Chapter 6: Skeletal System
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Bone
A hard and rigid component of the skeletal system.

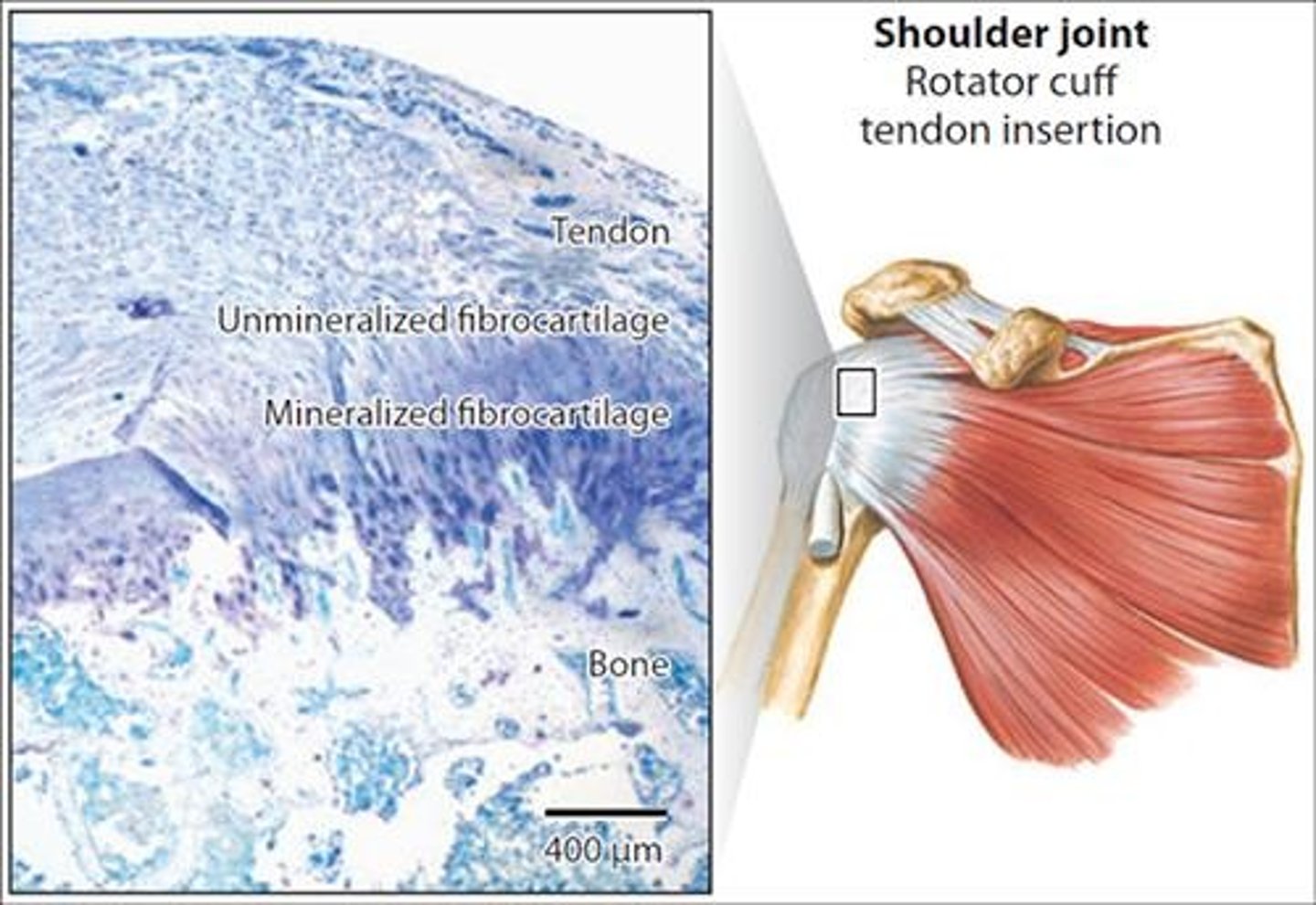
Cartilage
A flexible yet strong tissue that comes in three types: hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic.
Tendons
Connective tissues that attach muscles to bones.
Ligaments
Connective tissues that connect bones to other bones and allow some movement while preventing excessive movement.
Support
One of the functions of the skeletal system, providing a framework for the body.
Protection
Function of the skeletal system that safeguards vital organs.
Movement
Produced by muscles acting on bones via tendons.
Storage
Function of the skeletal system that includes storing calcium, phosphorus, and adipose tissue in marrow cavities.
Blood cell production
Process that occurs in red bone marrow.
