AP Macroeconomics Vocabulary
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
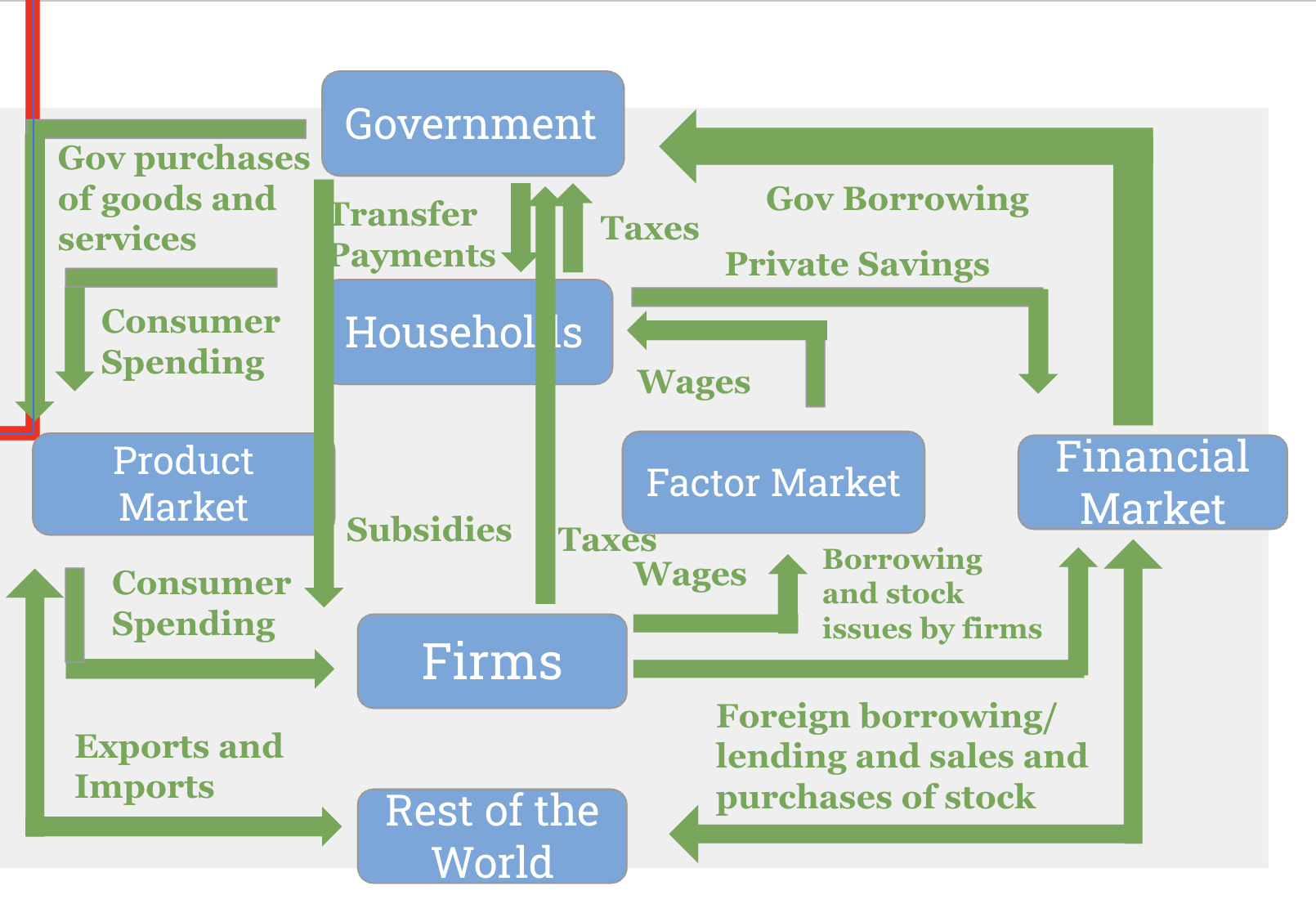
Circular Flow Model
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total market value of all final goods and services produced in a nation’s economy during a given year
Intermediate Goods and Services
Goods and services bought from one firm by another firm to be used as inputs in the production of final goods and services
Aggregate Spending Approach
C + G + I + (X-M)
Personal Consumption Expenditures
Includes durable goods, non-durable goods and services
Domestic Investment
All final purchases of machinery, equipment, and tools by businesses; construction; and changes in business inventories
Government Spending
Includes all direct government purchases of resources (labor in particular)
Income Approach
Rent + Wages + Profit + Interest
National Income
All income earned by American-supplied resources, whether here or abroad
Value-Added Approach
The value of a producer’s sales minus the value of its purchases of inputs
Business Cycle
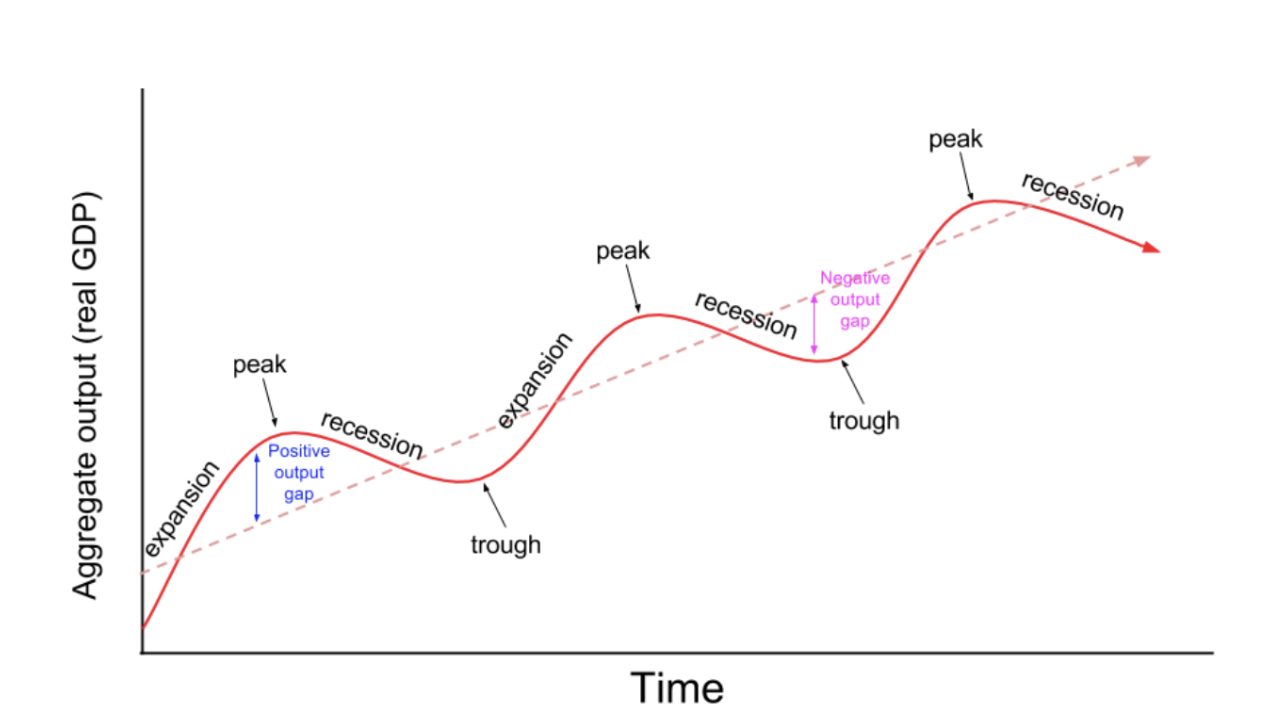
Expansionary Gap
Output is rising and unemployment is declining
Recessionary Gap
Output is declining and unemployment is rising
Peak
When business activity reaches a temporary maximum with full employment and near capacity output; unemployment is at its lowest
Trough
The bottom of the recessionary period; unemployment is at its highest; output is at its lowest
Aggregate Output (Y)
The economy’s total production of goods and services for a given time period, usually a year
Labor Force (LF)
Those who are working and those not working who are actively seeking work; must be 16 or older to be included; employed + unemployed
Employed
Those who:
Work at a job with pay for at least one hour or
Without pay for at least 15 hours
All who were temporarily absent from their regular jobs due to illness, vacation, bad weather, industrial dispute, or various personal reasons
Unemployed
Has no job, or is temporarily laid off but is actively looking for work in the 4-week period prior to the reference week
Labor Force Participation Rate (LFPR)
(Labor Force/% of pop. 16 or older) (100)
Unemployment Rate (UR)
(Unemployed/Labor Force) (100)
Economic Growth
An increase in the maximum possible output of an economy
Discouraged Workers
