Disorders of the Eye (PEARLS)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
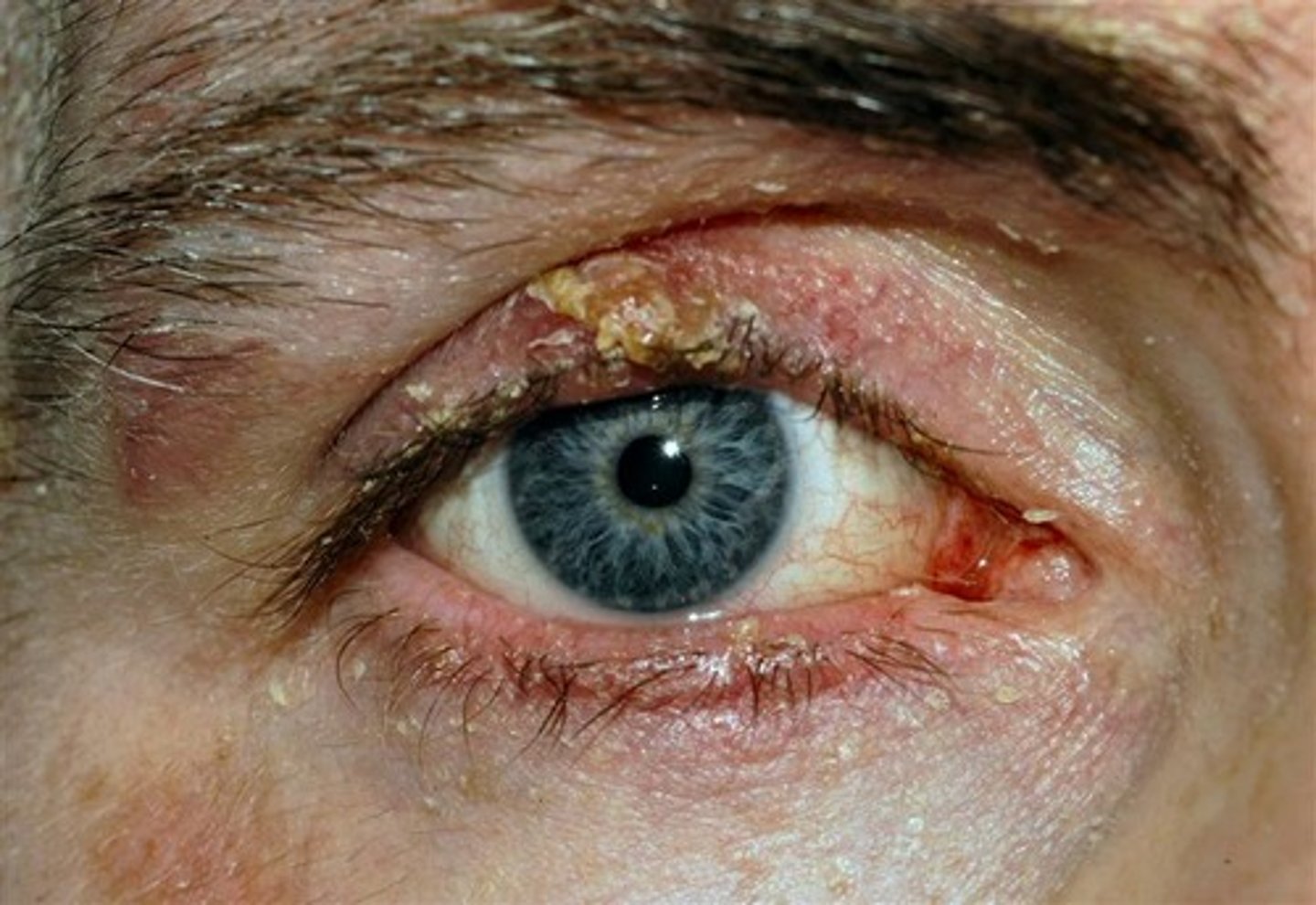
Eyelid changes: crusting, scaling, red-rimming of eyelid and eyelash flaking along with dry eyes and associated seborrhea and rosacea
Blepharitis
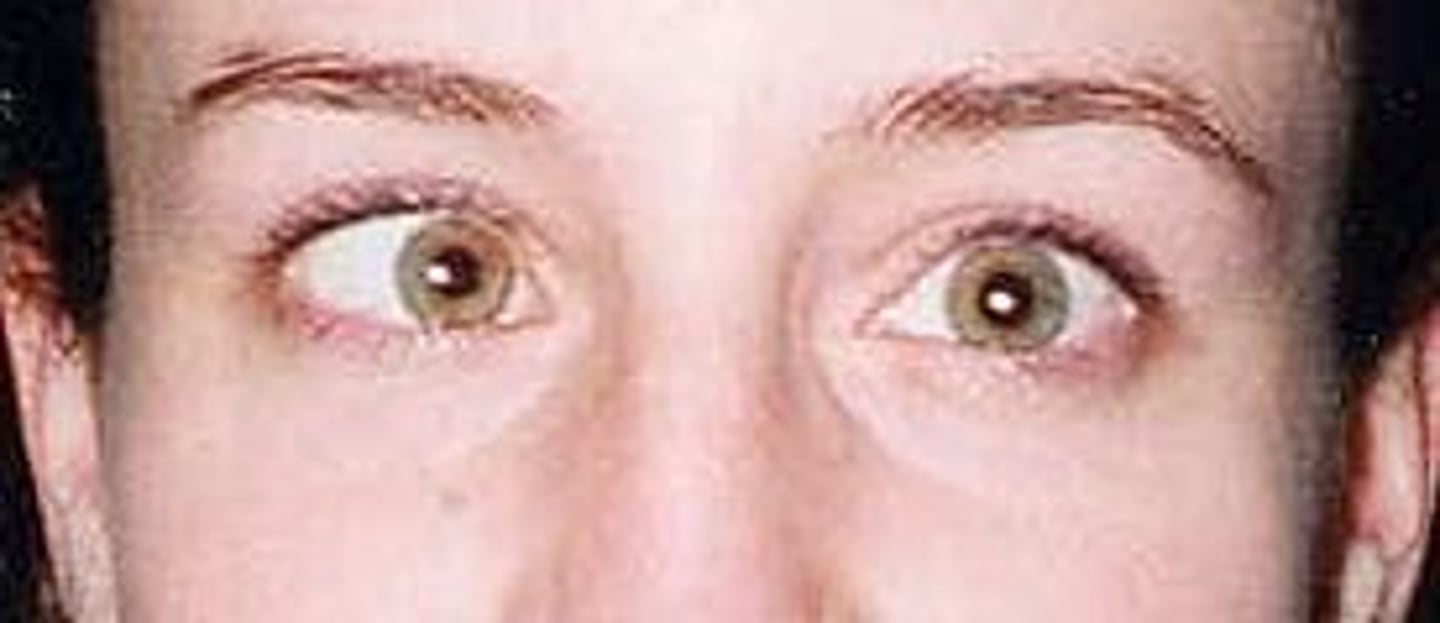
History of blunt trauma, eyelid swelling, decreased visual acuity, enophthalmos (sunken eye), anesthesia/paresthesia in the gums, upper lips and cheek due to damage to the infraorbital nerve
Blowout fracture
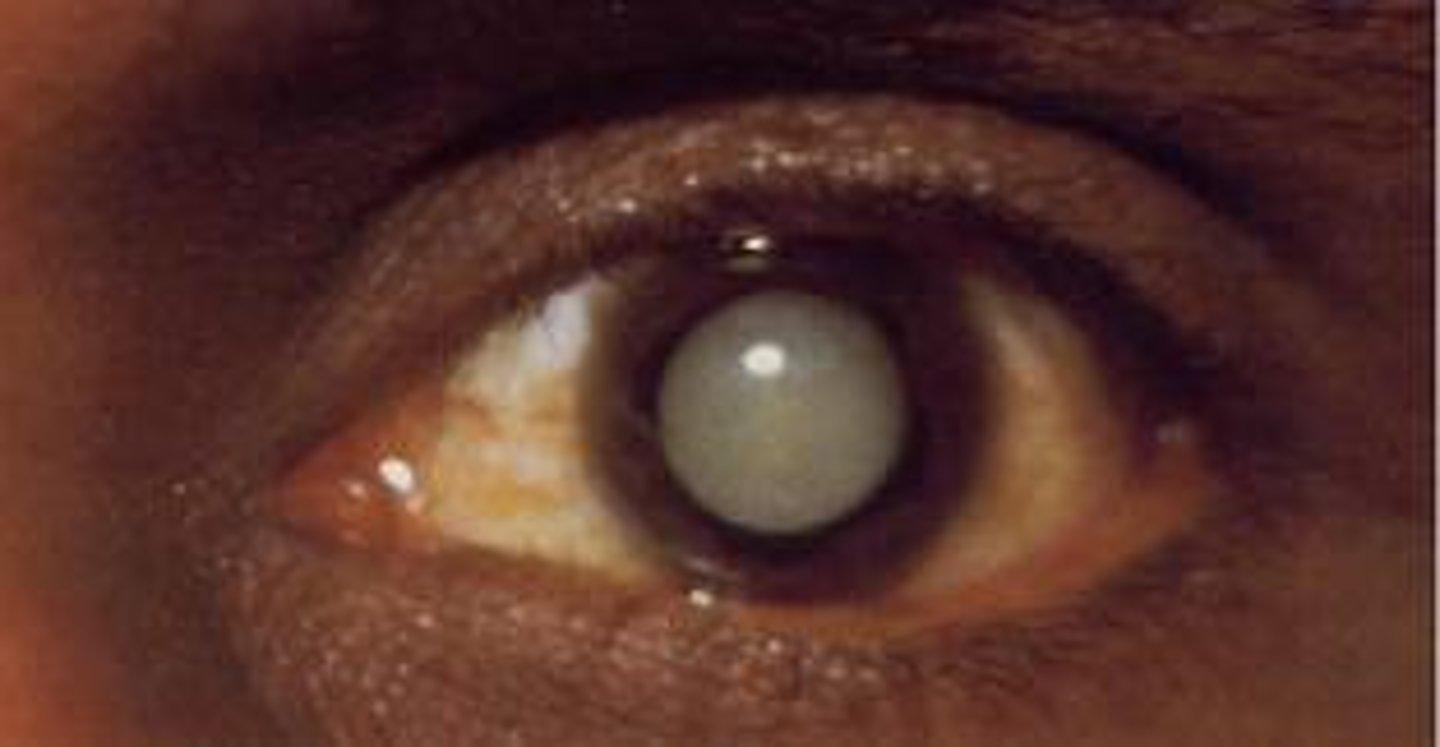
Blurred vision over months or years, halos around lights. Clouding of the Lens
