biochem unit 2
1/674
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
675 Terms
why is collagen unusual and not suitable for alpha helix or beta sheets
fits only a triple helix because the middle is glycine
hydrogen bonds stabilize
hypro and pro make up what percent of collagen residues
30%
what angle constraints are the structures of collagen helices
phi= -60 psi =-4.137 bars 120
interchain bonds H-bonds involving Hyp do what on the helix
stabilize
fibrils are strengthened by ___
intrachain lysine-lysine and interchain by hydroxyprridinium crosslinks
fibroin and b-keratin are composed of
-gly-ala/ser-gly-ala/ser
in fibrous proteins residues of a b sheet extend how
above and below the plane of the sheet
putting all glycine on one side and all Ala and see on other side
glycine interacts with glycine on the adjacent sheet
the surfaces of proteins are ____ to the molecules they bind to
complementary
the surface of a globular protein includes ____
water molecules - solvation layer
polar backbone and side chain group on the surface of globular proteins
make H bonds with the solvent
polypeptide chains containing more than 200 residue
usually fold into two or more globular clusters called domains which give these proteins bio multimodal appearance
why are proteins only marginally stable
flexibility and motion
what is the kd for two subunits
10^-8 and 10^-16 - this means the interaction is strong
entropy is gained in protein subunits by
burying hydrophobic groups
however there is entropy loss by association
quaternary structures are maintained by
stability; reduction of surface to volume ratio
genetic economy:;less dna to code for a monomer that assembles as a hetromultimer
brings catalytic sites together
the monomer may not constitute a complete enzyme active site
cooperatively: regulation of catalytic activity by means of subunit interaction
i
heterologous
interfaces formed by different surfaces on the two subunits
many proteins form tetramers by means of
2 sets of isologous interactions
the tetramer of transthyretin is formed by
isologous interactions between two large beta sheets of 2 dimers
disulfide bonds can occur between
two molecules (intersubunit) and within the same subunit (intrasubunit)
rank interactions from strongest to weakest in protein folding
hydrophobic interactions > ionic interactions > H-bonds> Van der Waals
what drives protein folding
hydrophobic interactions
ionic interactions usually occur in
on protein surface
where are hydrogen bonds formed on proteins
wherever possible
van der Waals interactions in proteins
ubiquitous
which noncovalent interactions stabilize the higher levels of protein structures
electrostatic interaction between a positively charged glutamate carboxyl group
what factors influence the folding process in proteins
certain regions along the chain may act as nucleation points
protein chain tries to reach the most stable conformation
chaperones may help
side chains of amino acids interact for structure
hydrophobic, h bonds,oxidation, electrostatic
ribonuclease can be unfolded by
treatment with urea and MCE (mercaptoethanol)
-mce reduces disulfide bonds
classic experiment that proved that sequent determined structure
the experiment showed that ribonuclease function and structure could be restored under appropriate conditions
proteins composed of less than 250 amino acids often have a
