MSM
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
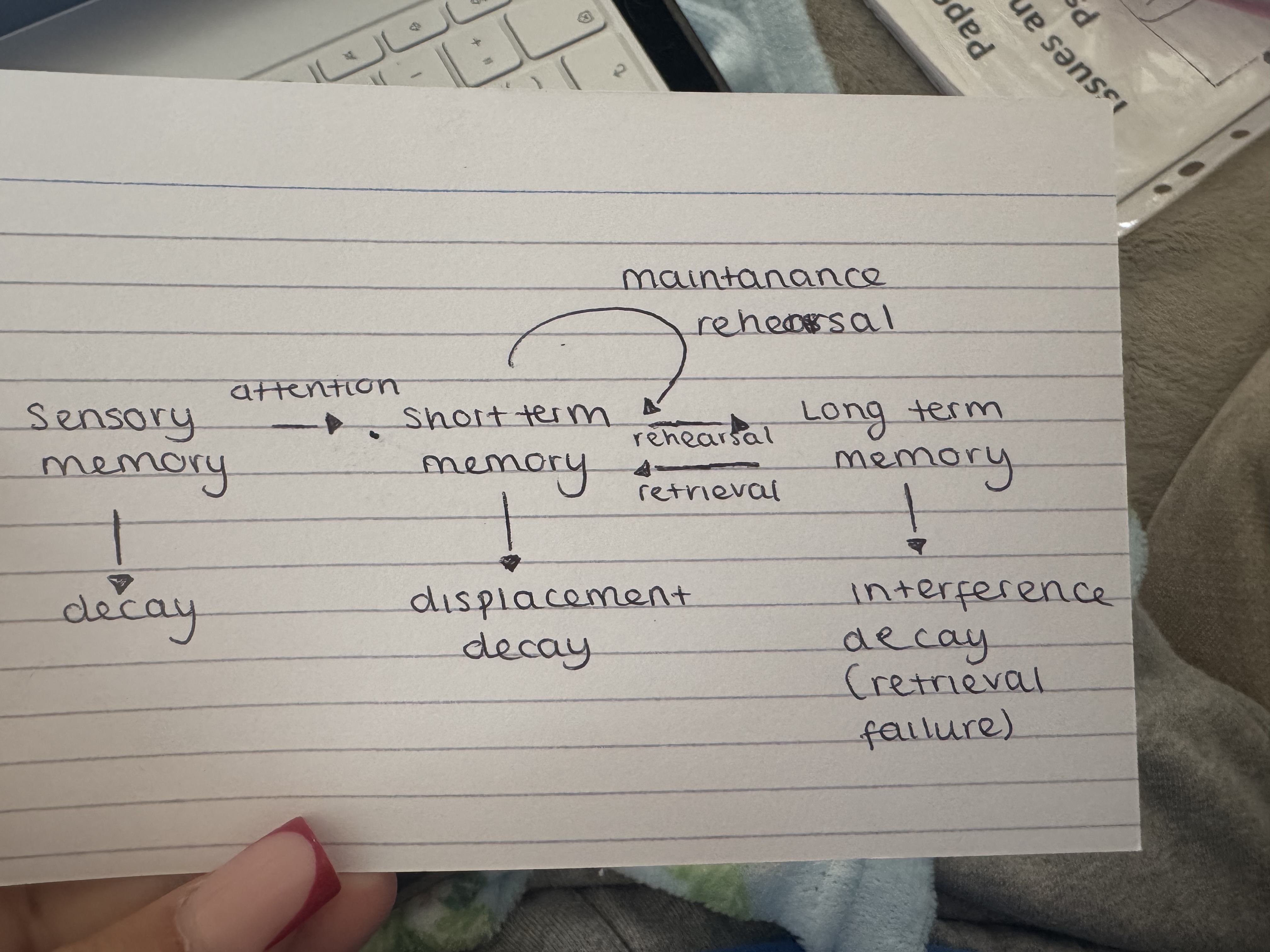
What does long term memory do?
Unlimited capacity
Potentially permanent duration
Coded semantically
What does STM do?
Acoustic (verbal)
Capacity is 7+/-2 (miller)
Info can be lost in 18-30 secs (Peterson and Peterson
What does sensory memory do?
Info from the environment
Will only stay there for ½ a sec
Fleeting impression
Echoic (acoustic) and iconic (visual)
Sensory memory can pass on info to the STM if we pay attention to it
Structure of the MSM
What did sperling research?
Pps saw a grid of digits and letters fro 50 milliseconds then had to write down either all 12 items from a grid or just one row after hearing a tone
Recall was worse for the whole grid (42%) compared to one row (75%)
This suggests that info decays so quickly in the sensory store we can’t write it down quick enough
One strength of the MSM
P. Psychological evidence does support its main claims
E. Modern brain scans enable us to see which region of the brain in active when a person is doing a memory tasks
E. In STM the prefrontal cortex has been shown whereas it is in the hippocampus with LTM
L. This suggests STM and LTM are processed/located in different parts of the brain as the MSM predicts
One limitations of the MSM?
P. It is oversimplified
E.the MSM assumes there is a single STM and a single LTM evidence shows there are several (eg: procedural, episodic)
E. KF was an amnesiac his STM for digits was very poor when they were read out to him but if he read them himself it was better, suggesting there is more than one STM
L. This evidence suggests that the model is not comprehensive enough