Cataract
Clouding of the Lens (versus clouding of cornea = glaucoma)
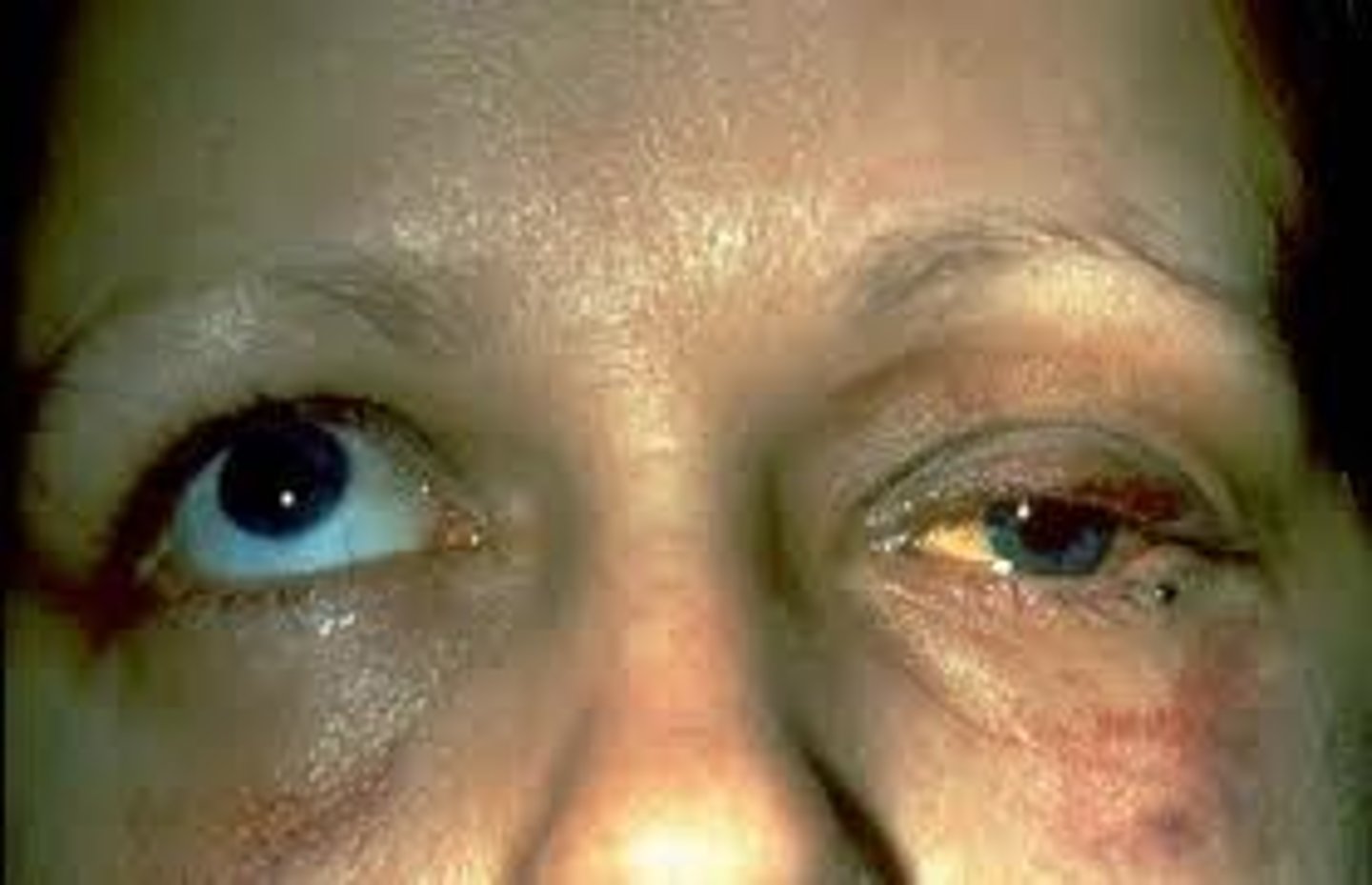
Painless (non-infectious) granuloma of the internal meibomian sebaceous gland
Chalazion
Painless, cold lid nodule, versus hordeolum, which is a painful infectious "hot" nodule
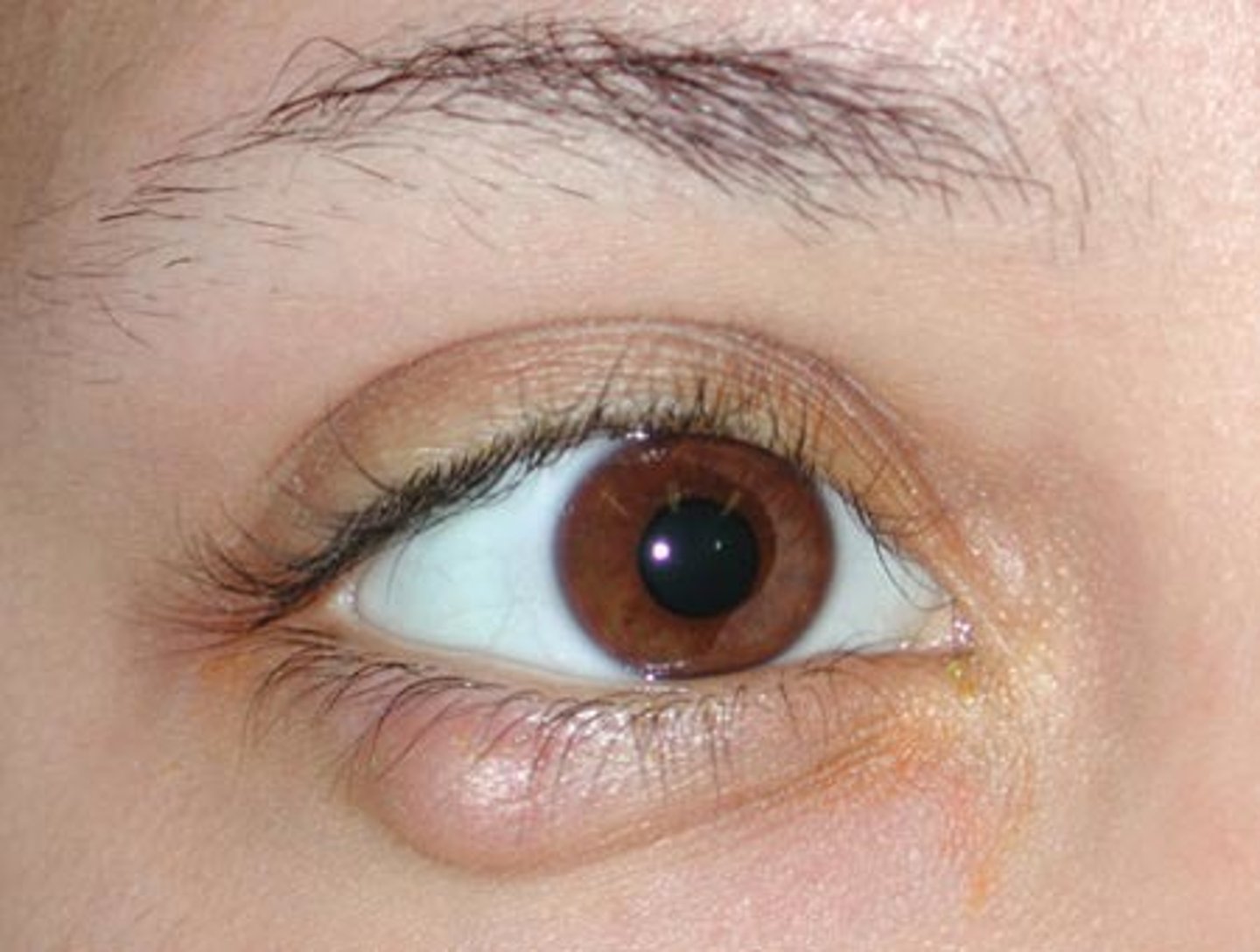
copious watery eye discharge, scant mucoid discharge
Viral Conjunctivitis
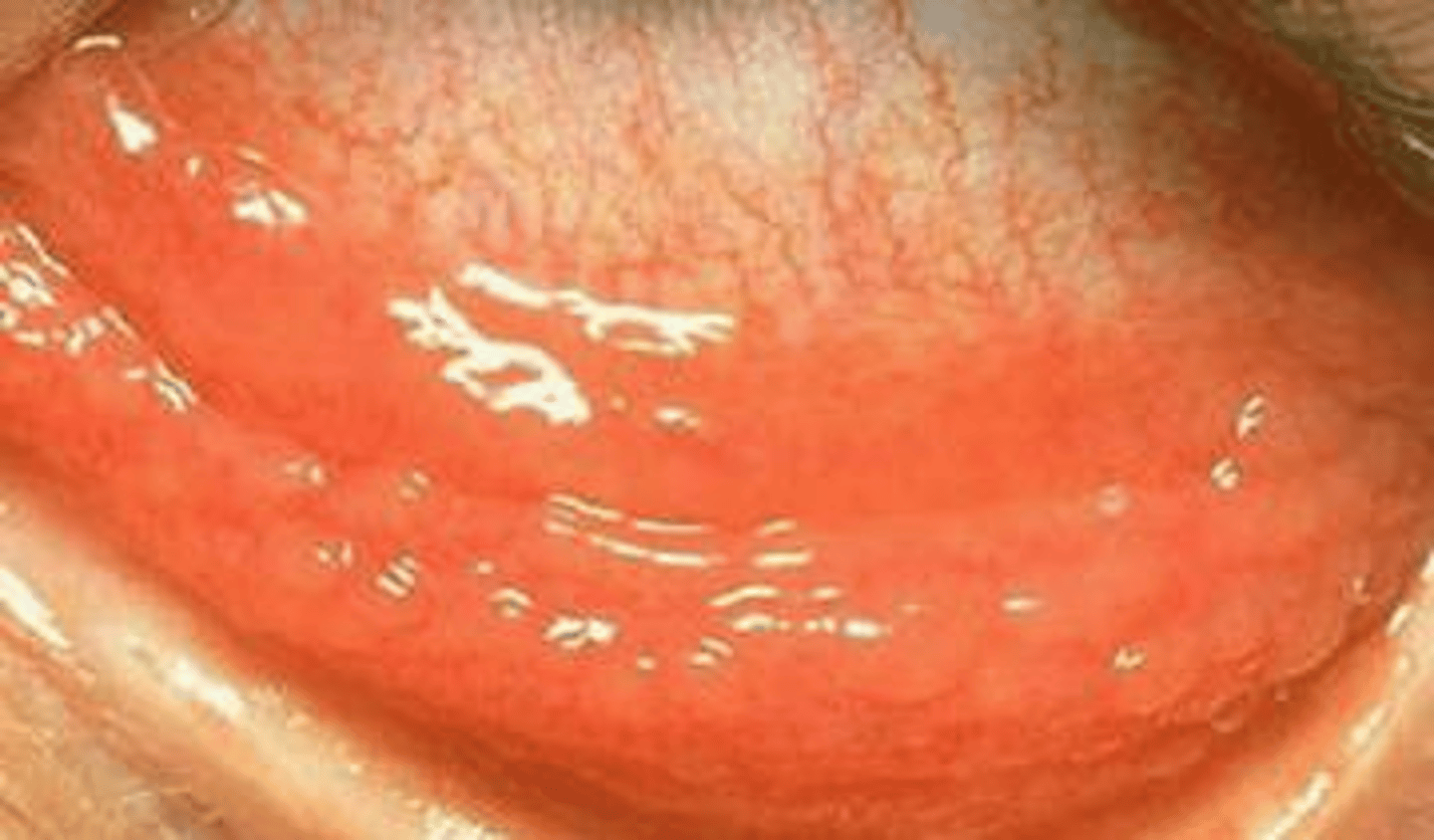
Purulent (yellow) eye discharge, crusting, usually worse in the morning
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
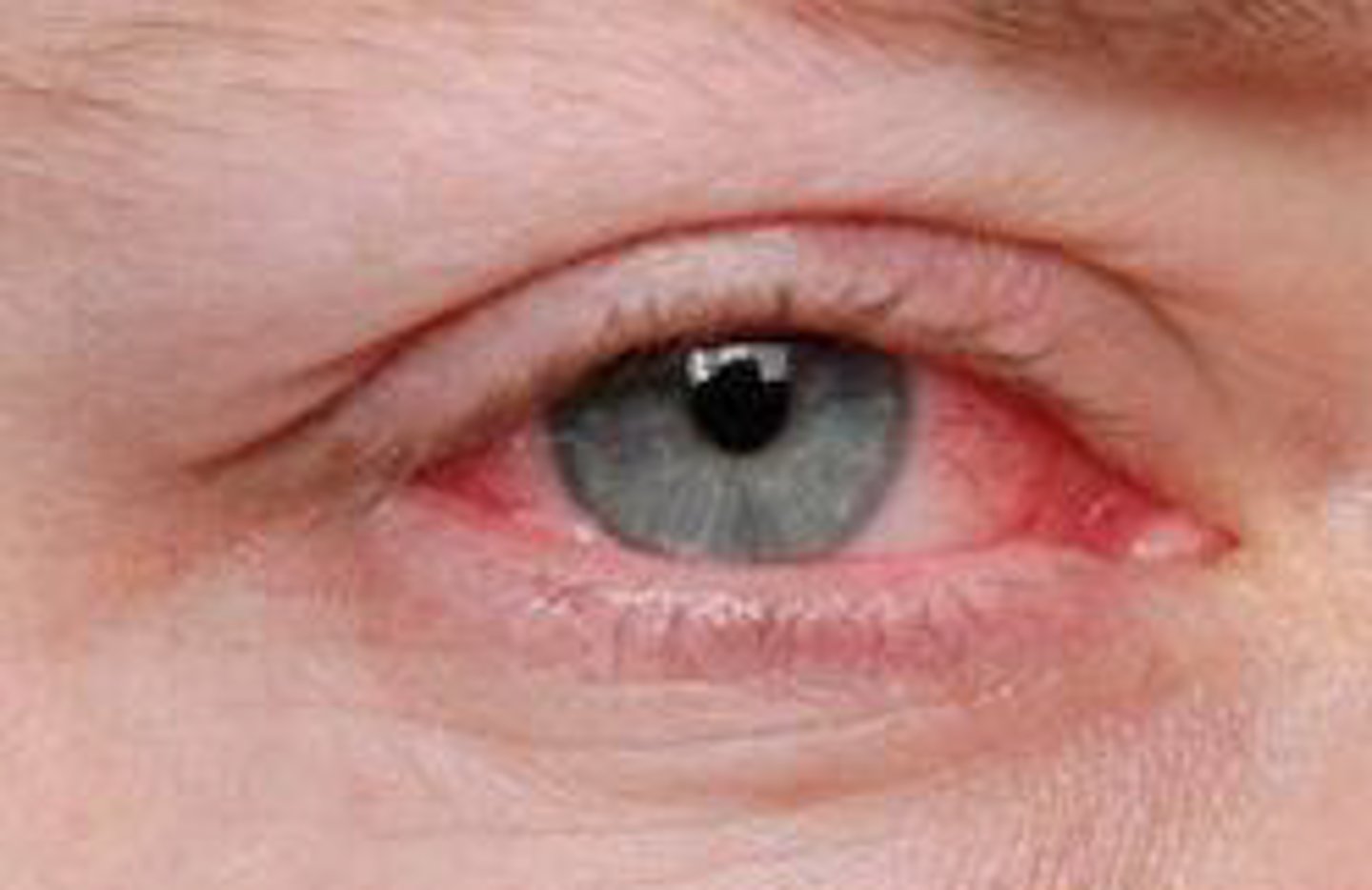