_____ structure
simple globular
larger globular proteins have ___ distinct structural features
2+ (domains and modules)
domains are
compact folded protein structures that are usually stable by themselves in aqueous solutions
in some proteins the domain sequence is interrupted by
a sequence belonging to another domain of the protein
malonyl CoA ACP transaclase
metabolic enzyme containing two subunits
large subdomain consists of a beta sheet surrounded by 12 alpha helixes
small subdomain consists of 4 stranded antiparallel beta sheets and two alpha helices
multi domain proteins are
the sum of the functional properties and behaviors of their constituent domains
evolved from the fusion of genes that once coded for separate proteins
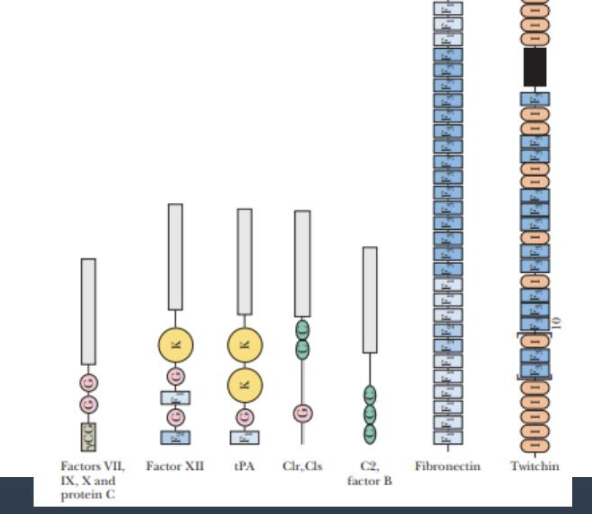
a sampling of proteins that consist of mosaics of individual protein modules
% of domains in proteins have been duplicated in other proteins
90%
many proteins contain _____ of the same domain
multiple copies
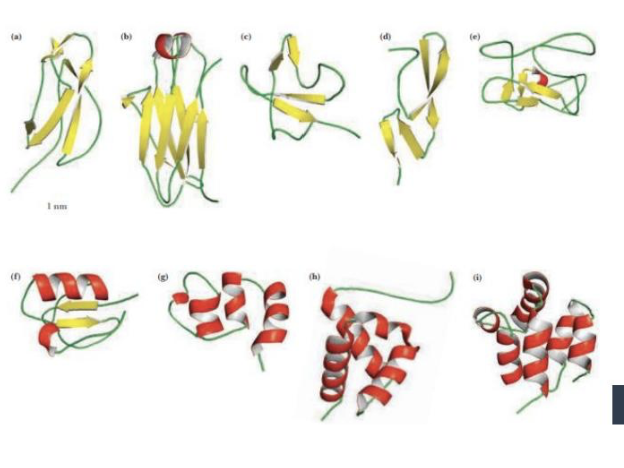
ribbon structures of several protein modules used in construction of complex multimodule proteins
some proteins share similar structural features but ______
carry out different functions
proteins with different structures can ______
carry out similar functions
the cellular environment is suited to
maintain weak forces that preserve protein function + structure
what can denature a protein
heat, chemical treatment
denaturization is
the process by which proteins lose their structure and functionality due to external stressors.
protein isolation
cells are collected from tissue or cell culture, lysed on a buffer system, sonicated, seared or incubated in mild detergents to disrupt cell membranes
liver tissue to liver extracts
minced tissue and suspend cells in isotonic buffer,
cell suspension
sonication, shearing, mold detergents
final form cell liver extraction
cell extracts can be separated and purified by
size, binding affinity and electrophoresis
salting out
uses high concentration of salts such as (NH4)2SO4 to make molecules come out of solution
more than one chain in a protein =
multimeric protein
more than one equal polypeptide chain
homomultimer
protein with two or more different chains
heteromultimer
the three structural classes of proteins
fibrous
globular
membrane
proteins are categorized by
shape and solubility
secondary and higher order protein structures are stabilized by
hydrogen bonds
ionic bonds
van der Waals forces
hydrophobic effects
configuration rearrangements for proteins
involves breaking and remaking bonds
structure of proteins depends on
amino acid sequence and weak, noncovalent forms
the number of protein folding patterns is very large but
finite
the structure of globular proteins are
marginally stable
marginal stability facilitates
motion
motion enables
function
hydrogen bonds in protein structures
can form wherever back bone aide N-H and carbonyl C=O groups or see chains can approach each other
hydrophobic interactions drive
burial of non polar side chains in the protein core
ionic bonds form
between oppositely charged side chains
in isolation ____ of these forces would be enough to fold a typical protein
NONE
all of the bonds in protein folding
release energy and create favorable entropy
the unfolded chains many possible shapes when collapsed into a single folded state
reduce disorder - entropy is lost
