Study guide bio cellular respiration
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/163
Last updated 12:18 PM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
1
New cards
Balanced aerobic respiration equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --\> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy
2
New cards
difference between breathing and cellular respiration
breathing: exchanging CO2 for o2
3
New cards
label the inner and outer membrane, cristae and matrix of a mitochondrion
label
4
New cards
label a diagram summarizing aerobic cellular respiration
label
5
New cards
what is the name of the enzyme that makes ATP from ADP and P
ATP synthase
6
New cards
what kinds of cells can survive (at least for a little while) without oxygen? (3)
yeast, bacteria, human muscle cells
7
New cards
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
8
New cards
How many (net) ATP molecules are made per 1 glucose molecule from glycolysis?
2
9
New cards
True or False! Glycolysis is aerobic.
false
10
New cards
Which electron carrier is made in glycolysis?
NADH
11
New cards
Which one of the following are required to make NADH?
NAD+
12
New cards
What is the goal of fermentation?
Regenerate NAD+ for use in glycolysis.
13
New cards
What do yeast cells produce during alcoholic fermentation (that also make them useful for producing products for human consumption)? Choose all that apply (2)
carbon dioxide, alcohol
14
New cards
What type of cells in your body do lactic acid fermentation?
muscle cells
15
New cards
Under what conditions will your cells do lactic acid fermentation?
exercising
16
New cards
An end product of the types of fermentation we have learned about is \_____ (check all that apply) (4)
alchohol and CO2 in yeast, 2 ATP from glycolysis, lactic acid in muscle cells and bacteria, regenerating NAD+ from NADH
17
New cards
Fermentation happens in the \____ of oxygen.
absence
18
New cards
which negatively charged subatomic particle is attracted to oxygen
electron
19
New cards
most of the ATP produced during cellular respiration is made during what step/process
ETC
20
New cards
Which molecule acts as a final electron acceptor in aerobic cellular respiration?
oxygen
21
New cards
which channel protein/enzyme is responsible for making ATP
atp synthase
22
New cards
during glycolysis, enzymes split a molecule of glucose into two molecules called
pyruvate
23
New cards
how many total atoms of oxygen are removed as waste in the Krebs cycle per 1 molecule of pyruvate
6
24
New cards
How many total atoms of oxygen are removed as waste in the ETC per molecule of glucose
6
25
New cards
which waste product of cellular respiration is exhaled by organisms with lungs
carbon dioxide
26
New cards
whe does glycolysis take place in a eukaryote
cytoplasm
27
New cards
how many atoms of carbon are in a single pyruvate molecule
3
28
New cards
where in the mitochondria does the kerbs cycle take place
matrix
29
New cards
which molecule is formed as a waste product of the Electron Transport Chain
water
30
New cards
which molecule is formed as a waste product of the Krebs cycle
carbon dioxide
31
New cards
when an electron and a proton are combined, which atom is formed
hydrogen
32
New cards
which molecule is necessary to perform aerobic respiration
oxygen
33
New cards
which step of cellular respiration is considered to be the oldest evolutionary
glycolysis
34
New cards
how many channel proteins in the ETC do the electrons from FADH2 pass through
2
35
New cards
another name for the Krebs cycle is the
citric acid cycle
36
New cards
atp synthase spins when this positively charged subatomic particle moves through it
proton
37
New cards
what are the 3 parts of aerobic respiration
glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain
38
New cards
Where does the ETC take place?
