Orthoses Proximal to the Knee - Module 4
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Indications for Conventional KAFO
fluctuating edema - minimal points of contact
skin sensitivity
Conventional KAFO Facts
fabricated from measurements and tracing (no casting involved)
responds well to changes in leg volume
attached to shoe, each pair of shoes needs to be modified.
Conventional KAFO is made from
metal and leather
What is the patient population most likely to ask for a conventional style KAFO?
people who are already using this style of brace
Thermoplastic (PP, Co-Poly, HDPE) or Laminated KAFO Facts
custom molded, easier to clean than conventional, poor heat dispersion
Total contact =
improved anatomic control
What patient population is it important for them to be able to clean their device frequently?
incontinence
Poor heat dispersion associated with a thermoplastic or laminated KAFO is specifically bad for what patient population?
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Total contact is advantageous because you can ________ the force over a larger area.
spread
Thermoplastic or Conventional style KAFO has more contact?
thermoplastic
Hybrid KAFO Facts
Combines the best features of both systems
ex. Thermoplastic distal section may control foot/ankle while leather top increases sitting comfort. Conventional distal section may accommodate edema while thermoplastic thigh provides more control.
You will most likely see volume change where when wearing a KAFO?
extremities (feet)
Double Upright Facts
most stable in all planes
necessary for axial loading
recommended for locking knee joints
prevent knee buckling
Single Upright Facts
small lightweight patients
can use locking or non-locking joint
Single Upright is most useful in what pathology?
useful in genu valgum - especially bilateral
Why is single upright the most useful for Genu Valgum?
so that the patient does not have their medial knee joints hitting each other while they walk.
There is higher torque in double/single uprights?
single
Disadvantage of Internal Uprights
if you have to make any adjustments it is really hard to adjust without risking integrity of the device
T or F. When choosing a KAFO with internal uprights you have to do a check orthosis before final fabrication
true
Advantage of Internal Uprights
looks great and doesn’t damage clothes as much
T or F Trimlines should include the joint head on an Internal Upright KAFO.
TRUE
The material strength increases/decreases upright strength in a laminated KAFO.
increases
Free Knee Joint Facts
simple hinge
single axis
small compact design
contoured joint head
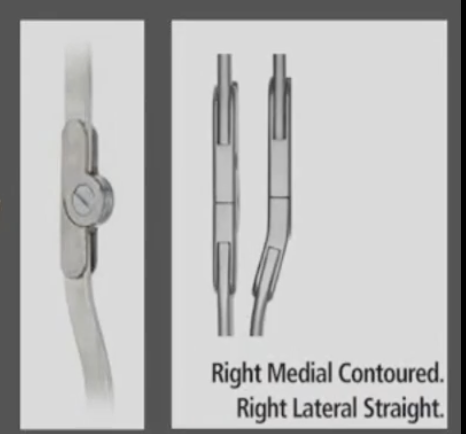
Free knee joint is aligned with the __________
anatomical knee joint
Free Knee joint is very stable in _______ and ______ planes.
frontal, transverse
Free Knee joint prevents
hyperextension and frontal plane motion
Polycentric Knee Joint Facts
mimics anatomic knee motion
less protrusion during flexion
Polycentric Knee joints are useful in treating
fractures or accomodating large ROM (sports)
How many articulations does a polycentric knee joint have?
2
T or F The articulations on a polycentric knee joint are not independent.
TRUE
Disadvantage of a Polycentric Knee Joint?
cant reach full knee flexion because the 2 articulations of the joint impinge on each other.
Scott-Craig KAFO Facts
very robust
locked knee
anterior calf band
reinforced stirrup
Scott-Craig is designed for
paraplegics
Scott-Craig weight line falls _____ to ankle and _______ to hip and knee
anterior, posterior
Sarmiento’s Principle
circumferentially wrapped, bivalve opening if needed
Sarmiento’s Principle is not applicable for what kind of fracture?
comminuted fractures
Fracture Bracing Facts
thermoplastic
most often custom fit
polycentric knee joints
clamshell design
free ankle
If the ____ of the bone that is fractured then the adjacent segment should be _______ .
third, immobilized or locked
Weight Bearing Designs must have
solid ankle and double upright locking knee
The Quad brim weight bearing design is good for _____ patients.
muscular
What is the problem with adding an ischial ring?
this is a proximal ring made up of padding, this is usually very round and does not provide a flat spot for the ischium to sit on
Ischial containment weight bearing design provides improved
comfort and control of fleshy limbs
Can you use a bical joint on a weight bearing design ?
yes, it provides a smoother gait but only if your patient can use this kind of joint
Is there any atrophy with weight bearing designs?
When using this orthosis we are more worried about locking their joints up.
This orthosis is for muscle weakness usually so we aren’t as concerned about this
Coronal Plane deformities
ligament laxity
osteoarthritis
ricketts
paget’s disease
blount’s disease
What is the KAFO treatment if we are correcting in the coronal plane?
KAFO with a free knee and ankle joint
To treat a coronal plane deformity make sure it is ______.
flexible
Genu Varum is associated with
LCL/Medial compartment
Conventional for Genu Varum consists of
5 buckle knee pad that wraps around the medial upright and pulls medially
OR
Lateral knee pad mounted on the lateral upright and pushes medially.

