MODULE 11 - [Anatomy 1.0] Histology
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Medulla
Inner Region of the Kidney
10 to 15
The Renal Medulla consists of ____ to ____ Renal Pyramids
Renal Columns of Bertin
The projections of cortical tissue that separate the renal pyramids and contain segments of the Loop of Henle
Medullary Rays of Ferrein
It is located between the cortical labyrinths in the renal cortex and consists of the: (MRCTLH)
Proximal segments of the Collecting Tubules
Papillary Duct where the DCT drains
Loop of Henle
Cortical Labyrinth / Pars Convoluta
The region between the cortex and the medullary rays that contains the: (CLRC)
Renal Corpuscles
Parts of the PCT and DCT (drains into the Collecting Tubules)
Arched segments of the Collecting Tubules
Renal Pyramids
Contains the:
Distal Segments of the Collecting Tubules
Papillary Duct
Segments of the Loop of Henle
Papillary Ducts
The collecting tubules drains into the?
Renal Lobe
Made up of Numerous Renal Lobules and consists of:
Renal Pyramid
Cortical Tissue
Renal Lobule
Consists of:
Medullary Ray at its center
Half of the adjacent cortical labyrinth
Interlobar Arteries
Branch of the Renal Artery that is found in between the renal pyramids and headed towards the cortex
Arcuate Artery
Branch of the interlobar arteries at the corticomedullary junction, these blood vessels form the outer boundaries of the renal lobules
Interlobular Arteries
Branch of the Arcuate Arteries
Afferent Arterioles
Branch of the Interlobular Arteries
Glomerular Capillaries
The Afferent arterioles will continue to be the ______
Efferent Arterioles
The Glomerular Capillaries will drain into a single ______
Glomerulus
Bowman’s Capsule / Glomerular Capsule
Comprises the spherical structure of the Renal Corpuscle (Malpighian Corpuscle)
Vascular Pole
Where the Afferent Arterioles enter and where the Efferent Arterioles leave the corpuscle
Located in the Cortex
Urinary Pole
Where the Renal Tubule begins
Located in the
Glomerulus
A ball-like structure that contains the: (GMG)
Glomerular Capillaries
Mesangial Matrix
Glomerular Mesangial Cells
Glomerular Mesangial Cells
Stellate Cells that are contractile and can influence the diameter of the glomerular capillaries
These types of cells are most numerous in the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle
Capable of Phagocytosis
Help remove debris from the glomerular filtration barrier
Produce the Mesangial Matrix
Mesangial Matrix
The glue that holds and binds the glomerular capillary together
Bowman’s Capsule (Glomerular Capsule)
Double-walled sac that envelopes the glomerulus
Contains two-layer
Visceral Layer
Parietal Layer
Visceral Layer
The inner wall which envelopes the glomerulus
Made up of Podocyte (these cells create a barrier that prevents large molecules from passing into the filtrate)
Parietal Layer
The outer wall that forms the outer boundary of the renal corpuscle
made up of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Bowman’s Space
Narrow cavity between the visceral and parietal layers of the bowman’s capsule
Podocytes
Makes up the Visceral Layer of the Bowman capsule
Stellate Cells which have cytoplasmic processes which give rise to the Foot Process or Pedicels
Pedicels
Wrap themselves around the glomerular capillary walls where they interdigitate with pedicels of the neighboring podocytes
Only part of the podocytes that rests on the basal lamina
Filtration Slits
Narrow gaps that are covered by the Slit Diaphragm or Slit Membrane which is dotted by very small pores
Glomerular Filtration Barrier
This allows an ultrafiltrate of blood to seep into the the Bowman’s capsule consists of: (FBS)
Fenestrated Endothelium
Basal Lamina
Slit Membrane of the filtration slits
Renal Tubule
consists of:
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Loop of Henle
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Direct continuation of the Bowman’s Capsule
Longest Segment of the Renal Tubule
Confined in the Cortex, comprises the majority of tubules seen in the cortex
Starts at the Urinary Pole
Lined by Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Has a Luminal surface lined with Microvilli that are Long and Numerous, forming a brush border
The Lateral Borders of the epithelial cells are Not Distinct because the cell membranes of adjacent cells interdigitate
