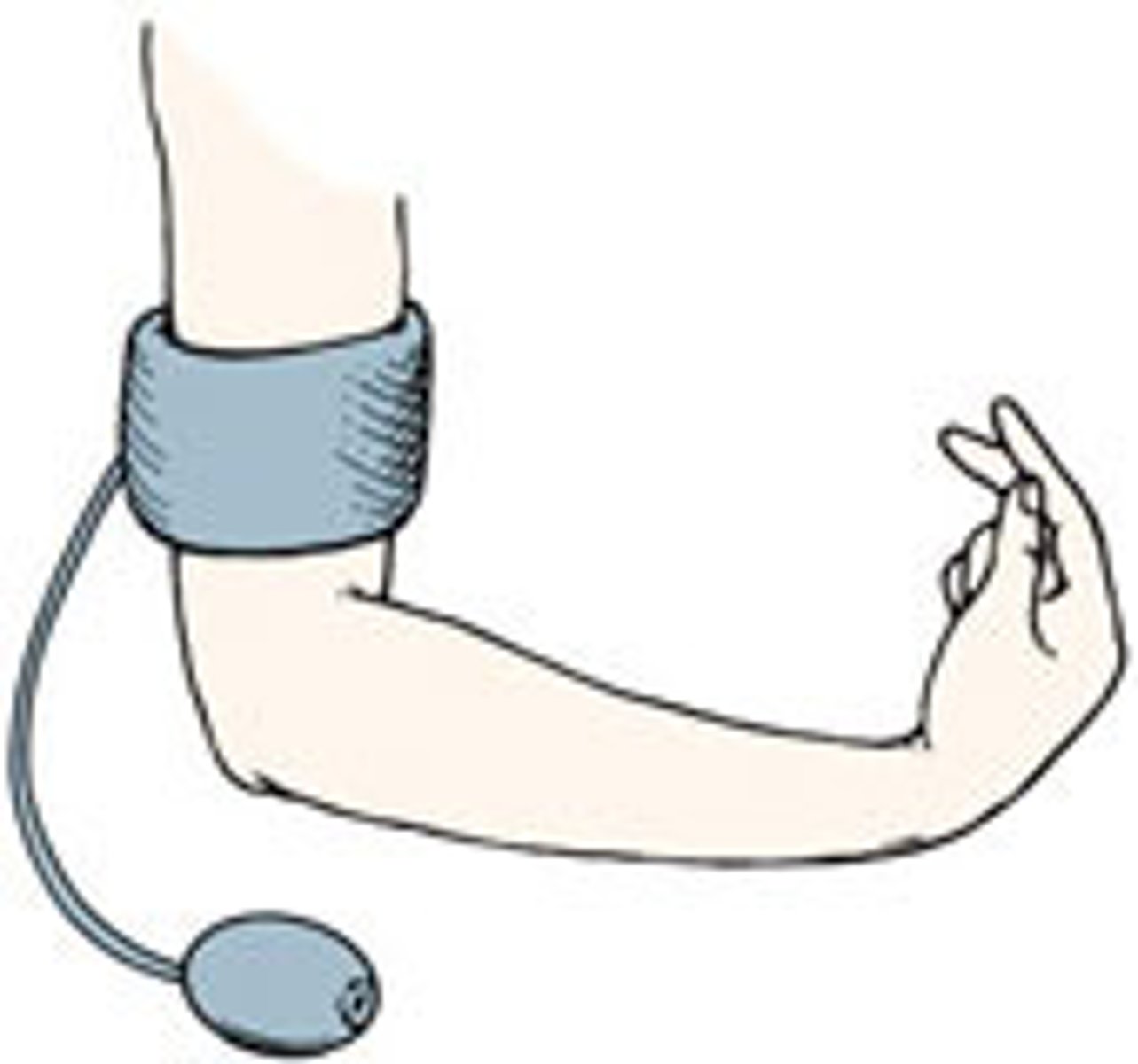
Hyponatremia Signs
-Hyperactive Bowels Sounds
-Muscle Weakness
-Increased Urine Output
-Decreased specific gravity of urine would be noted
Normal Phosphorus Level
2.7-4.5 mg/dL
Prothrombin time greater than 30 seconds places the client at risk for what?
bleeding
PT Male
9.6-11.8 seconds
PT Female
9.5-11.3 seconds
Warfarin Therapeutic PT
1.5 - 2 times higher than the normal level.