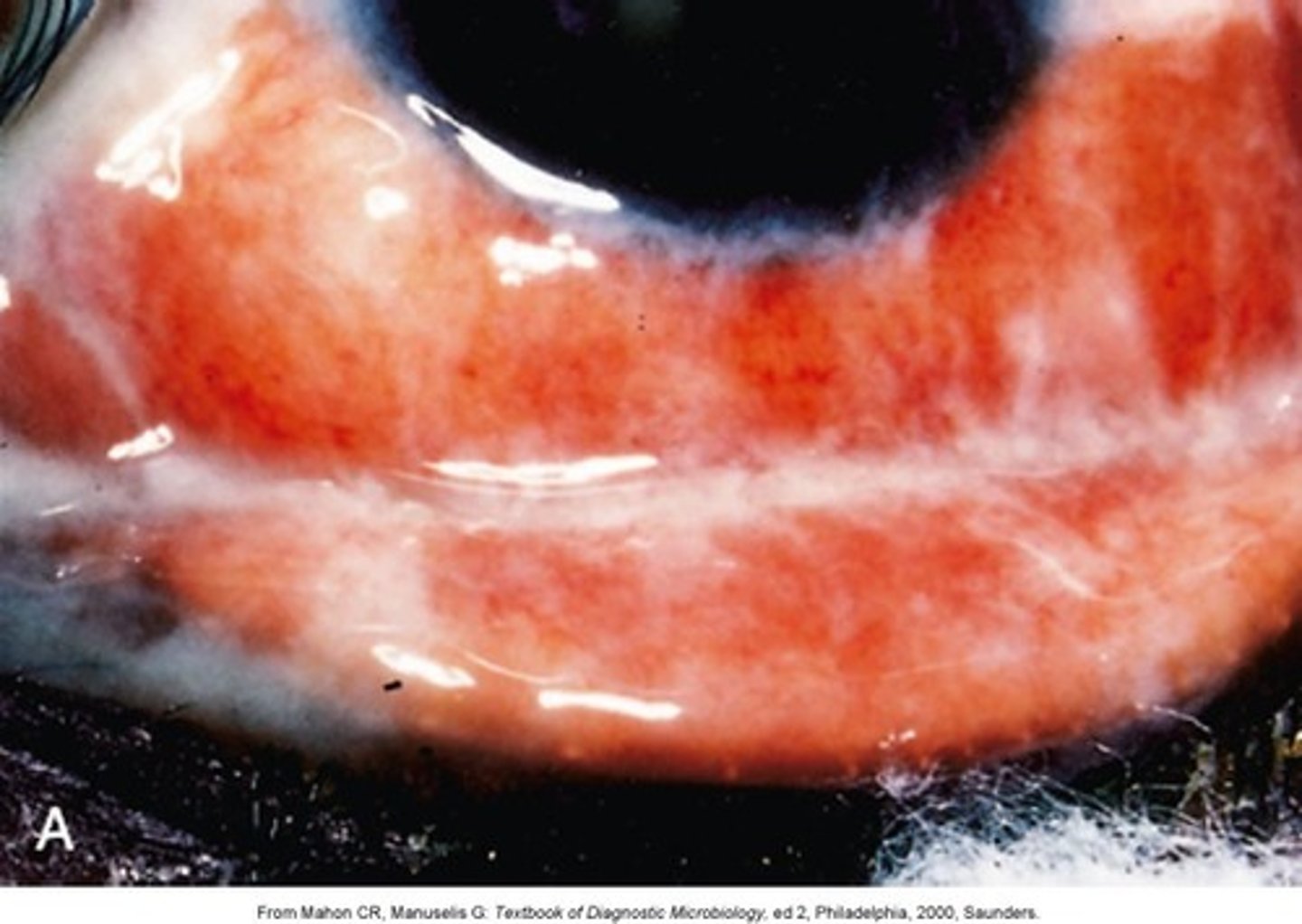
Red eyes, itching and tearing, usually bilateral, cobblestone mucosa on the inner/upper eyelid
Allergic Conjunctivitis
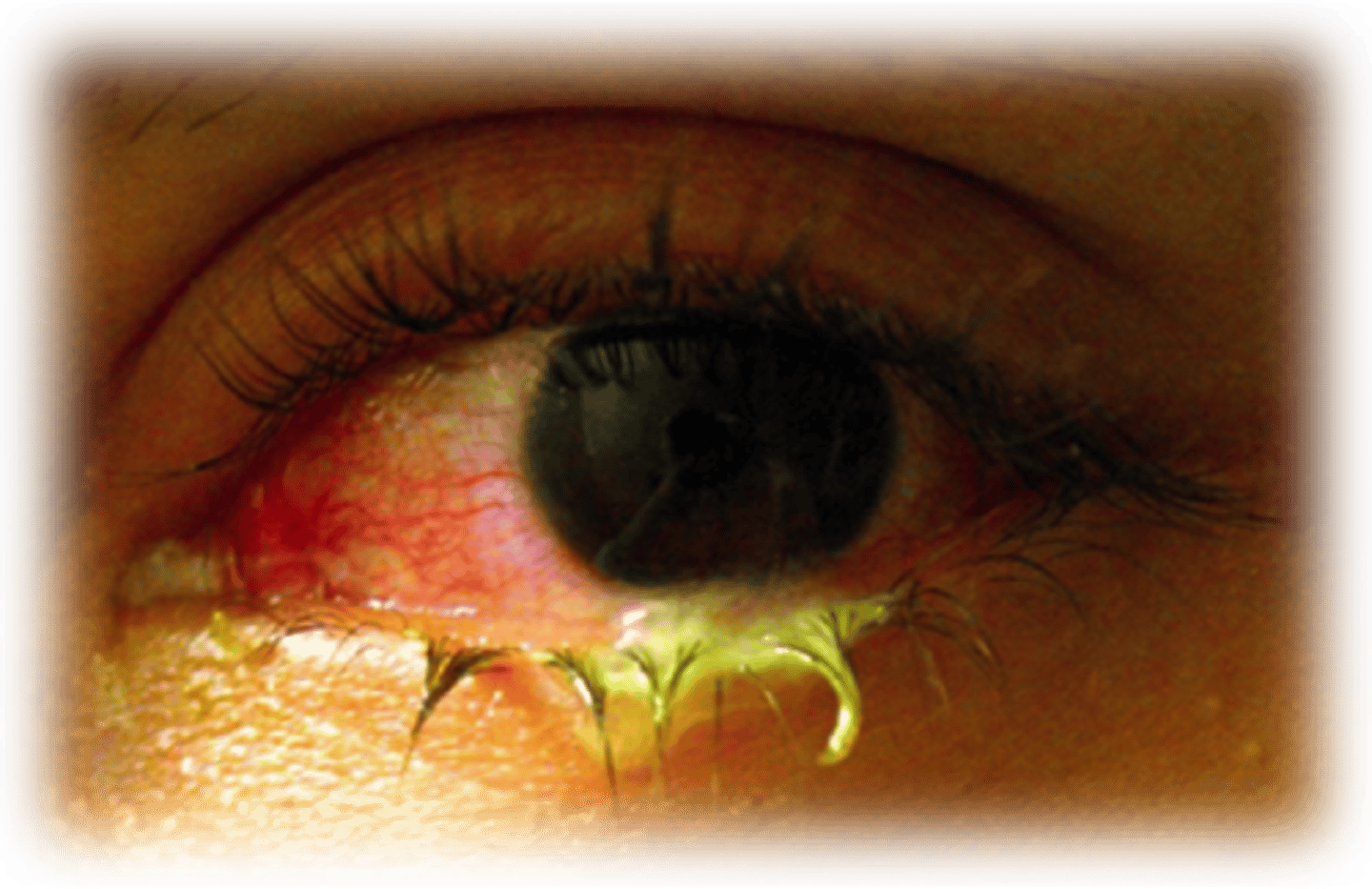
Copious purulent discharge, in a sexually active patient who is not responding to conventional treatment
Gonococcal Conjunctivitis
Giemsa stain - inclusion body, scant mucopurulent discharge
Chlamydial Conjunctivitis
Sudden onset of eye pain, photophobia, tearing, foreign body sensation, blurring of vision, and/or conjunctival injection, fluorescein dye - increased absorption in devoid area, antibiotic eye ointment, NO PATCHING!
