P12 - Wave properties
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What are mechanical waves?
Vibrations travel through a medium
What are electromagnetic waves?
Travel through a vacuum
What are the two types of waves?
Electromagnetic
Mechanical
What happens to the substance as the waves travel?
The substance does not move
What are transverse waves?
Oscillations that are perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
What are longitudinal waves?
Oscillations are parallel to the direction of energy transfer
What time of waves are mechanical waves?
Transverse of longitudinal
What type of waves are electromagnetic waves?
Transverse
What are the parts of a wave?
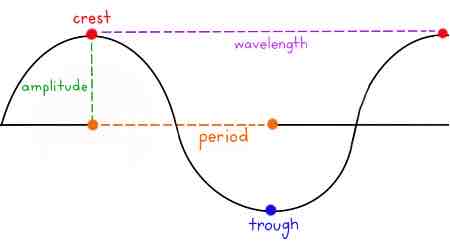
What is the amplitude?
Max. Displacement of a point on a wave from its undisturbed position
What happens to energy as amplitude increases?
The energy it carries increases
What is the wavelength?
Distance from a point of a wave to an equivalent point in the adjacent wave
What is frequency?
The number of waves passing a fixed point
What is the formula for period and frequency?
Period (s, seconds) = 1/frequency (Hertz, Hz)
What are plane waves?
Straight waves that all move at the same speed or stay at the same distance apart
What is the speed of a wave?
The distance a wave travels in a second
What is the equation for wave speed, frequency and wavelength?
Wave speed (metres per second, m/s) = Frequency (hertz, Hz) x wavelength (metres, m)
What is a wavefront?
Lines used to represent the vibrations
how are plane waves produced in ripple tanks?
By dipping a ruler in water
What are incident waves?
Waves reflected by the barrier
How do reflections occur?
When the wavefront of an incident ray is not parallel to the barrier
What is a refraction?
Change of the direction waves travel when they cross a boundary
What happens to waves at a non-zero boundary to another medium?
Waves change direction
What happens to waves perpendicular to the boundary to another medium?
Waves do not change direction but change speed
What happens to the waves if the wavefront travels slower in a new medium?
Their waves are closer together and at a smaller angle to the boundary due to the waves traveling at different speeds
what do materials determine of a wave?
Whether it is reflected or absorbed
What happens to a material and the wave of a wave is absorbed?
The material gets hotter as it is gaining energy while the amplitude of the wave decreases as the substance absorbs the energy
How is sound heard?
By vibrations vibrating the next layer of air causing vibrations to be sent out and reach your ears which vibrates the eardrum
How is an echo formed?
Soundwaves reflect from smooth, hard surfaces
How do you measure the speed of water using a lamp?
The signal generator attached to the dipper of a ripple tank creates water waves at a sad frequency
The lamp shows the wave crest on the screen making sure the waves on the screen are the same size as the ones on the water
The distance between each shadow line is one wavelength
Measure deck distance of 10 wavelengths and divide by 10 for the average wavelength by taking a photo
Use V = f x wavelength to Calculate the wave speed
How do you find the speed of waves using string?
Attach a Signal generator to the vibration Inducer
Attach a stretch string to the vibration transducer and pulley attached to a clamp with a mass at the bottom
Turn on the signal generator and vibration inducer so the strings start vibrating
Adjust the frequency wave is produced
Measure the amount of wave lines and the distance between them and divide them to get the main half wavelength
You can get the full wavelength by multiplying
The frequency is the generator to
You can use v = f x wavelength for speed
Why does music sounds nice to listen to?
It’s sound waves change smoothly and the wave pattern repeats regularly while general noises have frequencies without patterns
What frequency can the human ear detect?
20Hz to 20,000 Hz
Why is there a limited frequency for hearing?
Soundwaves change into vibrations and solids, but only which only happened in limited frequencies
How does the wave change from the Air to the ear?
The frequency of the wave doesn’t change, but the wavelength does
What is echo pulsing?
Using pulses of high frequency sound waves to detect objects in deep water to measure the water depth
How does echo pulsing work?
Pulses from the transmitter are reflected at the same depth as the transmitter and the time is measured
How is the total Distance calculated in Echo pulsing?
½ x V x t
What is a carcinogen?
Can cause cancer
What is ultrasound?
Soundwaves above the audible frequency
what is ultrasound used for?
To see the inside of the womb or organs or metal castings
What does the ultrasound scanner have to see organs?
Transducer, a control system and the display system
What is a transducer?
Electronic device placed on the body which detect pulses of an ultrasound
How does ultrasound detect inside the body?
The pulses partially reflect from different tissue boundaries and return to the transducer as a sequence arriving a different times
What are the advantages of ultrasound?
They reflect at boundaries between different types of tissue to see organs and soft tissues
They are non-ionising which means they do not have enough energy to remove an electron to ionised atoms
What is a flaw in metal?
Internal cracks and metal Castings
How do ultrasound waves detect flaws?
Ultrasound waves can reflect from the flow in the metal, so the transducer against the waves as they are picked up by the oscilloscope
How do you calculate a distance travelled by ultrasound?
Distance travelled = speed of ultrasound x time
When does an earthquake happen?
When forces in the earth increase and becomes strong enough and move layers of rock
What is seismic waves?
Energy transferred from earthquakes, create shock waves that travel through the earth
Where are earthquakes generated?
In the crest
What is the structure of the inside of the earth?
