lab 3 - biological molecules
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
proteins: polymer and monomer?
polymer: protein
monomer: amino acids
how are amino acids joined?
peptide bond (type of covalent bond) formed by dehydration reaction between C and N terminus
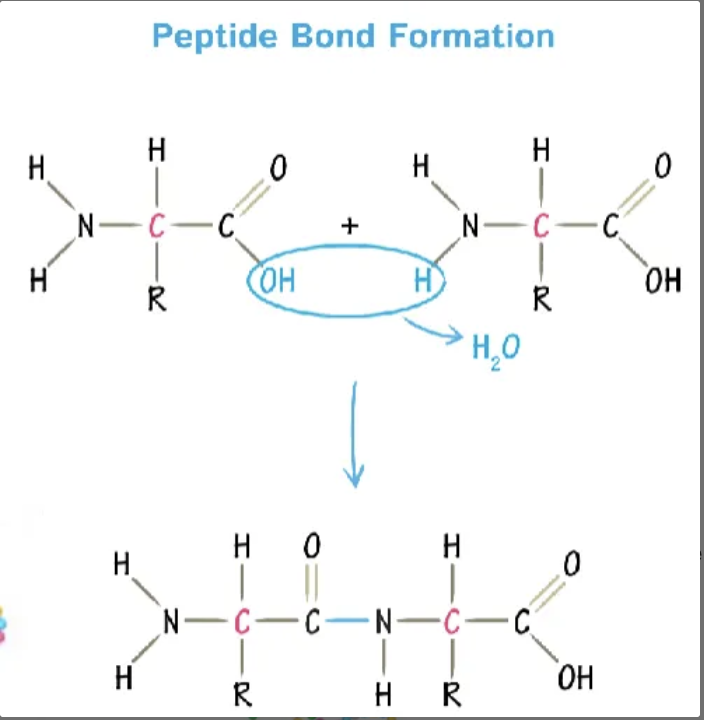
peptides
a string of amino acids, connected by peptide bonds
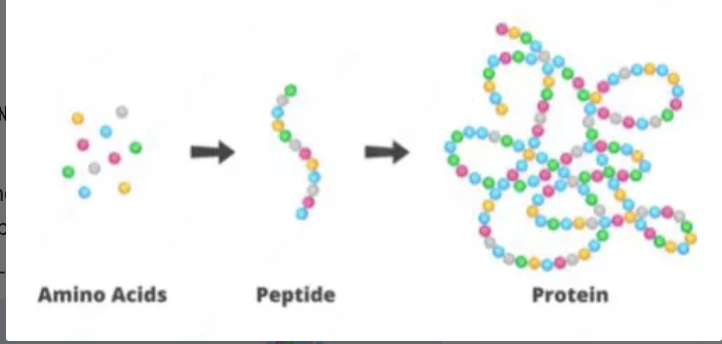
structure of proteins
amino group with N+ terminus
carboxyl group with C- -terminus
R group
H
carbohydrates: polymer and monomer?
polymer: carbohydrate
monomer: monosaccharides
monosaccharides
basic monomer unit of carbohydrates, simplest form of sugar
types of monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
dissacharides
two monomers bound together by a glycosidic bond
types of dissacharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
what monosaccharides make sucrose?
glucose + fructose
what monosaccharides make lactose?
glucose + galactose
what monosaccharides make maltose?
glucose + glucose
polysaccharides
larger sugars with repeating monomers
types of polysaccharides
starch
what are lipids made of?
glycerol and fatty acids
what bonds help form lipids?
Ester bonds create lipids by linking glycerol and fatty acids
dehydration synthesis: connects carboxyl group (-COOH) of carboxylic acid with hydroxyl group (-OH), releases a water molecule
what forms the hydrophilic head?
glycerol and phosphate group
what forms the hydrophobic tail?
saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
unsaturated fatty acids → kink
triglycerides
3 fatty acid chains
are lipids polar or nonpolar?
mostly nonpolar molecules- don’t dissolve well in water
nucleic acids: polymer and monomer?
polymer: nucleic acids
monomer: nucleotides
structure of nucleotides
1 phosphate group
pentose sugar- differentiates DNA and RNA
deoxyribose = DNA
ribose = RNA
nitrogenous bases
DNA = A, T, C, G
RNA = A, U, C, G
what bonds help form nucleic acids?