inner membrane of mitochondria
39
New cards
why is glycolysis the oldest step of respiration (3)
all cells do it, occurs in all types of cells, does not require oxygen
40
New cards
why is glycolysis considered to be anaerobic
does not require oxygen
41
New cards
how many ATP are made in glycolysis
2
42
New cards
how many ATP are made in the Krebs cycle per pyruvate
1
43
New cards
how many ATP are made in a prokaryote per glucose
2
44
New cards
how many ATP do you get from 1 NADH in the ETC
3
45
New cards
how many ATP do you get from 1 FADH2 in the ETC
2
46
New cards
how many FADH2 are made in glycolysis
0
47
New cards
how many FADH2 are made in the Krebs cycle per pyruvate
1
48
New cards
how many FADH2 are made in a prokaryote per glucose
0
49
New cards
How many FADH2 are brought to the ETC per glucose
2
50
New cards
How many NADH are made in the Krebs cycle per pyruvate
4
51
New cards
how many NADH are made in a prokaryote per glucose
2
52
New cards
How many NADH are brought to the ETC per glucose
10
53
New cards
how many protein channesl does 1 FADH2 pass through in the ETC
2
54
New cards
anaerobic
does not use oxygen, fermentation
55
New cards
breathing
exchanging Co2 for O2 in the lungs, not cellular respiration
56
New cards
respiration
ATP from glucose
57
New cards
glycolysis is the
oldest step of respiration
58
New cards
glucose
is broken down into 2 halves called pyruvates
59
New cards
pryvate
also called pyruvic acid, 3 carbons, a branching point
60
New cards
ATP
the energy that is obtained from cellular respiration
61
New cards
what cells in the body may undergo lactic acid fermentation during exercise
muscle cells
62
New cards
what directly powers ATP synthase
protons moving along their gradient
63
New cards
which cellular respiration waste product is made in the Krebs cycle
co2
64
New cards
which waste product of aerobic cellular respiration is created by the electron transport chain
water
65
New cards
why is yeast used to bake bread
the waste gas, co2, makes bread rise
66
New cards
How many molecules of NADH are produced during glycolysis?
2
67
New cards
in the absence of oxygen, the process of \____ follows glycolysis
fermentation
68
New cards
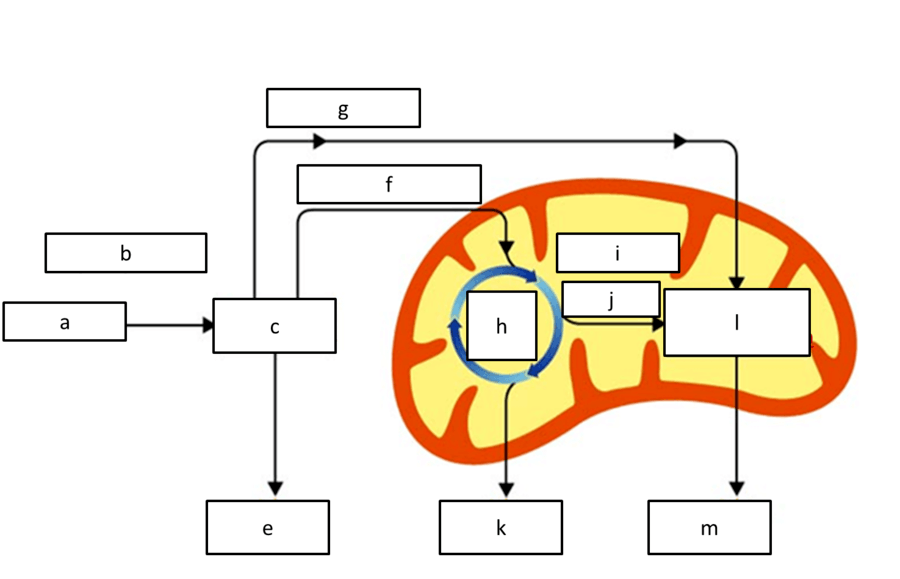
what product is represented by e, K, and M
atp
69
New cards
true or false: fermentation is an anaerobic process
true
70
New cards
in which way are photosynthesis and cellular respiration different
photosynthesis uses co2, cellular respiration makes co2
71
New cards
in yeast cells….
