Chapter 9 Emotion and Motivation
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
motivation
factors of differing strength that energize, direct, and sustain behavior
need
a state of biological or social deficiency
need hierarchy
an arrangement of needs, in which basic survival needs must be met before people can satisfy higher needs.
drive
a psychological state that, by creating arousal, motivates an organism to engage in a behavior to satisfy a need.
arousal
physiological activation (such as increased heart rate, sweating, or muscle tension)
incentives
external objects or external goals, rather than internal drives, that motivate behaviors
extrinsic motivation
a desire to perform an activity because of the external goals that activity is directed toward
extrinsic motivation
a desire to perform an activity because of the external goals that activity is directed toward
intrinsic motivation
a desire to perform an activity because of the value or pleasure associated with that activity, rather than for an apparent external goal or purpose
insulin
a hormone, secreted by the pancreas, that controls glucose levels in the blood
ghrelin
a hormone that is associated with increasing eating behavior based on short-term signals in the bloodstream
leptin
a hormone that is associated with decreasing eating behavior based on long-term body fat regulation
need to belong theory
the need for interpersonal attachments is a fundamental motive that has evolved for adaptive purposes
achievement motivation
the need, or desire, to attain a certain standard of excellence
emotion
feelings that involve subjective evaluation, physiological processes, and cognitive beliefs
primary emotions
evolutionarily adaptive emotions that are shared across cultures and associated with specific physical states; they include anger, fear, sadness, disgust, happiness, and possibly surprise and contempt
secondary emotions
blends of primary emotions; they include remorse, guilt, shame, submission, and anticipation
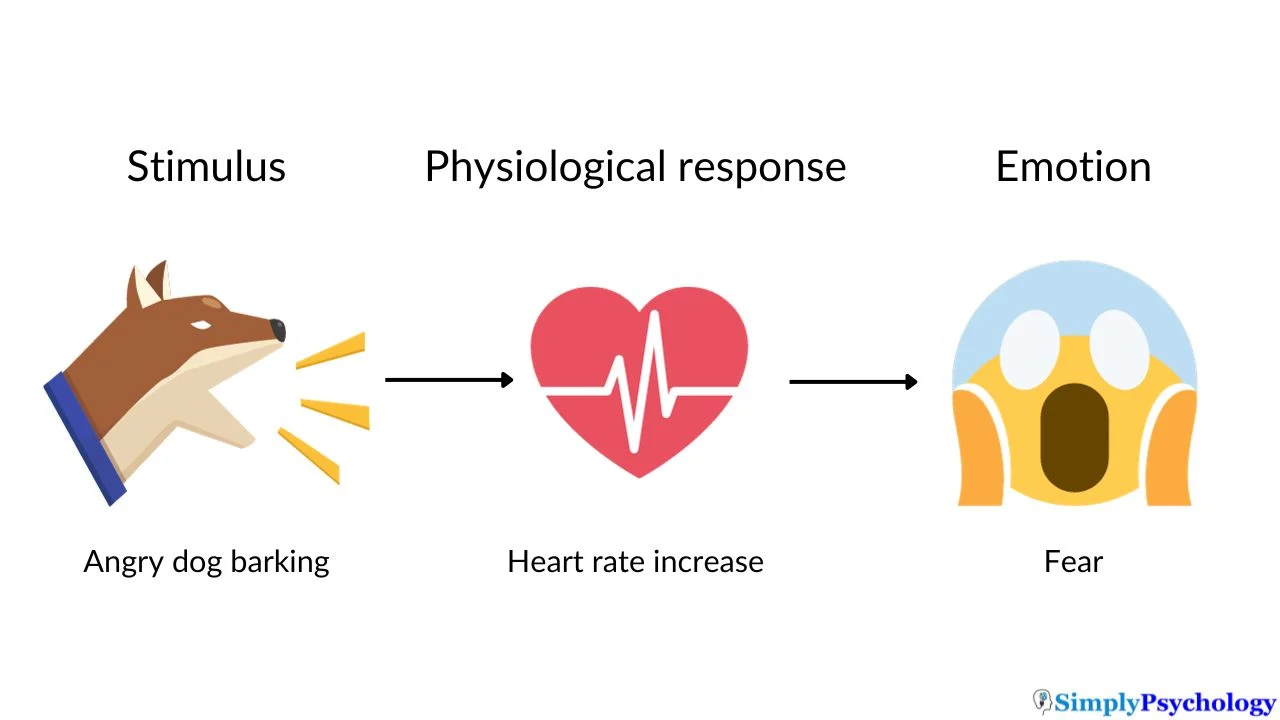
James-Lange theory
emotions result from the experience of physiological reactions in the body
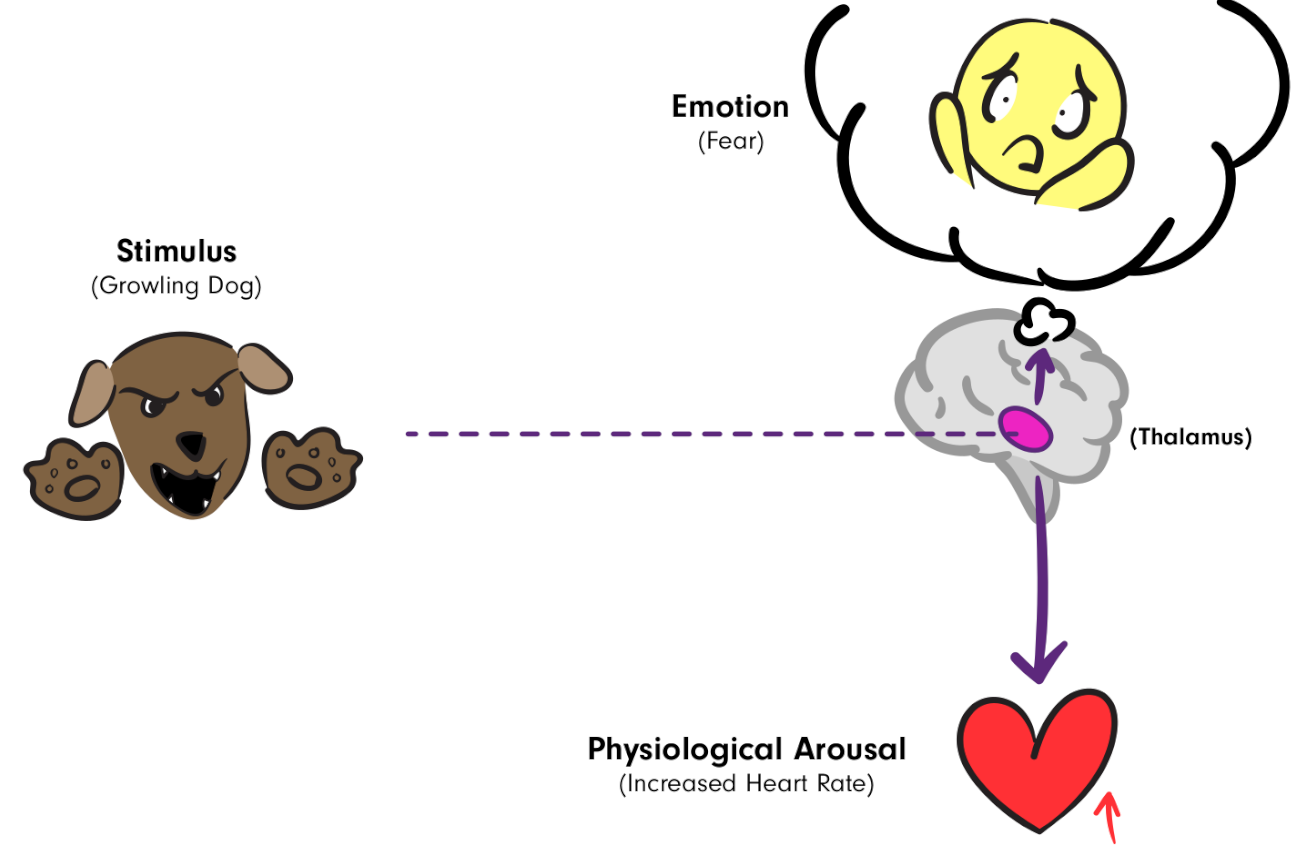
Cannon-Bard theory
emotions and bodily responses both occur simultaneously due to how parts of the brain process information
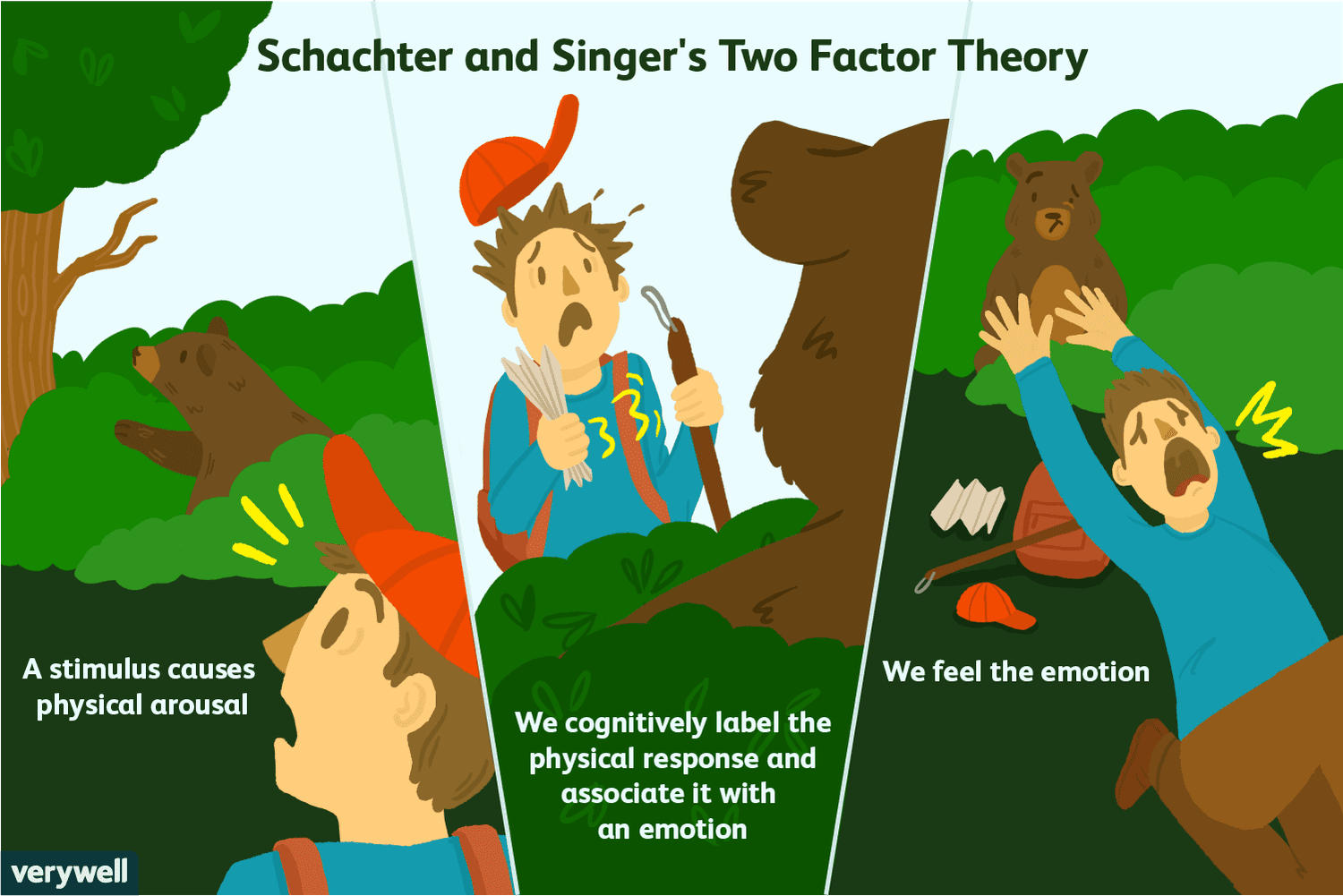
two-factor theory
how we experience an emotion is influenced by the cognitive label we apply to explain the physiological changes we have experienced
display rules
rules that are learned through socialization and that dictate what emotions are suitable in certain situations
affect-as-information theory
people use their current moods to make decisions, judgments, and appraisals, even if they do not know the sources of the mood
guilt
a negative emotional state associated with anxiety, tension, and agitation
Although it is difficult to tease apart nature from nurture, there is evidence that in North America, women display emotions more easily than men. To the extent that this is based on culture and not biology, how and when we express emotions is governed by which of the following?
A. the eyes and mouth
B. display rules
C. hormonal differences
D. classical conditioning
B. display rules
Around the world, most people eat lunch at about the same time of day. Why is this?
A. Across cultures, noon is of special significance, and it was originally celebrated by feasting.
B. Hormones like ghrelin surge around midday.
C. We are classically conditioned to eat at midday.
D. The hypothalamus is very active when the sun is at its peak height.
C. We are classically conditioned to eat at midday.
Harper's mother always told him that even if he felt sad, if he smiled he would soon feel happier. Which theory of emotion best aligns with this advice?