People who have been unemployed for more than 4 weeks and have stopped seeking employment; not part of LF
Marginally Attached Workers
Employees who would like to be working, are available for work, but have given up looking in the recent past (within the 4 weeks); part of LF
Underemployed Workers
Part-time workers who would like to have full-time jobs; part of LF
Frictional Unemployment
Unemployment due to the time workers spend in job search
Structural Unemployment
When there are more people seeking jobs in a labor market than are available at the current wage rate, often due to being replaced by technology or skills becoming obsolete
Cyclical Unemployment
The share of unemployment that arises from the business cycle
Natural Rate of Unemployment (NRU)
Structural + Frictional
Actual Unemployment Rate
NRU + Cyclical
Price Stability
Avoiding prolonged inflation and prolonged deflation
Inflation
Reduces our ability to purchase goods and services
Deflation
A decrease in the overall price level; causes consumers to hold onto their dollars, waiting for lower prices
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
A measure of the average change over time in purchasing power for a fixed “market basket” of goods and services; drawbacks include:
Substitution bias
New Goods bias
Quality change bias
Disinflation
The process of bringing the inflation rate down; inflation is increasing at a diminishing rate
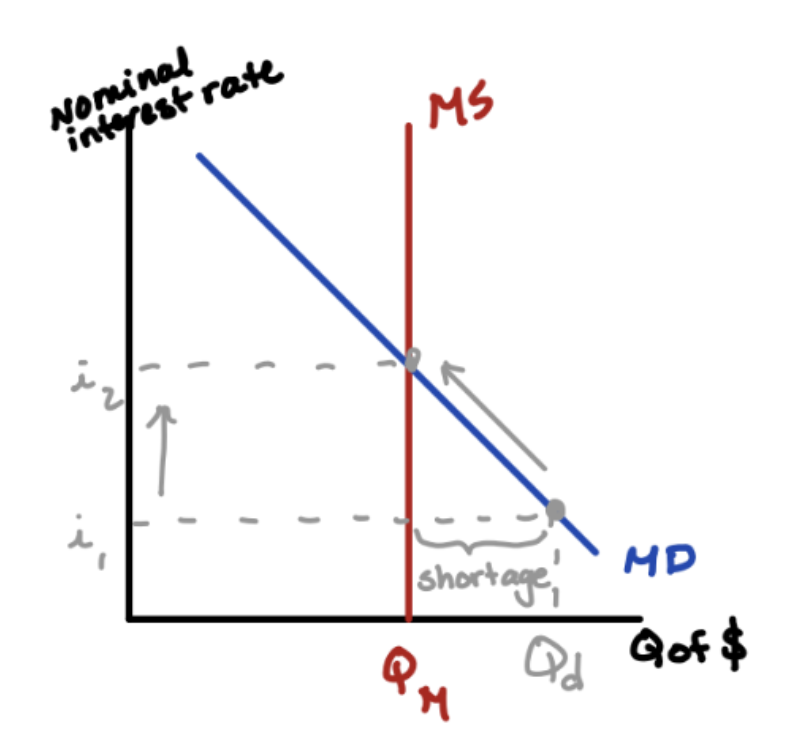
Nominal Interest Rate (NIR)
The interest rate actually paid for a loan; Fisher Equation: RIR + expected inflation
Real Interest Rate (RIR)
NIR - Expected Inflation
GDP Deflator
Used to determine how output has changed over time; reflects all goods and services produced in an economy; (Nominal GDP/Real GDP) (100)
Real Value
Nominal Value/(Price Index/100)
Shoe Leather Costs
The increased costs of transactions caused by inflation
Menu Costs
The real costs of changing listed prices for producers
Unit-of-Account Costs
The costs that arise from the way inflation makes money a less reliable unit of measurement
Nominal GDP
PL * Y
Real GDP
(PBY1 Q CY1) + (PBY2 Q CY2) + (PBY3 * Q CY3) + . . .
Inflation Rate (IR)
(GDP Deflator CY - GDP Deflator Base Year) / GDP Deflator BY
Disposable Income (Yd)
Income left after a person pays taxes; C + S
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
ΔC/ΔYd