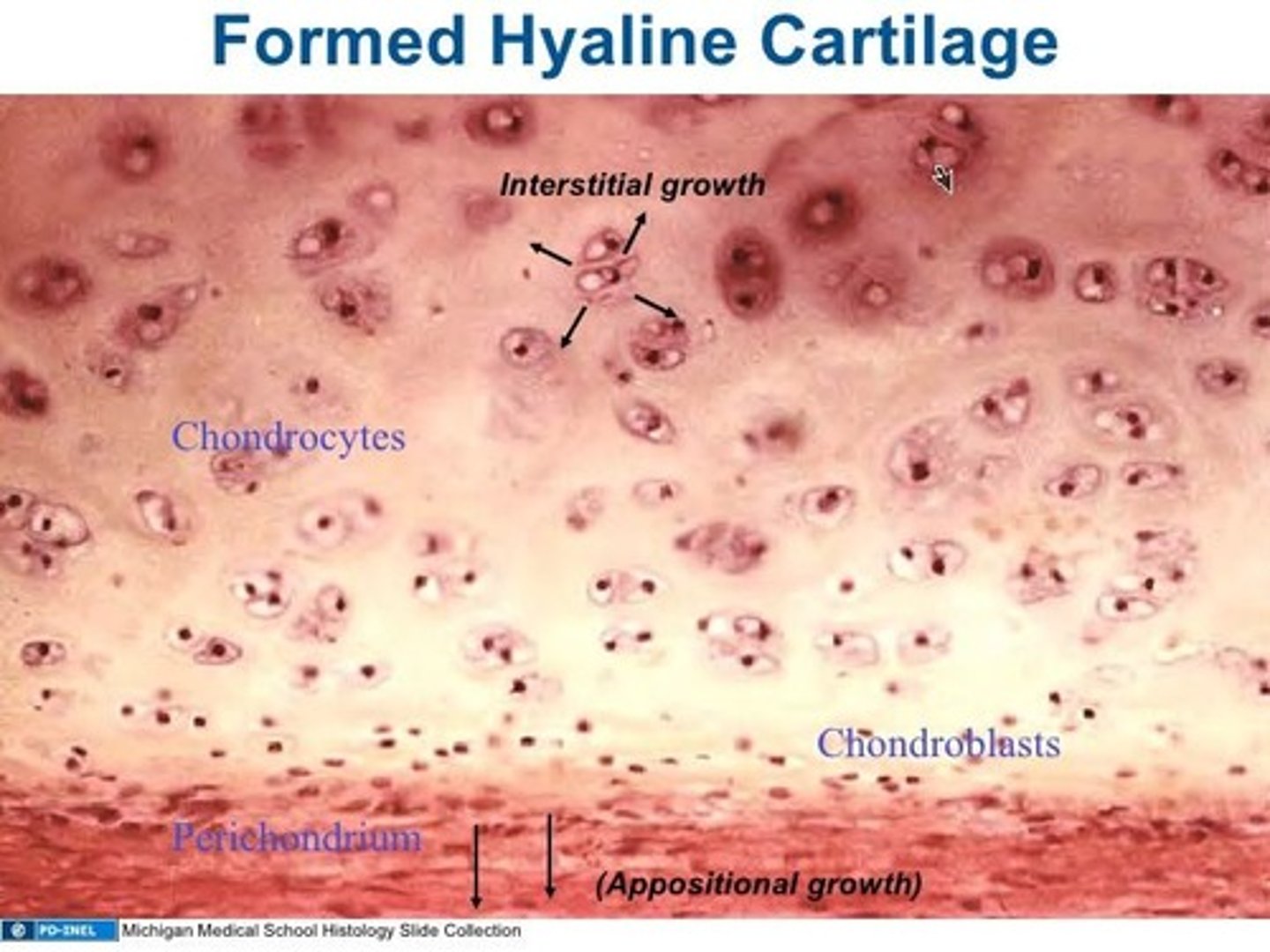
Chondroblasts
Specialized cells that form the cartilage matrix.
Chondrocytes
Cells surrounded by cartilage matrix and located in lacunae.
Matrix
The extracellular material in cartilage that contains collagen fibers for strength and proteoglycans for resiliency.
Perichondrium
A double-layered connective tissue sheath that covers cartilage except at articulations.
Articular cartilage
Cartilage that covers bones at joints and lacks perichondrium, blood vessels, or nerves.
Appositional growth
Type of cartilage growth where new chondrocytes and matrix are laid down at the periphery.
Interstitial growth
Type of cartilage growth where chondrocytes within the tissue divide and add more matrix between the cells.
