Connect Assignment - Body Orientation
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Body Orientation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Body Orientation FINAL
Activity 1: Dissection
Module: Body Orientation
Topic: Body Position
View: Anterior, Supine, and Prone
Anterior
Definition: Toward the front of the body; in front of.
Example: The sternum (breastbone) is anterior to the heart.
Memory Tip: Think “ant” → front — anterior means toward the front.
Posterior
Term: Posterior
Definition: Toward the back of the body; behind.
Example: The spine is posterior to the lungs.
Memory Tip: “Posterior” sounds like “posterior side” (backside) — it means toward the back.
Anatomical Position
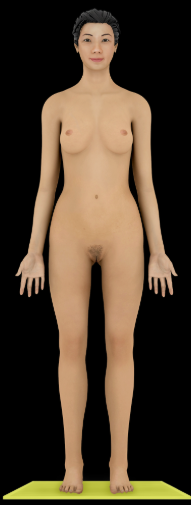
Description:
Reference position for anatomical description
An individual in anatomical position is standing erect with arms at sides, palms facing forward with fingers pointing downward, feet parallel to each other and flat on the floor, and eyes directed forward
Prone

Description:
Position of the body when lying face down
Comment:
For forearm movement (in anatomical position), pronation directs palm posteriorly
Opposite of supine
Supine
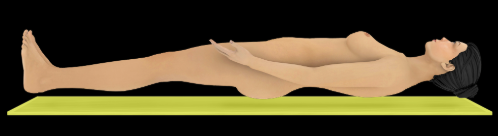
Description:
Position of the body when lying face up
Comment:
For forearm movement (in anatomical position), supination directs palm anteriorly
Opposite of prone
Activity 2: Dissection
Module: Body Orientation
Topic: Planes of Section
View: Anterior and Anterior-Lateral
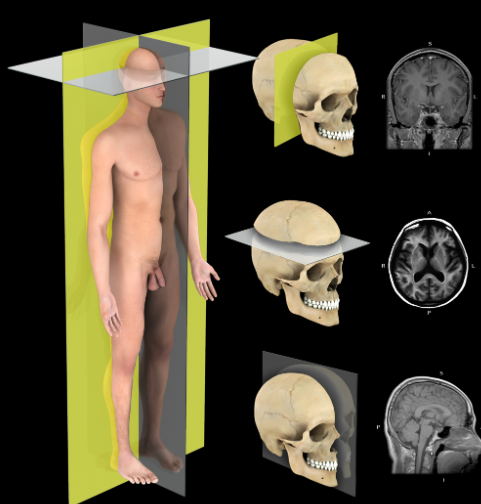
Coronal plane
