Periodontology Andy Board Review
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
207 Terms
What are the four parts of the periodontium?
Gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, alveolar bone
What is another name for the periodontium?
attachment apparatus
Which anatomy of the periodontium refers to the tissues that cover the cervical portion of the teeth and the alveolar processes of the jaws?
a. PDL
b. gingiva
c. cementum
d. alveolar bone
b. gingiva
Which anatomy of the periodontium refers to the fibers that surround the root of the tooth?
a. PDL
b. gingiva
c. cementum
d. alveolar bone
a. PDL
Which anatomy of the periodontium refers to the thin layer of mineralized tissue that covers the root of the tooth?
a. PDL
b. gingiva
c. cementum
d. alveolar bone
c. cementum
Which principle fiber group extends from cementum into the gingiva and supports the gingiva?
a. dentogingival
b. alveologingival
c. dentoperiosteal
d. circular
e. transseptal
a. dentogingival
Which principle fiber group extends from periosteum of alveolar crest into the attached gingiva ?
a. dentogingival
b. alveologingival
c. dentoperiosteal
d. circular
e. transseptal
b. alveologingival
Which principle fiber group extends from cementum, near CEJ and across alveolar crest and anchors tooth to bone and protects PDL?
a. dentogingival
b. alveologingival
c. dentoperiosteal
d. circular
e. transseptal
dentoperiosteal
Which principle fiber group encircles the entire tooth to the alveolar crest and supports the free gingiva?
a. dentogingival
b. alveologingival
c. dentoperiosteal
d. circular
e. transseptal
circular
Which principle fiber group extends from cementum of one tooth to the adjacent tooth and maintains relationship between teeth in arch?
a. dentogingival
b. alveologingival
c. dentoperiosteal
d. circular
e. transseptal
e. transseptal
Which anatomy of the periodontium surrounds and supports the roots of the teeth?
a. PDL
b. gingiva
b. cementum
c. alveolar bone
c. alveolar bone
The unattached portion of the gingiva that surrounds the tooth in the region of the CEJ is known as?
a. attached gingiva
b. gingival sulcus
c. gingival margin
d. free gingiva
d. free gingiva
The space between the tooth and the free gingiva is known as?
a. attached gingiva
b. gingival sulcus
c. gingival margin
d. free gingiva
b. gingival sulcus
The gingiva that fills the interdental embrasures between two adjacent teeth apical to the contact area is known as?
Interdental gingiva
Which gingiva continues with the free gingiva and is part of gingiva that is firm, dense and tightly bound to cementum on the cervical third of the root is known as?
a. attached gingiva
b. gingival sulcus
c. gingival margin
d. free gingiva
a. attached gingiva
The coronal most portion of the gingiva that follows the contours of the teeth creating a scalloped outline is known as?
a. attached gingiva
b. gingival sulcus
c. gingival margin
d. free gingiva
c. gingival margin
The scalloped linear area denoting the approximation or separation of the attached gingiva to the loosely attached and moveable alveolar mucosa is known as the?
mucogingival junction
Where is the attached gingiva the widest?
a. premolar area
b. incisor area
c. molar area
d. both b & c
d. both b & c
Where is the attached gingiva the narrowest?
a. premolar area
b. incisor area
c. molar area
d. canine area
a. premolar area
True or False: The width of the attached gingiva calculates the palatal surfaces along with the buccal.
False: does not calculate palatal surfaces
What are the five principe gingival fiber groups?
1. dentogingival
2. alveologingival
3. dentiperiosteal
4. circular
5. transseptal
What are the 6 secondary gingival fiber groups?
1. periosteogingival
2. interpapillary
3. transgingival
4. intercircular
5. semicircular
6. intergingival
Name two structures that are keratinized or parakeratinized?
free gingiva and attached gingiva
Name two structures that are non-keratinized:
COL and mucosa
A valley like depression of tissue between the buccal and lingual interdental papillae is known as?
COL
A tough fibrous structural protein that occurs in the outer layer of the skin and the oral epithelium is known as?
Keratin
What are the three layers of alveolar bone?