alcohol is produced after glycolysis
72
New cards
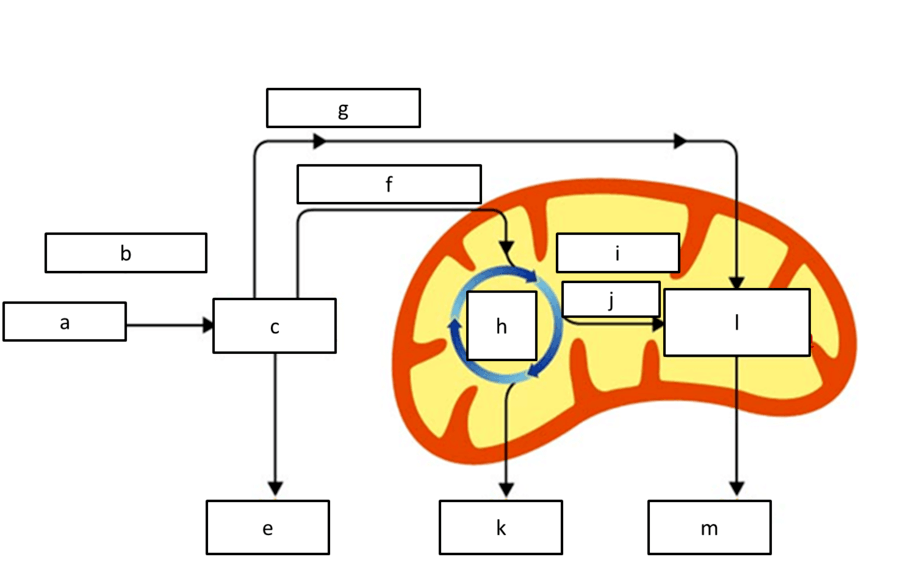
what product is represented by g, j/i
NADH
73
New cards
what enzyme in the ETC is responsible for generating the ATP molecules
atp synthase
74
New cards
which process produces the most ATP per molecule of glucose
aerobic respiration
75
New cards
both alcoholic and lactic acid fermentation begin with
pyruvate
76
New cards
the end products of the krebs cycle include all of the following except: pyruvic acid, NADH, ATP….
pyruvic acid
77
New cards
where does the krebs cycle take place
matrix
78
New cards
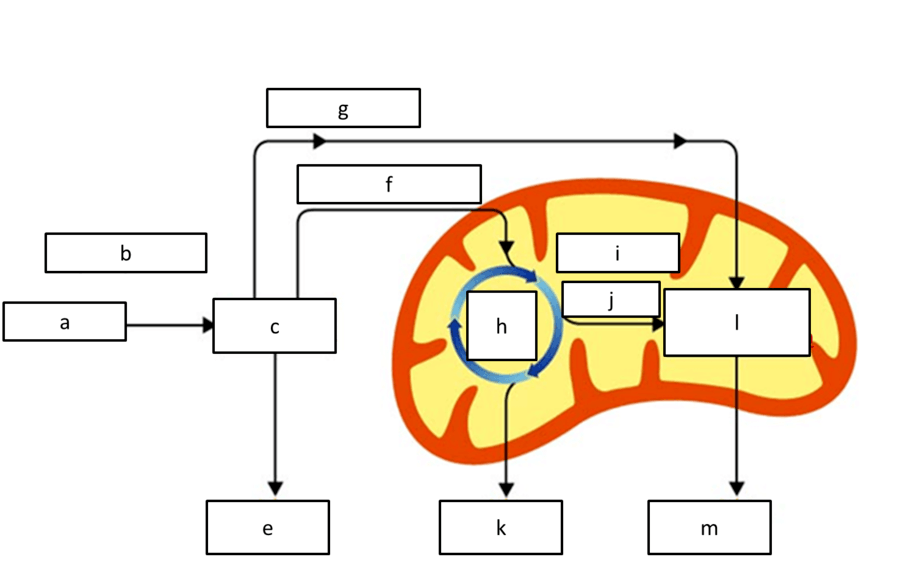
what process is represented by H
krebs cycle
79
New cards
which molecule is represented by F
pyruvate
80
New cards
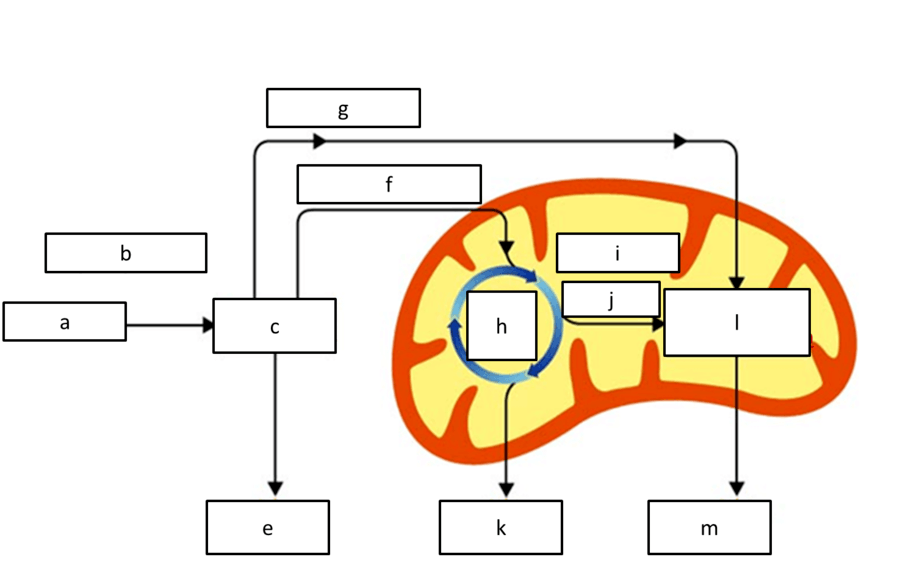
what respiration reactant is represented by A
glucose
81
New cards
each NADH molecule going to the ETC can produce a maximum of __ molecules of ATP
3
82
New cards
in order for fermentation to occur, what has to happen first