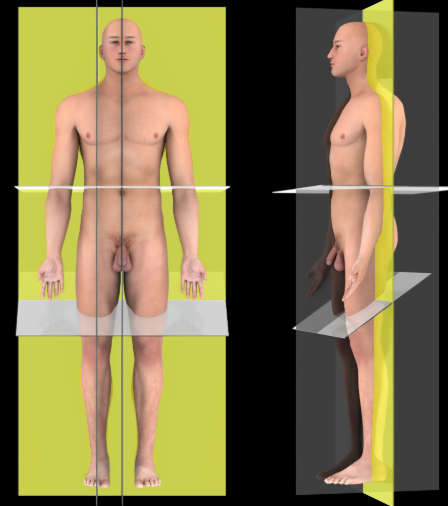
Description:
A vertical plane that passes parallel to the long axis of the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior portions
Also known as:
Frontal plane
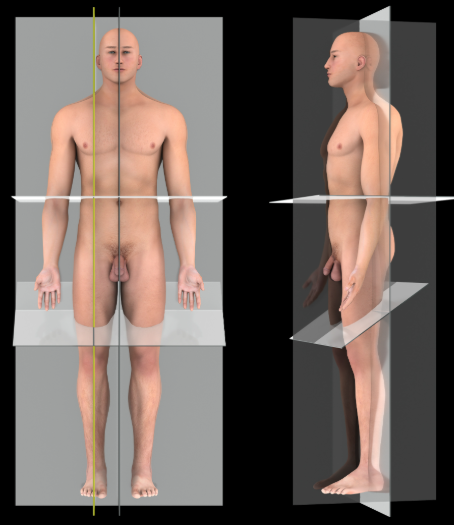
Median plane
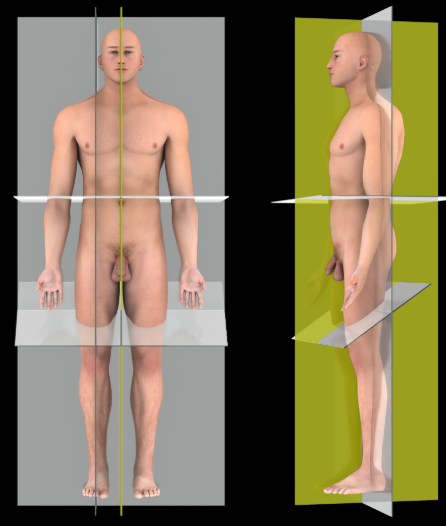
Description:
A vertical plane that passes parallel to the long axis of the body through the midline of the body, dividing it into equal right and left halves
Comment:
Median plane is a specific example of a sagittal plane
Also known as:
Midsagittal plane
Oblique plane
Description:
A plane that passes through the body on an angle, and is not one of the standard anatomical planes
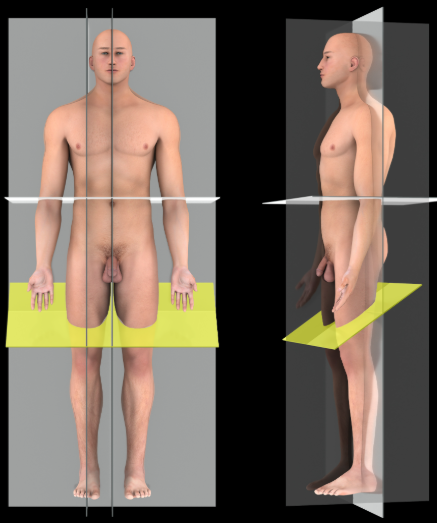
Sagittal plane
Description:
A vertical plane that passes parallel to the long axis of the body, dividing it into right and left portions
Comment:
Sometimes called parasagittal plane
Median (midsagittal) plane passes through midline of body and divides it into equal right and left halves
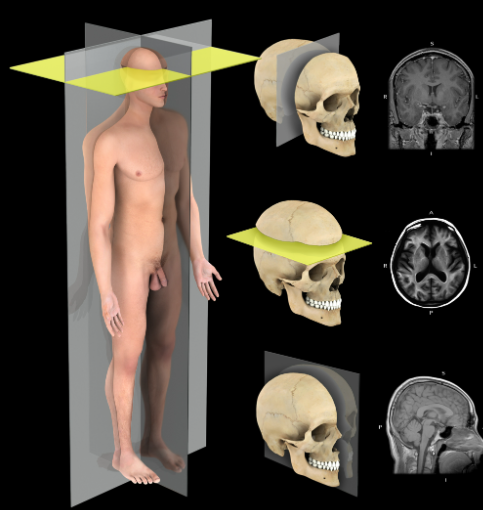
Transverse plane
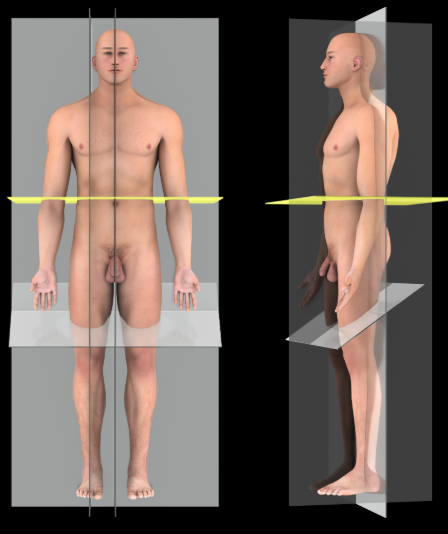
Description:
A horizontal plane that passes perpendicular to the long axis of the body, dividing it into superior and inferior portions
Comment:
Also called horizontal plane or cross-section
Transverse planes can also be named for specific landmarks that they pass through, e.g. subcostal plane, transumbilical plane, and intertubercular plane
Activity 3: Dissection
Module: Body Orientation
Topic: Planes of Section
View: Anterior-Lateral