Alveolar bone proper, cortical bone, cancellous bone
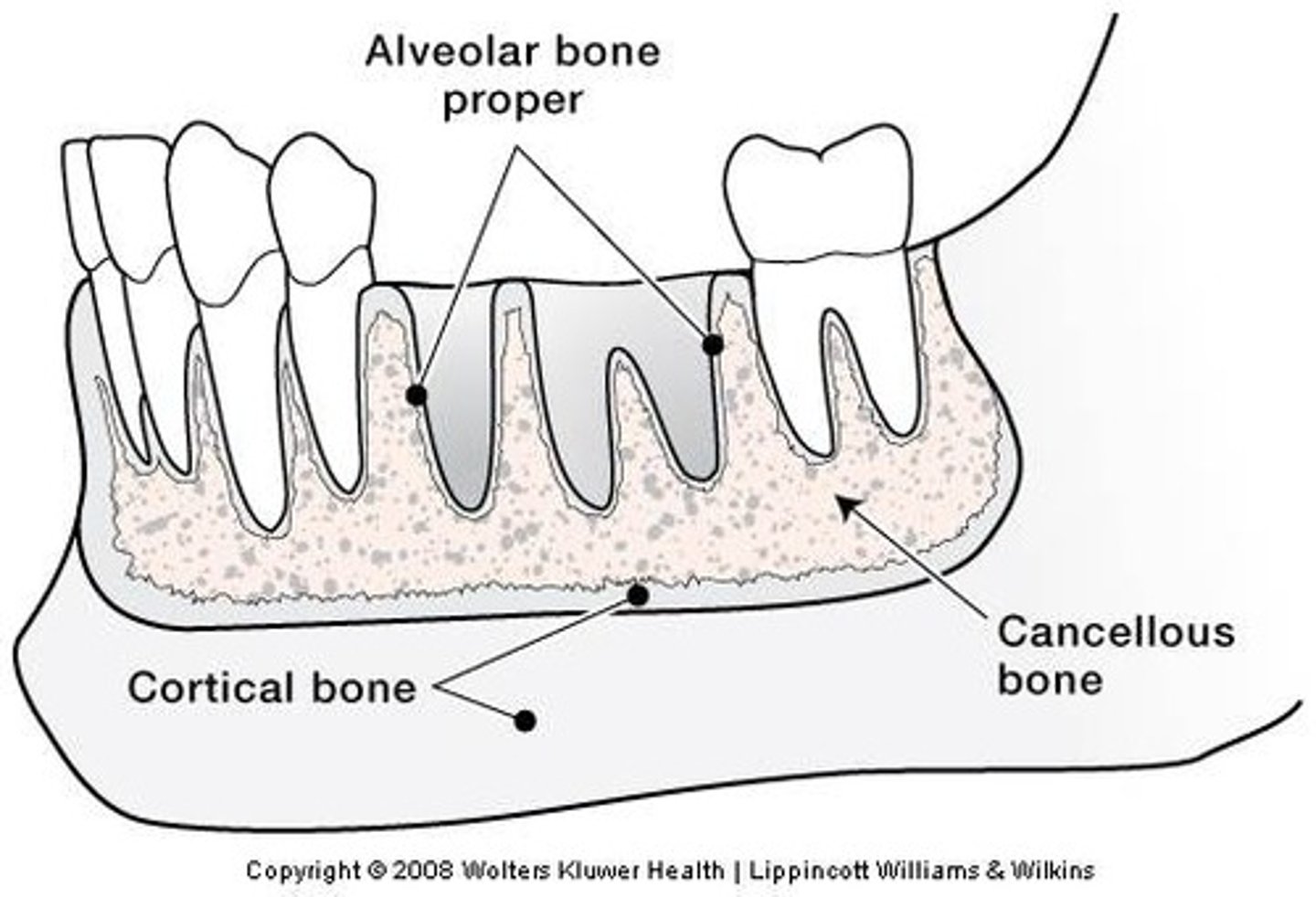
Tooth sockets lined by cribriform plate are commonly called?
alveoli
The wall of the sockets when viewed radiographically is termed?
lamina dura
Which layer of alveolar bone is a thin layer of bone lining the sockets that surrounds the root of the tooth where fibers of the PDL insert?
a. alveolar bone proper
b. cortical bone
c. cancellous bone
d. alveolar process
a. alveolar bone proper
The outer wall of bone of the jaws on the facial and lingual aspects is?
a. alveolar bone proper
b. cortical bone
c. cancellous bone
d. alveolar process
b. cortical bone (compact bone)
True or False: The cortical plate of cortical bone will not show up radiographically.
True
Lattice-like bone between the cortical bone and the alveolar bone proper, and is surrounded by marrow is?
a. alveolar bone proper
b. cortical bone
c. cancellous bone
d. alveolar process
c. cancellous bone (spongey)
True or False: There is less proportion of cancellous bone in the maxilla than the mandible.
False: in mandible than maxilla
The crest of the alveolar process follows what?
CEJ
How many millimeters is crest of the alveolar process apical to the CEJ?
2-3mm
True or False: Alveolar process is in a constant state of remodeling.
True: accommodates physiologic tooth migration, bone apposition and resorption
What are two variations in normal bone structure?
dehiscence and fenestration
A window of bone loss bordered by alveolar bone on its coronal aspect is known as?
a. bone loss
b. dehiscence
c. fenestration
d. occlusal trauma
c. fenestration
True or False: Fenestration is not commonly associated with recession.