phosphodiester bond made by dehydration synthesis, links nucleotides
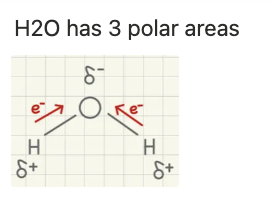
electronegativity
electron affinity; electronegative molecules pull electrons towards them (ex: oxygen)
dipole moment
occurs because electronegative molecules like pulling electrons towards them
dipole
created by differences in electronegativity between atoms, resulting in partial positive and negative charges
polar molecules
share electrons unequally
nonpolar molecules
share electrons equally
δ
shows polar areas/atoms
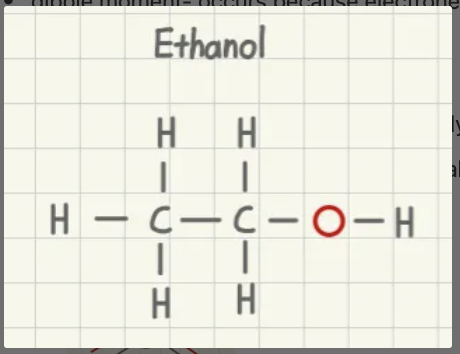
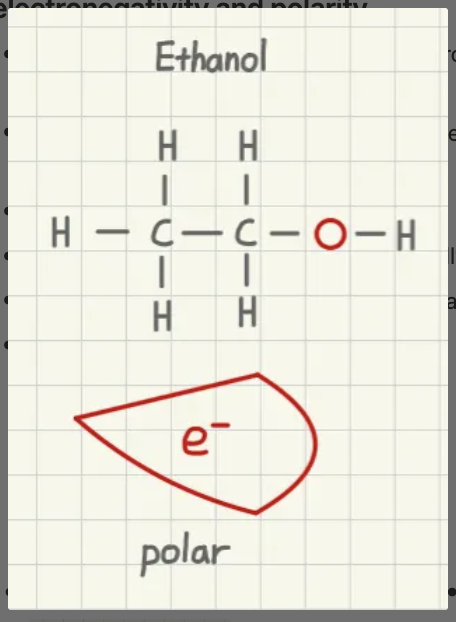
is ethanol polar or nonpolar?
polar
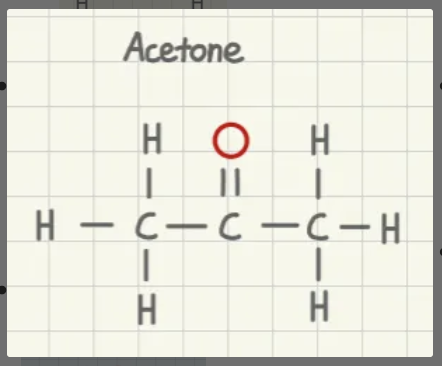
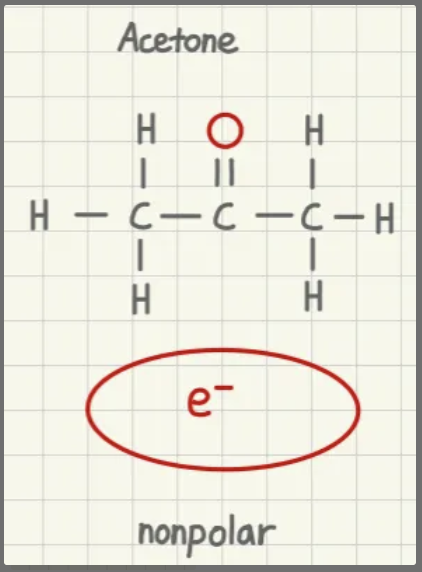
is acetone polar or nonpolar?
nonpolar
how do you know if a molecule will dissolve?