Coronal plane
Description:
A vertical plane that passes parallel to the long axis of the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior portions
Also known as:
Frontal plane
Median plane
Description:
A vertical plane that passes parallel to the long axis of the body through the midline of the body, dividing it into equal right and left halves
Comment:
Median plane is a specific example of a sagittal plane
Also known as:
Midsagittal plane
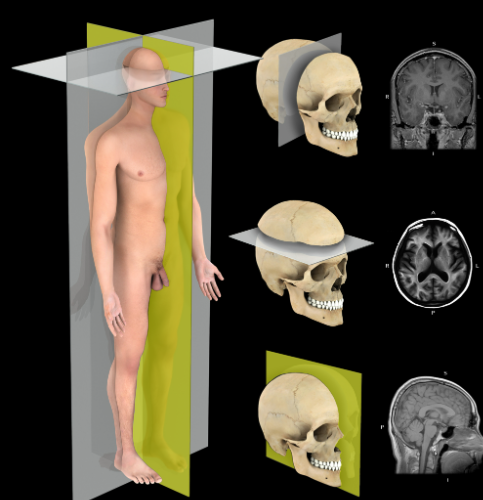
Transverse plane
Description:
A horizontal plane that passes perpendicular to the long axis of the body, dividing it into superior and inferior portions
Comment:
Also called horizontal plane or cross-section
Transverse planes can also be named for specific landmarks that they pass through, e.g. subcostal plane, transumbilical plane, and intertubercular plane
Anterior
Description:
Toward the front of the body (e.g., the sternum is anterior to the heart)
Opposite of posterior
Comment:
Ventral, sometimes used synonymously with anterior, relates to the belly
Activity 4: Dissection
Module: Body Orientation
Topic: Directional Terms
View: Anterior, Lateral, and Midsagittal
Deep
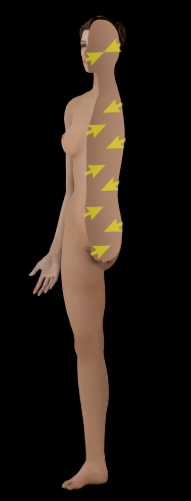
Description:
Away from the surface of the body or organ (e.g., Bones are deep to skin and skeletal muscles)
Opposite of superficial
Distal
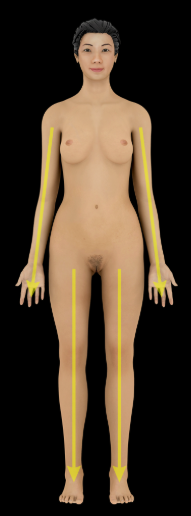
Description:
Farther from trunk or origin of a structure (e.g., the wrist is distal to the elbow)
Opposite of proximal
Inferior
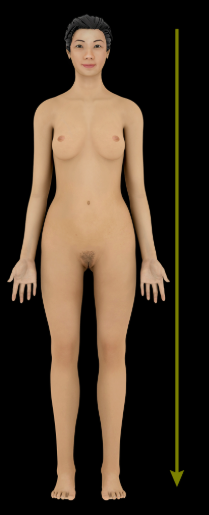