the overall free energy change of folding and delta g
is only slightly favorable
the peptide backbone in proteins is
rigid and planar
six atoms of each -CO-NH unit
stabilized by 80-90 kj mole of resonance energy
conformational flexibility arises only via
rotation about the two flanking bonds
phi vs psi bonds
phi= rotation around alpha carbon-N and psi = rotation around carbon alpha carbon bonds
these link the alpha carbon to its two amide planes
the most favorable secondary structure phi and psi conformations
phi=-60
psi=180
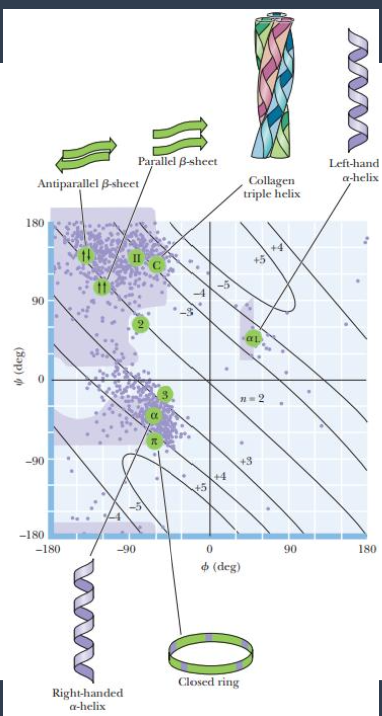
ramachandran map plotting phi vs psi
ramachandran map plotting reveals psi and phi for high resolution proteins
only a handful oof populated regions
a helix region
phi = -60 and psi=-50
beta sheet region
phi=-120 psi=140
types of secondary structures stabilized by h bonds
alpha helices
other helices
beta sheet (strands)
tight turns (beta turns/beta bends)
in an alpha helix each C=O of residue “I”
H-bonds to N-H, I+4 produces a 3.6 residue turn, rise per turn 5.4 pitch and rise per residue is 1.5
side chains project outward to avoid
steric clash
bond angles in right alpha helix
-60 degrees for phi and -45 degrees for psi
the helix core in alpha helix structures
tightly packed so that the atoms are at or near their van der Waals radii
what creates a large net dipole moment for the helix
the arrangement of N-H and C=O groups with each having an individual dipole moment
helix capping motifs are
specific patterns of hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions found at or near the ends of helices in both proteins and peptides
in a helix the first 4 N-H and last 4 C=O groups
necessarily lack intrahelical hydrogen bonds
these groups are often capped by alternative hydrogen bond partners
helix capping is a ____ from secondary to super secondary structures
bridge
for two helices connected by a short loop
the hydrophobic interactions spans the C-cap of one helix and the N cap of the other and the intervening non helical segment
capping _____ conformation
constrains
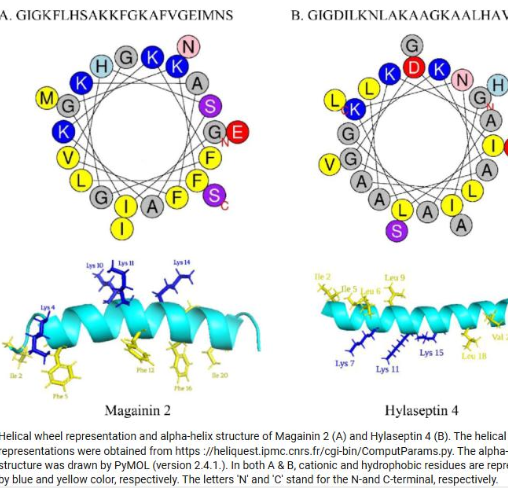
these are an example of
amphipathic helices
the b pleated sheet is composed of _____ and may be ____ or ____
beta strands, parallel, antiparallel
in beta sheets - the bonds
N-H backbone groups in one strand hydrogen bonds with the C=O groups of aha adjacent strand
strands adopt ____ backbones
zigzag
strands in beta sheets are packed side by side via
hydrogen bonds
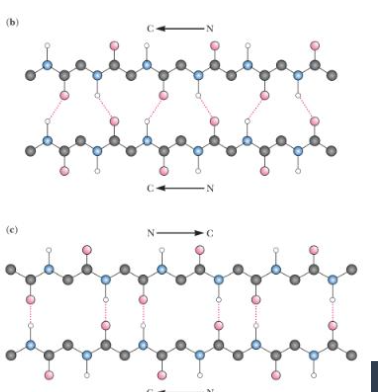
top vs bottom
top=parallel
bottom= antiparallel
in anti parallel sheets each N-H-O=C pair is nearly
linear
in parallel sheets H bonds are
somewhat distorted
in b pleated sheets side chains
alternate above and below the sheet so hydrophobic residues may form the sheet core or be solvent exposed in amphipathic sheets
spider web silks are composites of a-helices and b-sheets and the radial strands of webs must be strong and rigid meaning
higher percentage of beta sheets
circumferential strands must be flexible meaning
higher percent of alpha helixes
beta turns allow for
the peptide chain to reverse direction
in beta turns the carbonyl of one residue is ____ bonded to the amide proton of a residue ____ residues away
H-bonded, three
which amino acids are prevalent in beta turns
proline and glycine
which beta turns are more common
type I more common than type 2