Module 7 Integumentary System
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
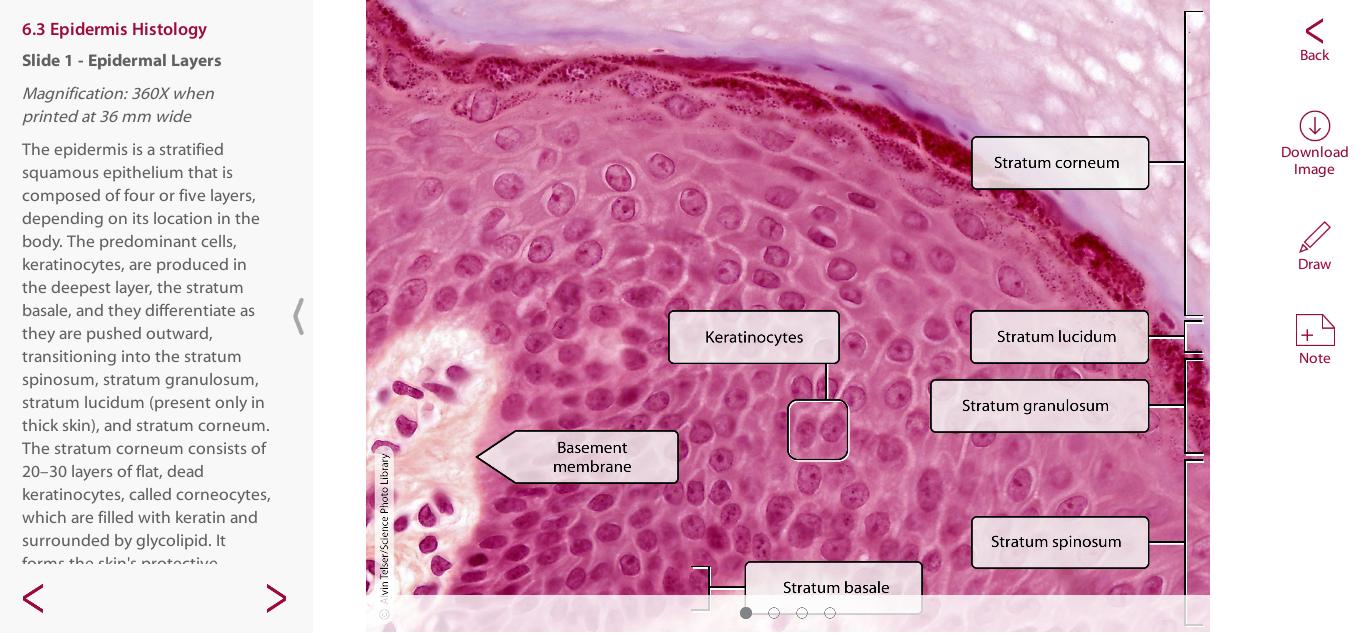
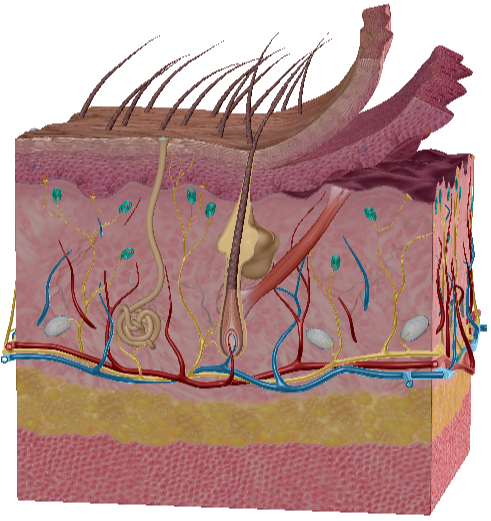
Layers of Epidermis deep - superficial
Stratum Basale, spinosum, granulosum, lucidum and corneum
Thick skin contains
Stratum lucidum and fiction lines
Thick skin lacks
Hair, sebaceous and apocrine glands
Thin Skin has
thicker dermis, more flexible
Keratinocytes
In epidermis, produced in basale layer, waterproof skin
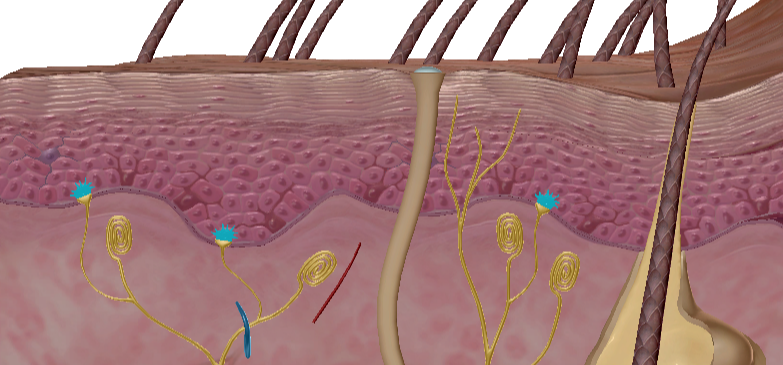
Merkel Cells
Touch receptors
Melanocyte
Produce melanin from UV light
Langerhan Cells
Immune cells in epidermis
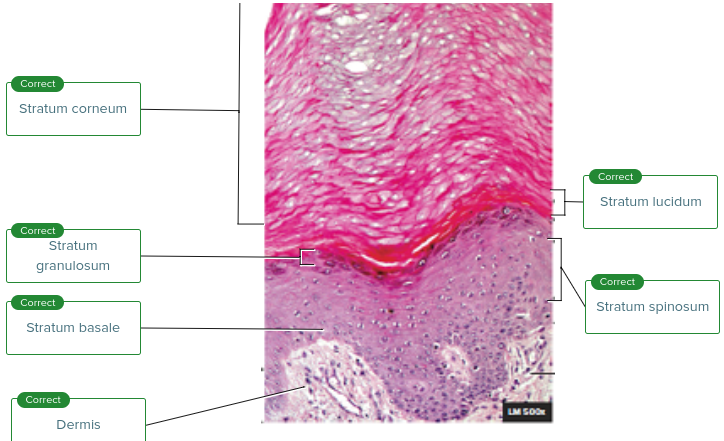
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Granulosum
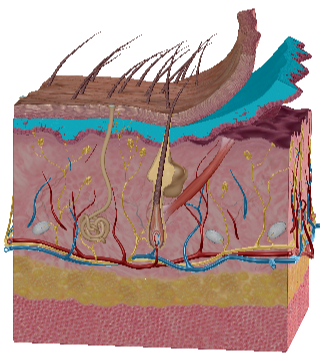
Stratum Spinosum
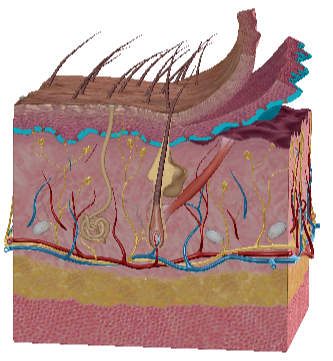
