Psychology - memory
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the name of the temporary memory store with which people can remember a few items for several seconds?
Short-term memory (STM)
State 2 ways in which STM is limited.
Limited capacity and limited duration.
Name the type of memory demonstrated below:
A) Being able to ride a bike.
B) Remembering your first day of school.
C) Knowing that an MP is a type of politician.
A) Procedural
B) Episodic
C) Semantic
Is memory best described as an active or passive process?
An active process.
Which of the following is true?
A) Encoding new memories happens fairly automatically
B) Memories are retrieved in exactly the same form as they were remembered
C) Both encoding and retrieval often involve mental effort
D) Items always enter long-term memory even if the person is not paying attention
C) Both encoding and retrieval often involve mental effort
Which of the following is an input process to memory?
A) Encoding
B) Storage
C) Retrieval
D) Forgetting
A) Encoding
Murdock (1962) conducted an important experiment into memory. What is the name for the graph showing the effects found in this study?
Serial position curve.
Explain how Murdock’s experiment can be used to evaluate the multi-store model. [3]
Murdock’s serial position curve supports the model [1]. The primacy effect is explained by items being rehearsed into LTM [1]. The recency effect is explained by a few items remaining within a limited capacity STM [1].
Is rehearsal a sufficient process to encode new information to LTM?
No - often rehearsal is not enough
Name 3 ways people might be in a different state when they try to retrieve a memory?
Different mood.
Drugs such as caffeine.
Consumption of alcohol.
(Also accept a different physical location)
Which of the following describes a schema?
A) A visual memory technique that can be used when revising
B) A mental concept, influenced by life experience and culture
C) the process of encoding things to LTM
D) A belief that people have about other cultures
B) A mental concept, influenced by life experience and culture
How long can items be held in the STM without making an effort to rehearse them?
Up to approx. 30 seconds
Is the STM best described as a permanent store or a temporary store?
A temporary store.
How much information can LTM hold?
Unlimited/ does not get full.
What is most important for encoding semantic long-term memories - understanding the meaning, or seeing the visual image?
Understanding the meaning (because it uses semantic encoding).
Name 2 things that can act as a cue to retrieving a memory.
Any 2 from:
The first letter
A questions
An image
An aspect of the learning context
Which of the following is another term for STM and emphasises that it is an active process?
A) LTM
B) Working memory
C) Free recall
D) Hard drive
B) Working memory
Which of the following is not true of STM?
A) Is it used for active processing of information in everyday tasks
B) People can use it to follow a series of instructions
C) It can rehearse items to store them for longer
D) It is simply used for storage
D) It is simply used for storage
Explain the role of attention in taking in new memories [2].
Information is only taken into memory if a person pays attention to it [1]. This typically happens when they find things interesting or emotional in some way/ if they don’t pay attention things will not enter STM and therefore will not be processed and encoded to LTM [1].
Explain the role of repetition in the process of encoding things to long-term [4].
It is important for memory, as more exposure increases the chances of encoding [1]. However, simply repeating things doesn’t always lead to encoding, particularly if information is hard to understand [1]. More important processes are active, such as linking new information to what is already known/ retrieving information from memory in a way that is spaced out over time helps to consolidate it [1]. Answers could also refer to the multi-store model of memory, which makes the over-simplistic claims that rehearsal is the only means of encoding items to LTM [1].
Draw (or describe?) a diagram of the multi-store memory.
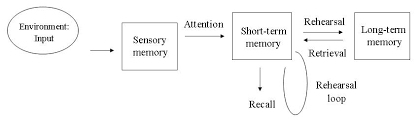
Name the researchers who devised the multi-story model of memory.
Atkinson and Shiffrin.
Name the 3 stores in the multi-story model of memory.
Sensory memory, STM and LTM.
What is the process by which information enters the STM? (Multi-story model of memory).
Attention.
What is the process by which information is kept in the STM for longer? (Multi-story model of memory).
Rehearsal.
What is the process by which information is encoded to the LTM? (Multi-story model of memory).
Rehearsal.
Briefly describe a possible experiment that could be run to demonstrate the primacy and recency effect. [3]
Reading out a list of random words to a group of participants [1]. Each participant would have to write down all of the words they could remember [1]. The researcher would count how many times each word was recalled, with the expectation that the words at the beginning and end of the list would be recalled more frequently on average [1].
How long does sensory memory last, and what it’s capacity? [3]
Visual memory is a very brief store [1]. The visual store was found by Sperling (1960) to have a large capacity but a duration of only 0.5 seconds [1]. The acoustic store is thought to last around 2 seconds [1].
What was the name of the British researcher who studied distortions in memory using folk stories?
Bartlett.
What 4 types of distortions did Bartlett find?
Additions, subtractions, transformations (to familiar) and preservation of detached detail.
Which of the following could result in a fake memory?
A) Being asked a leading question
B) Forgetting something
C) A blow to the head
D) Consuming caffeine or drugs
A) Being asked a leading question
Why was the story Bartlett used hard for the participants to understand and remember?
It came from a culture that was unfamiliar to the participants [1]. Therefore they lacked schema knowledge to connect it to [1].