Description:
Downward or below (e.g., the diaphragm is inferior to the heart)
Opposite of superior
Comment:
In humans, synonymous with caudal (toward the tail)
Lateral
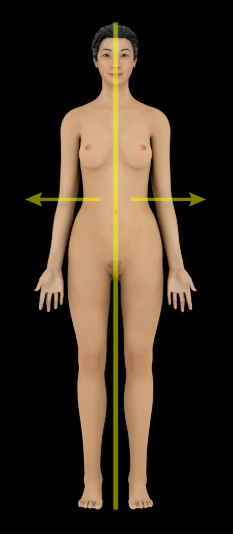
Description:
Away from the midline of the body (e.g., the lungs are lateral to the heart)
Opposite of medial
Medial
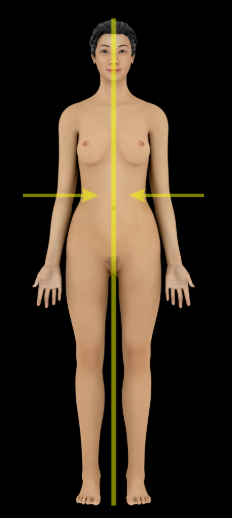
Description:
Toward the midline of the body (e.g., the heart is medial to the lungs)
Opposite of lateral
Posterior
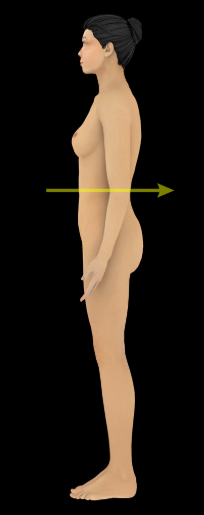
Description:
Toward the back of the body or relating to the back (e.g., the heart is posterior to the sternum)
Opposite of anterior
Comment:
Dorsal, sometimes used synonymously with posterior, relates to the back (L. dorsum = back of the body)
Proximal
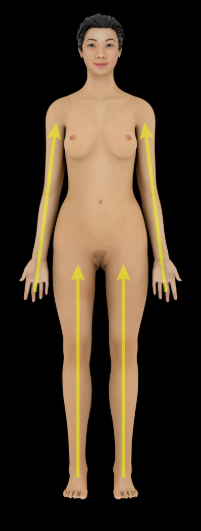
Description:
Closer to trunk or origin of a structure (e.g., the elbow is proximal to the wrist)
Opposite of distal
Superficial
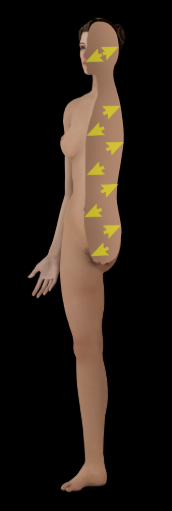
Description:
Toward the surface of the body or organ (e.g., Skin is superficial to muscles)
Opposite of deep
Superior
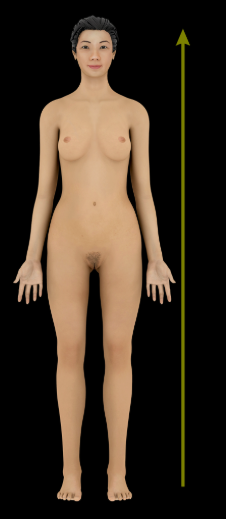
Description:
Upward or above (e.g., the heart is superior to the diaphragm)
Opposite of inferior
Comment:
Cranial, sometimes used synonymously with superior, relates to the head (L. cranium = head of the body)
Activity 5: Dissection
Module: Body Orientation
Topic: Body Cavities
View: Anterior and Lateral
Abdominal cavity
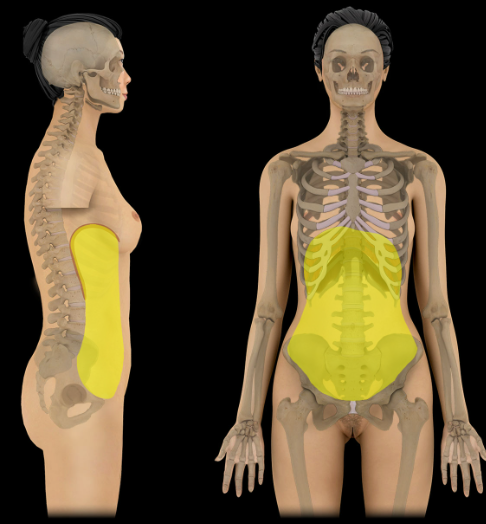
Location:
Abdominal region
Description:
Bounded by abdominal walls, thoracic diaphragm (superior), and pelvic brim (inferior)
Major organs include: stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and ureters, suprarenal glands, aorta, inferior vena cava, and lumbar nerve plexus
Comment:
Inferior part of abdominal cavity is the greater (or false) pelvis (i.e., between iliac fossae, superior to pelvic inlet)
Abdominal and pelvic cavities combine to form a continuous abdominopelvic cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity
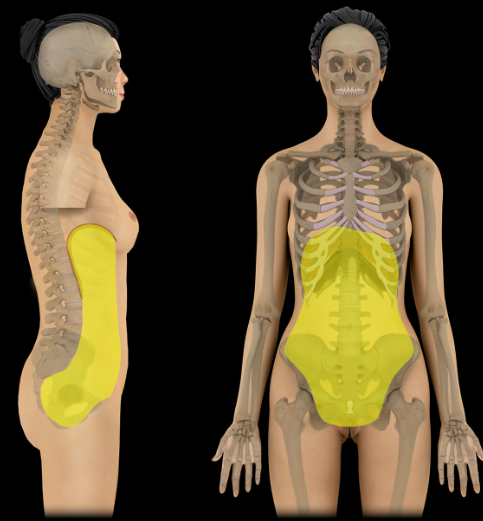
Location:
Trunk, between thoracic and pelvic diaphragms
Description:
Continuous cavity formed by abdominal and pelvic cavities
Major abdominal organs include: stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and ureters, suprarenal glands, aorta, inferior vena cava, and lumbar nerve plexus
Major pelvic organs include: urinary bladder, loops of small intestine, inferior part of sigmoid colon, rectum, and reproductive organs (ovaries, uterus, vagina in female; prostate and seminal glands in male)
Cranial cavity
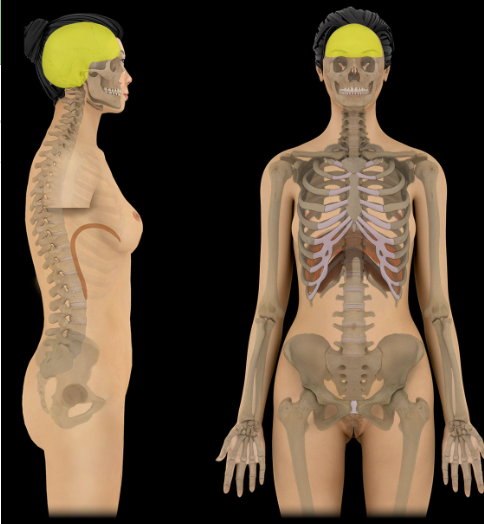
Location:
Skull
Description:
Space in skull that contains brain, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Formed by frontal, occipital, sphenoid, ethmoid bones, parietal, and temporal bones
Diaphragm
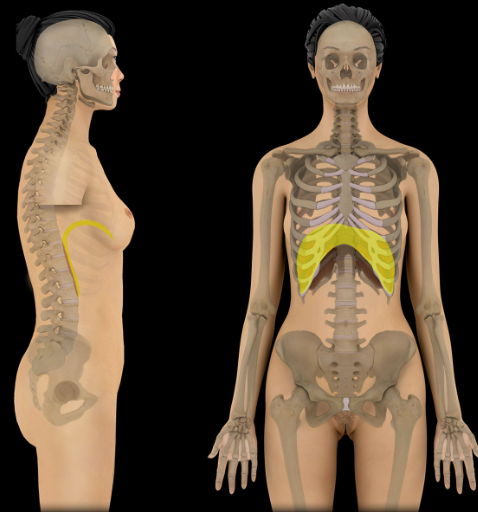
Action:
Dome of diaphragm flattens during inspiration
Contraction increases vertical dimension of thoracic cavity
Origin:
Sternal part (not always present): xiphoid process