Corneal abrasion
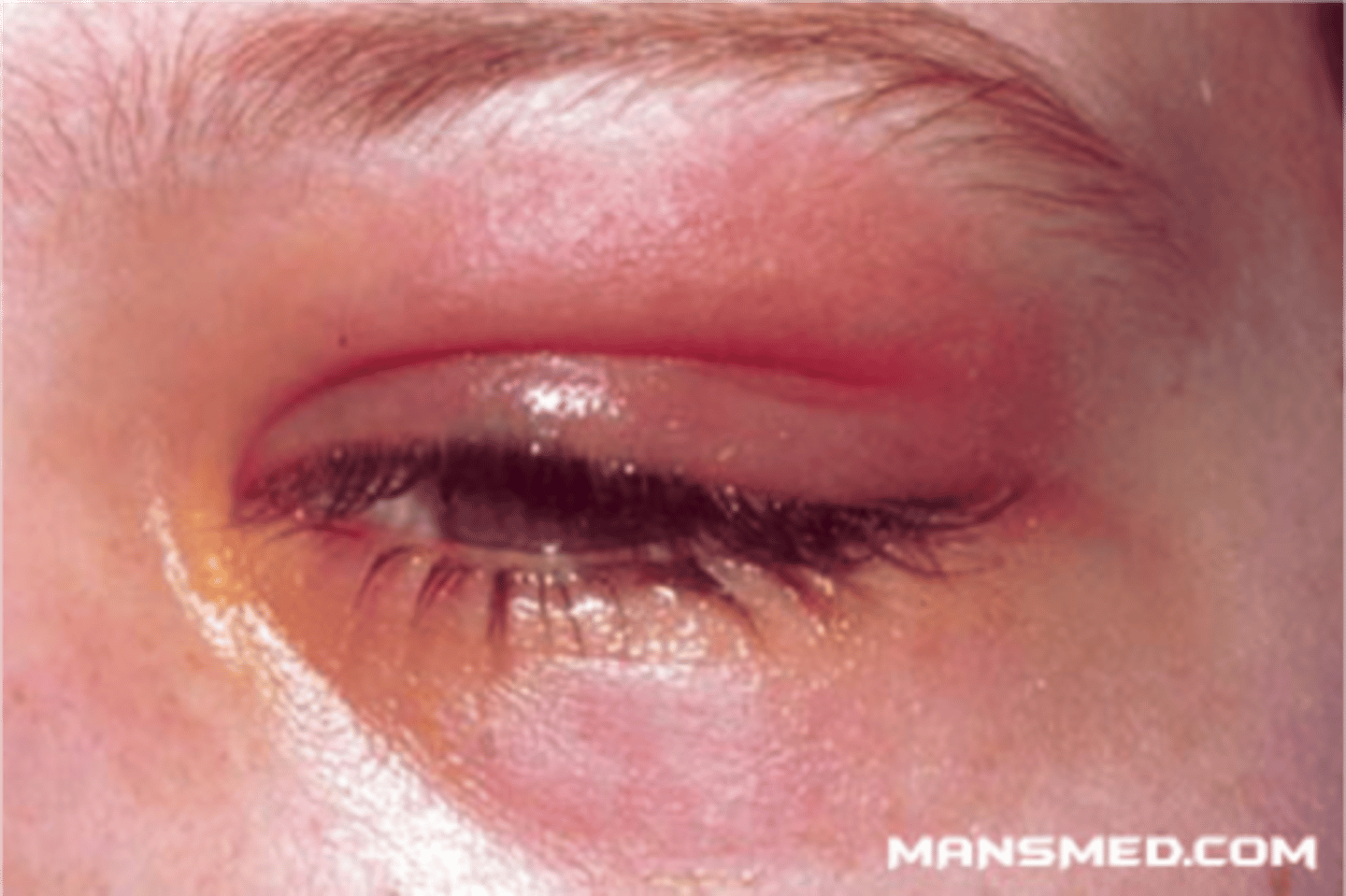
Inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct or the nasolacrimal gland (supratemporal)
Dacryoadenitis
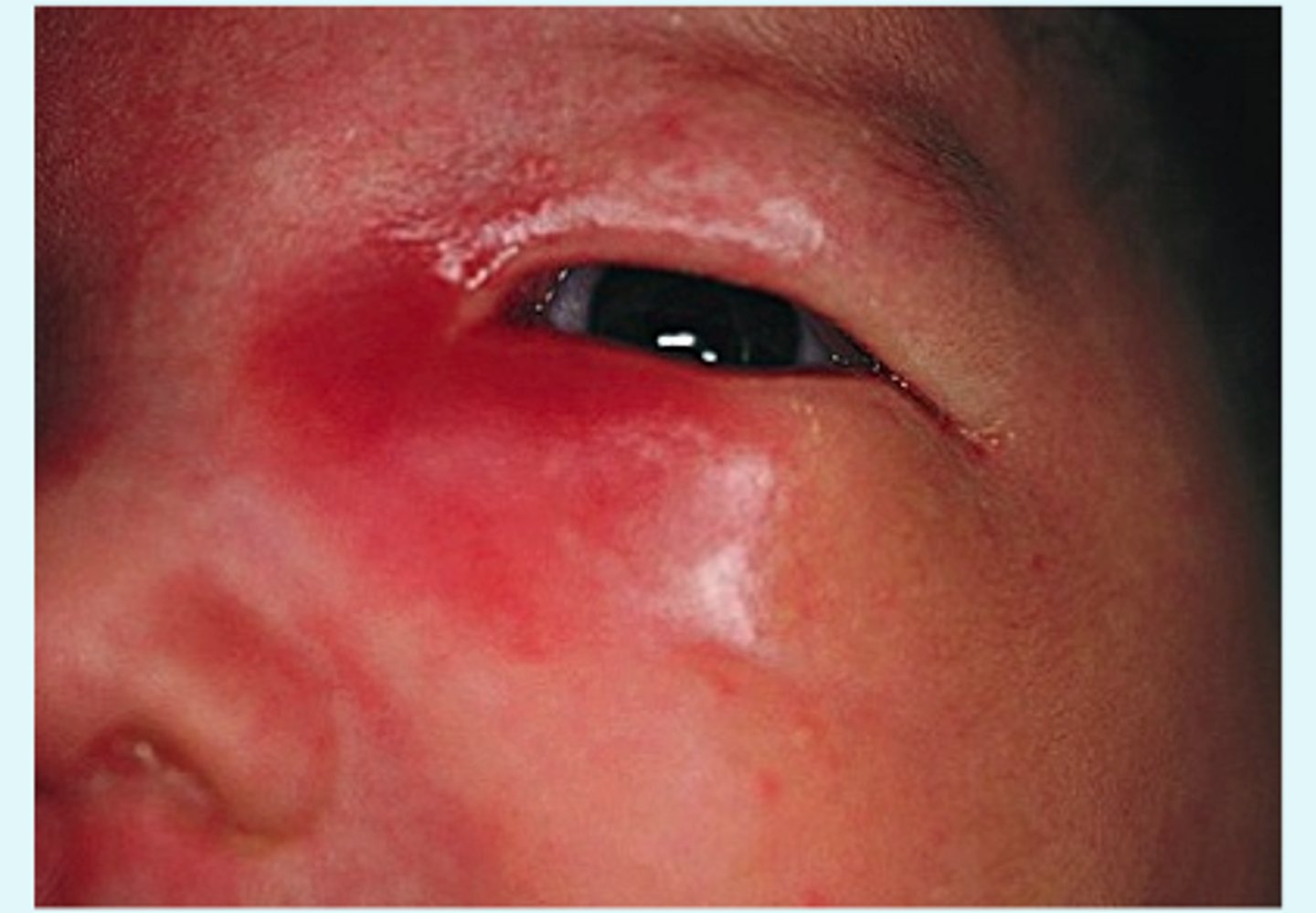
Infectious obstruction of nasolacrimal duct (inferomedial region)
Dacryocystitis
Occurs when the eyelid turns outward exposing the palpebral conjunctiva, conjunctiva will appear red from air exposure and inflammation
Ectropion
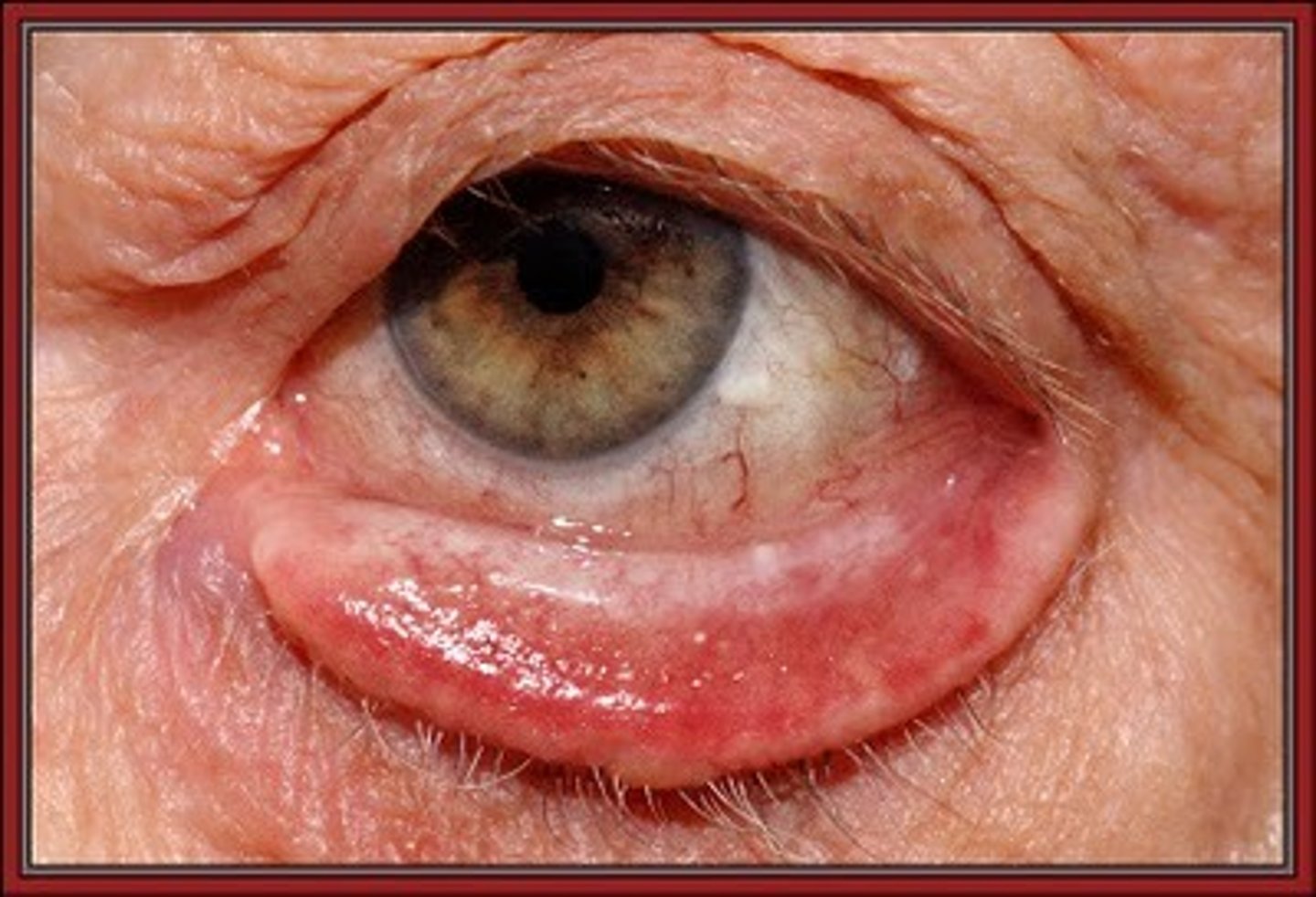
Inversion of an eyelid is most commonly caused by age-related tissue relaxation, surgical correction is definitive
