L7 Artificial selection
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is the first piece of evidence for natural selection?
On the origin of species, Chapter 1 = "Variation under domestication"
• "Any variation which is not inherited is unimportant to us...like produces like"
• "a statement often made by naturalists - namely, that our domestic varieties when run wild, gradually but certainly revert in character to their aboriginal stock
If it could be shown
I grant that we could deduce nothing from domestic varieties in regard to species. But there is not a shadow of evidence in favour of this view."
What is a second piece of evidence Darwin stated for natural selection?
• "When we look to the hereditary varieties or races of our domestic animals and plants, and compare them with species closely allied together, we generally perceive in each domestic race..
less uniformity of character than in true species."
• "It has often been assumed that man has chosen for domestication animals and plants having an extraordinary inherent tendency to vary...
but how could a savage possibly know, when he first tamed an animal, whether it would vary in succeeding generations, and whether it would endure other climates?"
What animals did darwin use to produce evidence for natural selection?
Pigeons
What is the definition for artificial selection?
The selection of particular forms as a result of environmental pressures deliberately imposed, with in plant or animal breeding or in in vitro cell cultures.
What is the definition of domestication?
a genetic selection process exerted -consciously or unconsciously - by humans to adapt wild plants and animals to cultivation and herding, respectively
What does artificial selection result in?
Artificial selection therefore results in the evolution of domesticated species
What are the effects of domestication on behaviour?
• Selection for one trait → positive or negative effects on other traits
• E.g. Increased egg production of layer chickens → decrease in behavioural repertoire
What is the effects of domestication on morphology and physiology?
• Behavioural traits correlated with morphological traits e.g. pelage in silver foxes
• Selection for small body size
• In horses, selection for large body size (mainly)
What are the global centres of crop domestication?
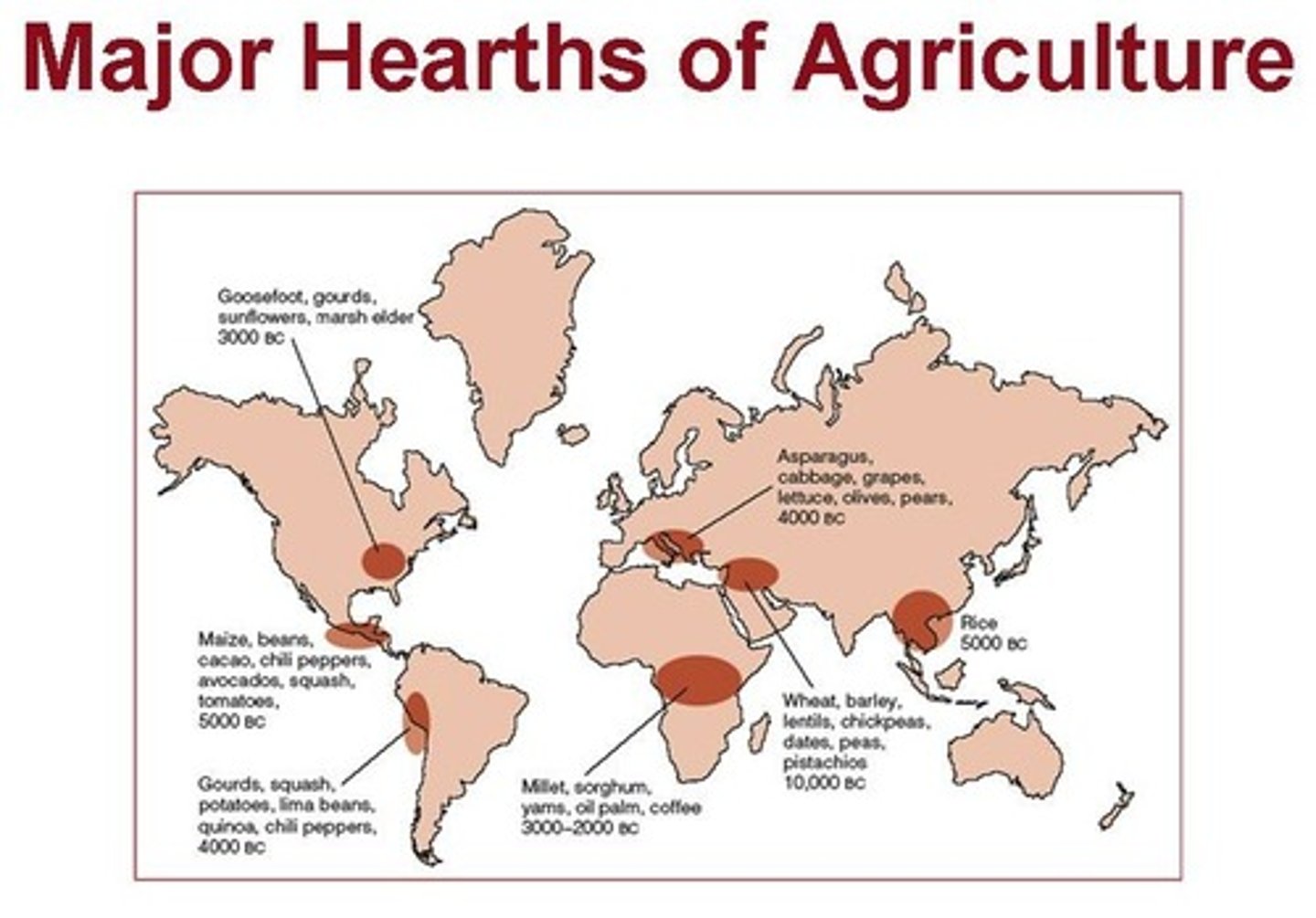
What is crop domestication?