True
Loss of alveolar bone on one aspect of the tooth, typically the facial aspect, that leaves the area of the root covered by soft tissue only is known as?
a. bone loss
b. dehiscence
c. fenestration
d. occlusal trauma
b. dehiscence
Dehiscence occurs in which type of patients?
labially inclined roots
What are the three features of dehiscence?
1. gingival recession
2. alveolar bone loss
3. root exposure
Bone builders or bone formers are known as?
osteoblasts
Bone consumers are known as?
osteoclasts
What forms the major component of the alveolar bone ?
collagen fibers and gel like substances
True or False: Alveolar bone does not contain blood vessels or nerve innervation.
False: DOES have
A layer of soft connective tissue that covers the root of the tooth and attaches it to the bone of the tooth socket is known as?
PDL
What are the main cells in the PDL?
Fibroblasts with some cementoblasts and osteoblasts
What are the 3 roles of the PDL?
1. physical
2. formative/resorptive
3. nutritive
Which structure provides nutrients to the cementum, bone, and gingiva via blood vessels?
PDL
What are the five PDL fiber bundle group?
1. alveolar crest
2. horizontal fibers
3. oblique fibers (**main support)
4. apical fibers
5. interradicular fibers
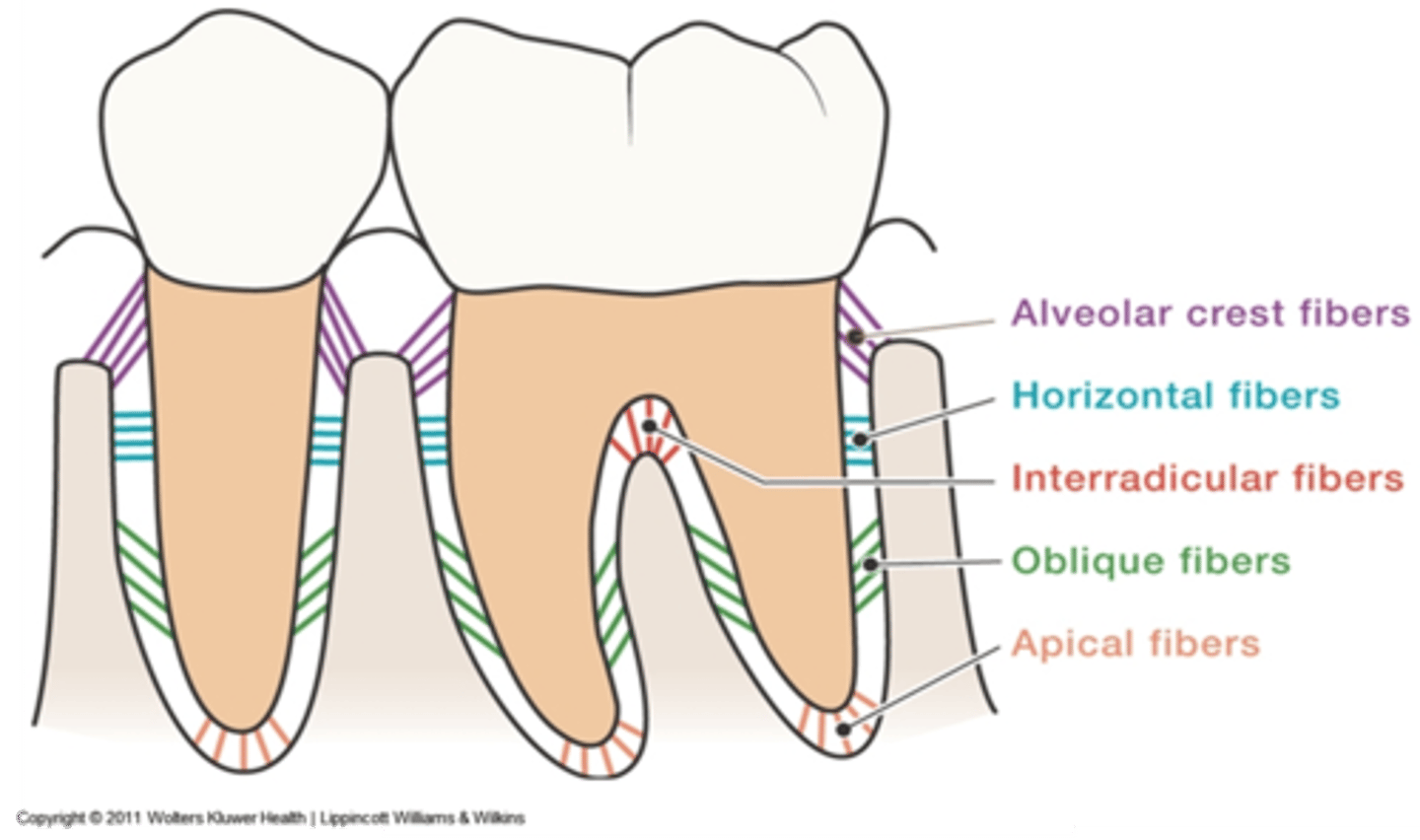
Which PDL fiber bundle provides the main support?