Costal part: ribs 5-10 and their costal cartilages
Lumbar part: arcuate ligaments and L1-3 vertebral bodies
Insertion:
Central tendon
Innervation:
Phrenic nerve
Comment:
Primary muscle of respiration
Contraction (flattening) decreases intrathoracic pressure and increases intra-abdominal pressure
Dorsal cavity
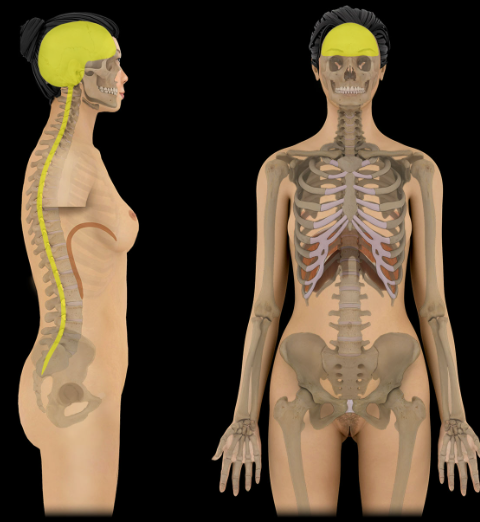
Location:
Skull
Vertebral column
Description:
Composed of two cavities - cranial cavity and vertebral canal
Cranial cavity enclosed within skull and vertebral canal enclosed by vertebrae
Comment:
Also known as posterior aspec
Mediastinum
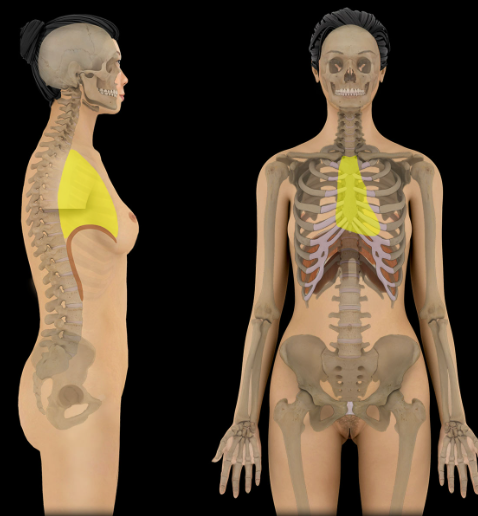
Location:
Thoracic cavity
Description:
Middle region of thorax
Lies between sternum and thoracic vertebral bodies
Separates right and left pulmonary cavities
Divided into superior and inferior parts
Inferior mediastinum subdivided into middle, posterior, and anterior parts
Comment:
Superior mediastinum includes: great vessels, thymus (remnant in adult), thoracic duct, and parts of trachea and esophagus
Middle mediastinum includes: heart, pericardium, and roots of great vessels
Posterior mediastinum contains: thoracic aorta, esophagus, and thoracic duct
Anterior mediastinum contains: loose connective tissue (may include thymic remnant in adult)
Thoracic cavity divided into three parts: mediastinum and right and left pulmonary cavities
Latin: mediastinum = middle septum
Pelvic cavity
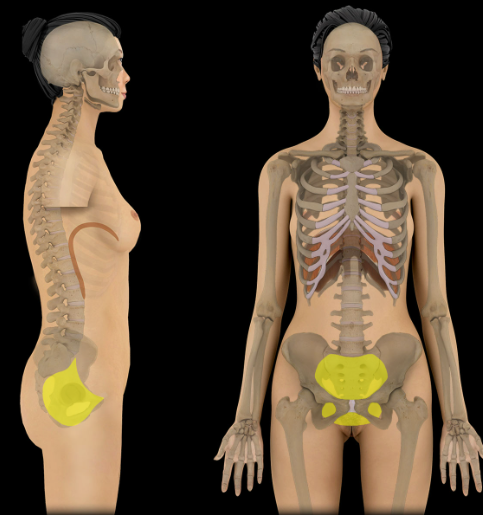
Location:
Pelvic region
Description:
Bounded by pelvic inlet (superiorly) and pelvic outlet (inferiorly)
