Labor and Delivery Complications - OB/GYN EOR
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Breech presentation
A fetus whose presenting part is the butt or feet (3-5%)
Developmental dysplasias of the hip, torticollis, mild deformation
Risk factors associated with Breech presentation
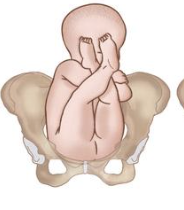
hips flexed, knee extended (feet are up near the hear)
Describe a Frank Breech presentation (most common)
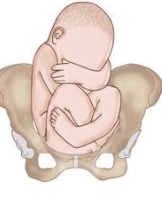
Both hips and knees are flexed
Describe a Complete Breech presentation
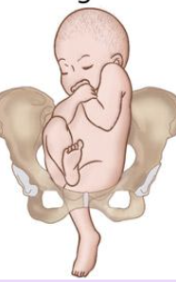
1 or both of the hips are not completely flexed
Describe an Incomplete (Footling) Breech presentation
Transverse lie, shoulder is closest to the cervix
Describe a shoulder presentation
Soft mass instead of the normal hard skull on PE, Leopold Maneuvers, U/S to confirm
Diagnostics for a Breech presentation
Leopold Maneuvers
A set of 4 maneuvers that can determine the estimated fetal weight and presenting part of the fetus
External cephalic version (externally rotates the fetus AFTER 37 weeks), tocolytic to prevent contractions during maneuver OR planned C-section
Management of a Breech presentation

Trial of labor
If the External cephalic version is successful, what is the next step
C-section OR trial of vaginal birth if low risk
If the External cephalic version is UNsuccessful, what is the next step
normal labor curve, 37+ weeks, fetal weight of 2500-4000g, frank or complete, absence of anomalies on U/S, BIRTHING HIPS, documentation of fetal head flexion, adequate amniotic fluid volumeA
Criteria for vaginal breech delivery
Dystocia
Abnormal labor that is characterized by a wack progression of labor (leading cause for C-section)
POWER, Passenger, Passage
What are the 3 Ps of normal labor (dystocia results from abnormalities )
Uterine contractions or maternal expulsive forces
Power is characterized by
Position, size, or presentation of the fetus
Passenger is characterized by
pelvis or soft tissues
Passage is characterized by
Uterine contractions don’t contribute enough pressure to cause fetal descent or cervical dilation, too frequent or not frequent enough
Ways that Power can contribute to Dystocia
Macrosomia, breech presentation, shoulder dystocia, wack baby position
Ways that Passenger can contribute to Dystocia
Maternal skeletal or soft tissue abnormalities, cephalopelvic disproportion, tumors, fibroids
Ways that Passage can contribute to Dystocia
Shoulder dystocia
An OB EMERGENCY that is due to the failure of shoulders to spontaneously transverse the pelvis after delivery of the fetal head due to impaction
macrosomia (like due to DM), post-term preg, multiparity, prolonged second stage, forceps delivery, maternal obesity, AMA, epidural anesthesia
