Physics Exam Formulas
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Formula's for the Physics 211 course at USC. Many of these are adapted from the College Board's AP physics formula sheet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
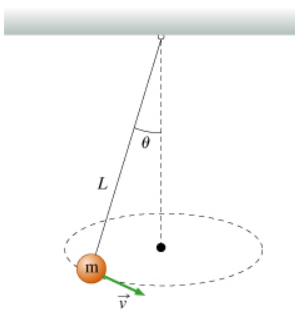
What is the formula for velocity for the conical pendulum?
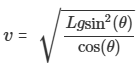
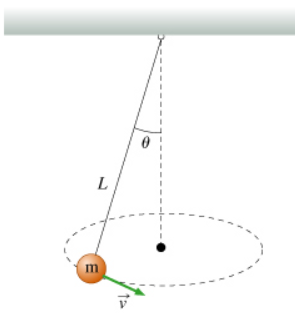
What is the formula for the period (time it takes for 1 revolution)?
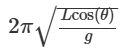
What is the formula for the center of mass?
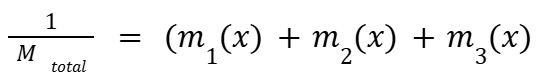
In circular motion what are the constants?
Speed, angular velocity, and magnitude of net force.
Angular momentum (L) formula (this one uses angular variables)
L = Iω, I is the moment of inertia, ω is the angular velocity.
Angular momentum formula (this one does NOT use angular variables)
L = m*v*r, m = mass, v = velocity, r = radius
How does inertia relate to velocity?
More inertia means there is a slower velocity while less inertia means there is a faster velocity.
In an elastic collision is kinetic energy conserved? Why?
Yes, kinetic energy is conserved because both momentum and kinetic energy remain constant throughout the interaction.
In an inelastic collision is kinetic energy conserved? Why?
No, kinetic energy is not conserved because some of the energy is transformed into other forms of energy such as heat or sound during the collision.
Elastic collision formula
m1*v1 + m2*v2 = m1*v1 + m2*v2
Inelastic collision formula
m1*v1 + m2*v2 = v*(m1 + m2)
Formula for torque (using angular variables)
T = I*α, I = moment of inertia, a = angular acceleration