Entropion
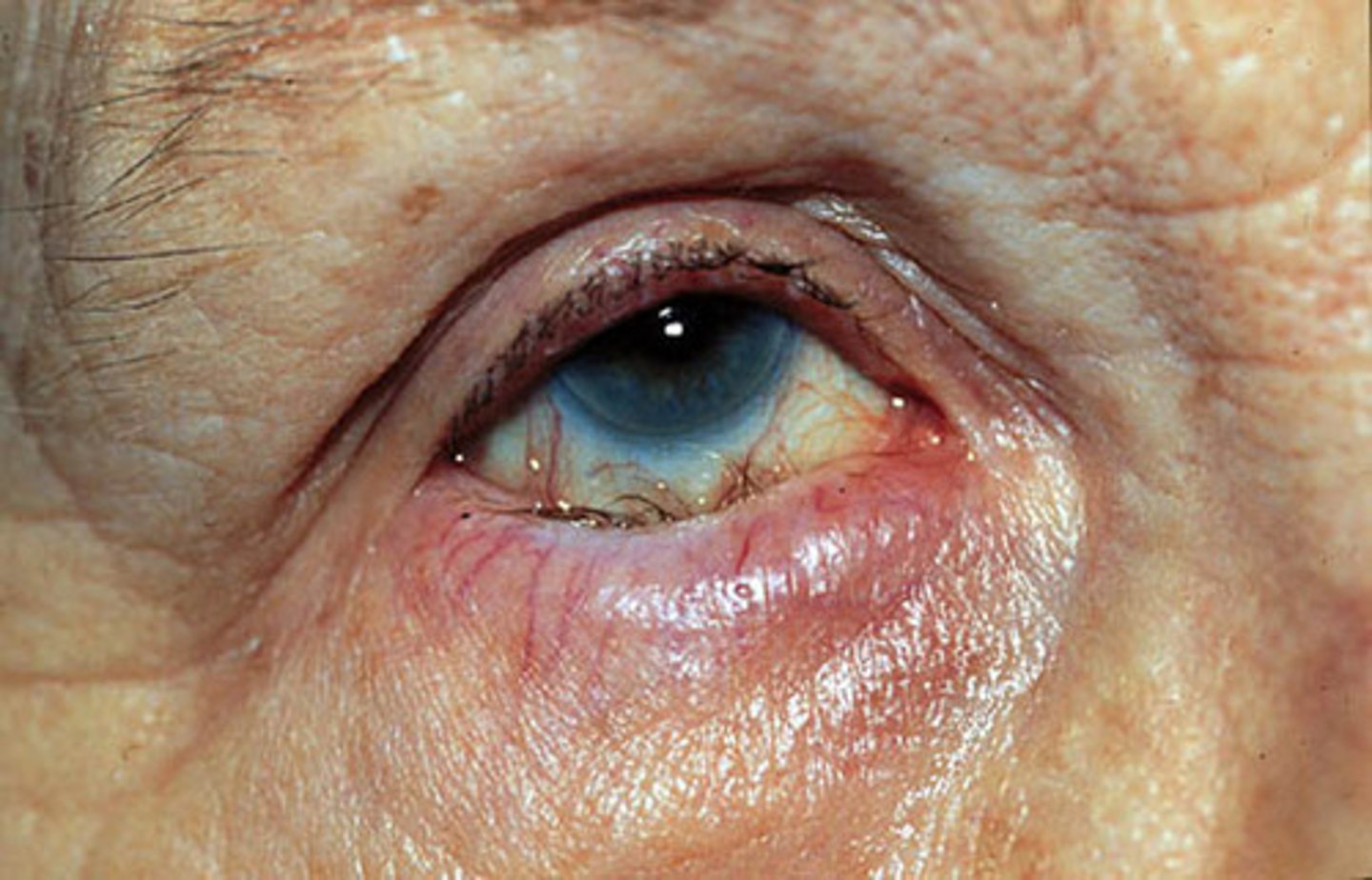
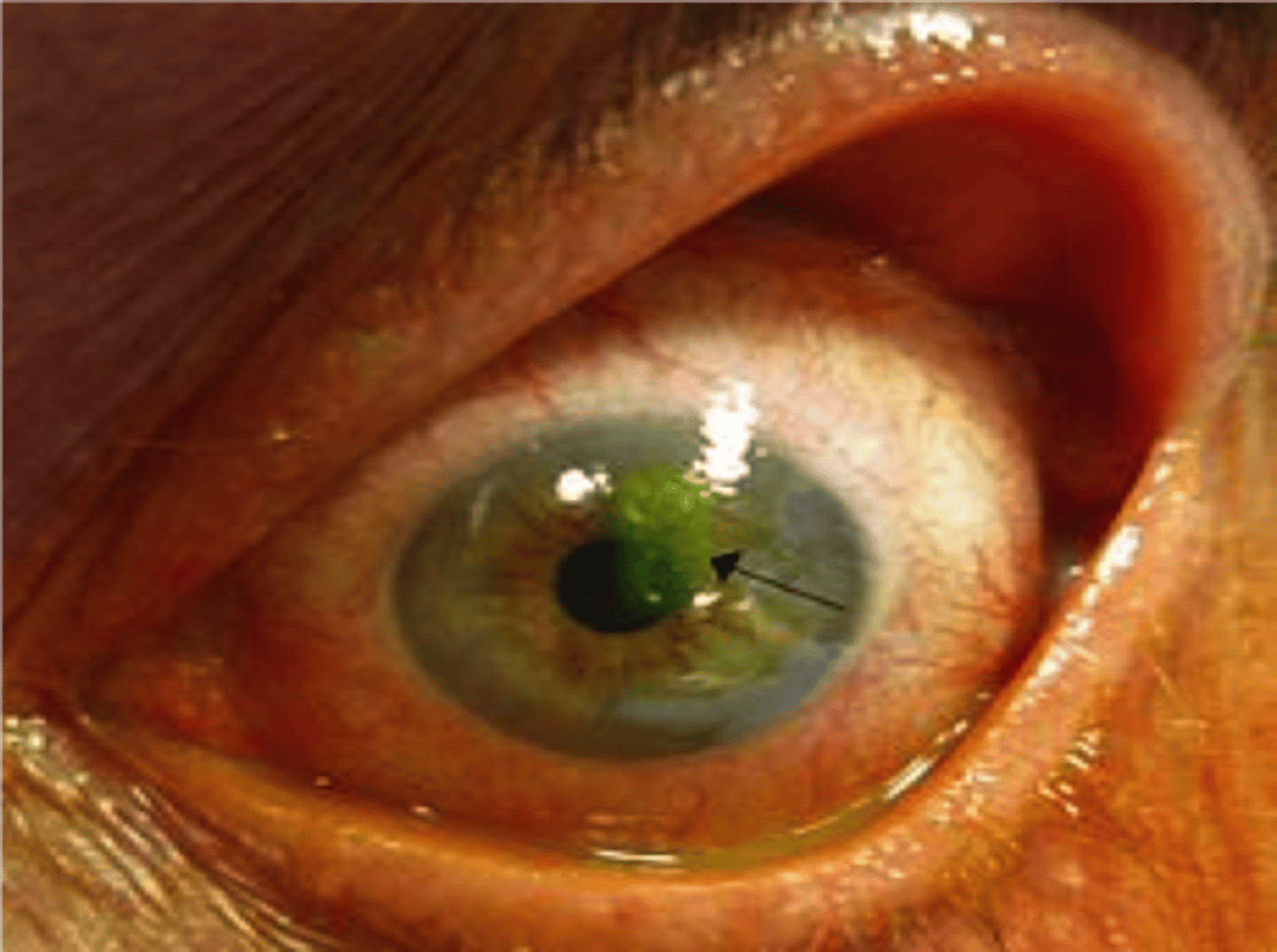
Eye pain, if not addressed promptly may leave a rust ring, irrigation, immediate surgical removal by an ophthalmologist
Ocular Foreign body
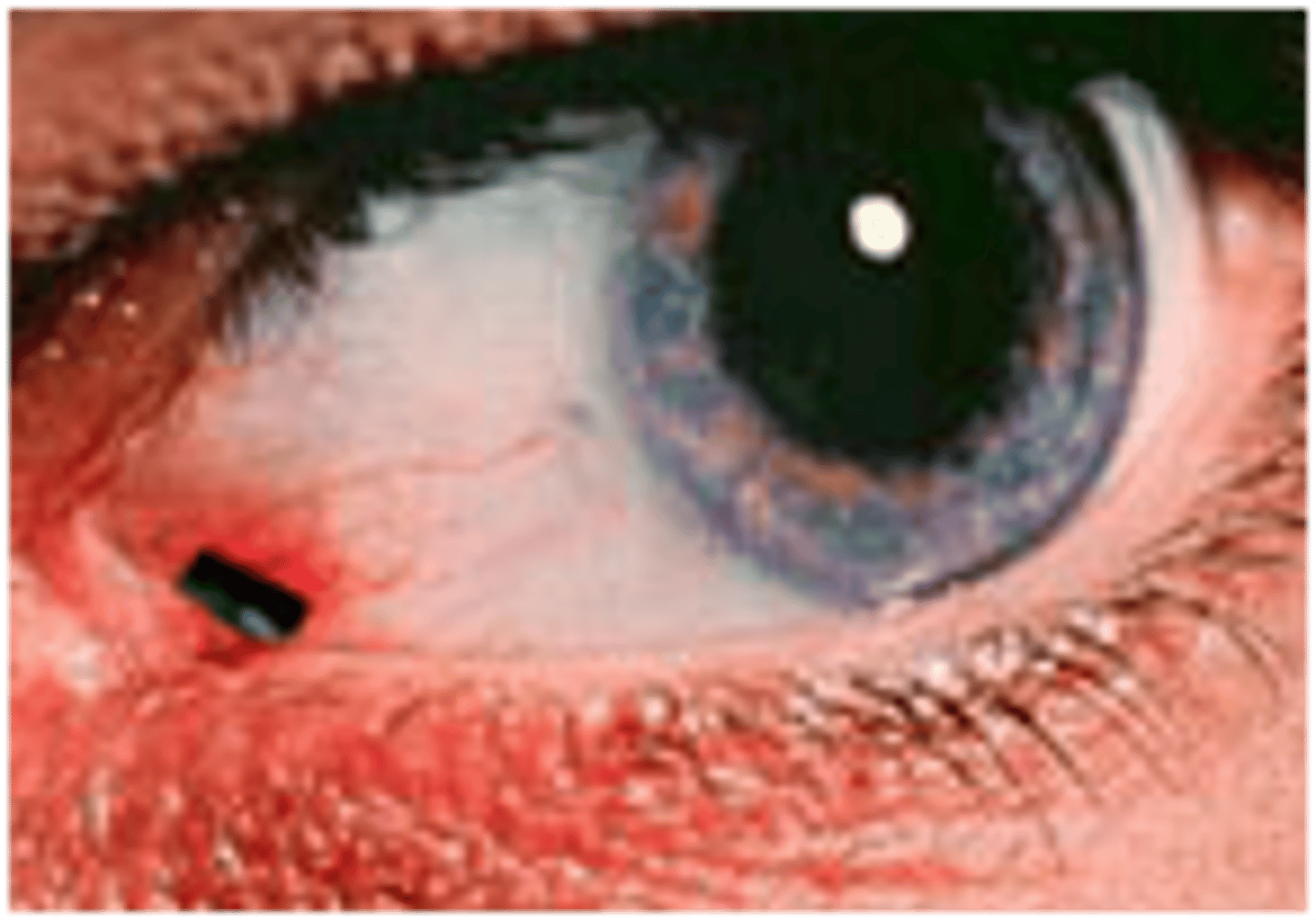
Peripheral to central, gradual visual loss
Open angle glaucoma
(versus macular degeneration which is central loss)
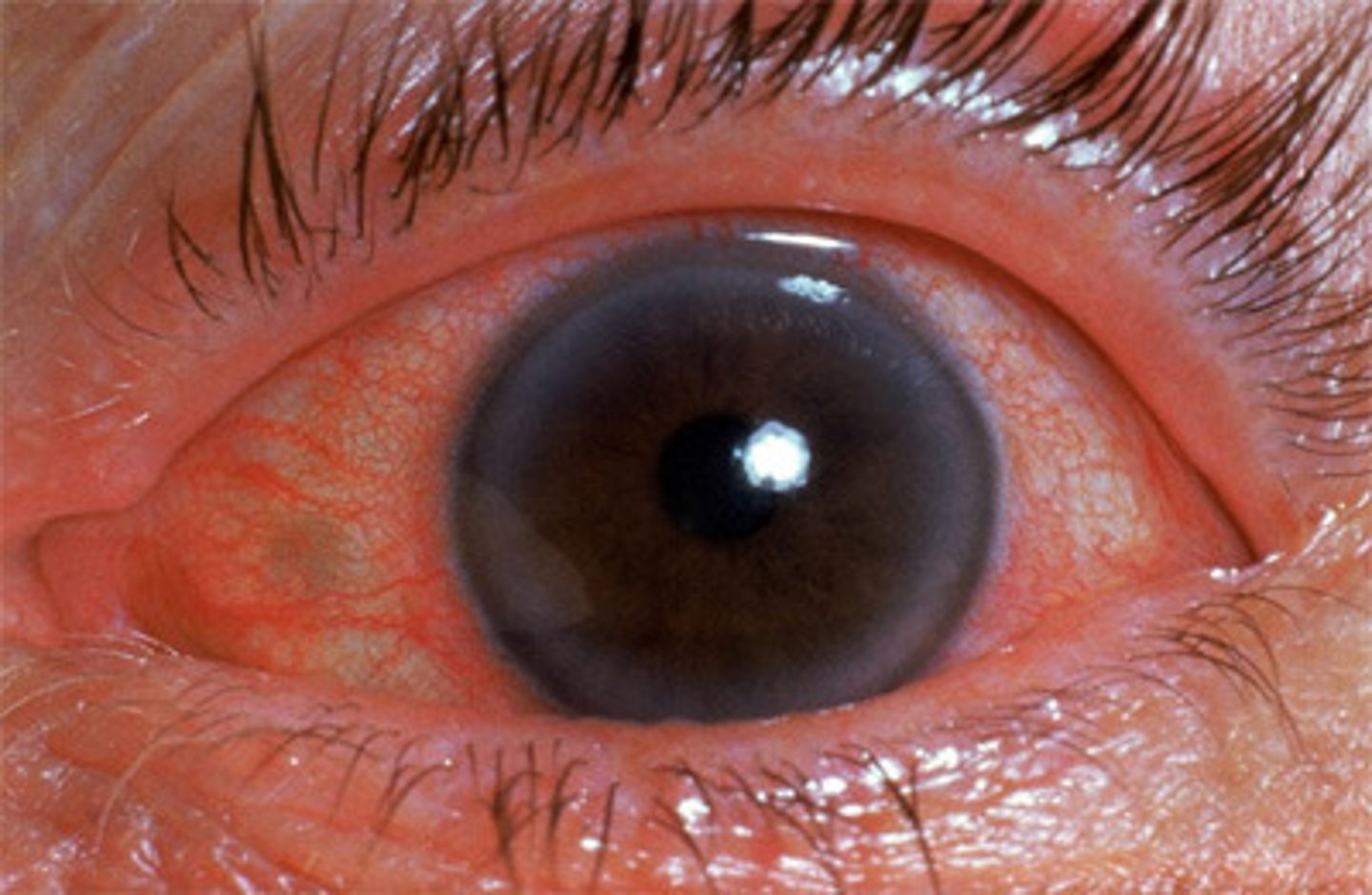
Classic triad: injected conjunctiva, cloudy or "steamy" cornea, and fixed dilated pupil, this is an ophthalmic emergency.
