Chapter 24: White Blood Cells
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Normal WBC count:
5,000-10,000
LOW WBC COUNT STATES:
Leukopenia:
Low WBC count.
LOW WBC COUNT STATES:
Neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count less than 500):
Low neutrophil count; this patient would be at extremely high risk of infection.
LOW WBC COUNT STATES:
Aplastic anemia:
Loss of bone marrow function, not able to make cells.
CAUSES OF LOW WBC COUNT STATES:
Medications:
Chemotherapy intendly lowers WBC count
Medications that limit bone marrow function.
Infection (viral, bacterial, parasites, AIDS)
Disease:
Lupus
Autoimmune disorders
Infectious Mononucleosis:
Lymphoproliferative Disorder.
Lymphoproliferative Disorder:
Self-containing
Not life threatening
Cause of Lymphoproliferative Disorder:
Epstein Barr Virus (EBC)
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
How long does lymphoproliferative disorder last?
Typically lasting 4-6 weeks:
Shouldn’t surround themselves with other people.
Symptoms of lymphoproliferative disorder:
Fevers
Fatigue/Malaise
Lymphadenopathy:
Increase size of the lymph nodes.
Splenomegaly
Everything is swelling up and filling up with all of these excess WBC
Concern for splenic rupture
No contact sports
Main Concern:
The spleen gets so large that it becomes relatively fragile and can possibly rupture.
Leukemia:
Too many WBC.
Blood/Liquid.
Faulty cells grow in marrow:
Blasts.
Bone Marrow.
Faulty cells impact the ability to make healthy cells.
Faulty cells not capable of fighting infection.
Blasts:
Immature WBC that don’t provide defense, but they crowd out the bone marrow and multiple.
Bone Marrow:
Make cells, they have the ability to produce healthy cells.
Lymphoma:
Solid Tumors (Lumps/Bumps).
Enlarged lymph nodes: These are where the cells are housed.
Tumors formed in the Lymphatic system.
“B”- Symptoms:
Itching.
Night sweats.
Lumps.
Fevers.
Weight loss.
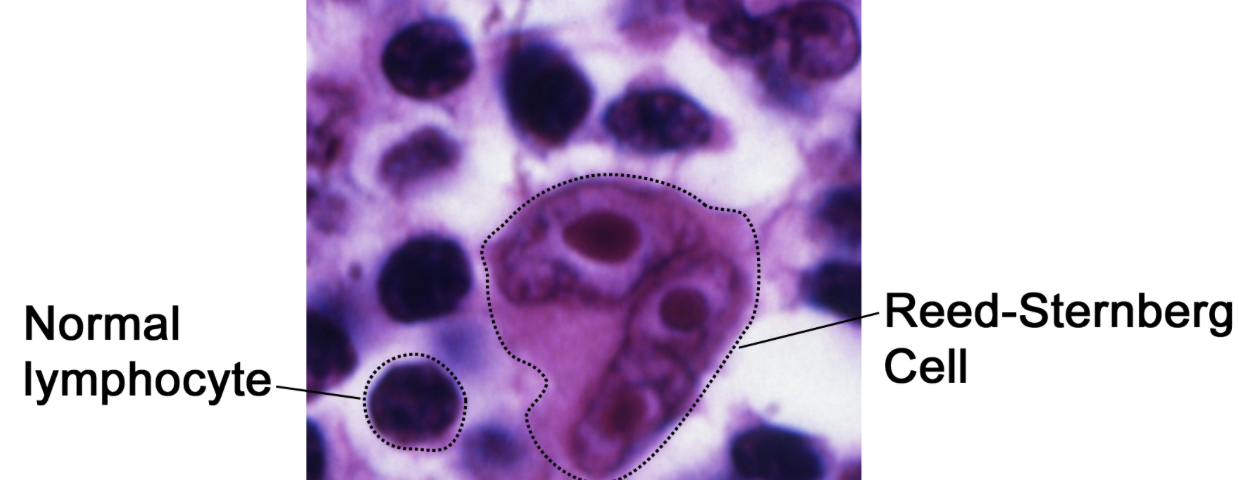
Hodgkin VS. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma:
Hodgkin: Has the reed-sternberg cells.
Non-hodgkin: Does not have the reed-sternberg cells.
Lymphoma Treatments:
Blood tests.
Bone marrow test.