like dissolves like
polar molecules dissolve in polar solvents
nonpolar molecules dissolve in nonpolar solvents
ions dissolve in polar solvents (due to having charge)
hydrogen bonds
formed by the positive dipole of hydrogen + negative dipole of electronegative atom (FON)
typically formed by water
H is weak alone, strong together
oxidation vs reduction
LEO GER:
lose electrons = oxidation
gain electrons = reduction
reducing agent
reduces OTHER things, causes itself to be oxidized (charge increases)
is a reactant
oxidizing agent
oxidizes OTHER things, causes itself to be reduced (charge decreases)
is a reactant
oxidized product
comes from reducing agent, atom’s charge has increased
reduced product
comes from oxidizing agent, atom’s charge has decreased
are reducing sugars a reducing agent or reduced product
reducing agents (oxidation) because they donate electrons to reduce other electrons
what test is used to test for lipids?
sudan IV testis used to identify the presence of lipids in a sample.
explain the Sudan IV test
used for lipids
nonpolar dye turns red-orange when interacting with fatty acids of lipids
positive test: red-orange color (lipids present)
negative test: no color change (appears more blue)
what type of test is the Sudan IV test: qualitative or quantitative?
qualitative
what were the test solvents in the Sudan IV lab?
water, ethanol acetone
procedure for sudan IV test
mix vegetable oil + sudan IV with each solvent, gently invert
what test is used to test for carbohydrates?
Benedicts reagent
how does Benedicts reagent work?
Cu2+ gets reduced by a reducing sugar (reducing sugar donates electrons) and changes color
color change: red is highest amount of reducing sugars, blue is lowest. rainbow order:
blue = no reducing sugars
green/yellow = low reducing sugar amount
orange = medium amount of reducing sugars
brick-red = large amount of reducing sugars
color change = proportional to reducing sugar concentration