Acute angle closure glaucoma
Painful, warm (hot), swollen red lump on the eyelid
Hordeolum
(different from a chalazion which is painless) Think "H" for Hot = Hordeolum
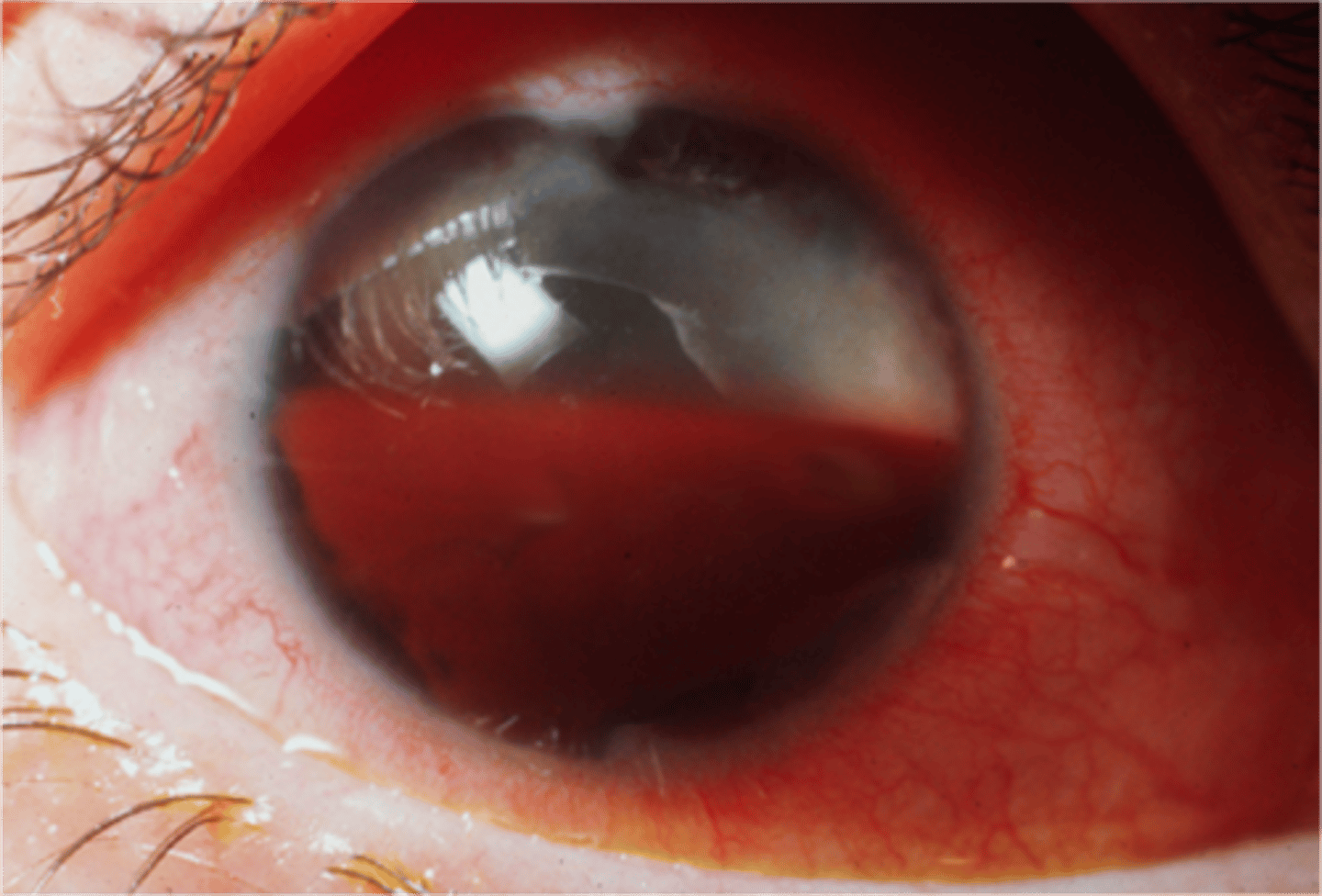
Collection of blood inside the front part of the eye (called the anterior chamber, between the cornea and the iris). The blood may cover part or all of the iris (the colored part of the eye) and the pupil, and may partly or totally block vision in that eye
Hyphema
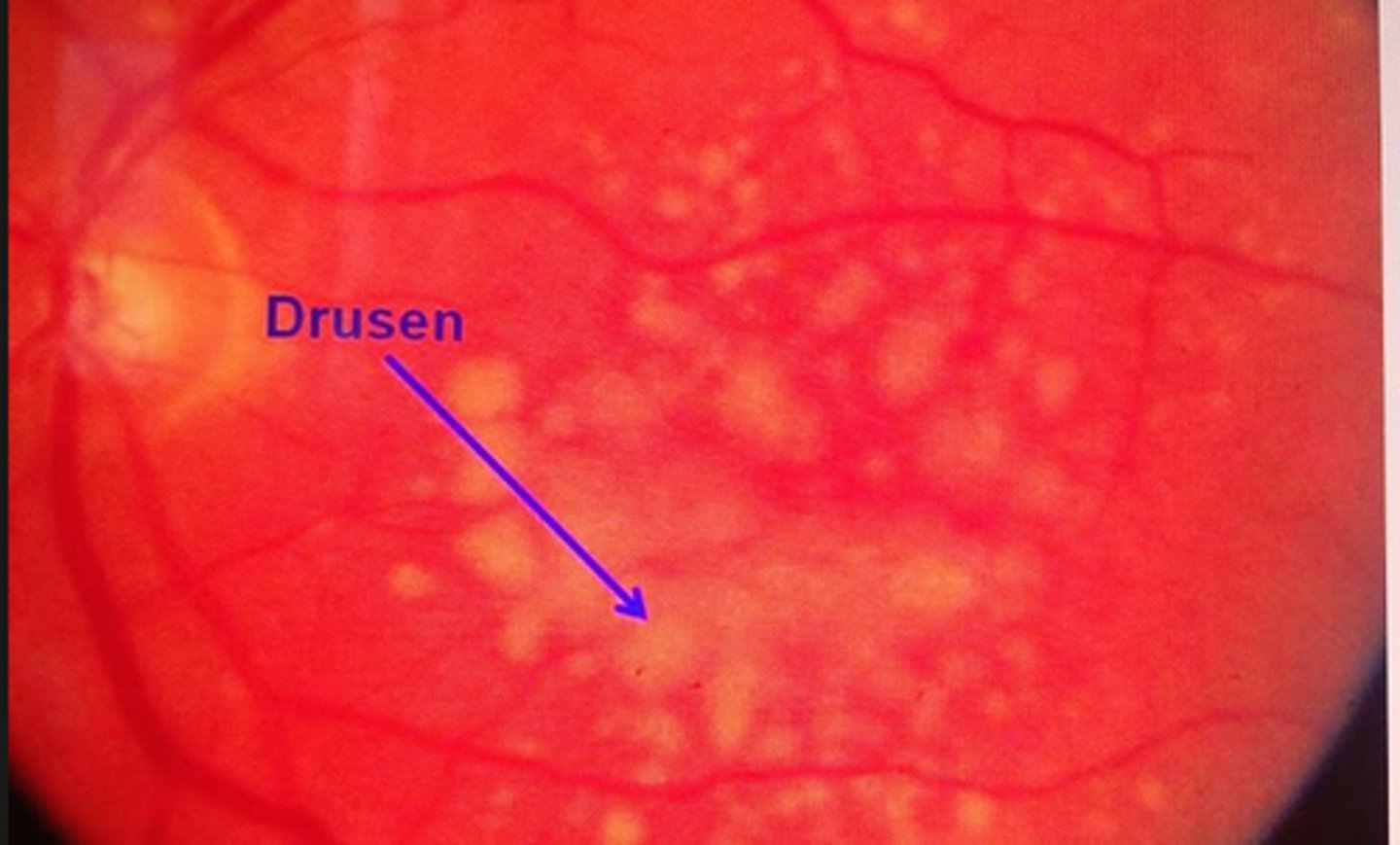
Gradual central field loss. Drusen
Macular degeneration
Acute inflammation and demyelination of the optic nerve leads to acute monocular vision loss and pain in the affected eye, Multiple sclerosis is the most common cause