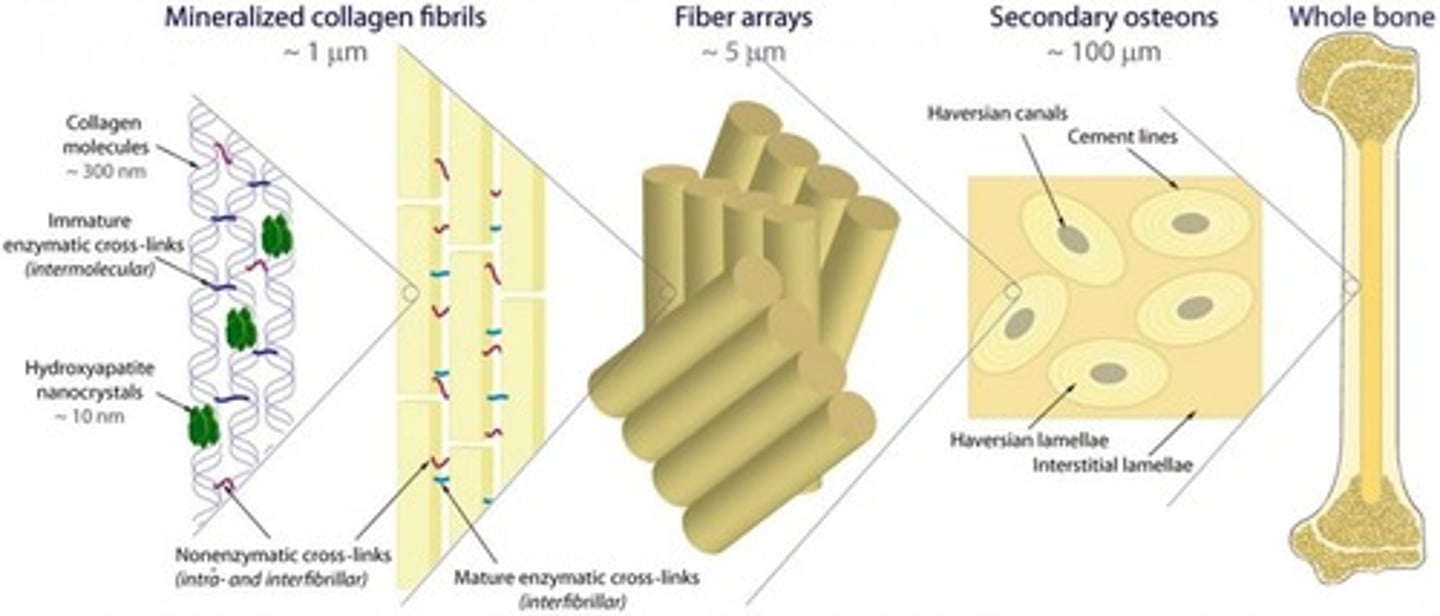
Bone matrix
Similar to reinforced concrete, consisting of collagen fibers (steel rods) and hydroxyapatite (cement).
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
A condition characterized by a deficiency of collagen, leading to fragile bones.
Osteochondral Progenitor Cells
Stem cells that develop into either chondroblasts or osteoblasts, located in the periosteum.
Osteoblasts
Cells responsible for the formation of bone through ossification.
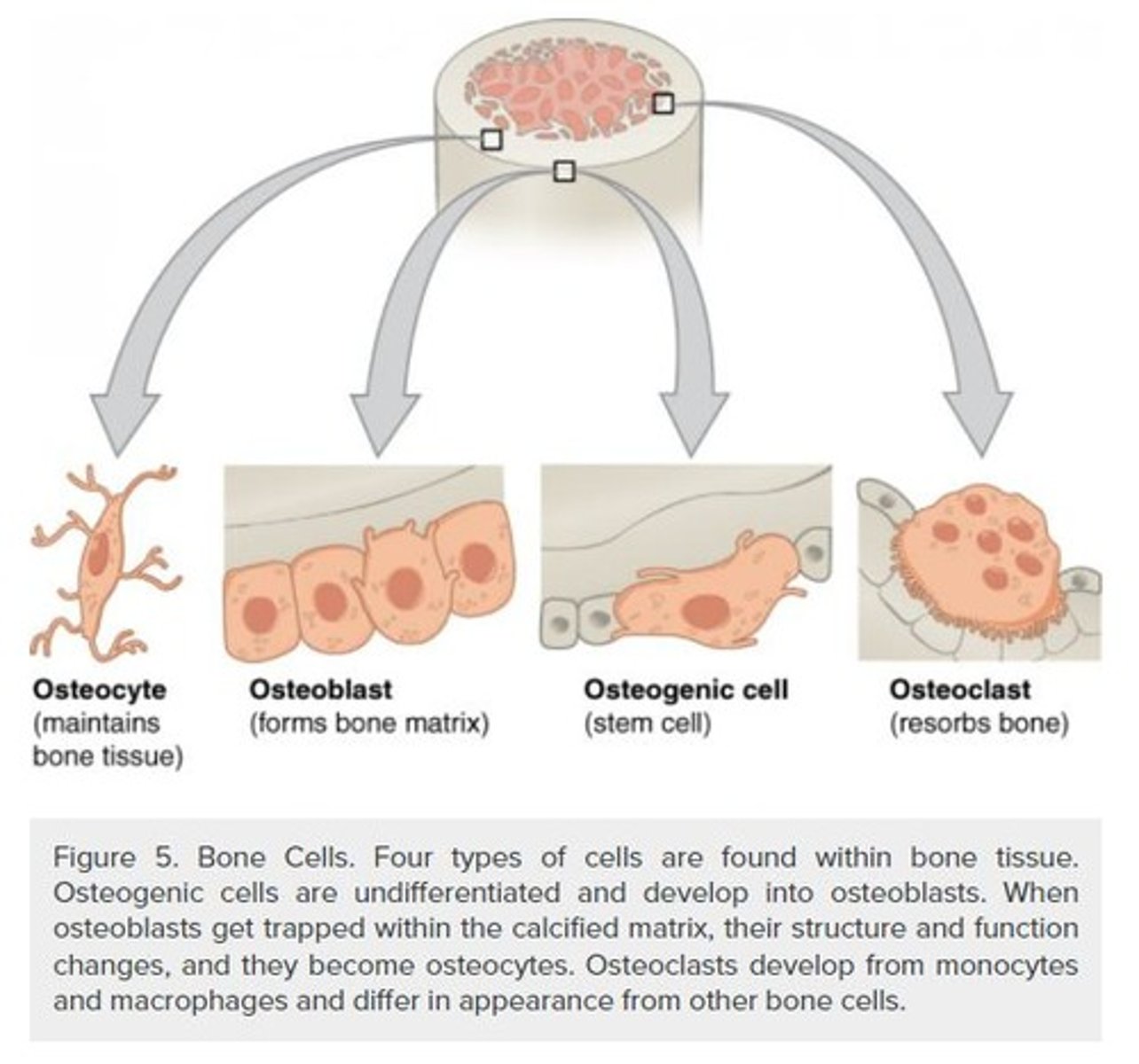
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells that are surrounded by matrix and reside in lacunae.