glycolysis
83
New cards
which organisms go through cellular respiration
plants and animals
84
New cards
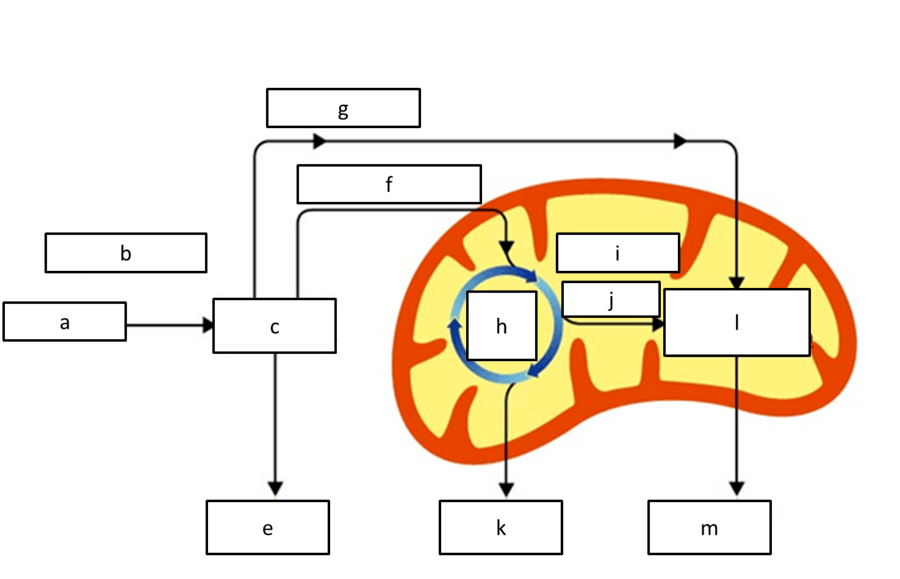
what process is represented by l
etc
85
New cards
how many NADH are produced by the Krebs cycle per pyruvate
4
86
New cards
what is pyruvate
3 carbon molecule made from glucose
87
New cards
which of the following is found in eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells
mitochondria
88
New cards
which fermentation process produces CO2 as a waste product
alchoholic fermentation
89
New cards
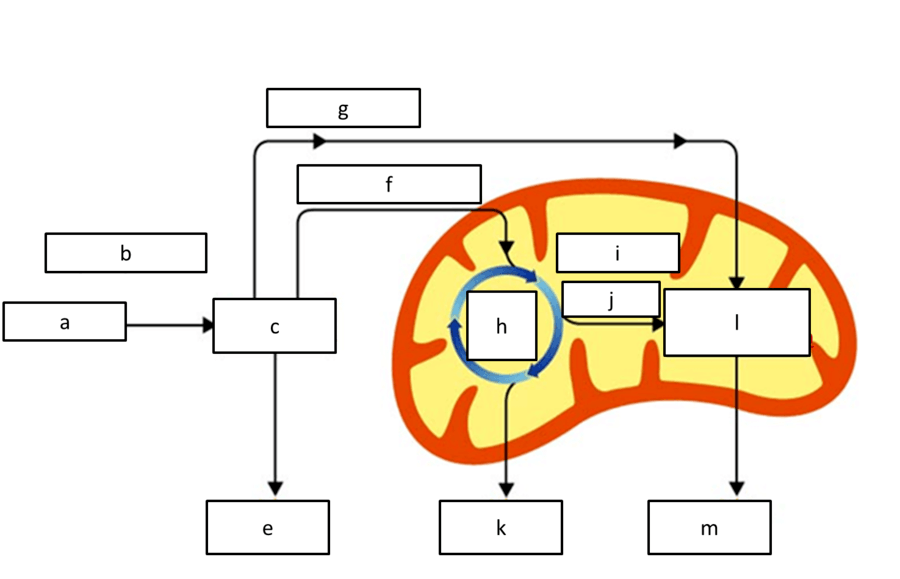
what process is represented by C
glycolysis
90
New cards
after strenusous exercise, a muscle cell would contain decreased amounts of __ __and would produce__ ______ from respiration
oxygen, lactic acid
91
New cards
what is the job of NADH during cellular respiration
delivers its electron load to the molecule that needs it
92
New cards
in eukaryotic aerobic respiration, which option best describes the location of the electron transport chain