Optic neuritis
Decreased extraocular movement, pain with movement of the eye and proptosis, signs of infection
Orbital cellulitis
Optic disc swelling that is caused by increased intracranial pressure. The swelling is usually bilateral and can occur over a period of hours to weeks
Papilledema
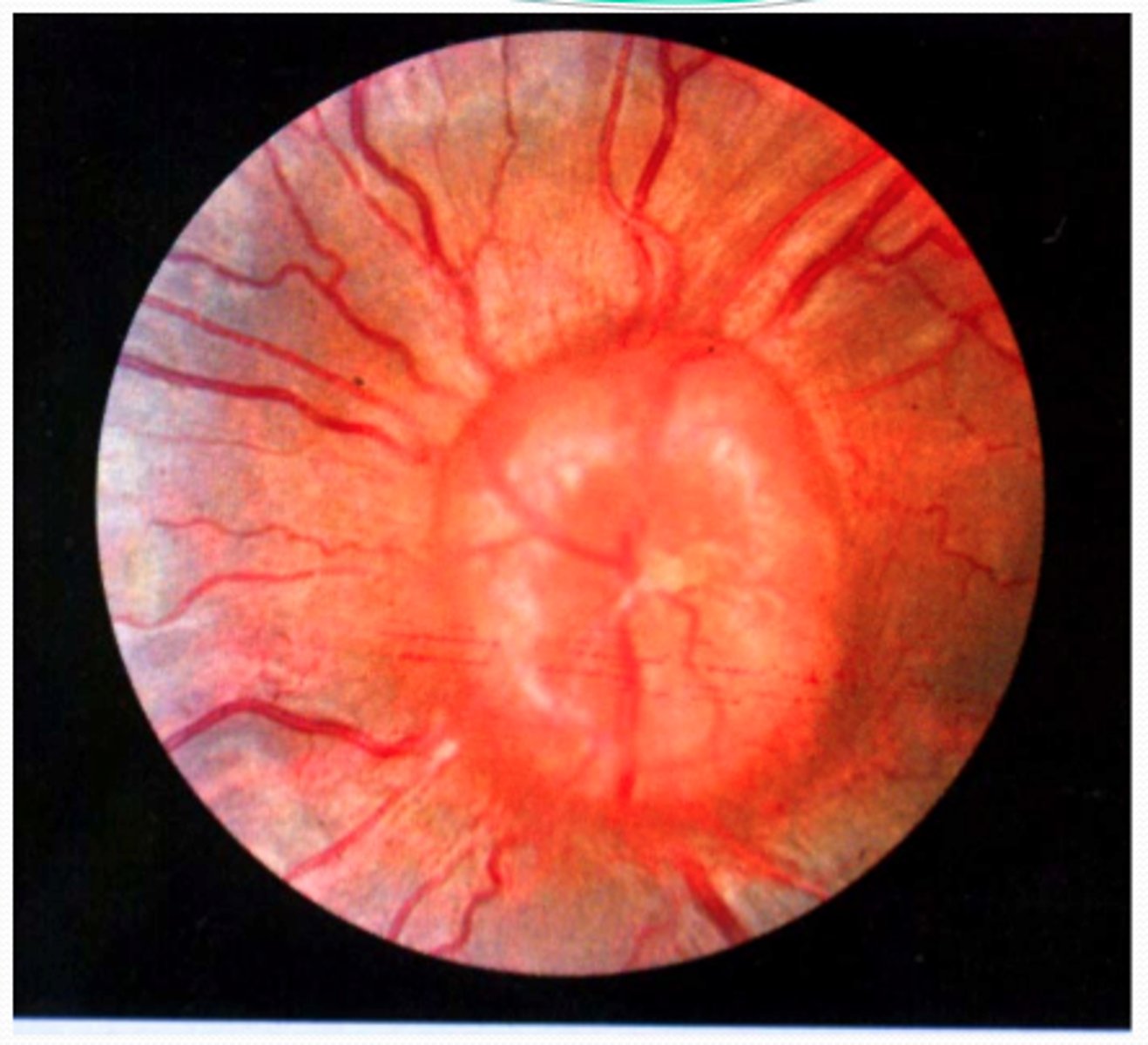
Elevated, superficial, fleshy, triangular-shaped "growing" fibrovascular mass (most common in inner corner/nasal side of the eye
Pterygium
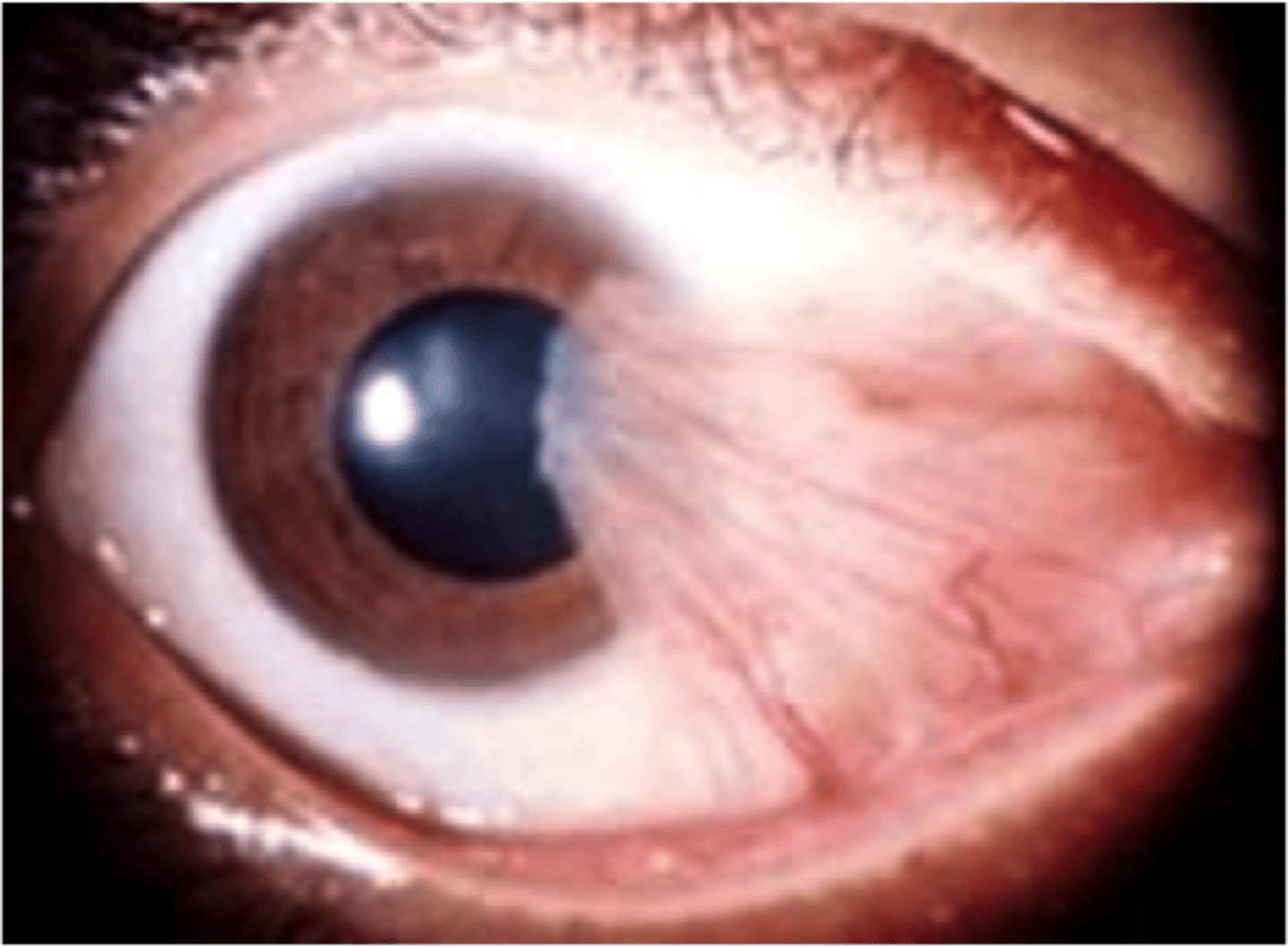
Flashers, floaters, asymmetric red reflex, described as a curtain or dark cloud coming across the field of vision, Keep patient supine (lying face upward)