Thermoplastic trimlines for Genu Varum
thigh - high medial and lower lateral
calf - high lateral
How does the patient know how tight to pull their straps?
you make a line that they should pull to everytime they don the orthosis
Genu Valgum is associated with
MCL, lateral compartment
Conventional for Genu Valgum consists of
5 buckle knee pad that wraps around lateral upright and pulls laterally
OR
medial knee pad that is mounted on the medial upright and pushed laterally
Thermoplastic trimlines for Genu Valgum
thigh - high lateral and lower medial
calf - high medial
Sagittal plane abnormalities are ____ to treat than coronal.
more challenging
Sagittal plane abnormalities
contractures caused by - injury, surgery, positioning
weakness caused by - polio, CVA, paralysis, spina bifida, PVD, neuropathy
neuromuscular caused by - CVA, MS, ALS, MD
A knee contracture <_____° required for ambulation.
30
How can you accommodate for contractures concerning the uprights?
pre-flexed uprights
What kinds of knee joint locks can you use for contractures?
step lock, adjustable flexion/extension knee joint, Ultraflex joints, and Monodos

Step lock
locks in 15° increments using a ratcheting system
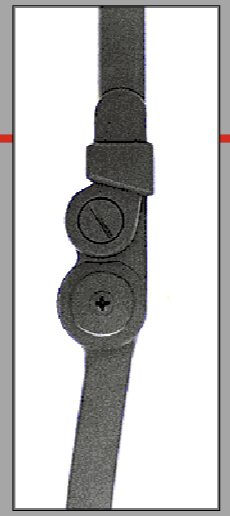
Adjustable flexion/extension knee joint
available in drop lock or lever lock with a 6° increments (also available with a 6 position flexion stop)

The pre-flexed portion of the Adjustable Flexion/Extension Knee joint is positioned _______.
distally
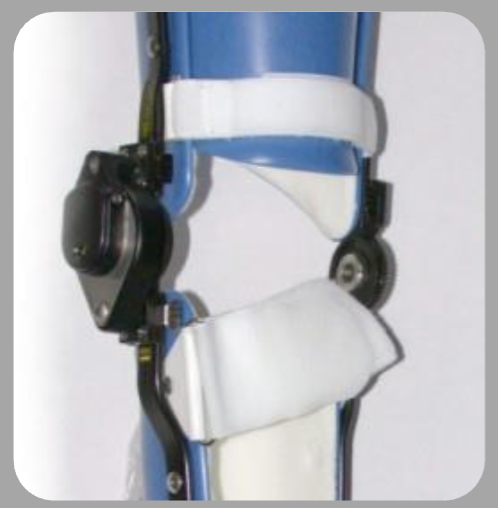

Ultraflex knee joint
uses concentric torsion mechanism to apply a stretch to a contracture
is NOT for ambulation
bulky

Monodos knee joint
provides unidirectional joint motion and is bulky.
NOT for ambulation
What are the Extension Assist Knee Joints
G-knee
GXL - knee
Ultraflex
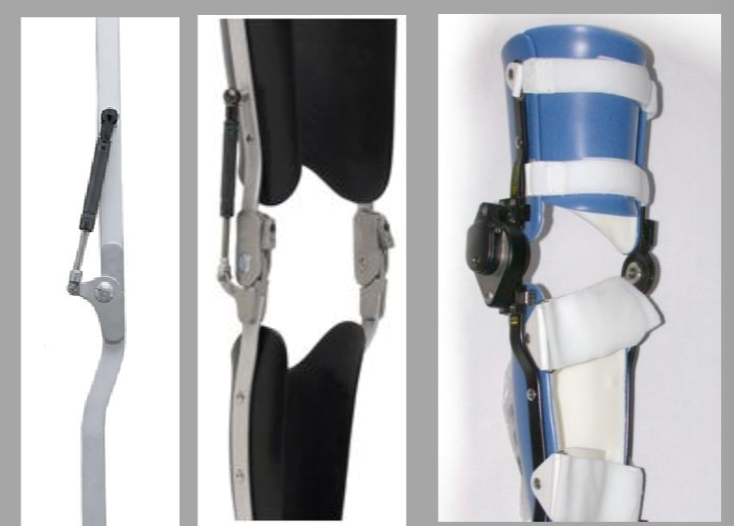

