C1 - Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Draw and label an atom
Protons
Neutrons
Electrons
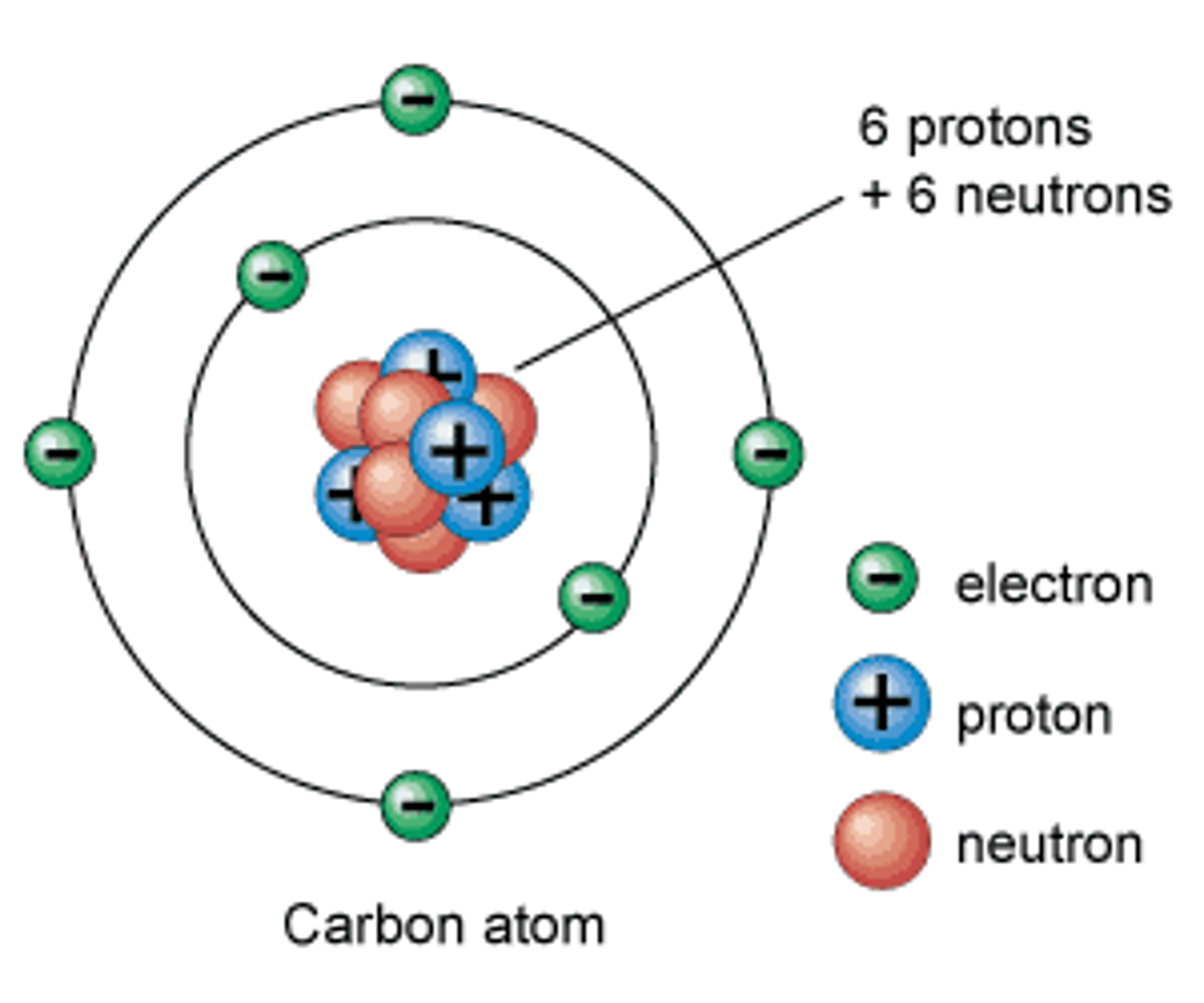
What are the masses and charges of these parts of an atom?
• Proton
• Neutron
• Electron
Protons = +ve
(mass 1)
Neutrons = neutral
(mass 1)
Electrons = -ve
(mass 1/2000th)
Why do atoms usually have no overall electrical charge?
Atoms usually have no overall charge because they have equal numbers of protons (+ve) and electrons (-ve), which cancel one another out
All atoms of a particular element (e.g. carbon) all have the same number of what?