Approx. 18-23 seconds
Troponin
-a regulatory protein found in striated muscle. The troponins function together in the contractile apparatus for striated muscle in skeletal muscle and in the myocardium.
-Increased amounts of troponins are released into the bloodstream when an infarction causes damage to the myocardium.
- A troponin T value that is higher than 0.1 to 0.2 ng/mL is consistent with a myocardial infarction.
-A normal troponin I level is lower than 0.6 ng/mL.
Activated Partial Thromboplastin
-The normal aPTT varies between 20 and 36 seconds, depending on the type of activator used in testing.
-The therapeutic dose of heparin for treatment of deep vein thrombosis is to keep the aPTT between 1.5 and 2.5 times normal.
-This means that the client's value should not be less than 30 seconds or greater than 90 seconds.
RACE
-Rescue Patients
-Alarm
-Confine
-Extinguish
Excess Fluid Volume
use 5% sucrose in 0.9% normal saline
Cerebral Edema/Cerebral Swelling
use 0.45% normal saline
Isotonic IV Solutions
0.9% Normal Saline
5% dextrose in water (D5W)
5% Dextrose in 0.225% Saline
Lactated Ringers
-Causes an increase in Extracellular fluid volume
-Dehyrdration
Hypotonic IV Solutions
0.45% Saline
0.22% Saline
0.33% Saline
-Cause cell lyses
-Deplete circulatory systems fluids
-These solutions hydrate the cell
-Don't use in patients with an increase in intracranial pressure, burns, trauma its w/ hypovolemia
Hypertonic IV Solutions
-3% saline
-5% Saline
-10% Dextrose in Water
-5% Dextrose in 0.9% Saline
-5% Dextrose in 0.45% Saline
-5% Dextrose in LR
-Causes the cell to shrink, fluid overload w/pulmonary edema
-Give to patients with cerebral edema (reduces pressure), hyponatremia (pulls sodium back into the intravascular system)
Which assessment data would provide the most accurate determination of proper placement of a nasogastric tube?
A) Aspirating gastric contents to assure a pH value of 4 or less.
B) Hearing air pass in the stomach after injecting air into the tubing.
C) Examining a chest x-ray obtained after the tubing was inserted.
D) Checking the remaining length of tubing to ensure that the correct length was inserted.
C) Examining a chest x-ray obtained after the tubing was inserted
Both (A and B) are methods used to determine proper placement of the NG tubing. However, the best indicator that the tubing is properly placed is (C). (D) is not an indicator of proper placement
The nurse is instructing a client with high cholesterol about diet and life style modification. What comment from the client indicates that the teaching has been effective?
A) If I exercise at least two times weekly for one hour, I will lower my cholesterol.
B) I need to avoid eating proteins, including red meat.
C) I will limit my intake of beef to 4 ounces per week.
D) My blood level of low density lipoproteins needs to increase.
C) I will limit my intake of beef to 4 ounces per week
Limiting saturated fat from animal food sources to no more than 4 ounces per week (C) is an important diet modification for lowering cholesterol. To be effective in reducing cholesterol, the client should exercise 30 minutes per day, or at least 4 to 6 times per week (A). Red meat and all proteins do not need to be eliminated (B) to lower cholesterol, but should be restricted to lean cuts of red meat and smaller portions (2-ounce servings). The low density lipoproteins (D) need to decrease rather than increase
A resident in a skilled nursing facility for short-term rehabilitation after a hip replacement tells the nurse, "I don't want any more blood taken for those useless tests." Which narrative documentation should the nurse enter in the client's medical record?
A) Healthcare provider notified of failure to collect specimens for prescribed blood studies.
B) Blood specimens not collected because client no longer wants blood tests performed.
C) Healthcare provider notified of client's refusal to have blood specimens collected for testing.
D) Client irritable, uncooperative, and refuses to have blood collected. Healthcare provider notified
C) Healthcare provider notified of client's refusal to have blood specimens collected for testing
When a client refuses a treatment, the exact words of the client regarding the client's refusal of care should be documented in a narrative format (C). (A, B, and D) do not address the concepts of informatics and legal issues
While instructing a male client's wife in the performance of passive range-of-motion exercises to his contracted shoulder, the nurse observes that she is holding his arm above and below the elbow. What nursing action should the nurse implement?