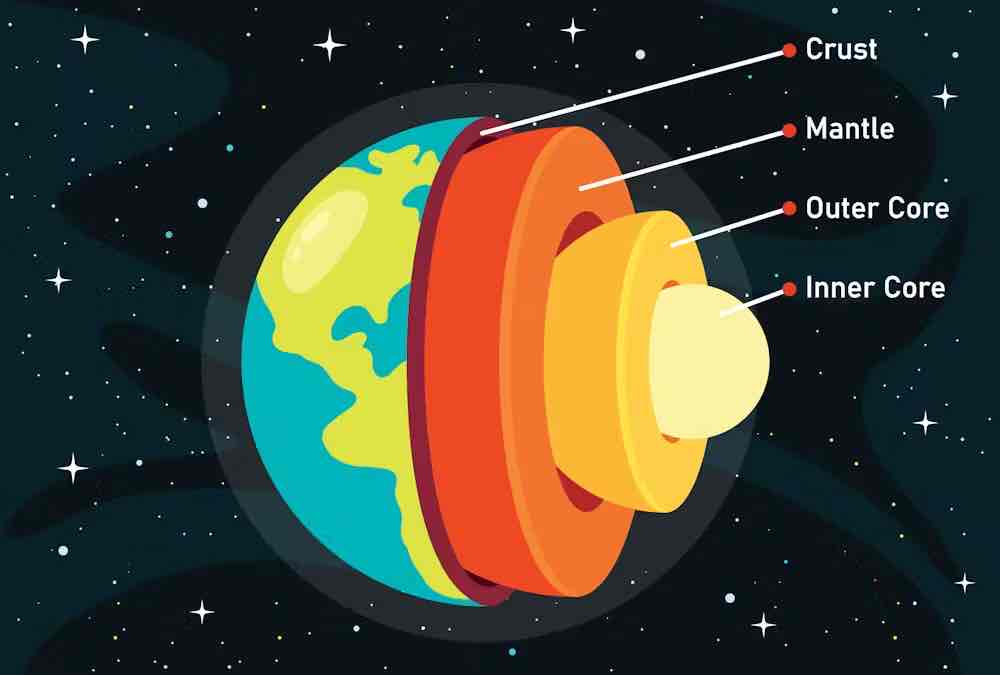
What is the crust?
Solid layer of rock
What is the mantle?
Thicker layer of molten rock
What is the origin?
The point where the earthquake generates
What is the epicentre?
Nearest point on the surface of the focus
What is a seismometer?
Detector detect earthquakes
What are three types of seismic waves?
Primary waves - initial tremors lasting one minute
Secondary waves – cause more tremors later
L waves – last and cause of violent movement on the surface upward And downward and back-and-forth
What are P-waves?
Longitude waves as they push materials back-and-forth
What are S waves?
Transverse waves as they shake materials while passing side to side
How fast are the different types of waves?
P-waves are fastest than S waves and out waves
What happens when waves travel through the mantle?
P-waves and S waves change direction as the speed and depth change
How does the P-wave travel through the Earth?
Pee-wee the fact that the boundary from mental and outer core As Speed changes
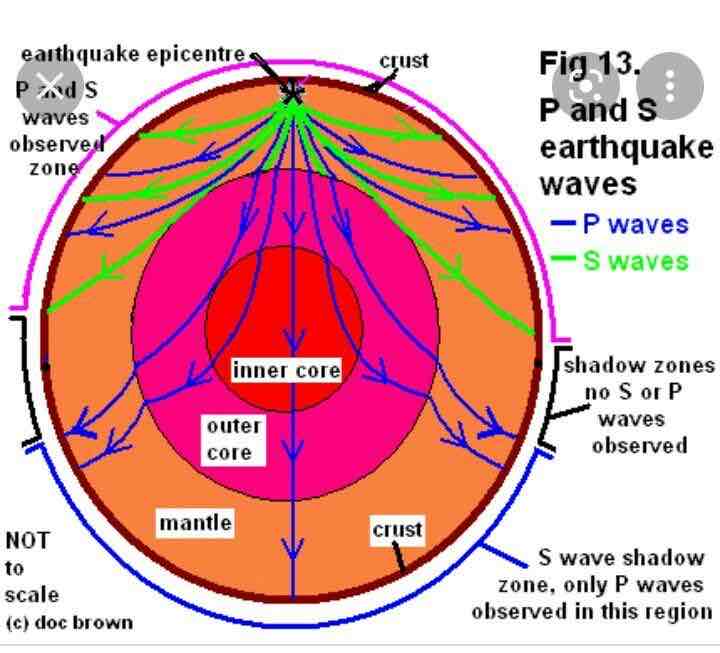
How do S waves travel through the Earth?
As waves are transfers so they cannot travel through the liquid outer core
What does seismometers record?
Some seismometers only record out waves as they are in the shadow zone where no P waves or S waves are recorded
What is the shadow so tell us about the inside of the Earth
Shadow zone shows that there is a liquid outer core under the mantle as pews are refracted at the boundary. As The second refraction is down the way cannot reach the shadow zone.
What do S waves tell us about the inside of the earth?
S waves cannot travel to the outer core as they can’t travel through liquid
What do we P-wave show about the inside of the earth?
We P waves show that there is a solid in cord that reacts P-waves into the shadow zone
How is the boundary between the Crust and Mantle Found ?
When the speed of Seismic waves changed at around 50 km
How can ultrasound be used medically
To remove kidney stones
repair damage, tissues
Remove plaque teeth
Why are x-rays better than ultrasound?
They have higher quality
can be done in any direction
Any part of the body
Easier to see a problem
Once scientist find that ultrasound is bad. What should they do?
Published their results to the public