APES UNITS 1-5: FINAL REVIEW
1/270
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
271 Terms
Individual
one organism (ONE elk)
Population
group of individuals of same species (herd of elk)
Community
all living organisms in an area
Ecosystem
all living and nonliving things in an area (plants, animals, rocks, soil, water, air)
biome
large area with similar climate conditions that determine plant and animal species there (ex: tropical rainforest)
Competition
organisms fighting over a resource like food or shelter; limits pop. size
Predation
one organism using another for energy source (hunters, parasites, even herbivores)
Mutualism
relationship that benefits both organisms
Commensalism
relationship that benefits one organism and doesn’t impact the other (birds nest in trees)
herbivores
(plant eaters) eat plants for energy
true predators
(carnivores) kill and eat prey for energy
parasites
use a host organism for energy, often without killing the host and often living inside host
parasitoids
lay eggs inside a host organism; eggs hatch and larvae eat host for energy
symbiosis
any close and long-term interaction between two organisms of different species (mutualism, commensalism, parasitism)
lichen
composite organism of fungi living with algae; algae provide sugars (energy) and fungi provides nutrients
resource partitioning
different species using the same resource in diff. ways to reduce competition
temporal partitioning
using resource @ different times, such as wolves and coyotes hunting at different times (night vs day)
spatial partitioning
using diff, areas of a shared habitat (diff. length roots)
morphological partitioning
using diff. resources based on diff. evolved body features
annual temp and precip. average
biomes are defined by…
latitude
what determines temp. and precip.?
permafrost
ground (soil, rock, sediment) that stays frozen below 0°C (32°F) for at least two consecutive years, acting like cement that binds it with ice, and it contains vast amounts of trapped organic carbon
tropical rainforest
name the biome: nutrient poor soil (high competition from so many diff. plant species)
boreal forest (taigas, coniferous)
name the biome: nutrient poor soil (low temp. and low decomp. rate of dead org. matter) are found at latitudes between 50° and 60° north of the equator. These forests experience short, warm, moist summers and long, cold, dry winters. The coniferous trees of these forests have thin, needle-like leaves that do not shed in winter. They also produce seeds in cones, which forms the root term of the name coniferous.
temp. forest
name the biome: nutrient rich soil (lots of dead org. matter leaves and warm temp/moisture for decomp)
climate change
what causes biomes to shift in location?
salinity
how much salt there is in a body of water, determines which species can survive and usability for drinking (fresh water vs. estuary vs. ocean)
depth
influences how much sunlight can penetrate and reach plants below the surface for photosynthesis
flow
determines which plants and organisms can survive, how much O2 can dissolve into water
temp
warmer water holds less dissolved O2 so it can support fewer aq. organisms
turbidity
the measure of the clarity of water and suspended solids, may be the result of soil erosion, urban runoff, algal blooms and bottom sediment disturbances.
carbon cycle
the movement of carbon across the earth, process by which carbon is changed between the Earth’s atmosphere, land, and oceans
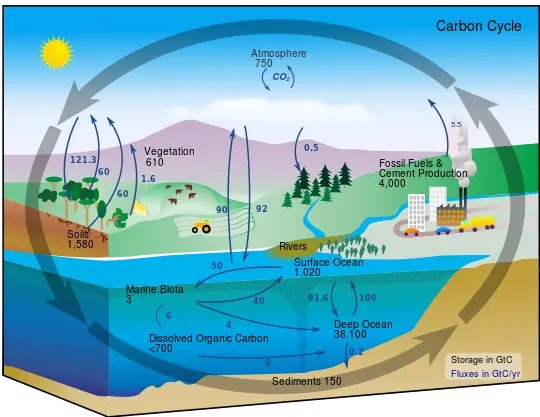
carbon sink
a carbon reservoir that stores more carbon than it releases (ocean is the largest)
carbon source
processes that add C to atm.
Fossil fuel (oil, coal, nat gas) combustion
Animal ag. (cow burps & farts = CH4)
Deforestation, releases CO2 from trees
FF combustion
fast step in carbon cycle
sedimentation and burial
slow steps in carbon cycle
photosynthesis
Removes CO2 from the atmosphere & converts it to glucose, how plants get energy, fast process
cellular respiration
Done by plants & animals to release stored energy, Uses O2 to break glucose down & release energy, fast process
direct exchange
CO2 moves directly between atmosphere & the ocean by dissolving into & out of ocean water at the surface, happens very quickly, balances levels of CO2 between atm and ocean
algae and phytoplankton
these organisms take CO2 out of the ocean & atm. through photosynthesis
coral reef and marine org
these aquatic organisms also take CO2 out of the ocean to make calcium carbonate exoskeleton
sedimentation
when marine org. die, their bodies sink to ocean floor where they’re broken down into sediments that contain C
burial
over, long, periods of time, pressure of water compresses C-containing sediments on ocean floor into sedimentary stone (limestone, sandstone) - long-term C reservoir
nitrogen cycle
Movement of N containing molecules between sources & sinks/reservoirs
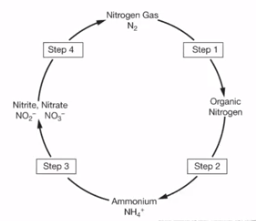
the atmosphere
largest nitrogen reservoir
nitrogen
what’s the critical plant and animal nutrient?