Risk factors for shoulder dystocia
Brachial plexus injuries (Klumpke palsy, cerebral palsy), Erb-Duchenne Palsy, clavicular fractures, long bone fractures, fetal
Fetal complications of shoulder dystocia
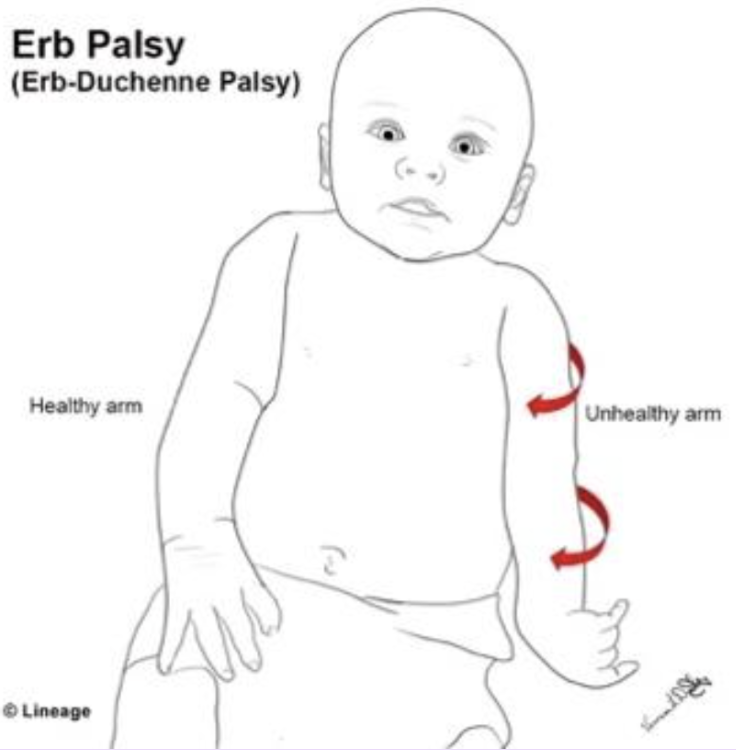
Erb-Duchenne Palsy (Erb’s Palsy)
A lesion in the upper trunk that presents with a “waiter’s tip” deformity
Arm in adduction with elbow extension, forearm pronation, wrist flexion with fingers curled up
Describe the Waiter’s tip deformity
Retraction of the baby’s head (turtle sign) into the peritoneum or a red puffy face
Signs of shoulder Dystocia during delivery
McRoberts Maneuver, Wood screw maneuver, intentional fracture of the clavicle, Zavanelli Maneuver (last resort - push head back in and c-section that hoe)
Management of Shoulder Dystocia
Hyperflexion and abduction of the Mother’s hips toward the abdomen with application of suprapubic pressure
Describe the McRoberts Maneuver - resolves most dystocias
110-160
Normal fetal heart rate
Maternal beta blocker therapy, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, hypothyroidism, fetal heart block, interruption of fetal oxygenation, Non-reassuring fetal status (baseline under 80 bpm)
Fetal Bradycardia (under 110) is usually due to
Chorioamnionitis (m/c), maternal fever, infections, medications, hyperthyroidism, elevated catecholamines, fetal anemia, arrhythmias, interruption of fetal oxygenation
Fetal Tachycardia is usually due to
Decreased variability, repetitive late OR severe variable declerations
Signs of non-reassuring fetal status = tachycardia +
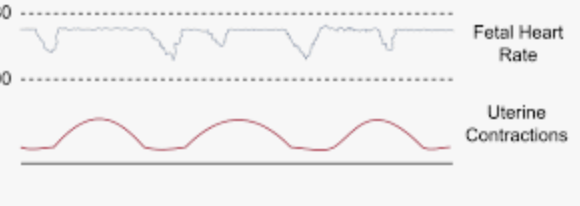
Cord compression
Variable decels are due to
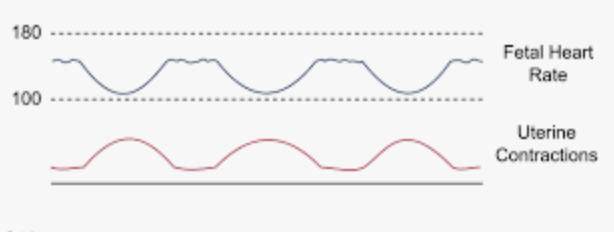
Head compression
Early decels are due to
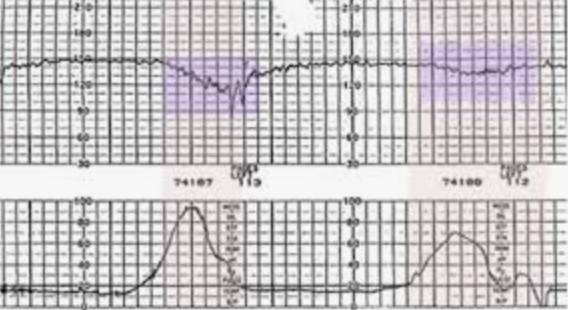
Uteroplacental insufficiency
Late decels are due to
mirror contraction in timing and shape
Describe the pattern of an early decel
Peak (nadir) occurs after the peak of contraction (only a concern IF recurrent with absent variability or without accelerations)
Describe the pattern of a late decel
decline and return to baseline FHR that vary in timing with contraction (only a concern if repetitive or reaches under 60 bpm)
Describe the pattern of a variable decel (abrupt)
Decrease in FHR by 15+ bpm for more than 2 min but less than 10 (anything over 10 is a change in baseline)
Define a Prolonged deceleration
peaks at 10+ bpm for over 10 sec (under 32 weeks), peaks at 15+ bpm for over 15 secs (32+ weeks)
How are accelerations of FHR defined
Sinusoidal pattern (associated with fetal anemia)
A smooth sine-wave like undulating pattern in FHR baseline with a cycle frequency of 3-5 min of regular amplitude of 5-15 bpm that last longer than 20 min