Protons
What does relative atomic mass tell you about the atom?
The number of protons and neutrons in the atom
What does atomic number tell you about the atom?
The number of protons (usually the same as the number of electrons)
What is an isotope?
An isotope is an atom with a different amount of neutrons
How many electrons can occupy the 1st and 2nd shell (energy level) of an atom?
2 in the 1st shell and 8 in the 2nd shell
The electron structure of sodium can be represented as 2,8,1 - what does this mean?
Represent these atoms: -
• Fluorine
• Oxygen
• Potassium
• Magnesium
2,8,1 means 2 electrons in the 1st shell, 8 electrons in the 2nd shell and 1 electron in the 3rd shell
Fluorine = 2,7
Oxygen = 2,6
Potassium = 2,8,8,1
Magnesium = 2,8,2
Define these terms: -
• Element
• Compound
• Mixture
Element - a pure substance made from 1 type of atom only
Compound - 2 or more elements chemically bound
Mixture - 2 or more elements or compounds mixed together which are not chemically bound
What happens to the electrons of 2 atoms when they chemically react?
During a chemical reaction electrons are either given away, taken, or shared
What is an ion?
How are +ve ions formed?
How are -ve ions formed?
An ion is an atom with a charge
+ve ions have lost electrons
-ve ions have gained electrons
Explain how the following atoms become ions (will they be +ve or -ve)?
• Potassium
• Magnesium
• Chlorine
• Oxygen
Potassium - loses 1 electron (K+)
Magnesium - loses 2 electrons (Mg2+)
Chlorine - gains 1 electron (Cl-)
Oxygen - gains 2 electrons (O2-)
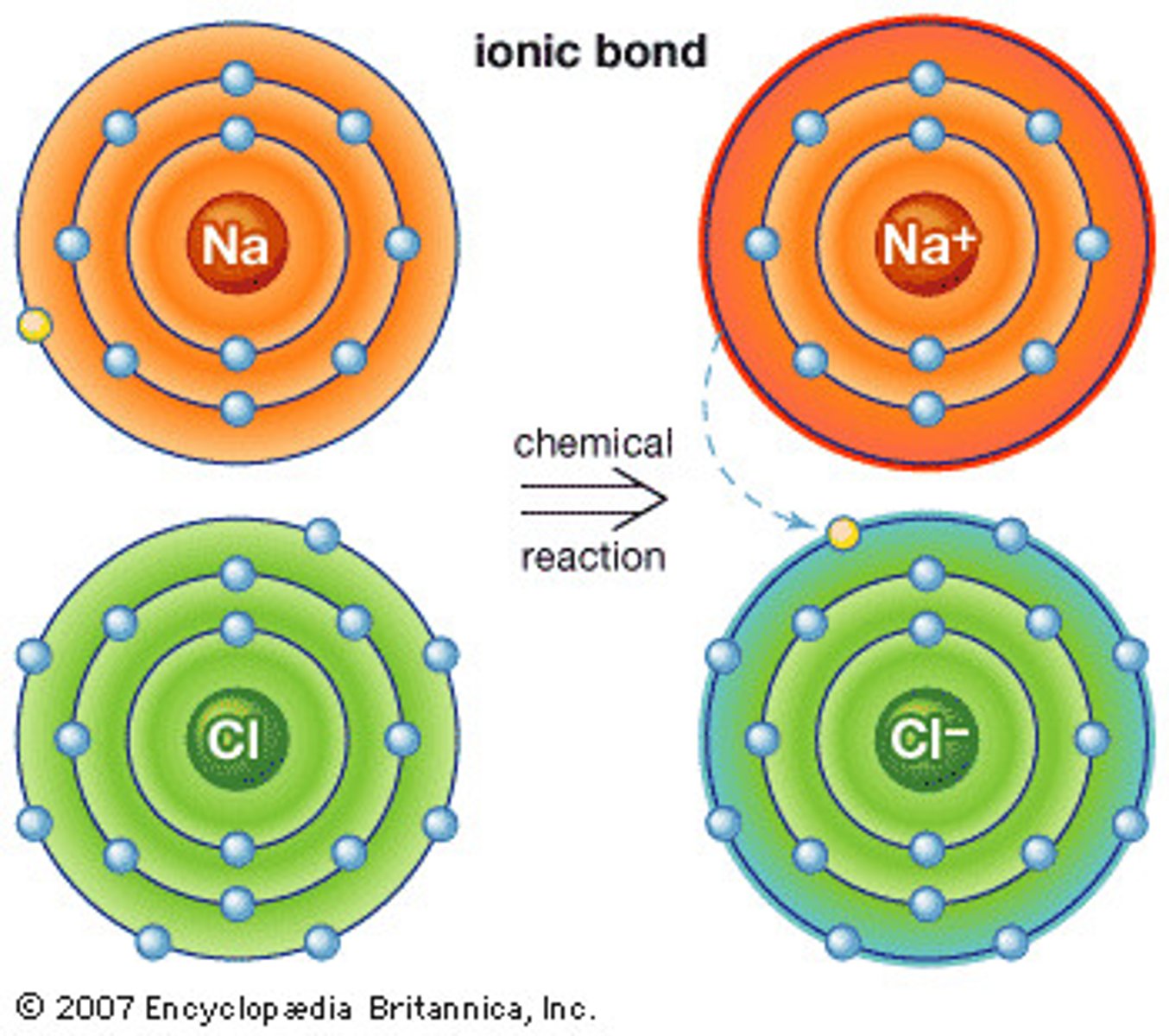
Describe the structure of ionic compounds
Ionic compounds have a giant structure - they are bonded to 6 other ions by electrostatic bonds
What are the melting and boiling points of ionic compounds like?
Why is this?
Ionic compounds have high melting points and boiling points - to melt them you have to supply enough energy to break the 6 bonds attached to each ion
What happens to the electrons when atoms form ionic bonds and covalent bonds?
Which is the strongest?
Ionic bonds - 1 atom loses electrons and another gains electrons
Covalent bonds - electrons are shared
An individual covalent bond is stronger than an ionic bond
What are the melting and boiling points of covalent compounds like?
Explain why this is
Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points (are often gases) are there is no attraction between the molecules
How are the elements of the periodic table arranged?
What are the rows called?
What are the columns called?