inner membrane/ cristae
93
New cards
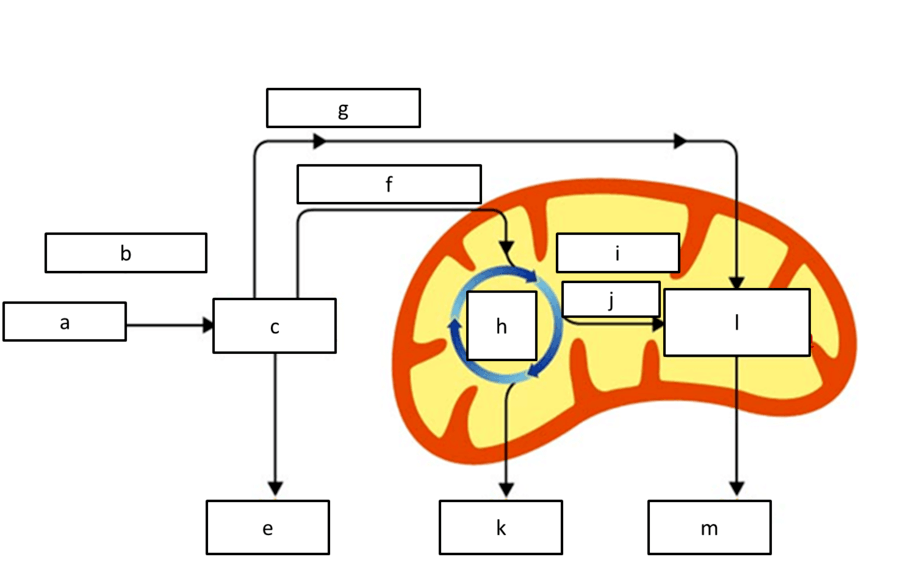
what location of the cell is represented by B
cytoplasm
94
New cards
the role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to
accept electrons at the end of ETC
95
New cards
which molecules are made during the Krebs cycle to power the electron transport chain
NADH and FADH2
96
New cards
the goal of aerobic cellular respiration is to make
atp
97
New cards
two different species of bacteria are examined. Scientists find that species X always produces CO2 and H2O during cellular respiration. Species Y alwasy produces ethanol and CO2. Which conclusion can be made from these observations
only species Y is anaerobic
98
New cards
the number of ATP molecues produced out of Krebs cycle is
2
99
New cards
in the ETC, electrons are passed from one electron transport molecule to another and are finally accepted by
oxygen
100
New cards
glycolysis occurs in
every living thing we know about