Canaliculi
Canals occupied by osteocyte cell processes that connect to other osteocytes.
Osteoclasts
Multinucleated cells involved in the resorption of bone.
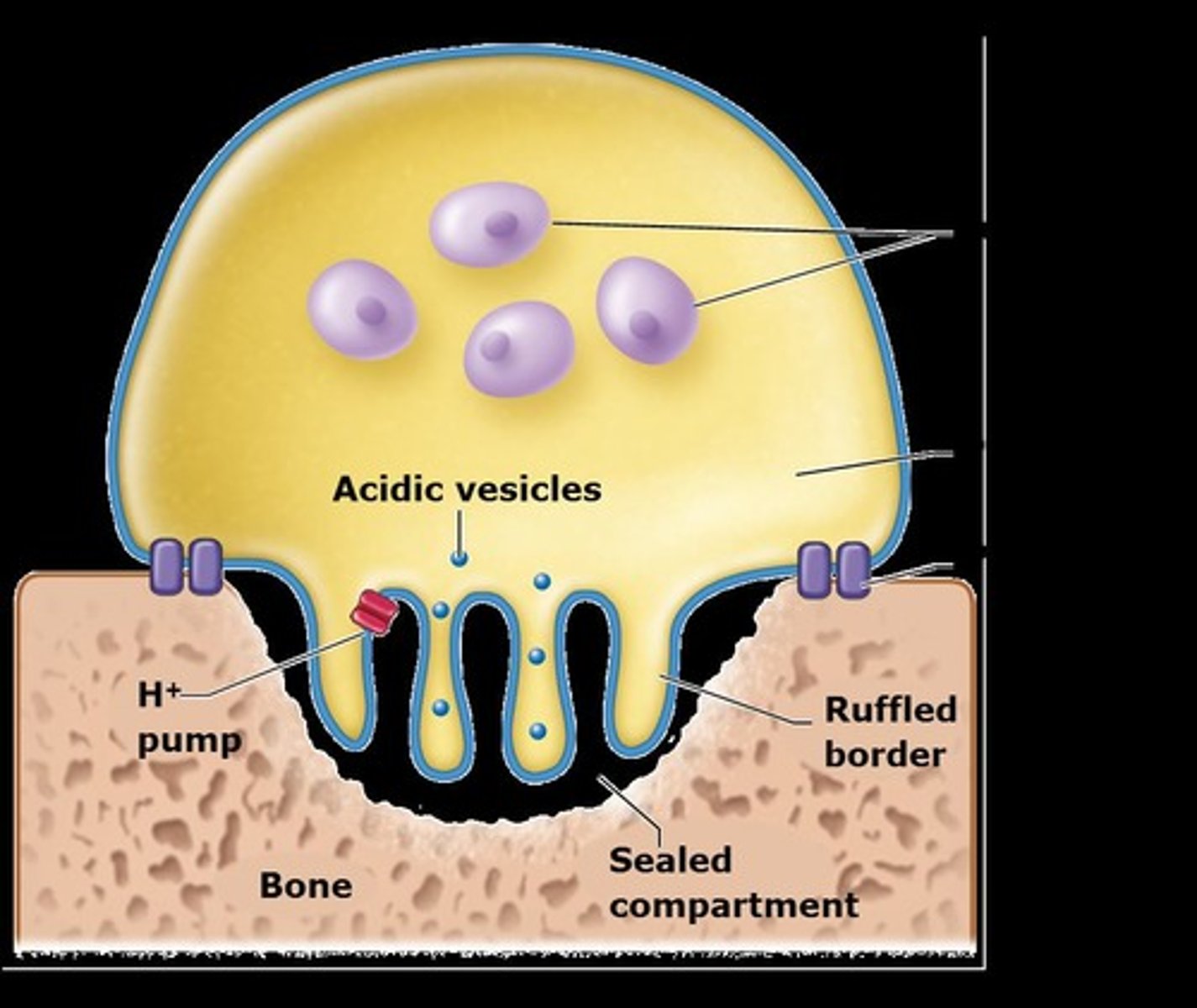
Resorption
The breakdown of bone into its constituent parts.