oblique
The ends of the PDL fibers that are embedded in the cementum and alveolar bone are known as ?
sharpey's fibets
Thin layer of hard, mineralized connective tissue that covers the surface of the root is known as?
cementum
True or False: Cementum is softer than dentin.
True: and than enamel too
Which structure attaches the PDL to the tooth?
cementum
True or False: Cementum does not have blood vessels or nerves and therefore will receive its nutrients from the PDL.
True
What are the three types of relationships at the CEJ?
1. overlap ***most common)
2. meet
3. gap
What are the two types of cementum?
acellular and cellular
Which type of cementum forms before teeth are in occlusion?
acellular
Which type of cementum forms after teeth have reached occlusion?
cellular
Which type of cementum covers the cervical 2/3 of root?
acellular
Which type of cementum covers the apical 1/3 of root?
cellular
Which type of cementum does not have cells?
acellular
Which type of cementum plays an important role in tooth support?
acellular
Which type of cementum compensates for active eruption and normal tooth wear by continuous deposition of cementum?
cellular
What are the two types of collagen fibers of cementum?
extrinsic (sharpeys) and intrinsic (creates cementum matrix)
After how many days does gingivitis develop after discontinuation of oral hygiene?
10-21
Gingival inflammation resolves in approximately how many days with initiation of oral hygiene?
7 days
True or False: Oral biofilm is easily removed through rinsing.
False: not easily removed
Communication between the bacteria organized in a biofilm is known as ?
quorum sensing
True or False: The acquired pellicle protects the enamel from acidic activity and forms within minutes after cleaning.
True
Which type of plaque is predominately gram positive aerobic cocci and rods?
supragingival
Which type of plaque is predominately gram negative anaerobic?
subgingival
List 4 biofilm characteristics in disease:
1. gram neg
2. motile
3. spirochetes and rods
4. anaerobic
List 4 biofilm characteristics in health:
1. gram pos
2. non-motile
3. cocci and rods
4. aerobic
Microorganisms that can exists and grow in only partial or complete absence of oxygen are known as?
anaerobic
Name the three red complex bacteria:
1. p. gingivalis
2. T. forsythia
3. t. denticola
The way that an individuals body responds to an infection is known as?
host response
What are the two types of immunity?
innate and adaptive
Which type of immunity is present at birth and is not antigen specific?
innate
Which type of immunity is always present immediate after infection and will NOT improve with repeated exposure to an infectious agent?
innate
Which cells are mostly associated with innate immunity? (5)
1. neutrophils
2. macrophages
3. mast and dendritic cells
4. NK cells
5. basophils/ eosinophils
Which cells are mostly associated with adaptive immunity? (3)
t cells
B cells
plasma cells
Which type of immunity develops throughout life and is antigen specific?
adaptive (memory)
Which type of immunity develops memory?
adaptive
What is the first cell to arrive in an infection?
neutrophils
What are the second cells to arrive in an infection?
macrophages
Which type of cell is the most numerous in chronic inflammation?
macrophages
Which two main type of lymphocytes are important in defense against bacteria in plaque biofilms ?
T and B cells
What are the four histologic stages in the development of periodontal disease?
1. initial lesion
2. early lesion
3. established lesion
4. advanced lesion
Which stage of development of periodontal disease develops within 2-4 days after biofilm accumulation with NO clinical changes?
initial lesion
Which stage of development of periodontal disease develops within 4-7 days with clinical signs of gingivitis present such as erythema and edema?
early lesion (stage 2)
Which stage of development of periodontal disease has slight collagen destruction and PMNs are now in the sulcus?
early lesion (stage 2)
Which stage of development of periodontal disease develops after a 21 day mark and plasma cells dominate the area?
Established gingivitis/lesion (stage 3)
Which stage of development of periodontal disease involves an apical migration of biofilm and pocket epithelium formation ?
Established gingivitis/lesion (stage 3)
True or False: In the established lesion of the development of periodontal disease, slight bone loss is present.
false: no bone loss
Which stage of development of periodontal disease involves extensive collagen destruction with edema and BOP increasing?
Established gingivitis/lesion (stage 3)
Which stage of development of periodontal disease involves subgingival plaque?
Established gingivitis/lesion (stage 3)