Major organs include: urinary bladder, loops of small intestine, inferior part of sigmoid colon, rectum, and reproductive organs (ovaries, uterus, vagina in female; prostate and seminal glands in male)
Continuous superiorly with abdominal cavity
Also known as:
Lesser (or true) pelvis
Pulmonary cavity
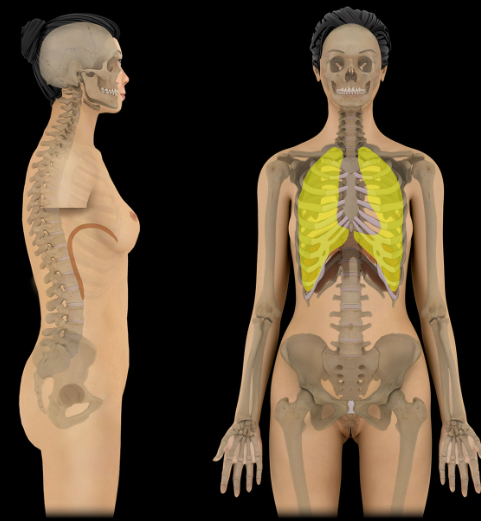
Location:
Thorax
Description:
Bilateral subdivision of thoracic cavity (separated by mediastinum)
Contain lungs and pleurae
Lined by parietal pleura
Comment:
Thoracic cavity has three subdivisions: a central mediastinum (contains heart and thoracic parts of great vessels, trachea, esophagus, and thymus) and bilateral pulmonary cavities (contains lungs and pleurae)
Thoracic cavity
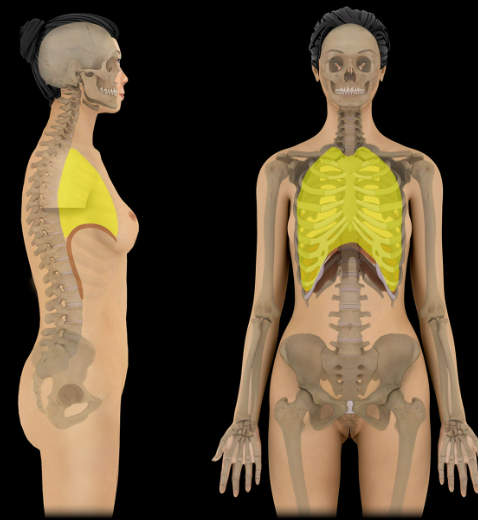
Location:
Thorax
Description:
Cavity of the chest
Bounded by sternum, ribs and costal cartilages, intercostal muscles, thoracic vertebrae, and diaphragm
Three subdivisions: a central mediastinum (contains heart and thoracic parts of great vessels, trachea, esophagus, and thymus) and bilateral pulmonary cavities (contains lungs and plurae)
Ventral cavity
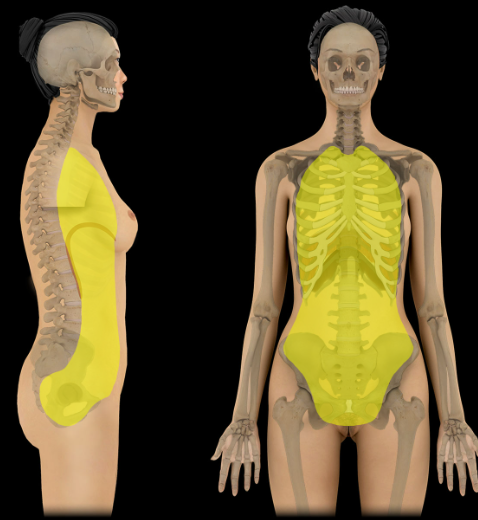
Location:
Trunk
Description:
Composed of two large cavities - thoracic and abdominopelvic
Diaphragm separates these two cavities
Both cavities lined by serous membranes
Vertebral canal
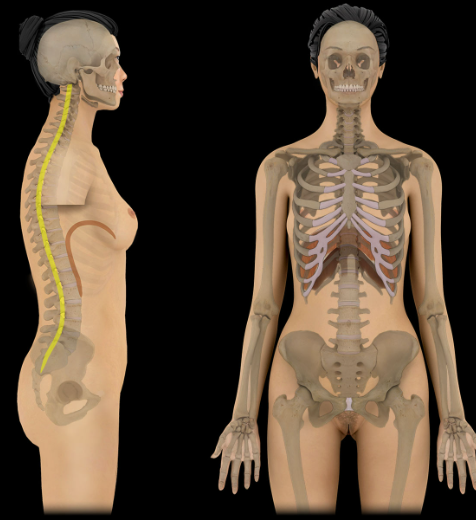
Location:
Vertebral column
Description:
Canal formed by combined vertebral foramina
Comment:
Contains spinal cord, meninges, spinal nerve roots, blood vessels, and fat