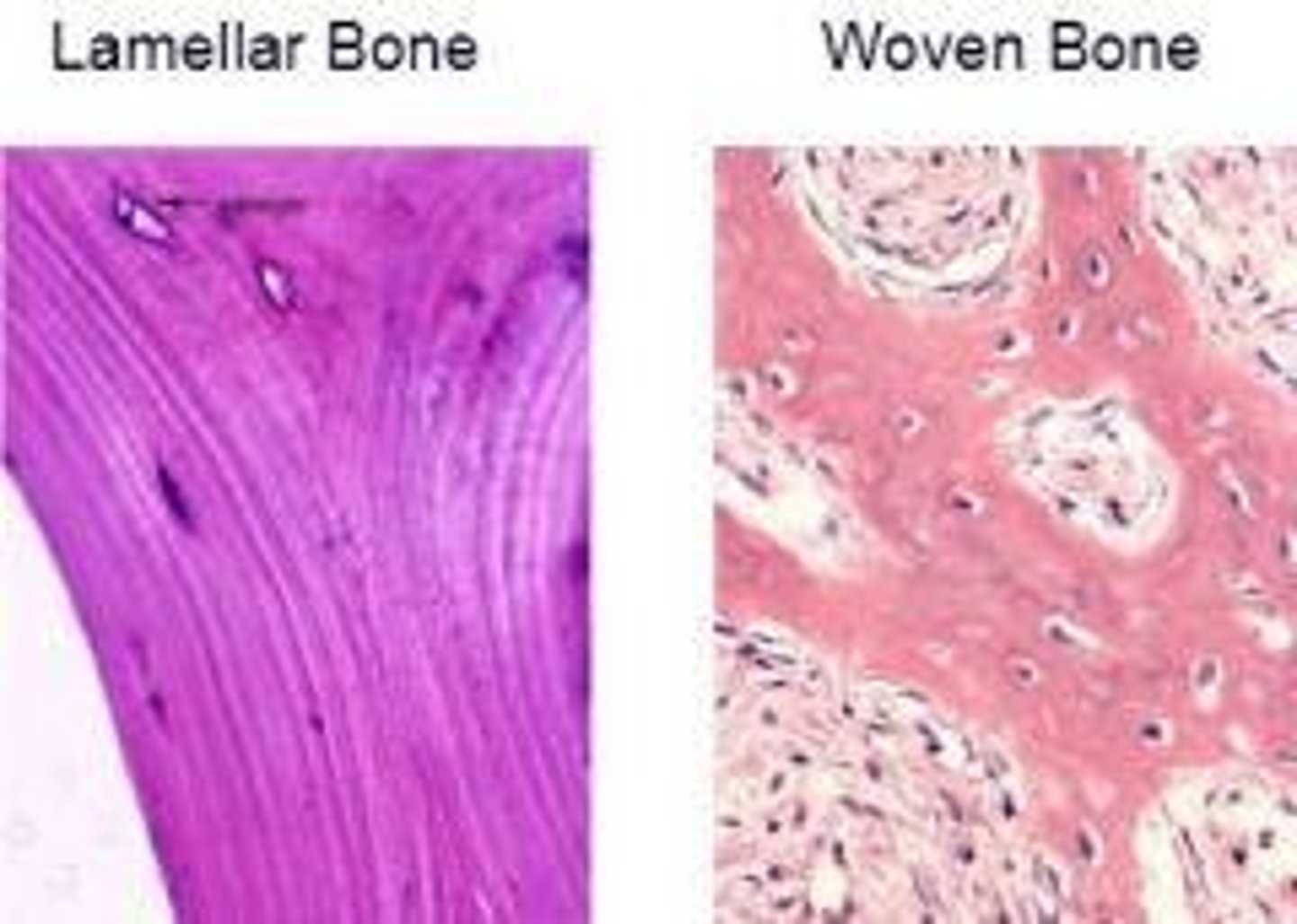
Woven bone
Bone with collagen fibers randomly oriented, laid down during fetal development and fracture repair.
Lamellar bone
Mature bone organized in sheets called lamellae, providing strength through fiber orientation.
Spongy bone
A type of bone that has a porous structure, providing lightweight support.