Have Striations due to the presence of infoldings of the basal plasmalemma as well as the presence of numerous Longitudinally Oriented Mitochondria
Basal Plasmalemmal Infoldings increase the absorbing capacity
The main function is to Reabsorb 70% to 80% of the water and sodium in the glomerular filtrate
Loop of Henle
Section of the Renal Tubule between the Proximal Convoluted Tubule and Distal Convoluted Tubule
Starts in the Cortex, then dips into the Medulla, where it makes a hairpin Turn, then returns back to the cortex
Thick Descending Limb
Thin Limb
Thick Ascending Limb
Segments of the Loop of Henle
Thick Descending Limb
Initial Segment of the Loop of Henle
Located Partly in the Cortex and the Medulla
Same histologic structure and function as the PCT
Lined by Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
The main function is to Reabsorb 70% to 80% of the water and sodium in the glomerular filtrate
Thin Limb of the Loop of Henle
Confined in the Medulla
Wall is composed of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Main function is to Concentrate Glomerular Filtrate
Thick Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle
Starts at the Medulla then heads for the Cortex where it gets into contact with the Vascular Pole of the renal corpuscle of its parent nephron
Histologically and functionally identical to the DCT
Walls are lined by Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Have Shorter epithelial cells causing the lumen to be bigger
Main function is to Reabsorb little amount of water and Secrete Potassium and Hydrogen Ions into the glomerular filtrate
Distal Convoluted Tubule
Last segment of the nephron
Located entirely within the Cortex
Shorter and Less Convoluted but have a Bigger Lumen than the PCT
Walls are lined by Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Have Shorter epithelial cells causing the lumen to be bigger
Distinct Cell Boundaries
Visible Lateral Border
Epithelial Cells do not have basal Plasmalemmal Infoldings but there are numerous mitochondria located within the basally located interdigitating processes on the basal portion of the cuboidal cells lining the DCT which can account for the Basal Striations
the Apical Domain does not form brush borders
Less numerous and shorter Microvilli
Cytoplasm is less Eosinophilic
Main function is to Reabsorb little amount of water and Secrete Potassium and Hydrogen Ions into the glomerular filtrate
Short Looped / Cortical Nephrons
Long Looped Nephrons / Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Classifications of Nephrons according to the length of their Loop of Henle
Short Looped / Cortical Nephron
Comprise the Great Majority of Nephrons in the Kidney
Their Renal Corpuscle is located in the outer portions of the cortex
Their Loops of Henle which form part of the Medullary Rays barely make it to the Medulla
Their Hairpin Loop or Arch is formed by the initial portions of their Thick Ascending Limb
Long Looped Nephrons / Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Their Renal Corpuscle is also located in the cortex but near the Corticomedullary Junction
Their Henle’s Loop extends deep into the Medulla
Long Thin Limb forms the hairpin Loop or Arch
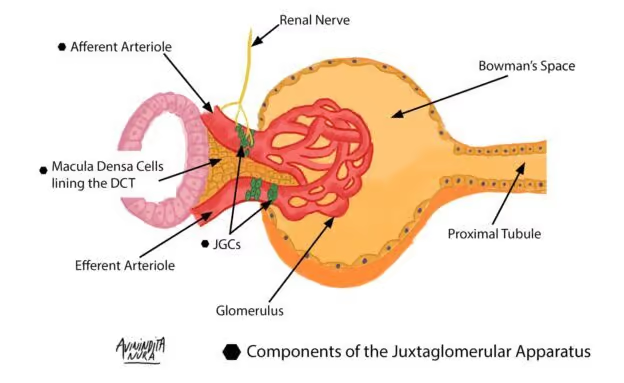
Juxtaglomerular Complex (JG Complex)
Only present in the DCT and Afferent Arteriole
Found at the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle
Has three groups of Atypical Cell that form it: (JEM)
Juxtaglomerular Cells (JG Cells)
Extraglomerular Mesangial Cells
Macula Densa
Helps regulate systemic blood pressure and some of its cells Secrete Hormones
Juxtaglomerular Cells (JG Cells)
Found in the Tunica Media of the Afferent Arteriole
Secretes: (JRT)
Renin
Thrombopoietin
Polyhedral Cells
Located in the Tunica Media of the Afferent Arteriole just before it enters the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle
Extraglomerular Mesangial Cells
Conical Mass that occupies the space between the macula densa (of the DCT) and the Afferent Arteriole (Containing the JG Cells)
Flat
Light Staining
Involve in the signal transmission between the Macula Densa and the. Glomerular Mesangial Cells
Macula Densa
Found only in the Distal Convoluted Tubule
In contact with the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle
More Crowded and Narrower than those in the other segments of the DCT
Intensely staining Nucleus
Rest on a Very Thin Basal Lamina
Sensitive to sodium ion concentration and water volume in the DCT