Stratum Basale
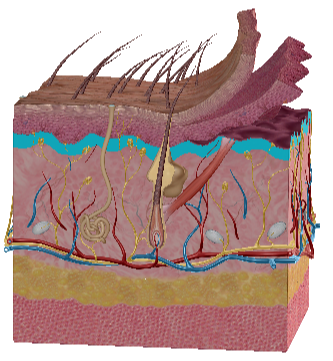
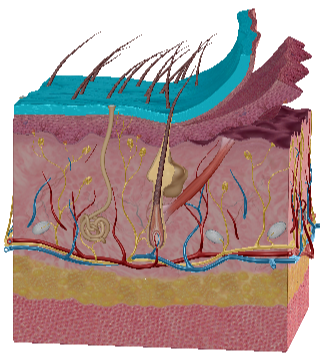
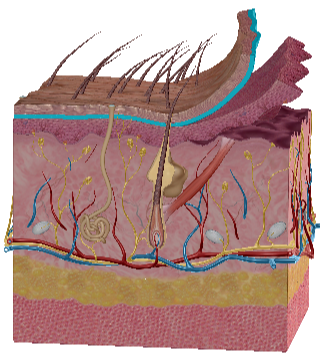
Papillary Dermis
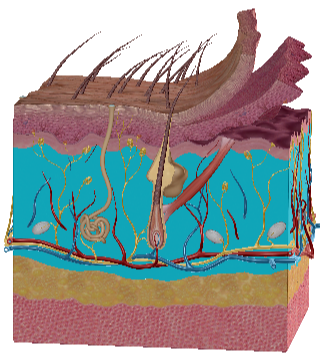
Reticular Dermis
Meissner corpuscles
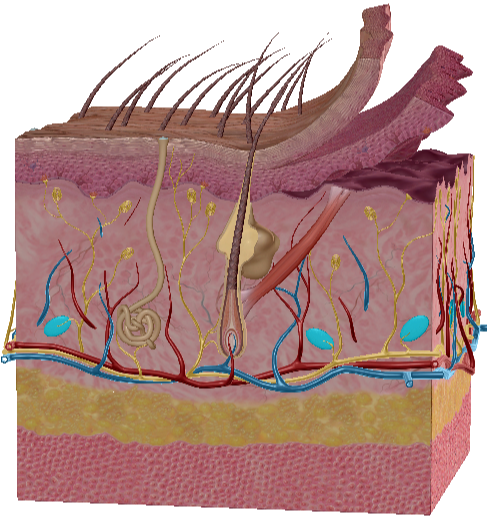
Pacinian corpuscles
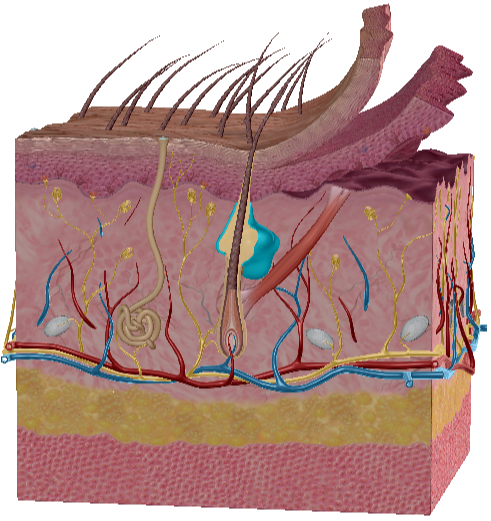
Sebaceous gland
Merkel cells
Stratum Corneum
superficial layers of dead cells
Stratum Lucidum
Thick skin, 3-5 layers of clear dead keratinocytes
Stratum Granulosum
2-5 layers of dead keratinocytes
Stratum Spinosum
Mitotic division occurs in the 8-10 layers
Stratum Basale
Cells divide and move up
What does hypodermis do?
Attach dermis to bone and muscles
Hypodermis tissue
Loose connective, elastic, collagen
Papillary Dermis
Loose connective with fibers
Reticular Dermis
Dense irregular connective
Sebaceous gland
Holocrine, produce sebum
Eccrine
Sweat gland using ducts
Apocrine
Sweat glands that open to hair, start use in puberty
Ceruminous
Modified eccrine gland, secrete earwax
Free nerve cells
Touch receptors, little force needed, close to surface
Pacinan
pressure receptor in reticular dermis
Epidermis tissue consists of….
Stratified squamous epithelial cells
Subcutaneous layer tissue type
Loose connective
Carotene color + cause
Yellow orange due to increased intake of carotene
Jaundice color + cause
Yellow, increased amount of bile
Erythema color + cause
Red due to increased blood flow
Cynaosis color + cause
Blue due to decreased oxygen
Merkel Cells
In nerve endings in epidermis for light touch
Ruffini end organ detects
Stretch, pressure, continuous touch
Hair cortex
Bulk of hair
Cuticle
Hair surface