Elements are arranged in order of atomic number
Rows are called periods
Columns are called groups
Which 2 elements would be out of order in the periodic table if they were arranged by atomic mass instead of atomic number?
Potassium and Argon
Why do elements in the same group have similar properties?
Elements in the same group have similar properties as they all have the same number of electrons in their outer shell
What do these symbols mean?
• (s)
• (l)
• (g)
• (aq)
(s) = solid
(l) = liquid
(g) = gas
(aq) = aqueous
What are the symbols for these compounds?
• Calcium carbonate
• Sodium chloride
• Hydrochloric acid
Calcium carbonate - CaCO3
Sodium chloride - NaCl
Hydrochloric acid - HCl
Why do covalent compounds not conduct electricity when dissolved?
Covalent compounds do not conduct because they do no break down into ions
Give the names of 3 covalent compounds which have giant ionic structures?
What is the structure of each like?
Diamond - 4 carbon-carbon covalent bonds
Graphite - 3 carbon-carbon covalent bonds
Silicon dioxide - 2 double silicon-oxygen covalent bonds
Why does graphite conduct electricity?
Graphite conducts electricity because it is only bonded 3x (meaning there is a delocalised electron to pass the charge)
Explain why ionic compounds have a giant structure
Ionic compounds have giant structures because the ions keep their charge and attract up to 6 other ions - forming a giant lattice
What does monatomic mean and why are noble gases monatomic?
Monatomic means an atom which only exists on its own (does not react)
Noble gases are monatomic as they have a full shell and are un-reactive
What does diatomic mean and why are elements such as the halogens, hydrogen and oxygen diatomic?
Diatomic - atoms in pairs, e.g. H2 and O2
Halogens will form diatomic molecules because they covalently bond with each other, forming pairs
What is the bonding in metals like?
The bonding in metals creates delocalised electrons (free to move and pass on electrical current)
Why do metals conduct electricity?
The bonding in metals creates delocalised electrons (free to move and pass on electrical current)
Why do ionic compounds conduct electricity when they are dissolved / molten?
Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved or molten because they remain as ions (which will pass a current)
What are the symbols for these compounds?
• Sulfuric acid
• Sodium hydroxide
• Nitric acid
Sulfuric acid = H2SO4
Sodium hydroxide = NaOH
Nitric acid = HNO3
What are the symbols for these compounds?