Chest X-ray.
Scans (X-Ray, CT, MRI, PET).
Lymphoma Common Treatments:
Watchful waiting.
Chemotherapy.
Targeted Therapy.
External radiation.
Acute Leukemias:
Happening relatively fast.
100,000 WBC count: Too many.
These blasts are not helpful, do not provide function.
Chronic Leukemias:
It happens relatively slow.
100,000 WBC count: Too many.
These blasts are not helpful, do not provide function.
Where do Leukemias come from?
Lymphoid blasts: Granulocytes, monocytes.
Myeloblast: Lymphocytes.
Leukemia AML:
The cells crowd out bone marrow so they can’t make cells. As a result, these patients will have bleeding because they have low platelet levels.
Overproduction of cells in the bone marrow will cause pain.
Short of breath because of overcrowded bone marrow.
Leukemia CML:
All these cancer cells use up our resources, which causes:
Unexplained weight loss.
Night sweats.
Asymptomatic.
Leukemia Treatments:
Stem cell transplant.
Chemotherapy.
Prevention of infection.
Hematopoietic stem cells:
Cells that are capable of only making various types of blood cells.
These cells are able to make new RBC, WBC, and platelets.
Multiple Myeloma:
Disease within the limb.
Affects the plasma cells, which they usually help make antibodies.
Have issues with bone marrow function properly.
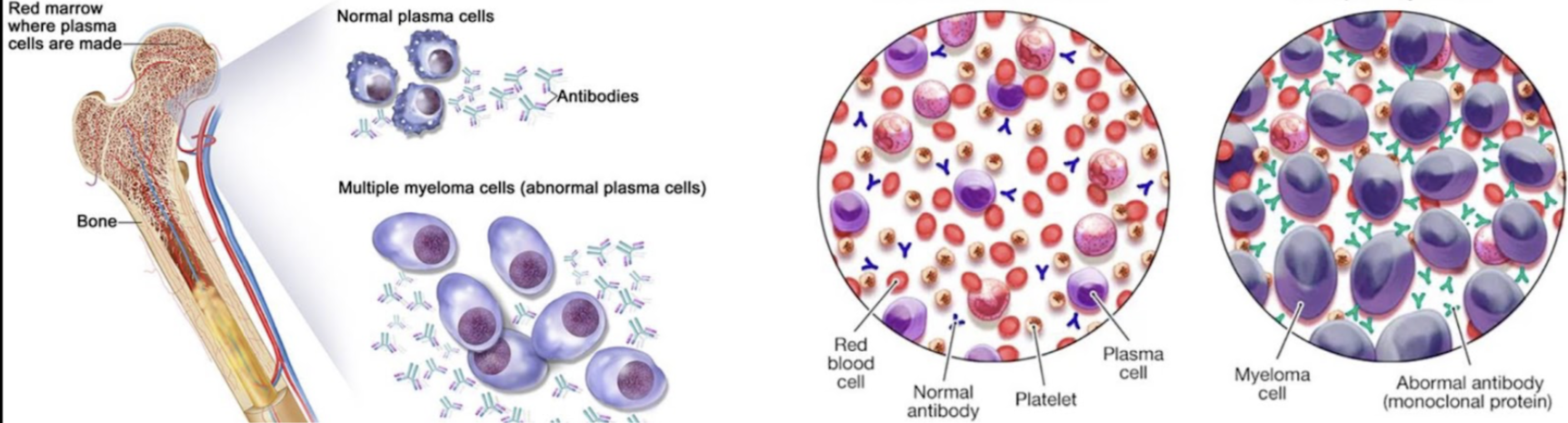
Multiple Myeloma Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Anemia, high levels of calcium, bone pain and fractures, kidney problems, excessive bleeding, and numbness.
It pulls a lot of calcium from the bones into the blood, weak bones and high levels of calcium in the blood. The kidneys get overwhelmed by all of the calcium and causes a chain effect.
Multiple Myeloma Treatments:
Chemotherapy
Steroids.
Bisphosphonates.
Targeted Therapy.
Patients have lived up to 10 years.
Chemotherapy:
Kills cancer cells over the course of four to six weeks.
Steroids:
Reduce the discomfort.
Bisphosphonates:
Medication that slows the damage and reduces overall pain.
Targeted Therapy:
Trying to heighten your immune response.