A) Acknowledge that she is supporting the arm correctly.
B) Encourage her to keep the joint covered to maintain warmth.
C) Reinforce the need to grip directly under the joint for better support.
D) Instruct her to grip directly over the joint for better motion.
A) Acknowledge that she is supporting the arm correctly
The wife is performing the passive ROM correctly, therefore the nurse should acknowledge this fact (A). The joint that is being exercised should be uncovered (B) while the rest of the body should remain covered for warmth and privacy. (C and D) do not provide adequate support to the joint while still allowing for joint movement
The nurse is caring for a client who is receiving 24-hour total parenteral nutrition (TPN) via a central line at 54 ml/hr. When initially assessing the client, the nurse notes that the TPN solution has run out and the next TPN solution is not available. What immediate action should the nurse take?
A) Infuse normal saline at a keep vein open rate.
B) Discontinue the IV and flush the port with heparin.
C) Infuse 10 percent dextrose and water at 54 ml/hr
D) Obtain a stat blood glucose level and notify the healthcare provider.
C) Infuse 10 percent dextrose and water at 54 ml/hr
TPN is discontinued gradually to allow the client to adjust to decreased levels of glucose. Administering 10% dextrose in water at the prescribed rate (C) will keep the client from experiencing hypoglycemia until the next TPN solution is available. The client could experience a hypoglycemic reaction if the current level of glucose (A) is not maintained or if the TPN is discontinued abruptly (B). There is no reason to obtain a stat blood glucose level (D) and the healthcare provider cannot do anything about this situation
At the beginning of the shift, the nurse assesses a client who is admitted from the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU). When should the nurse document the client's findings?
A) At the beginning, middle, and end of the shift.
B) After client priorities are identified for the development of the nursing care plan.
C) At the end of the shift so full attention can be given to the client's needs.
D) Immediately after the assessments are completed
D) Immediately after the assessments are completed
Documentation should occur immediately after any component of the nursing process, so assessments should be entered in the client's medical record as readily as findings are obtained (D). (A, B, and C) do not address the concepts of legal recommendations for information management and informatics.
The healthcare provider prescribes furosemide (Lasix) 15 mg IV stat. On hand is Lasix 20 mg/2 ml. How many milliliters should the nurse administer?
A) 1 ml.
B) 1.5 ml.
C) 1.75 ml.
D) 2 ml.
B) 1.5 ml
An elderly resident of a long-term care facility is no longer able to perform self-care and is becoming progressively weaker. The resident previously requested that no resuscitative efforts be performed, and the family requests hospice care. What action should the nurse implement first?
A) Reaffirm the client's desire for no resuscitative efforts.
B) Transfer the client to a hospice inpatient facility.
C) Prepare the family for the client's impending death.
D) Notify the healthcare provider of the family's request.
D) Notify the healthcare provider of the family's request
The nurse should first communicate with the healthcare provider (D). Hospice care is provided for clients with a limited life expectancy, which must be identified by the healthcare provider. (A) is not necessary at this time. Once the healthcare provider supports the transfer to hospice care, the nurse can collaborate with the hospice staff and healthcare provider to determine when (B and C) should be implemented
A client who has been NPO for 3 days is receiving an infusion of D5W 0.45 normal saline (NS) with potassium chloride (KCl) 20 mEq at 83 ml/hour. The client's eight-hour urine output is 400 ml, blood urea nitrogen (BUN) is 15 mg/dl, lungs are clear bilaterally, serum glucose is 120 mg/dl, and the serum potassium is 3.7 mEq/L. Which action is most important for the nurse to implement?
A) Notify healthcare provider and request to change the IV infusion to hypertonic D10W.
B) Decrease in the infusion rate of the current IV and report to the healthcare provider.
C) Document in the medical record that these normal findings are expected outcomes.
D) Obtain potassium chloride 20 mEq in anticipation of a prescription to add to present IV.
C) Document in the medical record that these normal findings are expected outcomes
The results are all within normal range.(C) No changes are needed. (A,B, and D)
The nurse is teaching a client proper use of an inhaler. When should the client administer the inhaler-delivered medication to demonstrate correct use of the inhaler?
A) Immediately after exhalation.
B) During the inhalation.
C) At the end of three inhalations.