Generate Signals that promote Renin Secretion by the JG Cells
Renin
The enzyme that participates in the Renin-Angiotensin System that regulates Arterial Blood Pressure
Thrombopoietin
Used in Platelet Production
Collecting Tubules
Papillary Ducts of Berlin
The Intrarenal Ducts consists of
Arched Collecting Tubule
Straight Collecting Tubule
Types of collecting tubules
Arched Collecting Tubules
Starts in the cortex as a short segment that curves towards the medulla
Lined with Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Epithelium contains:
Typical Epithelial Cells of the Collecting Tubules
Intercalated Cells
Straight Collecting Tubule
straight tubule which heads towards the medulla
The Proximal Segments (segments in the cortex) of this collecting tubule are the main components of the medullary rays
Is lined with Simple Cuboidal Epithelium in its Initial Segment
Epithelium contains:
Typical Epithelial Cells of the Collecting Tubules
Intercalated Cells
Typical Epithelial Cells of the Collecting Tubules
This type of epithelial cell of the collecting ducts secretes Potassium
Intercalated Cells
This type of epithelial cell of the collecting ducts are:
Darker Staining
Found in the cortex
Maintains the Acid-Base Balance of the body fluids
Papillary Ducts
Large tube in the medulla formed by convergence of straight collecting tubules
These ducts are bigger than the collecting tubules
Has a Tall Columnar Epithelium
Straight Collecting Tubules
Papillary Ducts
Main components of the Renal Pyramids
Renal Pyramid
Has 25 Papillary Ducts whose terminal portions come together to form the Renal Papilla or Apex of the Pyramid that fits into the Minor Calyx
Area Cribrosa
Region of the renal papilla that contains the Openings of the Papillary Ducts
Transitional Epithelium
Epithelium of the urinary passages and urinary bladder/urothelium
Longitudinally Arranged (Inner Layer)
Circularly Arranged (Outer Layer)
Muscle Cells in the urinary passages
Internal Urethral Sphincter
A sphincter made out of smooth muscle found at the junction of the Urinary Bladder and Urethra in Males
Male Urethra
20cm in length
has three segments
Prostatic Urethra
Membranous Urethra
Penile Urethra
Prostatic Urethra
First Segment of the Male Urethra
Lined with Transitional Epithelium
Receives the Ducts of the Prostate Glands and the Ejaculatory Duct
Membranous Urethra
Passes through the External Urethral Sphincter
1cm long
Lined with Pseudostratified Columnar or Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Surrounded by Circularly arranged Skeletal Muscle
Penile Urethra
Third and Longest segment
Transverses the Penis
15cm long
Lined with Pseudostratified or Stratified Columnar
except in the penile opening where it is Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous
Receives ducts from the Bulbourethral Glands of Cowper
Bulbourethral Glands of Cowper
Pair of small mucous-secreting glands embedded in the sphincter urethrae muscle of either side of the membranous urethra
Female Urethra
Shorter than the Male Urethra
4cm long
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is more common in female due to their short urethra
Lined with Transitional Epithelium in most of its length
Becomes Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous when it is near the Urethral Orifice
Peritubular Fibroblasts or Interstitial Cells
Fibroblasts like cells
Embedded in the Interstitial Tissue of the Kidney in the Peritubular and Periarterial Spaces
Contains Lipids like Granules in their Cytoplasm
Have Long Processes
Synthesizes and Secretes Erythropoietin
Erythropoietin
Used in the formation of new Red Blood Cells
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Secondary effect of Long Standing Poorly Controlled Hypertension
Secondary effect of Long Standing Poorly Controlled NIDDM (Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus)
Anemia of Renal Etiology
Urinary Tract Infection
More Common in Females than in males
Secondary effects of Shorter Urethral Length in Females
Ascending Infection in females
Urethritis, Cystitis, and Acute Pyelonephritis
Routine Urinalysis
Simple and Affordable diagnostic procedure for the screening of patients with:
Pyuria and Hematuria which are urinary tract infection symptoms
Glycosuria which is seen in suspected diabetic patients
Proteinuria, which is seen in diagnosed NIDDM and Hypertension for CKD