• Magnesium oxide
• Ammonia
• Methane
Magnesium oxide = MgO
Ammonia = NH3
Methane = CH4
Which group of the periodic table do not form ions?
Explain why this is
Noble gases do not form ions as they already have a full outer shell
What are the names of the following groups in the periodic table?
• Group 1
• Group 2
• Middle metals
• Group 7
• Group 0
Group 1 = alkali metals
Group 2 = alkaline Earth metals
Middle metals = transition metals
Group 7 = halogens
Group 0 = Nobel gases
What are nano-materials and what are they used for?
Nano-materials are very small (one nano-metre = one-thousand-millionth of a metre)
They are used for self-cleaning coats on glass etc...
What are smart materials and what are they used for?
Smart materials return to their original shape, e.g. metals which can be stretched and then return to their original shape (metals used in braces / spectacles)
What is a macromolecule?
Give some examples
Macromolecules - are formed by giant covalent bonds, e.g. diamond, graphite, silicon dioxide etc...
What is the bonding like in diamonds?
Each carbon atom forms 4 covalent carbon-carbon bonds with the carbons around them creating a giant structure and makes them very hard
What is the bonding like in graphite?
Each carbon forms 3 covalent carbon-carbon bonds with the carbons around them creating a sea of delocalised electrons which will pass an electrical current
Why are metals easily shaped?
Metals are easily shaped because the atoms are closely arranged and can slide past one another
How can you calculate atomic mass?
Add the relative atomic masses of the elements within the compound
How can you calculate empirical formula?
Empirical formula (the simplest possible compound) - divide each element by its mass
Divide each result by the smallest result
Round the numbers up to find out the number of each element
How can you calculate percentage yield?
Percentage yield - work out the masses for each compound
Divide the mass of one compound by the mass you have been given
Divide the other compounds by this result
What is relative atomic mass based on?
Relative atomic mass used on a comparison of the mass with 12C isotope
What is a mole and how can the mass of a mole of an element be worked out?
The relative formula mass of a substance (grams) is known as one mole of that substance
How can you calculate the percentage of an element in a compound?
(mass of element / mass of compound) x 100
Give 3 reasons why a reaction may not give the theoretical yield
The reaction may not go to completion because it is reversible
Some of the produce may be lost when it is separated from the reaction mixture
Some of the reactants may react in ways different to the expected reaction
What is theoretical yield?
The maximum yield that could be obtained if all atoms reacted
What is atom economy?
In reactions with high atom economy all the atoms react and are not 'wasted'
What is a reversible reaction?
Give 3 examples
A reversible reaction is not a permanent reaction and will break back down into the reactants
What is equilibrium?
Equilibrium is reached when the reactions occur at exactly the same rate in both directions
What is the Haber process used to manufacture and what is the equation?
Ammonia
N2 + 3H2 --> 2NH3
What are the raw materials used for in the Haber process, and where can these be obtained?
Nitrogen - from the air
Hydrogen - from natural gas / water
What are the conditions needed for the Haber process?
• Temperature
• Pressure
• Catalyst
Temperature = 450°C
Pressure = 200atm
Catalyst = iron
What happens to the unused nitrogen and hydrogen?
Unused nitrogen and hydrogen are recycled
During the Haber process how is the ammonia removed?
It is liquefied
How can the relative amounts of substances in a reversible reaction be altered?
Changing the temperature ÷ pressure
How does increasing the temperature affect a reversible reaction?
Increasing the temperature increases the amount of the endothermic side of the reaction
How does decreasing the temperature affect a reversible reaction?
Decreasing the temperature increases the amount of the exothermic side of the reaction (however it also slows it down)
How does increasing the pressure affect a reversible reaction?
Increasing the pressure increases the side of the reaction with the lowest volume
How does decreasing the pressure affect a reversible reaction?
Decreasing the pressure increases the side of the reaction with the highest volume
Why may it be important to companies to understand the conditions of a reversible reaction?
So they can get the most amount of product (and therefore the most amount of profit)
What type of salts are made from the following?
• Hydrochloric acid
• Sulfuric acid
• Nitric acid
Hydrochloric acid - chlorides
Sulfuric acid - sulfates
Nitric acid - nitrates
What is electrolysis used for?
Separating ions in solution
What types of ions do the following form?