D) Immediately after inhalation
B) During the inhalation
The client should be instructed to deliver the medication during the last part of inhalation (B). After the medication is delivered, the client should remove the mouthpiece, keeping his/her lips closed and breath held for several seconds to allow for distribution of the medication. The client should not deliver the dose as stated in (A or D), and should deliver no more than two inhalations at a time (C).
A client with acute hemorrhagic anemia is to receive four units of packed RBCs (red blood cells) as rapidly as possible. Which intervention is most important for the nurse to implement?
A) Obtain the pre-transfusion hemoglobin level.
B) Prime the tubing and prepare a blood pump set-up.
C) Monitor vital signs q15 minutes for the first hour.
D) Ensure the accuracy of the blood type match.
D) Ensure the accuracy of the blood type match
All interventions should be implemented prior to administering blood, but (D) has the highest priority. Any time blood is administered, the nurse should ensure the accuracy of the blood type match in order to prevent a possible hemolytic reaction
On admission, a client presents a signed living will that includes a Do Not Resuscitate (DNR) prescription. When the client stops breathing, the nurse performs cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and successfully revives the client. What legal issues could be brought against the nurse?
A) Assault.
B) Battery.
C) Malpractice.
D) False imprisonment.
B) Battery
Civil laws protect individual rights and include intentional torts, such as assault (an intentional threat to engage in harmful contact with another) or battery (unwanted touching). Performing any procedure against the client's wishes can potentially poise a legal issue, such as battery (B), even if the procedure is of questionable benefit to the client. (A, C, and D) are not examples against the client's request
An elderly male client who is unresponsive following a cerebral vascular accident (CVA) is receiving bolus enteral feedings though a gastrostomy tube. What is the best client position for administration of the bolus tube feedings?
A) Prone.
B) Fowler's.
C) Sims'.
D) Supine.
B) Fowler's
The client should be positioned in a semi-sitting (Fowler's) (B) position during feeding to decrease the occurrence of aspiration. A gastrostomy tube, known as a PEG tube, due to placement by a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy procedure, is inserted directly into the stomach through an incision in the abdomen for long-term administration of nutrition and hydration in the debilitated client. In (A and/or C), the client is placed on the abdomen, an unsafe position for feeding. Placing the client in (D) increases the risk of aspiration
An older client who is a resident in a long term care facility has been bedridden for a week. Which finding should the nurse identify as a client risk factor for pressure ulcers?
A) Generalized dry skin.
B) Localized dry skin on lower extremities.
C) Red flush over entire skin surface.
D) Rashes in the axillary, groin, and skin fold regions
D) Rashes in the axillary, groin, and skin fold regions
Immobility, constant contact with bed clothing, and excessive heat and moisture in areas where air flow is limited contributes to bacterial and fungal growth, which increases the risk for rashes (D), skin breakdown, and the development of pressure ulcers. (A, B, and C) do not address the concepts of inflammation and tissue integrity
An Arab-American woman, who is a devout traditional Muslim, lives with her married son's family, which includes several adult children and their children. What is the best plan to obtain consent for surgery for this client?
A) Obtain an interpreter to explain the procedure to the client.
B) Encourage the client to make her own decision regarding surgery.
C) Ask the family members to provide an interpretation of the surgeon's explanation to the client.
D) Tell the surgeon that the son will decide after explanation of the proposed surgery is provided.
D) Tell the surgeon that the son will decide after explanation of the proposed surgery is provided
Traditional Muslim women live in a patriarchal family where decisions are made by men. Most likely, the son will make the decision for his mother, so (D) provides the surgeon with culturally sensitive information. (A) may be necessary if a language barrier exists, but the son is the patriarch in the client's family at this time. It is culturally insensitive to encourage the woman to go against her religious and cultural worldview, as in (B). Family members are more likely to misinterpret medical information, but the son should be the primary decision-maker for his mother (C).
Which response by a client with a nursing diagnosis of Spiritual distress, indicates to the nurse that a desired outcome measure has been met?
A) Expresses concern about the meaning and importance of life
B) Remains angry at God for the continuation of the illness.
C) Accepts that punishment from God is not related to illness.
D) Refuses to participate in religious rituals that have no meaning.
C) Accepts that punishment from God is not related to illness
Acceptance that she is not being punished by God indicates a desired outcome (C) for some degree of resolution of spiritual distress. (A, B, and D) do not support the concept of grief, loss, and cultural/spiritual acceptance.