Chemical Reactions/ Rates of Reactions
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
physical change
a change that does not result in the formation of any new substance
chemical change
a change that results in the formation of one or more new substances
chopping wood
physical change
burning wood
chemical change
what is the difference between a physical and a chemical change?
in a physical change there is a no new substance created, in a chemical change there is a new substance created
what is the law of conservation of mass
it is a fundamental scientific law that states that when a chemical reaction occurs, the total mass of the reactants is always equal to the total mass of the products
the law of conservation of mass as an =
total mass of reactants = total mass of products
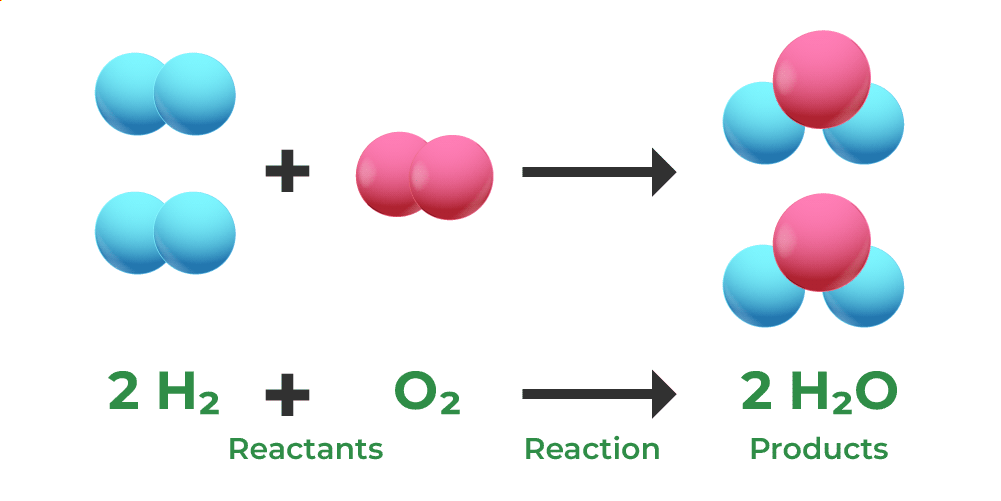
mass is conserved during this reaction. what evidence is there for this?
there are equal numbers of each type of atom on each side of the equation, showing that there is no change in mass.
rate of reaction
the change in concentration per unit time of any one reactant or product
is particle size a factor that affects the rate of reaction?
particle size does affect the rate of reaction
is the type of reactants a factor that affects the rate of reaction?
the type of reactants does affect the rate of reaction
is the concentration of the reactants a factor that affects the rate of reaction?
the concentration of the reactants does affect the rate of reaction
is the temperature a factor that affects the rate of reaction?
the temperature does affect the rate of reaction
are catalysts a factor that affects the rate of reaction?
catalysts do affect the rate of reaction
characteristics of a Physical Change (5)
change in appearance
no new products
easy to reverse
no signs of change happening
mass is conserved
characteristics of a chemical change (5)
complete change in appearance
new products formed
difficult to reverse
signs of change taking place (bubbles, temp, colour, odour, light, sound)
mass is conserved
why does temperature affect the rate of reaction?
for a chemical change to occur, the particles in the reactants must collide with each other. When you add heat, those particles gain energy and move faster which results in more collisions. This results in faster reaction times.
why does particle size affect the rate of reaction?
for a chemical reaction to occur, the particles in the reactants must collide with each other. When you break the reactants into smaller pieces, there are then more exposed particles, creating more area for collisions to occur. This increases the rate of reaction.
why does the concentration of the reactants affect the rate of reaction?
for a chemical reaction to occur, the particles in the reactants must collide with each other. When you increase the concentration if the reactants, there are more particles. As a result, the number of collisions increases, and the reactions happen faster.
why does stirring affect the rate of reaction?
for a chemical reaction to occur, the particles in the reactants must collide with each other. Stirring keeps the reactant particles in motion, increasing the chances of collision. This increases the rate of reaction.
the collision theory
a scientific theory that states that for a chemical reaction to occur, the reacting particles must collide with each other. It also states that a collision will only result in the formation of a product if a certain minimum energy is reached in the collision. This type of collision is called an effective collision
preparation of carbon dioxide
set up apparatus as shown, add HCl to the buchner flask + stopper flask with para film, observe gas displacing water, remove gas jar when full, test gas for carbon dioxide
word equation for prep of carbon dioxide
calcium carbonate + Hydrochloric acid = calicum chloride + water + carbon dioxide
equation for prep of carbon dioxide
CaCO3 + 2HCl = CaCl + C02 + H2O
tests for CO2 (2)
a lit match will extinguish
it turns lime water milky - a white precipitate is formed (chalk)
test for O2 (1)
a glowing splint or paper will burst into flames
test for H2 (1)
a lit taper will burn with a popping noise
the steeper the slope the
faster the reaction