AP bio unit 1
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Polarity
Differences in atomic electronegativity across an atom
Hydrogen bond
a weak bond between the negative and positive regions of 2 separate molecules
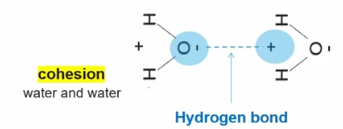
Cohesion
2 of the same molecule form hydrogen bonds with one another
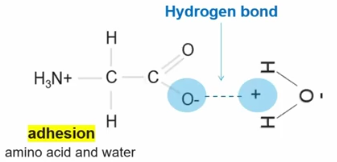
Adhesion
2 different molecules form hydrogen bonds with one another
Surface tension
The ability of water closer to the surface to pack closer together due to cohesion. (increased hydrogen bonding at the surface)
How does water’s adhesion property make it an essential substance?
Adhesion gives it high solvency ability in its liquid state.
because organisms need a variety of nutrients and are made up of water, the high solvency allows nutrients to be easily accessible for cells
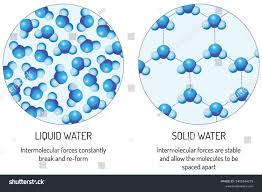
Why is ice less dense than liquid water?
Due to the cohesive properties of water.
the orientation of hydrogen bonds causes the water molecules to push out farther
How does water’s cohesive property related to thermal energy?
Its cohesive property allows it to absorb a lot of thermal energy before changing states, meaning it can resist sudden changes in temperature.
helpful for organisms that rely on the water to regulate their body temperature.
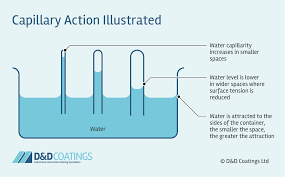
Capillary Action
The result of adhesive and cohesive properties.
plants utilize this to gather water through their roots
Law of the conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed
Why do living systems need a constant input of energy?
To grow, reproductive, and maintain organization
What are carbon skeletons and what are the 3 shapes they can form?
Multiple carbons bonded together, other atoms can attach
chains
Rings
Branches
What is formed between 2 interacting monomers?
A covalent bond
Dehydration synthesis
form covalent bonds
Create macromolecules
The sub components of water (H and OH) are removed and replaced by a covalent bond
The H and OH form a water molecule separate from the macromolecule (byproduct)
Hydrolysis
cleave covalent bonds
Breaks a macromolecule into its monomers
A water molecule is hydrolyzed (broken) into its sub components (H and OH) and each is added to a different monomer.
How are the properties of biological molecules determined?
By their structure and thus function.
Primary structure
The specific order of amino acids of a protein
R-groups
The atoms attached to the central carbon
can be hydrophilic
Hydrophobic
Or ionic
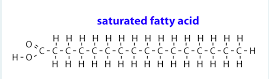
Saturated fatty acid
Add a picture
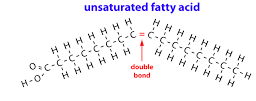
Unsaturated fatty acid
Add a picture
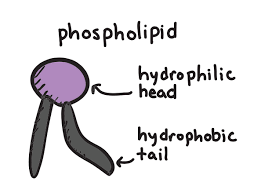
Phospholipid: name the regions
Insert picture
What are the 2 main molecules that make up membranes?
Phospholipids and proteins
What do hydrogen bonds between base pairs do in a DNA molecule?
Stabilize it
What connects nucleotides?
Covalent bonds
What is the directionality of the sub components of a protein?
Amino terminus and carboxyl terminus
Where are new amino acids added on a protein?
To the c (carboxyl) terminus
Secondary structure
Local folding of the amino acid chain (beta-sheets and alpha-helixes)
Tertiary structure
The overall 3d shape of the protein
Quaternary structure
The interactions between multiple polypeptides
Starch
Stored form of sugars and energy in plants
Glycogen
Stored form of energy and sugars in animals/vertebrates
Cellulose
Commonly provides strength in cell walls