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
ΔS/ΔYd
Autonomous Expenditures
Spending that occurs regardless of income
Consumption Function
C = a + MPC x Yd
Spending Multiplier
The ratio of the total change in real GDP caused by an autonomous change in aggregate spending to the size of that autonomous change; 1/MPS or 1/(1-MPC)
Tax/Transfer Multipliers
-MPC/MPS; MPC/MPS
Automatic Stabilizer
Government spending and taxation rules that cause fiscal policy to adjust according to an inflationary or recessionary turn in the economy
Inventory Investment
The value of the change in total inventories held in the economy during a given period of time
Unplanned if higher than intended
Aggregate Supply (AS)
It shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output supplied in the economy
Sticky Wages
Nominal wages that are slow to fall even in the face of high unemployment and slow to rise even in the face of labor shortages and high inflation
Potential Output (Yf) (a.k.a. Marginal Productive Capacity)
The level of real GDP the economy would produce if all prices, including nominal wages, were fully flexible; at full employment
Demand Shock
An event that shifts the aggregate demand curve
Supply Shock
An event that shifts the short run aggregate supply curve
Demand Pull Inflation
Inflation caused by an increase in AD; output and employment increase
Stagflation (a.k.a. Cost-Push Inflation)
Inflation caused by a decrease in supply; prices are higher, but output and employment are lower
Money
Anything that can be used to purchase goods and services
Wealth
Accumulation of savings that occurs over time
Income
Money received on a regular basis for work or through investments
Financial Asset
Paper claim that entitles the buyer to future income from the seller
Physical Asset
Claim on a tangible object
Liquidity
How easily an asset can be turned into cash
Liability
A requirement to pay money in the future
Loan
A lending agreement between an individual lender and an individual borrower
Bond
The seller promises to pay a fixed sum of interest each year and to repay the principal (the value stated on the face) to the owner on a particular date
Stocks
A share in the ownership of a particular company
Financial Intermediary
An institution that transforms funds gathered from many individuals into financial assets
Mutual Funds