A. James-Lange theory
B. Cannon-Bard theory
C. affect-as-information theory
D. Schachter-Singer two-factor theory
A. James-Lange theory
Hiromi's parents have taught him to keep his emotions inside. "You should be careful not to let people know too much about what you are feeling," his father tells him. Hiromi is being taught which __________ are appropriate in different situations.
A. extrinsic motives
B. intrinsic drives
C. display rules
D. need hierarchies
C. display rules
Marion has just spent 2 hours mowing the lawn, and she is sweaty and tired. She comes into the house feeling very dehydrated and goes right to the kitchen for a glass of water. In this case her biological deficiency is an example of a
A. incentive.
B. drive.
C. homeostasis.
D. need.
D. need
Mbenga woke up grumpy so her mother tells her to "Turn that frown upside down." When Mbenga goes to school she tries to smile as much as possible during the day. Much to her surprise she does feel happier after smiling all day. Mbenga's happy feeling is consistent with the __________ theory of emotions.
A. sociobiological
B. James-Lange
C. Schachter-Singer two-factor
D. Cannon-Bard
B. James-Lange
McKenzie has not had anything to eat since she had a small breakfast 6 hours ago. Her empty stomach is now producing a hormone that should stimulate her to get something to eat. What is that hormone?
A. leptin
B. ghrelin
C. insulin
D. glucose
B. ghrelin
Miranda has been feeing sad a lot lately. Her wife notices that she is sad in nearly every situation, even when it is not appropriate. Luckily, Miranda's wife is a psychologist so she knows that the best way to help her regulate this __________ emotion is through the use of
A. secondary; distraction.
B. secondary; rumination.
C. primary; rumination.
D. primary; distraction.
D. primary; distraction
Rumination
Involves dwelling on negative thoughts and feelings, often repeatedly replaying problems without finding solutions.
Distraction
involves actively shifting attention away from negative thoughts and focusing on something else
Patient I.K. has a normal IQ, has functional memory and attention, and does well in school. However, she shows no fear conditioning. Even though she can tell you that a certain noise is associated with a painful electric shock, her body shows no physical signs of fear when she hears the noise. Which part of her brain is most likely to be damaged?
A. hypothalamus
B. pituitary gland
C. amygdala
D. hippocampus
C. amygdala
The saying that "humans are social animals" is a reference to which of the following motivations?
A. drive reduction
B. the need to belong
C. optimal level of arousal
D. the need for achievement
B. the need to belong
Vico is about to get evicted from her apartment, so she does not have the energy to return a call from a friend wanting to make lunch plans. According to Maslow's need hierarchy, Vico's __________ needs must be satisfied before higher needs such as __________.
A. physiological; belonging and love
B. safety; esteem
C. extrinsic; intrinsic
D. physiological; self-actualization
A. physiological; belonging and love
When choosing a roommate, your housing adviser suggests that you choose someone with a similar optimal level of arousal to yours. If you follow her advice, whom will you choose to live with?
A. Just like you, Katie is fairly tidy, but not a total neat freak.
B. Just like you, Tawny has a serious sweet tooth, but you both also love eating sushi.
C. Just like you, Meredith enjoys the occasional party, but mostly she likes to hang out in small groups watching movies and playing board games.
D. Just like you, Kristina is academically ambitious and hopes to go to graduate school in a scientific field.
C. Just like you, Meredith enjoys the occasional party, but mostly she likes to hang out in small groups watching movies and playing board games.
When Steve wanted to bake a pumpkin pie, Brett pointed out that it was the middle of the summer, and not the time of year for pumpkin pie. Steve told Brett that she was being overly influenced by which of the following?
A. familiarity
B. classical conditioning
C. hormones
D. cultural factors
D. cultural factors
Which story is most consistent with the affect-as-information theory?
A. Jimmie is in a fantastic mood when she goes with her realtor to look at houses. Each house seems so elegant, but Jimmie decides to take some time to make a decision rather than rush into a commitment.
B. Colonel Star has been in a bad mood all day, ever since she had a flat tire on the freeway. She is evaluating her employees today, and without realizing it, she ranks them all a bit lower than she did last year.
C. Although Jordan has felt depressed for the past several weeks, he still would rate his life as highly satisfactory: he has a great job, a supportive family, and lots of friends.