order the types of carbohydrates from most reducing to least reducing.
Monosaccharides (reducing)
Disaccharides (some reducing, some non-reducing)
Polysaccharides (generally non-reducing)
what test is used to test for proteins?
biuret reagent
how does biuret reagent work?
used to test for proteins
Cu2+ binds peptide bonds → color changes blue to purple
is biuret reagent qualitative or qualitative?
quantitative
what does color intensity depend on with the biuret reagent?
color intensity is directly proportional to number of peptide bonds
blue = no peptide bond
purple = high peptide bond
how do you determine λmax of biuret
prepare standard protein solutions (known concentrations)
measure absorbance across wavelengths
λmax = wavelength with biggest absorbance
For purple Biuret reaction: absorbs green light (~490–570 nm)
how do you make a λmax graph
y-axis: absorbance of ____
x-axis :wavelength (nm)
highest point determines λmax
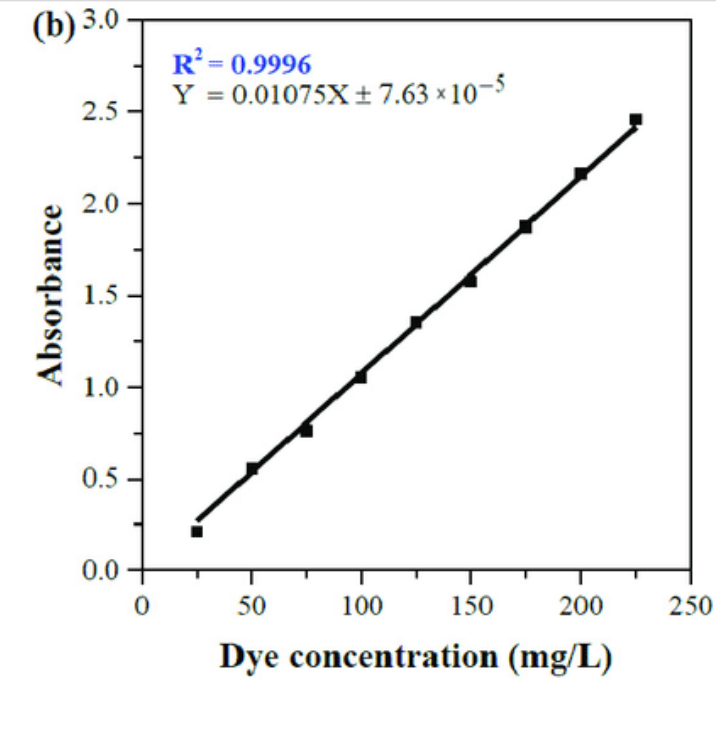
how do you make a standard curve of ___ graph
y-axis: absorbance at determined $\lambda \text{max}$ (nm)
x-axis: concentration of ____ (units for concentration)
trendline equation can be used to determine unknown concentrations, given absorbance
λmax graph vs standard curve graph
λmax graph shows absorbance at different wavelengths
standard curve graph plots absorbance at λmax against known concentrations
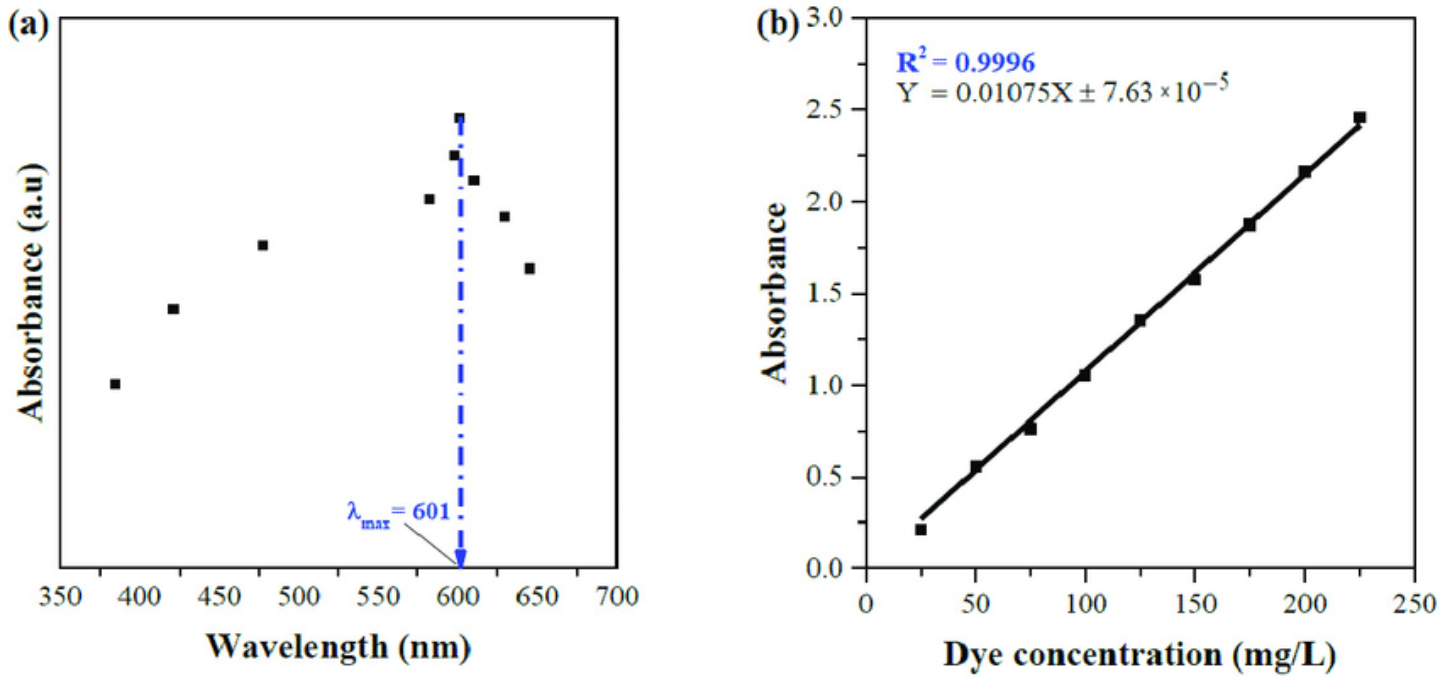
how do you use the standard curve graph to solve for unknown concentration?
y = mx + b
y = absorbance of unknown concentration
x = unknown concentration of the solution ‘
unknown solution: x = (y-b)/m
how do you use a spectrophotometer
Always blank the instrument after changing wavelength
Blank contains solvent/reagent without sample
what test is used to test for nucleic acids?
E+Br and SYBR safe
explain how E+Br works
tests for nucleic acids
intercalates between base pairs
explain how SYBR safe works
dye for nucleic acids
binds to nucleic acid backbone