nitrogen fixation
Process of N2 gas being converted into biologically available (useable by plants) NH3 (ammonia) or NO3- (nitrate)
assimilation
plants & animals taking N in and incorporating it into their body
ammonification
soil bacteria, microbes & decomposers converting waste & dead biomass back into NH3 and returning it to soil
nitrification
conversion of NH4 into nitrite (NO2-) & then nitrate (NO3) by soil bacteria
denitrification
conversion of soil N (NO3) into nitrous oxide (N2O) gas which returns to atmosphere
nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, denitrification
order of nitrogen cycle
leaching
water-soluble substances, like minerals or pollutants, are washed away or dissolved and carried downward through soil layers by percolating water
eutrophification
the nutrient enrichment (especially nitrogen & phosphorus) of a water body, leading to excessive algae growth (algal blooms) that blocks sunlight, kills plants, and depletes oxygen when algae die and decompose, creating dead zones (hypoxia) that suffocate fish and other aquatic life
phosphorus cycle
Movement of P atoms & molecules b/w sources & sinks/reservoirs, VERY SLOW PROCESS
(weathering) rocks and sediments containing P minerals
major phosphorus reservoirs
what does the phosphorus cycle NOT have?
a gas phase
geologic uplift
tectonic plate collision forcing up rock layers that form mountains; P cycle can start over again with weathering & release of phosphate from rock
water cycle
Movement of H2O (in different states) b/w sources & sinks
energy from the sun
what drives the H2O cycle?
ocean and ice caps
largest water reservoirs?
transpiration
process plants use to draw groundwater from roots up to their leaves
evapotranspiration
amount of H2O that enters atm. from transpiration & evap. combined
infiltration
the process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil
percolation
the process of water slowly moving down through soil and rock layers into the ground, reaching groundwater, often following infiltration and contributing to aquifers, while also being key to soil health and septic system function
sublimation
A solid directly becoming a gas without becoming a liquid.
runoff
the draining away of water (or substances carried in it) from the surface of an area of land, a building or structure, etc.
primary productivity
rate that solar energy is converted into org. compounds via photosynthesis over a unit of time (rate of photosynthesis of all producers in an area over a given period of time)
typically higher biodiversity
what does high pp mean?
respiration loss
plants use up some of the energy they generate via photosynthesis by doing cell. respiration (movement, internal transportation, etc.)
gross primary productivity
The total amount of sun energy (light) that plants capture and convert to energy (glucose) through photosynthesis
net primary productivity
The amount of energy (biomass) leftover for consumers after plants have used some for respiration
GPP-RL
NPP equation
food web
Shows how matter & energy flow through an ecosystem, from organism to organism
trophic cascade
removal or addition of a top predator has a ripple effect down through lower troph. Levels
10% rule
in trophic pyramids, only about 10% of the energy from one level makes it to the next level; the other 90% is used by the organism & lost as heat
tertiary consumers
animals that eat secondary consumers or carnivores & omnivores (aka - top/apex predators)
secondary consumers
animals that eat primary consumers or herbivores (aka - carnivores & omnivores)
primary consumers
animals that eat plants (herbivores)
producers
“produce”- really convert sun’s light energy into chemical energy (glucose)
decomposers
organisms that feed on dead organic matter
biodiversity
Diversity of life forms in an ecosystem; measured on 3 different levels
ecosystem diversity
the number of diff. habitats available in a given area
species diversity
the number of diff. species in an ecosystem and the balance or evenness of the pop. sizes of all species in the ecosystem
genetic diversity
how different the genes are of individuals within a population (group of the same species)
higher ecosystem/population health
what does higher biodiversity mean?
species richness
the total number of different species found in an ecosystem
species evenness
a measure of how all of the individual organisms in an ecosystem are balanced between the different species
bottleneck event
An env. disturbance (natural disaster/human hab. destruction) that drastically reduces pop. size & kills organisms regardless of their genome
founder effect
a genetic phenomenon where a new, isolated population carries only a fraction of the original population's genetic diversity, leading to reduced variation and potentially higher frequencies of certain traits or rare genetic disorders present in the few founders
ecosystem resilience
the ability of an ecosystem to return to its original conditions after a major disturbance (wind storm, fire, flood, clear-cutting, etc.)
ecosystem services
Goods that come from natural resources or services/functions that ecosystems carry out that have measurable economic/financial value to humans
provisioning services
Goods taken directly from ecosystems or made from nat. resources (wood, paper, food)
regulating services
Nat. ecosystems regulate climate/air quality, reducing storm damage & healthcare costs
supporting services
Nat. ecosystems support processes we do ourselves, making them cheaper & easier(bees pollinate crops)
cultural services
Money generate by recreation (parks, camping, tours) or scientific knowledge
optimal range
range where organisms survive, grow, and reproduce
zone of physiological stress
range where organisms survive, but experience some stress such as infertility, lack of growth, decreased activity, etc.
zone of intolerance
range where the organism will die
island biogeography
Study of ecological relationships & community structure on islands