• Metals
• Non-metals
Metals = +ve
Non-metals = -ve
During electrolysis where are these ions attracted to?
• Positive
• Negative
+ve electrode = negative
-ve electrode = positive
What are the scientific names for the following?
• +ve electrode
• -ve electrode
+ve electrode = anode
-ve electrode = cathode
What is the gain of electrons called?
What is the loss of electrons called?
Oxidation = loss
Reduction = gain
OIL RIG
During electrolysis where does reduction occur?
Reduction occurs at the +ve electrode (electrons are gained)
Write out the half equations which happen during the electrolysis of brine
2Cl- --> Cl2 + 2e-
2H+ + 2e- --> H2
What are the products of the electrolysis of sodium chloride (brine)?
Hydrogen
(-ve electrode)
Chlorine
(+ve electrode)
Sodium hydroxide
(solution)
What are the products of the electrolysis of sodium chloride, and what are they used for?
Hydrogen - margarine / Haber process
Chlorine - swimming pools / cleaning products
Sodium hydroxide - soap / paper
How can electrolysis be used to obtain pure copper from impure copper?
Impure copper used as the +ve electrode
Pure copper as the -ve electrode
Solution containing copper ions (e.g. copper sulfate)
What is an insoluble salt and how can it be formed?
Insoluble salts will not dissolve in water
They are formed by mixing appropriate solutions and filtering the precipitate
How can precipitation of unwanted salts be used to treat drinking water?
Filter the precipitate (removing unwanted salts)
Give 3 ways in which a soluble salt can be prepared
Metal + acid
Insoluble base + acid
Acid + alkali
How can a solid salt be obtained from a salt solution?
Evaporating to leave the salt crystals
What is a base?
Give some examples
Metal oxides and hydroxides are bases
What is the difference between a base and an alkali?
Give some examples
Metal oxides and hydroxides are bases
Soluble hydroxides are alkalis (e.g. sodium hydroxide)
How are ammonium salts made?
What are they used for?
Ammonia is dissolved in water to produce an alkaline solution
This can then be used to neutralise an acid to produce an ammonium salt
These are important in the production of plant fertilisers
What type of ions are found in the following?
• Acids
• Alkalis
Acids = H+ (hydrogen)
Alkalis = OH- (hydroxide)
What happens to the H+ ions and the OH- ions during a neutralisation reaction?
Include an equation
H+ reacts with the OH- to produce water (H2O)
H+(aq) + OH-(aq) --> H2O(l)
Why are catalysts used in industry?
Catalysts lower the activation energy reducing the amount of energy needed (and therefore the cost)
They can also be used repeatedly as they are not used up in the reaction
What does a catalyst do to a reaction?
A catalyst lowers the activation energy needed to start the reaction
Iron - Haber process
Magnesium dioxide - decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
What happens to a catalyst at the end of a reaction?
Nothing - the catalyst is not used up and can be used again
How can the rate of a reaction be measured?
Amount of reactant used ÷ time
Or
Product formed ÷ time
Give 4 things which can increase the rate of a reaction?
Temperature
Concentration / pressure
Surface area
Catalyst addition
Why does temperature affect the rate of reaction?
Increasing the temperature gives the particles energy - the particles move faster, colliding more often and with more force
Why does concentration / pressure affect the rate of reaction?
The higher the concentration of a liquid or the higher the pressure of a gas then the higher the chance of a collision = an increased rate of reaction
Why does surface area affect the rate of a reaction?
The larger the surface area the more exposed particles there are to react
How can you increase the surface area of reactants?
The surface area can be increased by cutting the object into smaller pieces - powder has a very large surface area
What must happen for a reaction to take place?
Particles must collide with enough force
What is activation energy?
The energy needed to start a reaction (minimum energy required by the particles to react)
What is an exothermic reaction?
Give an example
A reaction which gives out energy (usually heat), e.g. combustion / respiration
What is an endothermic reaction?
Give an example
A reaction which takes energy in from the surroundings, e.g. photosynthesis uses light energy
What does accuracy mean? What can you do to increase the accuracy of an experiment?
Results are close to the true value - accuracy can be increased by controlling variables
What does reliability mean? How can you increase the reliability of an experiment?
Reliability means that the results would be the same if they were repeated - reliability is increased by more repeats
What is the independent variable?
The independent variable is the variable that is changed
What is the dependent variable?
The dependent variable is the variable that is measured