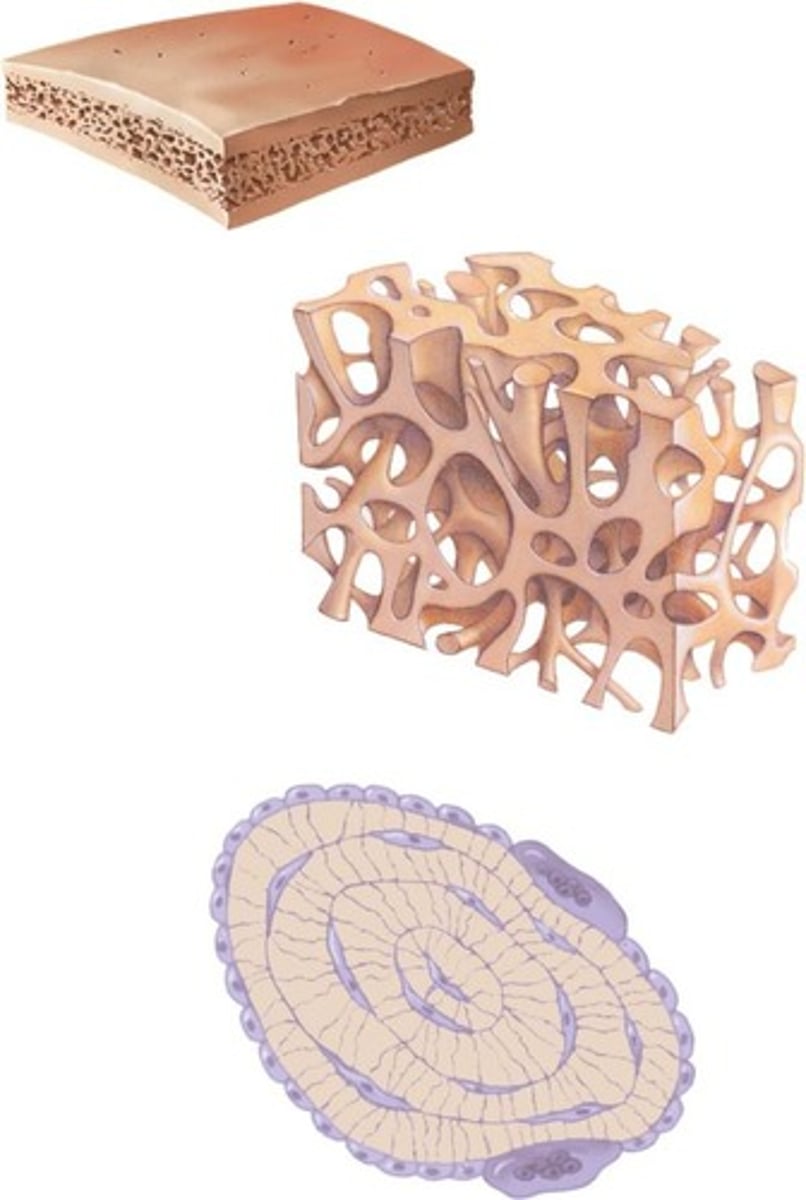
Trabeculae
Interconnecting rods or plates of bone.
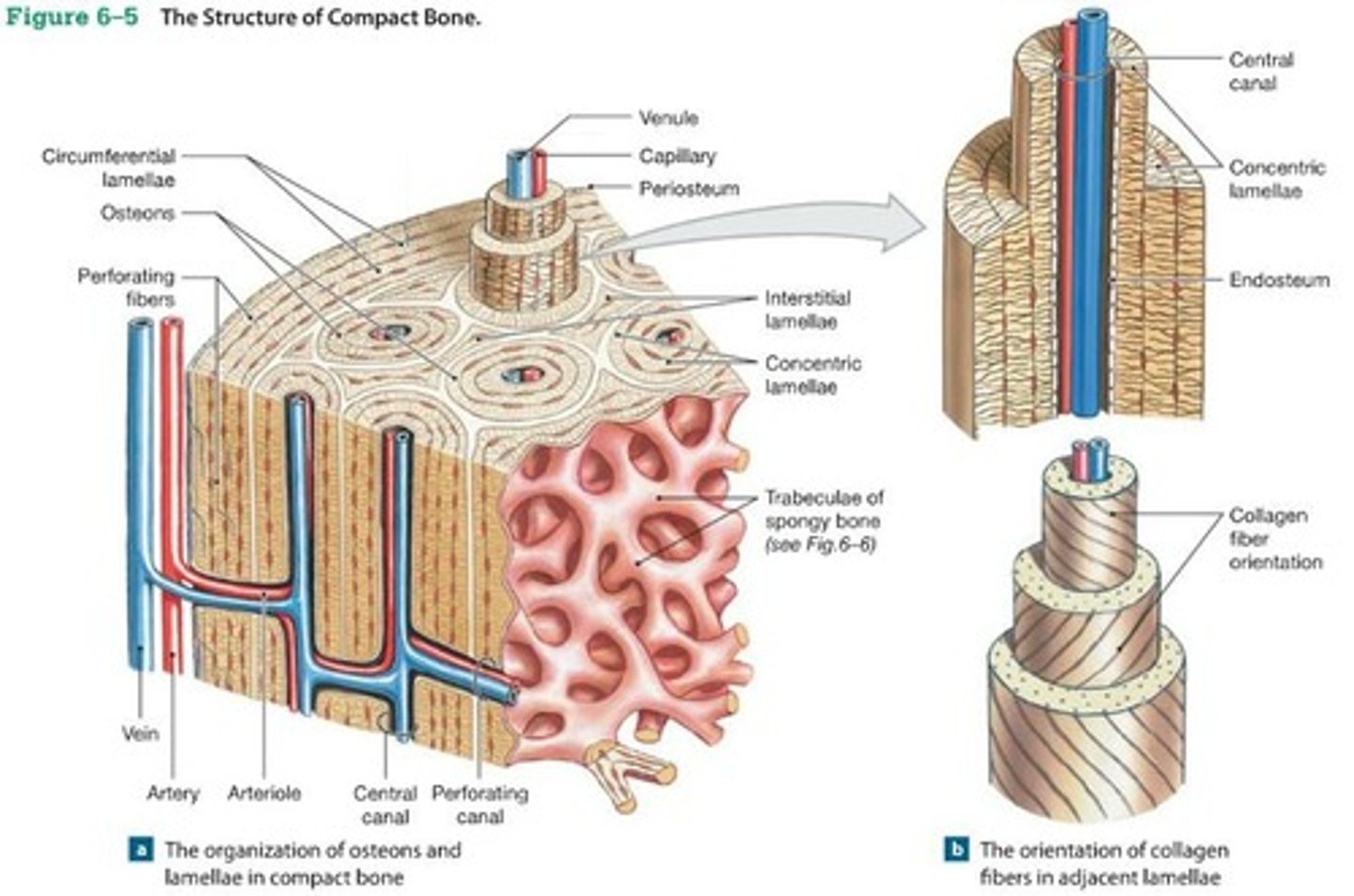
Compact bone
Dense bone that forms the outer layer of bone structures.