A financial intermediary that creates a stock portfolio by buying and holding shares in companies and then selling shares of the stock portfolio to individual investors
Banks
A financial intermediary that provides liquid assets in the form of deposits to lenders and uses their funds to finance the illiquid investment spending needs of borrowers
Commodity Money
An item that has value of its own and also can be used as money
Representative Money
Money that has value because it can be exchanged for a fixed amount of a valuable commodity
Fiat Money
Money that has been declared by the government to be legal tender, but is not backed by any commodity (i.e. USD)
Unit of Account
Function of money as a way to set prices
Store of Value
Ability of money to hold purchasing power over time
Medium of Exchange
Function of money as a way to trade goods and services
M0
Currency
Bank reserves
M1
Currency in Circulation
Demand Deposits
Savings Accounts
M2
M1
Money Market Deposit Accounts
Certificates of Deposits under $100,000
M3
M2
Certificates of Deposits over $100,000
Repurchase Agreements
Eurodollars
Reserve Requirement
% of customer demand deposits that a bank must hold in reserves
Total reserves
All the monetary funds that the bank has
Excess Reserves
Monetary funds that a bank chooses to hold onto after the rr
Securities
Bonds that the bank owns that earn the bank interest
Transaction Demands
The money people want to hold onto to buy goods and services as part of everyday life
Precautionary Demand
Money people hold onto in case of an emergency
Asset (a.k.a. Speculative) Demand
Money people hold onto in case of a good investment opportunity
Dual Mandate
Responsibility of the Federal Bank to influence the NIR to ensure:
Maximum employment
Stable Prices
Discount Rate (DR)
Interest rate banks pay when they borrow from the Fed
Policy (a.k.a. Federal Funds) Rate
The interest rate banks pay when they borrow from other commercial banks
Expansionary Monetary Policy
Targets a lower NIR
Contractionary Monetary Policy
Targets a higher NIR
Recognition Lag
Period during which central banks collect and analyze the data needed to identify problems in the economy
Impact Lag
Period during which the economy adjusts after policy action is taken by the Federal Reserve
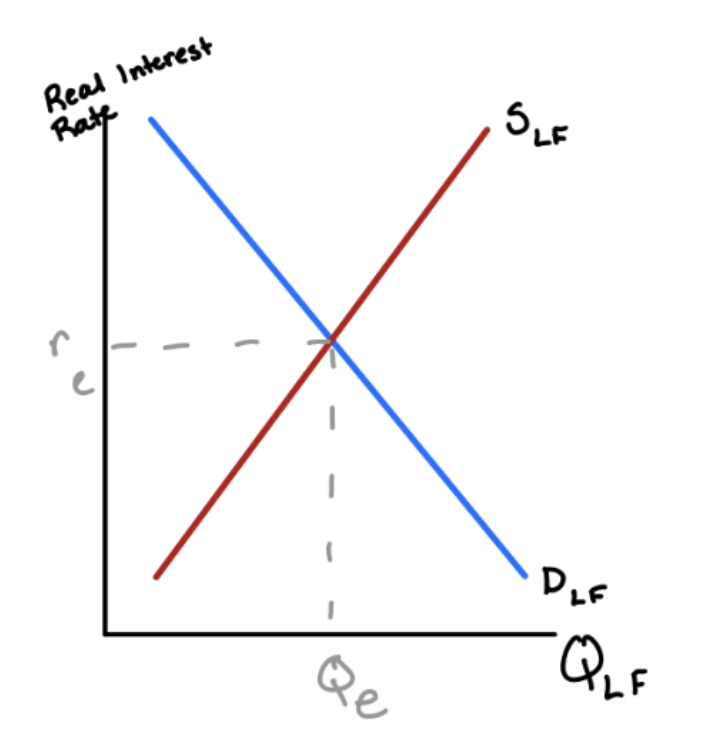
Loanable Funds Graph
Money Supply Graph