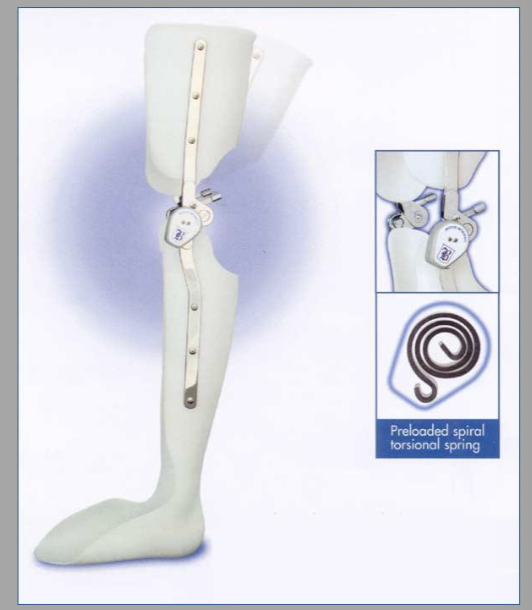
Stance Flexion joint
Load response joint.
Locks in full extension then allows up to 15° of attenuated motion.
Fully extended in swing.
Free when unlocked.
Stance Flexion knee joint allows up to ___° of attenuated motion.
15
Knee buckling management above the knee
manually locking knee joint
posterior offset joint
stance control knee joint
Trimlines for Knee-Buckling
Conventional use 4-Buckle knee pad
thigh - high posterior and low anterior
calf - high anterior (possibly molded shell)

Manually Locking knee joint (drop lock)
automatic lock via gravity and manual unlock.
can be used with ball retainers to prevent auto-lock.
Manual Locking knee joint is hard to unlock when ______.
loaded

Manually Locking knee joint (trigger lock, drop with lift loop)
automatic lock
proximal release
difficult to unlock under load
Contraindications for Trigger Lock, Drop with lift loop
spasticity and knee flexion contracture
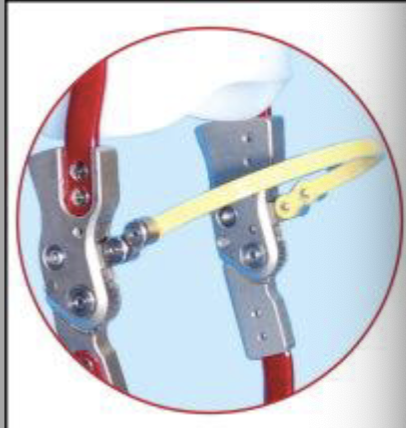

Manually Locking knee joint (bail lock or spring loaded lever lock)
one motion unlocks both joints
allows for hands free operation
great for UE impairment
Disadvantage of Bail Lock or Spring Loaded Lever Lock
may inadvertently unlock
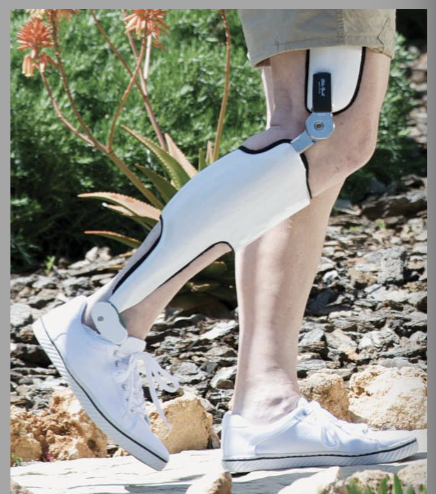