Osteoblast
Bone-forming cell.
Osteoclast
Bone-resorbing cell.
Osteocyte
Mature bone cell that maintains bone tissue.
Canaliculus
Small channels in bone that connect lacunae.
Lamellae
Concentric layers of bone matrix.
Osteon
Structural unit of compact bone, consisting of a central canal and concentric lamellae.
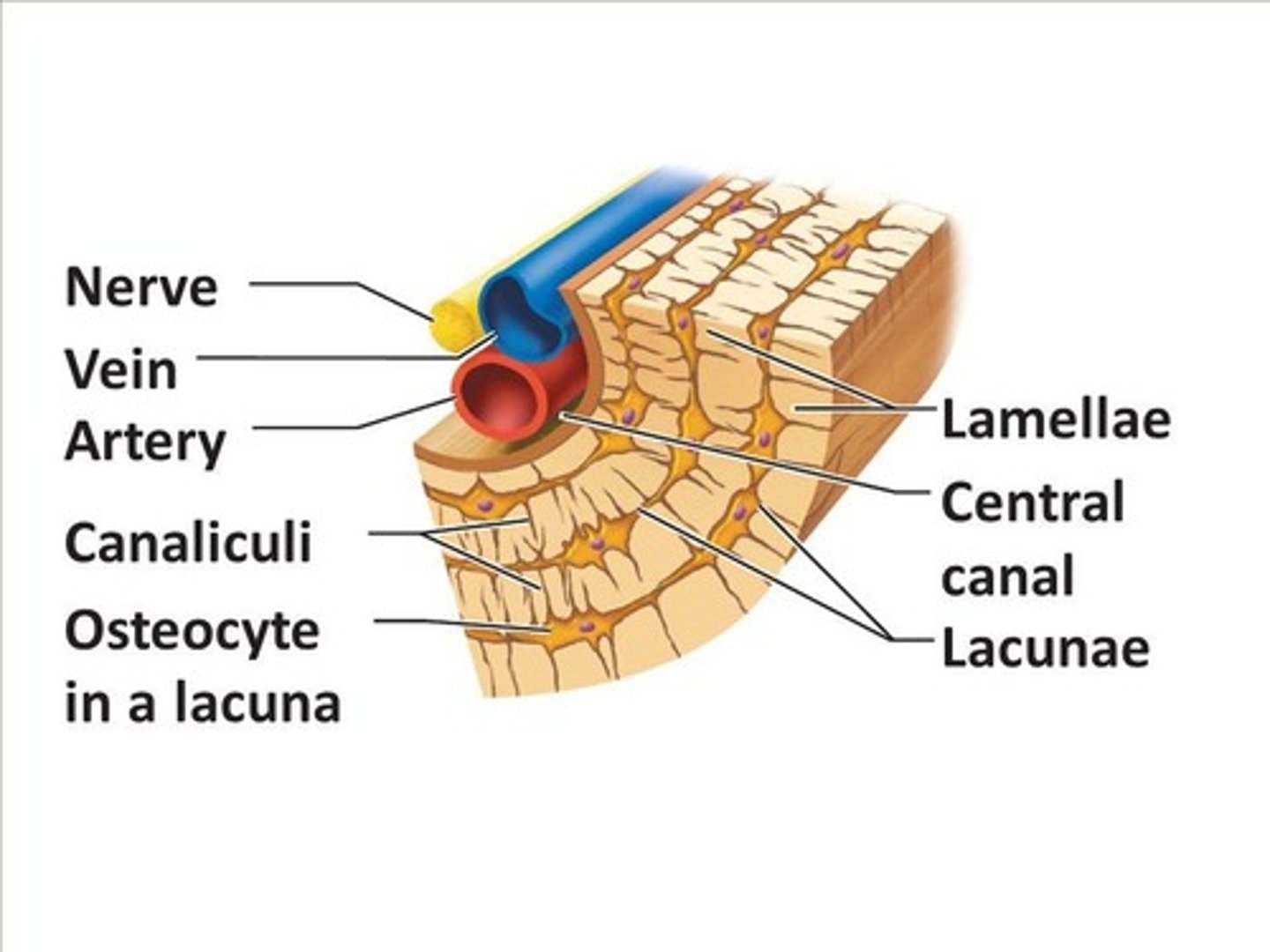
Central canals
Canals that run parallel to the long axis of the bone.