Retinal detachment
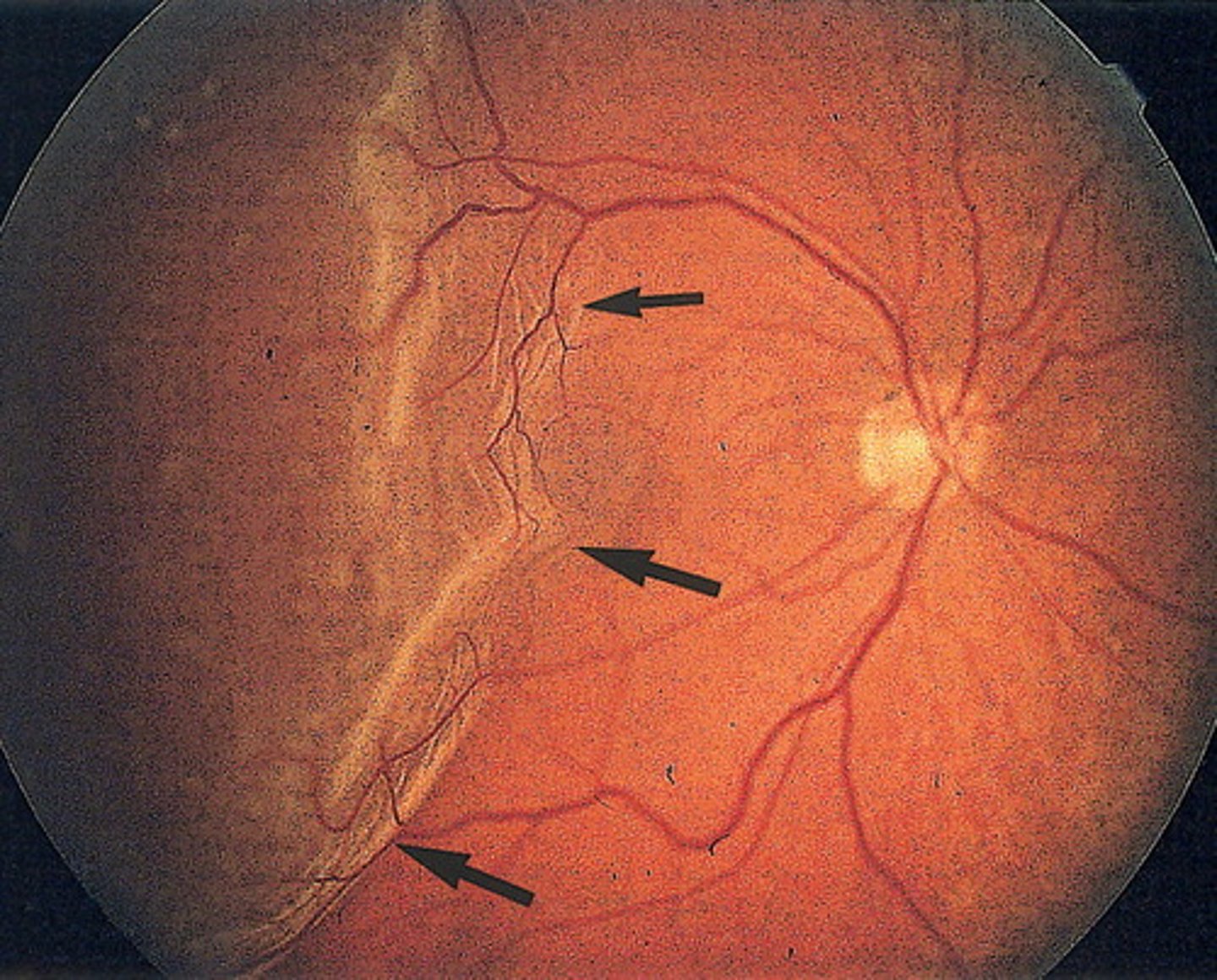
Sudden, painless, unilateral, and usually severe vision loss (Amaurosis fugax), ruptured plaque from same sided (ipsilateral) carotid artery. cherry red spot
Retinal vascular occlusion
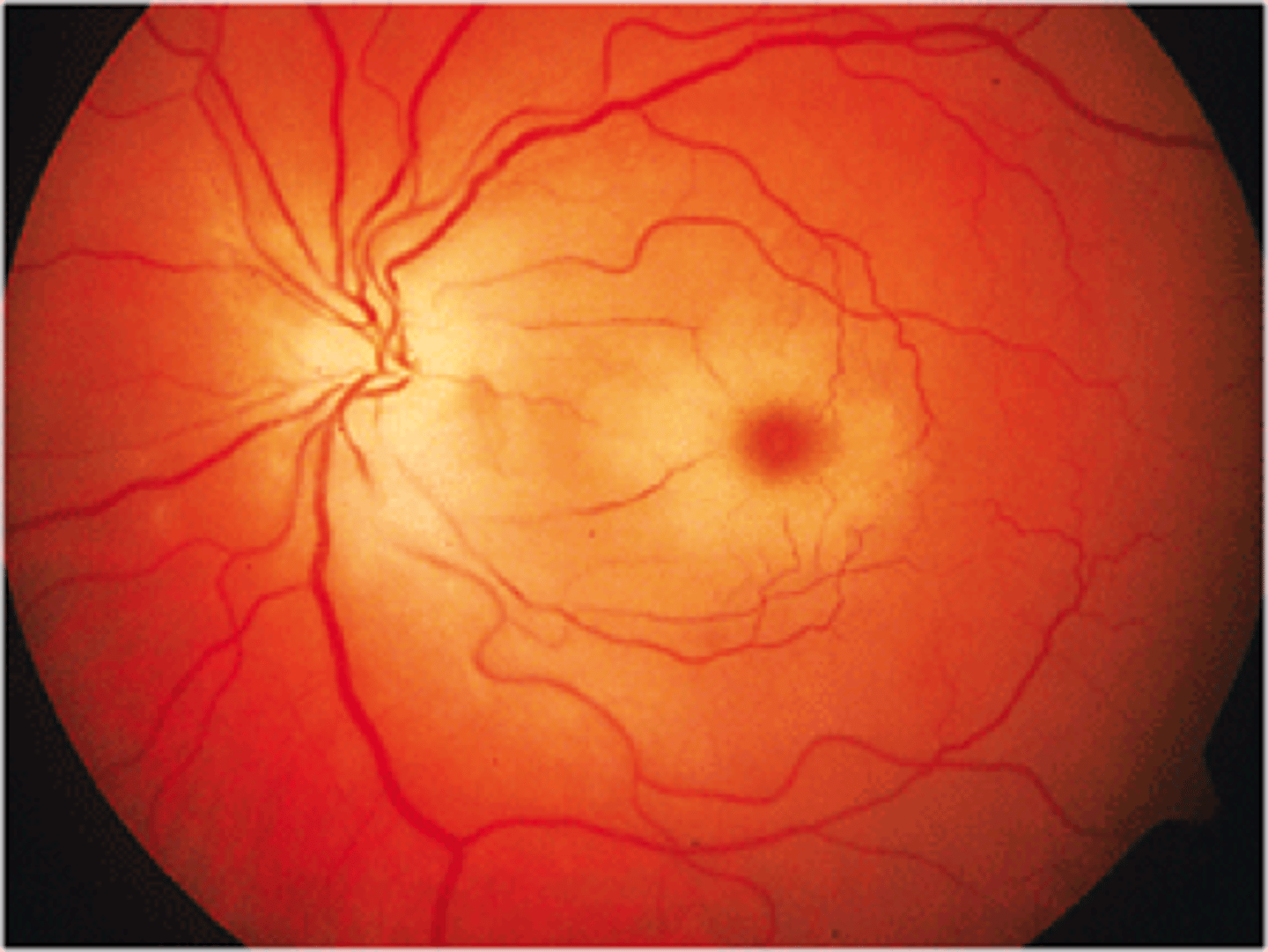
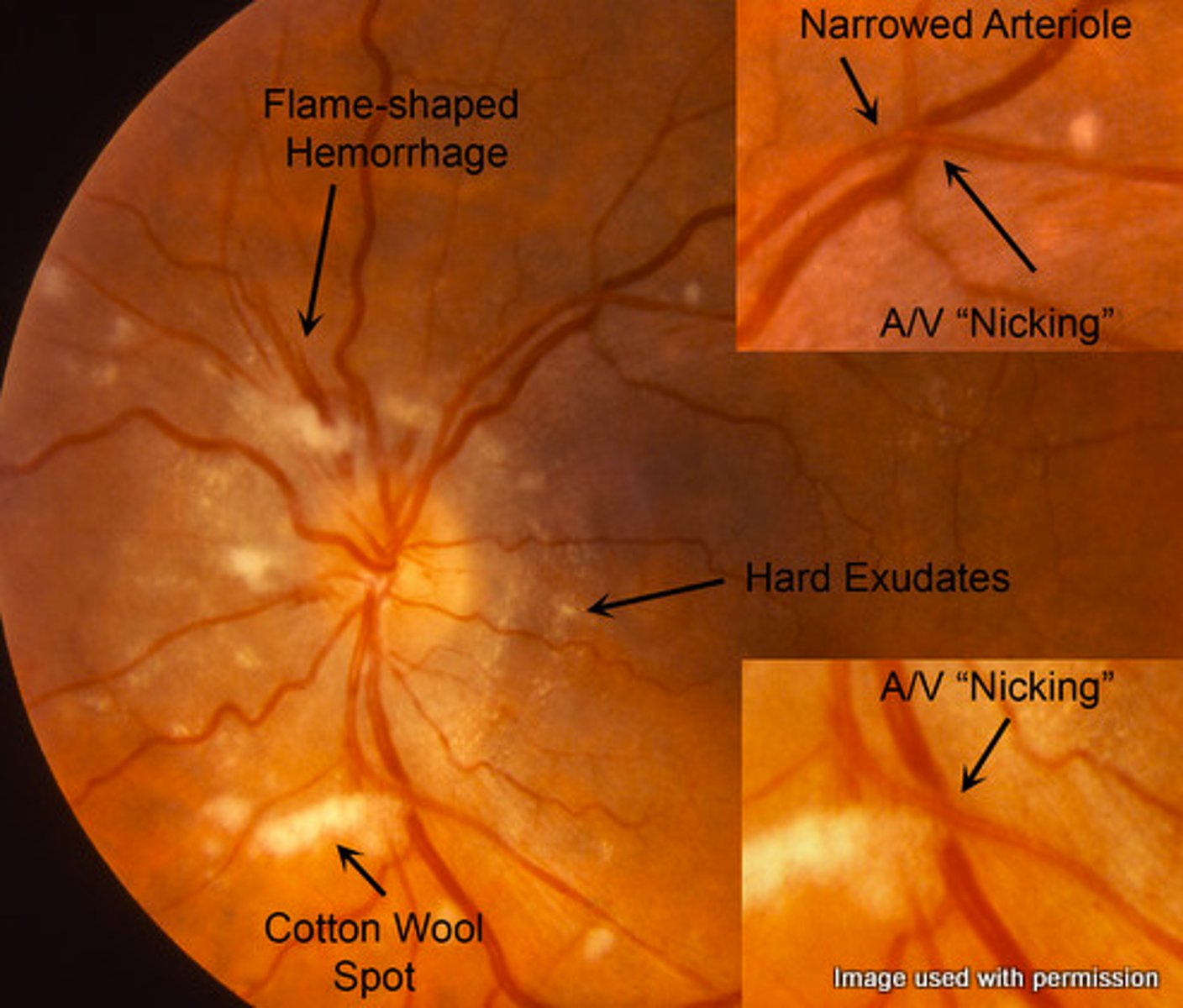
Cotton wool spots, hard exudates, blot and dot hemorrhages, neovascularization, flame hemorrhages, A/V nicking
Retinopathy
Any form of ocular misalignment, the cover/uncover test is used to aid in diagnoses
Strabismus
Out-turning of eyes
Exotropia
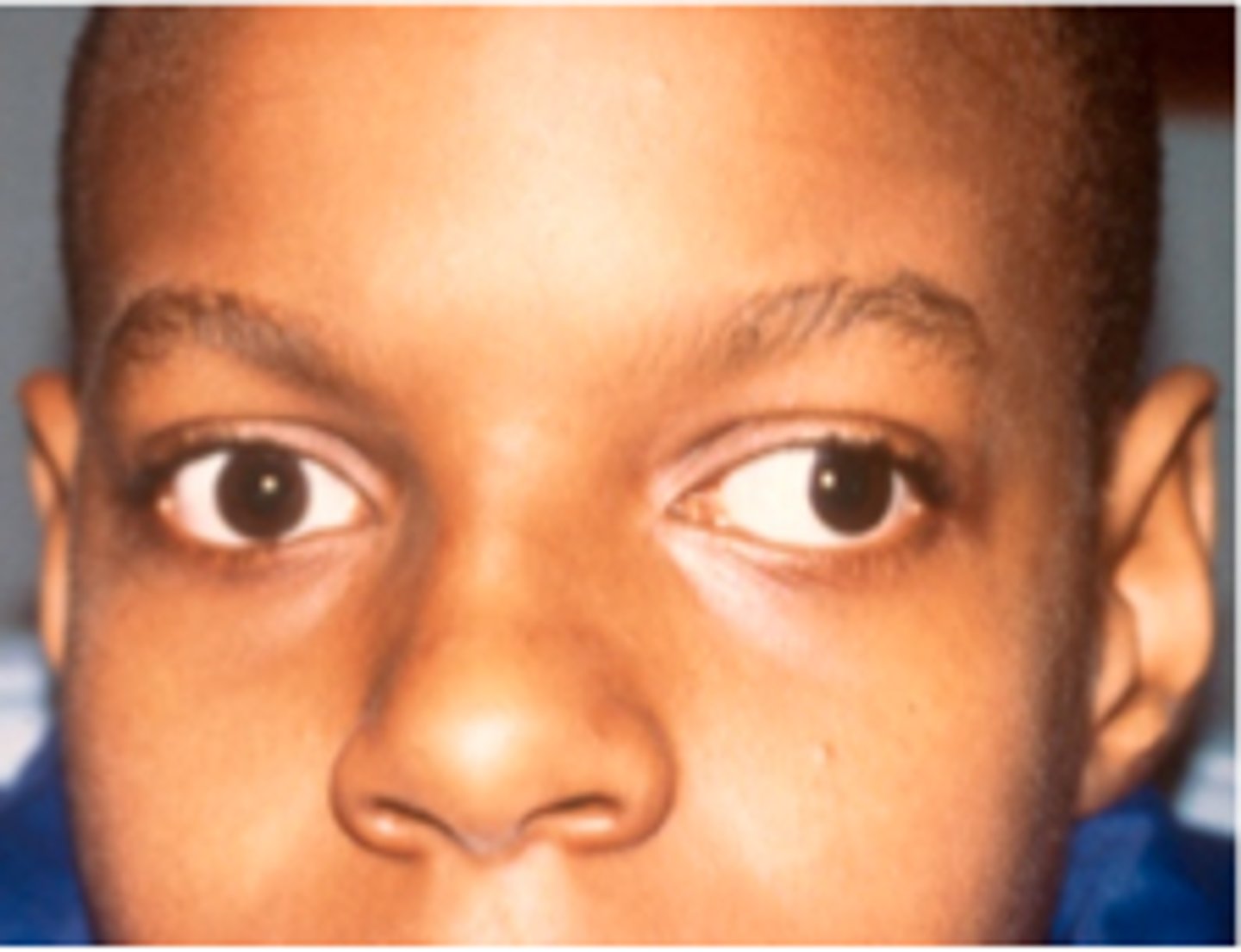
In-turning of eyes
Esotropia