- Loss of genetic diversity → disease susceptibility
- E.g. Potato famine: potato late blight (fungal disease)
• Also see for herbaceous species
- E.g. Dutch elm disease
- seed bank
What is a syndrome?
characteristics of a particular condition →controlled by a small number of genes
What is domestication syndrome?
- Common morphological changes that accompany the evolution of wild plants into domesticated crops
- E.g. Poaceae (corn, tice, wheat, barley, rye):
• Evolution of non-shattering (retaining seeds)
• Determinant growth (fewer and larger flowers/fruits at node)
• Increase in inflorescence size and number
• Greater seed size
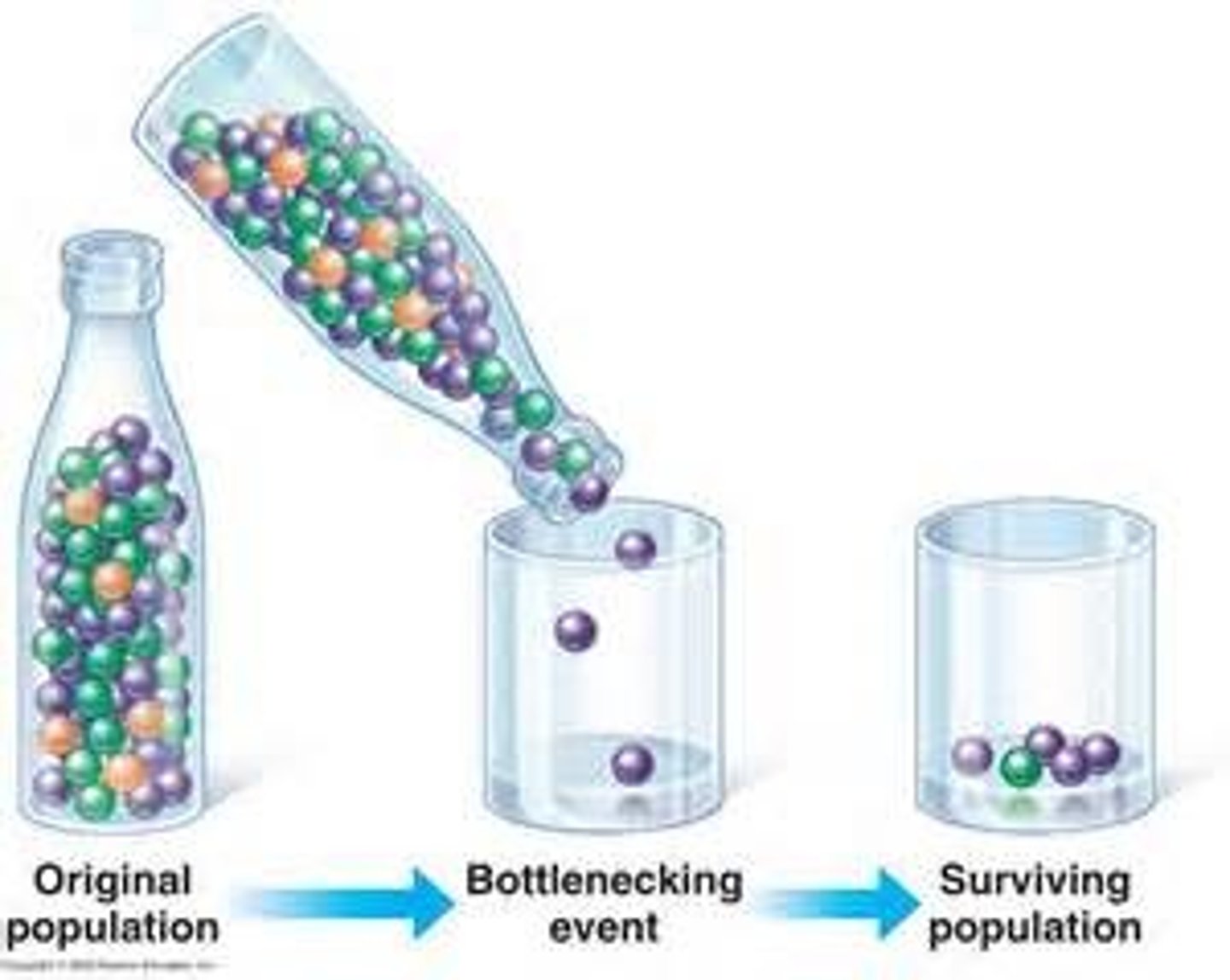
What is the effect of domestication bottle necks?
Founder effect, followed by a genetic bottleneck → lower levels of genetic variation
• But, increase in morphological variation (peculiar to domestication)
What is an example of domestication?
Dogs
Gray wolf → many different breeds (not separate species)
What has dog domestication resulted in?
- Many species
- Canid behaviours
- Brain differences
- Grazing behaviour
- Genetics
- Health effects
How can we see brain differences from dog domestication?
• MRI of 62 male and 33 female dogs
• Neuroanatomical variation across breeds → 6 networks which vary for breed group
How can we see grazing behaviour from dog domestication?
• Comparison of gazing in 3 breeds, products of different artificial selection pressures
• 4 trials of a solvable task (obtain food by manipulating metal container), then unsolvable task (container fixed onto plywood) → 17 CWD, 14 LR and 12 GS
• Experimenter and owner were either side of dog, 2 steps back
• Part 2 = impossible task
What are some of the health effects from dog domestication?
There are lots of breed associated genetic problems etc
What are the causes of artificial selection?
• Unconscious (initial domestication)
• Conscious- purposeful domestication- Genetic modification/engineering aka recombinant DNA (selection at a genome level) → useful for scientific research
What is the definition of genetic modification?
