
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
when do phase changed occur?
when the kinetic energy of the particles change
attractive forces between particle
intermolecular
attractive forces within a molecule
intramolecular
unequal sharing of valence electrons between two nonmetals with very different electronegativity values
polar covalent bond
equal sharing of valence electrons between two nonmetals with same or similar electronegativity values
nonpolar covalent bond
transfer of valence electrons from metal to nonmetal
ionic bond
solids have a _____ shape and ______ volume
definite; definite
liquids have a _____ shape and _______ volume
indefinite; definite
gases have a ______ shape and ______ volume
indefinite; indefinite
what are the three types of intermolecular forces?
dipole-dipole, hydrogen, and dispersion
dipole-dipole force occurs between two _____ molecules
polar
in dipole-dipole force, the ________ charge is attracted to a ________ charge
positive charge; negative charge
hydrogen bond occurs between two ____ molecules
polar
when the positive H of a molecule is attracted to the negative F, O, or N atom of another molecule, it’s known as a _______ _______
hydrogen bond
the hydrogen bond is the ______ intermolecular force.
strongest
dispersion force occurs between two ______ molecules
nonpolar
when the _____ end of one molecule is briefly attracted to the ______ end of the other molecule, it is called ________ _____
positive; negative; dispersion force (London)
what happens when molecules briefly collide with each other
electrons of the molecules repel each other and shift, creating a temporary positive and negative ends in the molecules.
what are the three intramolecular forces?
ionic, polar, and covalent
intramolecular forces are stronger than intermolecular forces (true or false)
true
strength of attractive forces (strongest to weakest)
ionic
polar covalent
nonpolar covalent
hydrogen bond
dipole-dipole force
dispersion force
what happens when energy (heat) is added to a substance?
state of matter changes from solid→liquid→gas; particles move faster and farther apart so intermolecular forces get weaker.
endothermic
energy is added
what happens when energy is removed from a substance?
state of matter changes from gas→liquid→solid; particles move slower and closer together so intermolecular forces become stronger.
exothermic
energy is removed
phase change diagram:
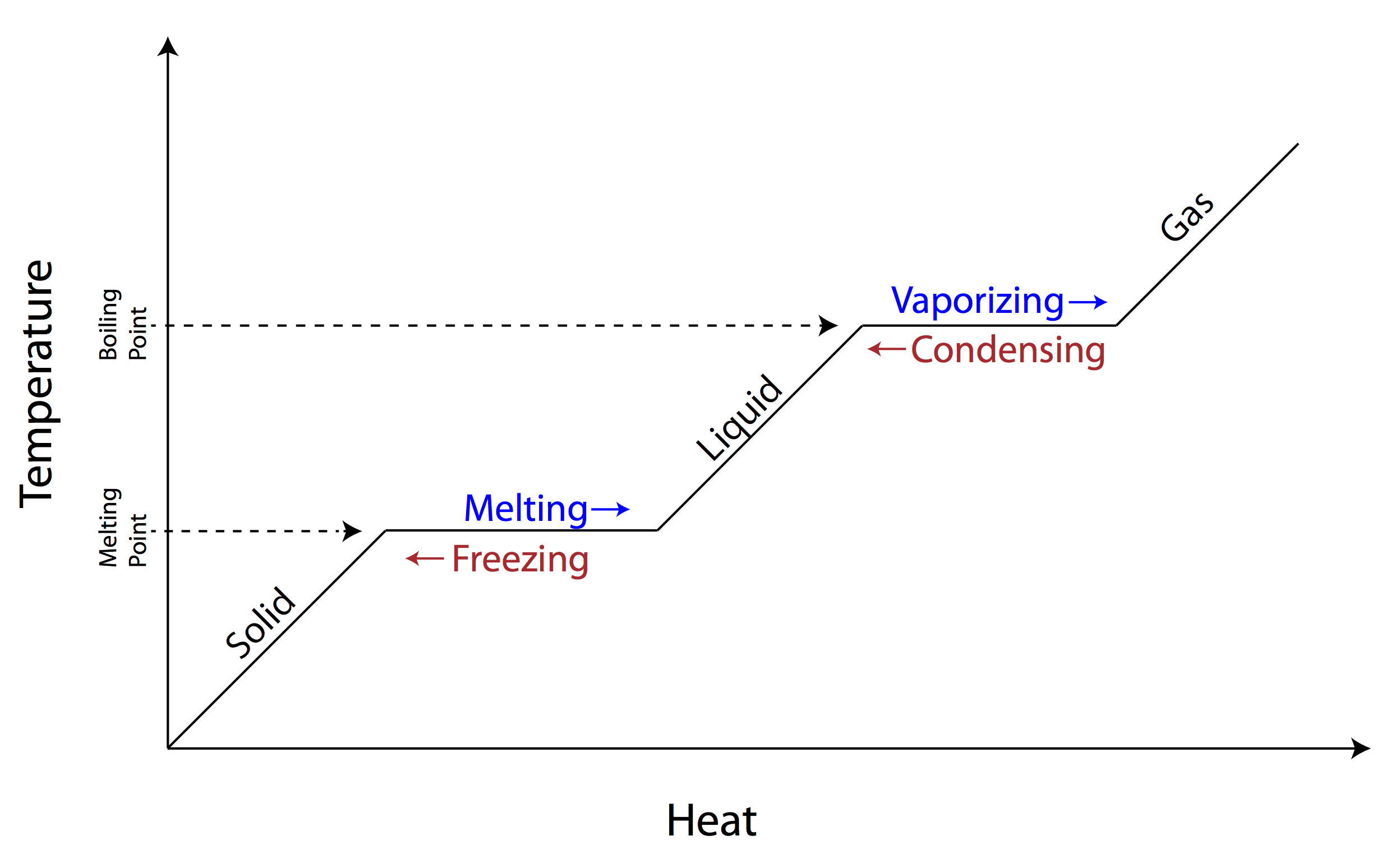
weak intermolecular forces= _____ to melt= _____ melting point
easy; low
strong intermolecular forces= ______ to melt= _____ melting point
hard; high
what are the three solids?
crystalline, amorphous, and allotrope
crystalline solids
repeating 3-D pattern called crystal lattice; have regular shapes that reflect the arrangement of the particles.
amorphous
non-crystalline solids; particles not arranged regularly; solid has no definite structure
allotropes
different forms of the same element; different ways atoms bond together
examples: carbon
diamond- arranged in crystal lattice
graphite- parallel layers held by dispersion
buckminsterfullerene (buckyball)- soccerball
surface tension
property of a liquid that causes the surface to act like weak skin
cohesion
sticking together of particles of the same substance
_______ IM force= ______ surface tension
stronger; higher
surfactant
acts on the surface and interferes with the IM forces between liquid particles, which lowers the surface tension
examples: soap, detergent, or rubbing alcohol
vaporization
phase change from liquid→gas
evaporation
phase change from l→g at the surface
in evaporation, molecules with ______ kinetic energy at the surface can ______ the liquid. Lower _____ is left therefore it has a lower ______
higher; leave—energy; temperature
when does boiling occur
when liquid is heated to a temperature at which the vapor pressure pushes up and is equal to the atmospheric pressure that pushes down.
______ intermolecular force= ____ energy needed for vapor pressure to overcome atmospheric pressure= ______ boiling point
stronger; more; higher
the behavior of gases is affected by ________ and ________ temperature
pressure; temperature
vacuum
space with no gas particles= no collisions= no pressure