Manually Locking knee joint (electronic lock)
solenoid engages lock with an audible signal to patient
remote control fob
minimal UE strength required
stance control version available
T or F Electronic locks are super common.
false
Posterior Offset joint moves weight line
posterior
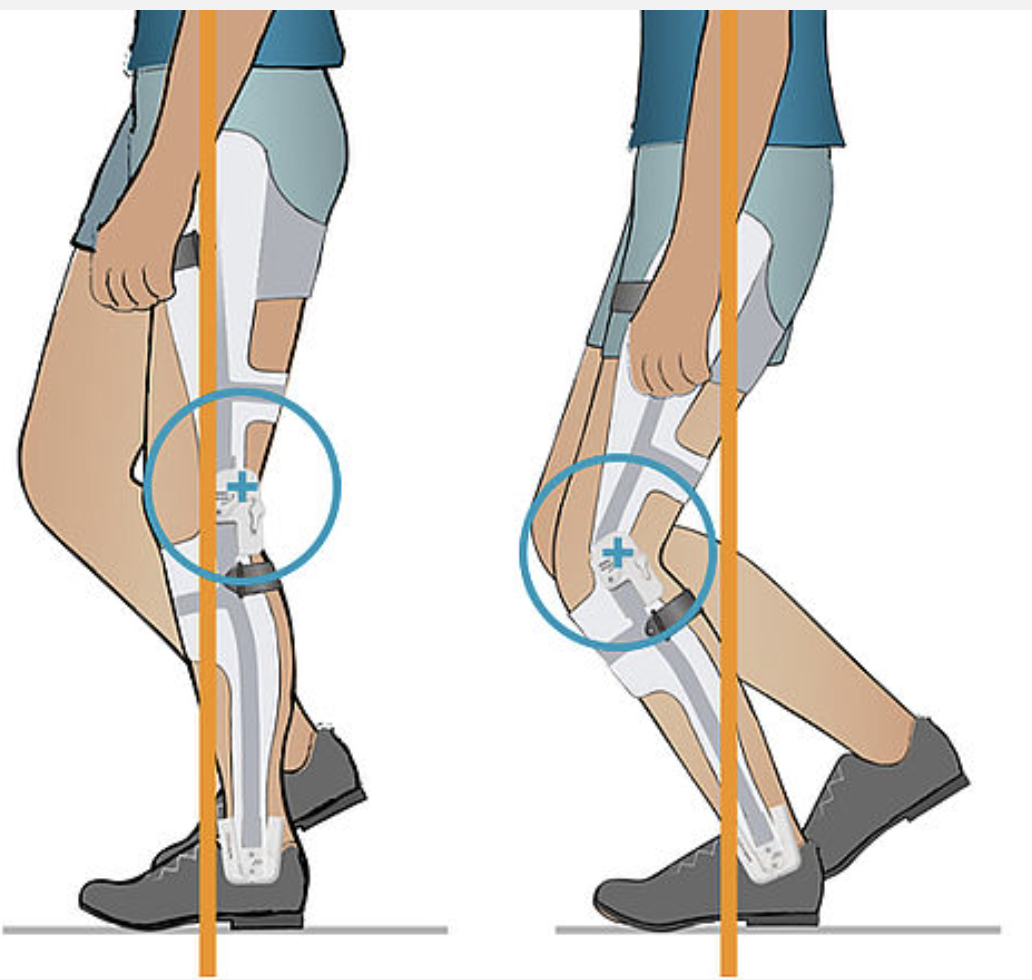
Contraindications for Posterior Offset Joint
knee or hip flexion contractures and PF stop

Use of _______ design enhances performance of posterior offset joint.
weight bearing
Stance Control Knees
Horton
UTX and Free Walk
E-Knee
Sensor Walk
Stride
C-Brace

Gait Activated Stance Control Knees
Lock in full extension and have a biomechanical trigger to unlock, these are sensitive to gait variations using gyroscopes
Need to have an MMT = 3 hip flexion

Weight Activated Stance Control Knees
sensor in foot plate triggers the device to lock
electronics are prone to environmental degradation
batteries make these options heavier than others
Disadvantages of weight activated stance control knees
electronics are prone to environmental degradation and batteries make these options heavier than others
bulkier and more expensive

Ankle Activated Stance Control Knee
Locked in full extension with dorsiflexion to a specified degree that unlocks the joint.
Adequate ankle motion is REQUIRED.
Cables that run through the device sense when to unlock and lock from PF/DF at the ankle.
Contraindications for Ankle Activated Stance Control Knees
s/p ankle fusion, OA, infection, quad weakness, knee buckling

Stance Control 4-Bar knee joint (ankle driven)
use of weight bearing design enhances performance
posterior cable disengages lock when pulled.
Contraindications for Stance Control 4-Bar Knee Joint
knee or hip flexion contracture
Genu Recurvatum is often secondary to
quad weakness
All orthotic knee joint should have a built in ______° extension stop
180
Genu Recurvatum treatment
shallow distal thigh and calf bands
Posterior knee strap (criss-cross) // 4 Buckle Knee Pad on Posterior
Trimlines
thigh - high anteriorly and low posteriorly
calf - high posteriorly (cannot interfere with knee flexion to 105°)
Double or single upright provide the best control in the transverse plane?
double
_______ stiffness is critical to transverse plane alignment.
Torsional
A KO may be converted to KAFO to control rotation of orthosis on a ____ limb.
fleshy - lamination?
Radius of curvature for aluminum must exceed ___ times the thickness of the upright.
6
Radius of curvature for stainless steel must exceed ___ times the thickness of the upright.
1
Strength Factors - Materials
patient weight
activity level
locking knee
double upright vs single upright
material
material thickness
orthosis design (internal vs. external joints)
Does the shape of the end of the upright affect strength of the upright?
yes - square vs round
Upright dimensions (Becker) represent
Moment of Inertia (MOI)