The deliberate alteration of the genetic constitution of a living organism or cell by artificial means (i.e. not by conventional selective breeding), such as the introduction of a gene from another species of the introduction of a mutation into a specific gene. Bacteria, cultured cells, plants and some animals can be altered in this way
What is a change in a frequency of alleles?
Evolution
How does genetic modification differ from traditional artificial selection?
Because new genes are inserted, they don't have to randomly appear due to mutations and then be selected for
What does genetic modification produce?
• Produces Genetically Modifies Organisms (GMOs) For:
- Agriculture
- Biomedical science
- Pharmaceuticals
What are advantages of genetically modified crops?
Increased yield; more food. GM crops can be engineered to contain nutrients that people in developing nations lack. GM crops are already being grown in some places, often without any problems.
Genes can be introduced from any source, relatively precise, can undergo testing, genes can be cut and pasted to change the properties of proteins the plants produce
Where are genetically modified crops used?
Widespread in US and Canada but strict regulations in the UK and EU (directive GM food and feed regulation (EC) No.1829/2003)
What have genetically modified crops been developed so far to do?
- Increase fruit shelf-life
- Herbicide tolerance = (epsps gene)
- Insect resistance (cry genes)
- Disease resistance
- Modified oil content
- Modified form for bioethanol (biofuel) and animal feed (amy797E gene)
- Drought tolerance (cspb gene)
- Biopharming e.g. insulin production
What is recombinant DNA technology for De-extinction?
Based on cloning methodology but mother is of an extant closely related species
The pyrenean ibex proved technology can work but calf dies just a few minutes after birth
Used by The Long Now Foundation now called Revive & Restore
What are nature based tourism effects?
response to humans along a gradient, from domestication to nature-based tourism