Perforating canal
Canals that run perpendicular to the length of bone.
Circumferential lamellae
Layers of bone matrix that encircle the bone.
Interstitial lamellae
Remnants of osteons that fill spaces between osteons.
Perforating (Volkmann's) canals
Blood vessels from periosteum that penetrate bone.
Diaphysis
Shaft of a long bone.
Epiphysis
End of the bone, primarily composed of spongy bone.
Epiphyseal plate
Growth plate composed of hyaline cartilage.
Epiphyseal line
Ossified remnant of the epiphyseal plate.
Medullary cavity
Hollow center of the diaphysis of long bones that contains bone marrow.
Endosteum
Membrane that lines all internal spaces including spaces in spongy bone.
Periosteum
Outer layer of bone that is fibrous and contains bone cells.
Red marrow
Connective tissue in the spaces of spongy bone or in the medullary cavity; the site of blood cell production.
Yellow marrow
Fat stored within the medullary cavity or in the spaces of spongy bone.
Intramembranous ossification
Takes place in connective tissue membrane.
Endochondral ossification
Forms from a pre-existing cartilage model.
Centers of ossification
Locations in membrane where ossification begins.
Fontanels
Large membrane-covered spaces between developing skull bones; unossified.
Bone collar
A layer of compact bone that forms around the diaphysis during endochondral ossification.
Secondary ossification centers
Form in the epiphyses of long bones; the original cartilage model is almost completely ossified.
Cartilage formation
Begins at the end of the fourth week of development.
Ossification
The process of bone tissue formation.
Interstitial cartilage growth
A type of growth where new cartilage is formed internally.
Closure of epiphyseal plate
The epiphyseal plate is ossified, becoming the epiphyseal line, which occurs between 12 and 25 years of age.
Proliferation zone
New cartilage is produced on the epiphyseal side of the plate as the chondrocytes divide and form stacks of cells.
Hypertrophic zone
Chondrocytes mature and enlarge.
Calcified cartilage zone
Matrix is calcified and chondrocytes die.
Ossification zone
Cartilage on the diaphyseal side of the plate is replaced by bone.
Appositional growth in bone width
Occurs only on old bone and/or on cartilage surface; interstitial growth cannot occur because the matrix is solid.
Factors affecting bone growth
Size and shape of a bone are determined genetically but can be modified by nutrition and hormones.
Vitamin D
Necessary for absorption of calcium from intestines; can be eaten or manufactured in the body.
Rickets
A condition resulting from a lack of vitamin D during childhood.
Osteomalacia
A condition resulting from a lack of vitamin D during adulthood leading to softening of bones.
Vitamin C
Necessary for collagen synthesis by osteoblasts; deficiency leads to scurvy.
Growth hormone
Stimulates interstitial cartilage growth and appositional bone growth.
Thyroid hormone
Required for growth of all tissues.
Sex hormones
Cause growth at puberty and closure of the epiphyseal plates.
Bone remodeling
Converts woven bone into lamellar bone, caused by migration of osteoclasts and osteoblasts.
Mechanical stress and bone strength
Stress causes bone remodeling to increase bone mass and align trabeculae with stress.
Osteoporosis
A condition characterized by decreased bone density resulting from an imbalance between bone resorption and formation.
Hematoma formation
Localized mass of blood released from blood vessels but confined within an organ or space.
Clot formation
The process of blood coagulation that occurs after hematoma formation.
Callus
mass of tissue that forms at a fracture site and connects the broken ends of the bone
Internal Callus
forms between the ends of the bones
Macrophages
clean up debris at the fracture site
Fibroblasts
produce collagen
External Callus
collar around opposing ends that stabilizes two pieces
Callus ossification
Callus replaced by woven bone
Calcium Homeostasis
Bone is major storage site for calcium
Blood calcium levels
depends upon movement of calcium into or out of bone
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Released when blood calcium levels are low; stimulates osteoclasts to resorb bone
Calcitonin
Released when blood calcium levels are high; inhibits osteoclasts and allows osteoblasts to take up calcium from blood
Effects of Aging on Skeletal System
Bone matrix decreases, leading to brittleness and decreased bone mass
Bone mass in men
Denser bone mass due to testosterone and greater weight
Bone mass by ethnicity
African Americans and Hispanics have higher bone masses than Caucasians and Asians
Rate of bone loss after menopause
Increases 10-fold
Bone loss effects
Causes deformity, loss of height, pain, stiffness, stooped posture, and loss of teeth