Neurons & Synaptic Transmission
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
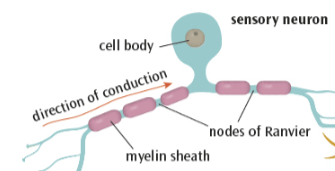
Explain the function and structure of sensory neurons
connects PNS to CNS
carries information from senses to brain / spinal cord
have long dendrites and short axons
Explain the function and structure of motor neurons
connected CNS to PNS
carries information from brain / spinal cord to muscles and glands
have short dendrites and long axons

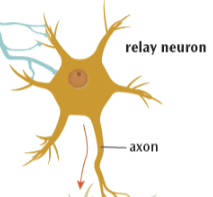
Explain the functions and structure of relay neurons
connect sensory neurons to motor neurons
connect relay neurons to other relay neurons
Process information
Analyse sensations + decide how to respond
Have short dendrites and short axons
Explain the difference between excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
Excitatory neurotransmitters
make neuron more positively charged
make post-synaptic neuron more likely to fire
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
make neuron more negatively charged
make post-synaptic neuron less likely to fire
Explain the term ‘summation’ in relation to neural transmission, with reference to excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
total electrical energy = result of summation of the impact of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
More excitatory neurotransmitters → increase chance of firing
More inhibitory neurotransmitters → decrease chance of firing
If: ‘result of summation > threshold’, neuron fires
What’s a synapse?
Microscopic gap between axon and dendrites of neurons
Explain the role of axons and dendrites in the process of synaptic transmission
carry electrical signals
They travel along the axon towards the synapse (pre-synaptic neuron)
And along the dendrites away from the synapse (post-synaptic neuron)
Explain what happens at the synapse itself during synaptic transmission
Electrical signal reachers end of the axon of the pre-synaptic neuron
This triggers the release of neurotransmitter from synaptic vesicles
The neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse
Then they bind to receptors on the post-synaptic membrane
Causing the electrical signal to continue along the dendrite
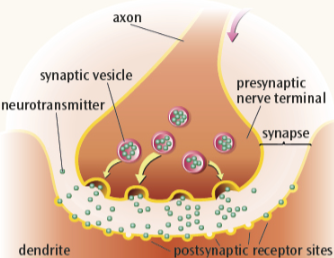
Explain why chemical transmission is a 1 way process
vesicles are only on presynaptic nerve terminals
Only a vesicle can release a neurotransmitter
Receptor sites are only on dendrites
Only a receptor can receive a neurotransmitter
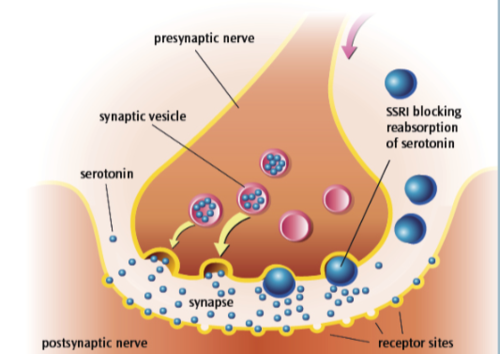
Explain the mode of action of SSRIs in the brain
Block presynaptic vesicle
Selectively preventing reuptake / reabsorption of serotonin
More serotonin available at post-synaptic receptor
Increases circulating levels of serotonin
This reduces depression and OCD