D. Lynn is trying to decide where to go for vacation. To make her final choice, she uses a complex ranking scheme that factors in rational information like cost, language skills, and climate.
B. Colonel Star has been in a bad mood all day, ever since she had a flat tire on the freeway. She is evaluating her employees today, and without realizing it, she ranks them all a bit lower than she did last year.
While Joey hopes his painting will win a prize at an upcoming art show, Colin has dozens of full sketchbooks that he never plans to show anybody. In doing artwork, Joey experiences __________ while Colin experiences __________.
A. a drive; a behavior
B. extrinsic motivation; intrinsic motivation
C. self-determination; self-perception
D. incentives; arousal
B. extrinsic motivation; intrinsic motivation
Dwayne enjoys spending calm, quiet evenings at home watching old movies. Debbie likes to engage in exciting activities, such as skydiving, on her days off. The fact that Dwayne and Debbie choose to spend their free time in these ways is best explained by ______.
A. satisfaction of needs
B. incentives
C. optimal level of arousal
D. drive reduction
C. optimal level of arousal
Vince and Edith are training for a marathon. When asked why they are running the race, Vince says he wants the medal that the race organizers give out to everyone who crosses the finish line. Edith responds that she enjoys trying new things. Vince’s behavior is most likely explained by ______, whereas Edith’s behavior is most likely explained by ______.
A. extrinsic motivation; intrinsic motivation
B. intrinsic motivation; extrinsic motivation
C. self-perception theory; self-determination theory
D. self-determination theory; self-perception theory
A. extrinsic motivation; intrinsic motivation
When Terry’s stomach starts growling, he decides it is time for lunch. After eating a burrito and tortilla chips, he feels full and does not want to eat more. Which of the following does NOT play a role in his short-term feeling of fullness?
A. increased glucose in his bloodstream
B. decreased ghrelin in his stomach
C. activation of his hypothalamus
D. release of leptin in his saliva
D. release of leptin in his saliva
Thomas sends his daughter Sophia to spend the summer with her grandparents, who eat dinner at 5:00 PM. Upon her return home, Sophia wants to eat dinner at 5:00 PM every night, because she now associates that time of day with eating. Sophia’s change in desired mealtime has most likely been influenced by ______.
A. drive reduction
B. classical conditioning
C. optimal arousal
D. low levels of the hormone ghrelin
B. classical conditioning
Mr. Ray is a middle school math teacher who wants to teach his students achievement motivation so they can achieve their long-term goal of doing well on the state math tests. Mr. Ray can help his students develop achievement motivation through all of the following methods EXCEPT ______.
A. helping them develop grit
B. showing them that their hard work leads to success
C. training them to delay gratification
D. teaching intrinsic motivation
D. teaching intrinsic motivation
Hannah enjoys playing video games because every time she scores a point, processing in her brain causes an excited emotion and an increase in her heart rate at about the same time. The ______ theory has been proposed to explain emotion in the way Hannah experienced it.
A. Cannon-Bard
B. Grison-Gazzaniga
C. James-Lange
D. two-factor
A. Cannon-Bard
After Bernadette is in a car accident, she is extra friendly to people she meets. In fact, she does not seem to realize when she might be revealing personal information to untrustworthy strangers. Bernadette may have brain damage in her ______.
A. right prefrontal cortex
B. left prefrontal cortex
C. amygdala
D. thalamus
C. amygdala
Bianca is sad and anxious because her sister is moving across the country to take a new job. To make herself feel better, Bianca thinks of her sister’s new city as a vacation destination—a place Bianca can visit and explore. Bianca is successfully regulating her emotional state by using ______.
A. rumination
B. distraction
C. thought suppression
D. positive reappraisal
D. positive reappraisal
Tori sometimes refrains from arguing with her colleagues in staff meetings because she believes it is not appropriate for women to show anger. Tori’s belief about emotional expressiveness in women is best explained by ______.
A. self-determination theory
B. thought suppression
C. display rules
D. affect-as-information theory
C. display rules
Madison frequently checks the cell phone of her husband, Max, to see if he is texting other women. Max catches her and is very hurt by her behavior. Madison loves Max very much and feels bad that she hurt him. In this situation, Madison is most likely to feel the emotion of ______.
A. guilt
B. pride
C. anger
D. fear
A. guilt
What are the four factors that affect achievement motivation?
setting good goals, feeling a sense of self-efficacy, being able to delay gratification, and having grit