110-160 bpm baseline, moderate variability, NO late/variable decels
Category I strip requirements
No variability + recurrent late OR recurrent variable OR bradycardia; sinusoidal
Category III strips are characterized by
Increased risk of fetal acidemia (if prolonged of amplitude over 15 bpm), increased risk of hypoxemia,
Interpretation of a cat III strip
All tracings that fall in the middle
Category II strip characteristics
prepare for delivery, Mom in left lateral, IVF bolus, NO uterotonic drugs, scalp stimulation (if acceleration occurs we good)
Gameplan for Cat II or III strips
Premature rupture of Membranes (PROM)
The rupture of the amniotic membrane BEFORE onset of labor
Premature Premature rupture of Membranes (PPROM)
PROM that occurs before 37 weeks
STIs, smoking, prior preterm deliveries, multiple gestation
Risk factors for PROM
gush of fluid or persistent leakage from the vag WITHOUT contractions
PROM is characterized by
Speculum exam (check for pooling of fluid), Nitrazine paper test (turns blue if pH above 6.5), Fern test (amniotic fluid dries in a fern pattern), U/S to check AFI
Diagnostics for PROM
Digital exam (unless delivery is imminent)
What are we NOT going to do with a PROM patient
chorioamnionitis or endometritis (if 24 hrs+), cord prolapse, placental abruption
Complications of PROM
admit with fetal monitoring, wait for labor, monitor for infection
Expectant management of PROM
Chorioamnionitis or labor does not occur within 18 hours
When should a PROM patient be induced (using oxytocin OR PG cervical gel)?
admit and wait for labor
Gameplan for PPROM at over 34 weeks and NO signs of infection or distress
Bethamethasone to enhance fetal lung maturity, Mg Sulfate (neuroprotection if 24-32 weeks), tocolytics to delay labor 48 hours to get the steroids on board (if no signs of infection, under 4 cm, or fetus is chilling)
Gameplan for PPROM at under 34 weeks
Preterm labor
Regular uterine contractions (4-6/hour) + progressive cervical effacement (20-30 mm) and dilatation (3 mm+) between 20-36 weeks
Maternal/Fetal stress (activation of HPA axis), Infection (decidual-chorioamniotic/systemic inflammation), Decidual hemorrhage, pathological uterine distention
Causes of preterm labor
Stress → increased cortisol → Increased corticotropin releasing hormone → Prostaglandins → Cervical changes and ROM
Hormonal changes in preterm labor
Multiple gestations, prior preterm birth, prior cervical procedures, under 17 y/o, over 35 y/o, poor access to healthcare, Type I DM, HTN, thyroid disease, asthma, kidney insufficiency, MDD, anemia, STIs, UTIs, pyelo, endometritis, EtOH, coke, heroin (singular), smoking, Short cervical length, + fetal fibronectin at 22 & 34wks, uterine contractions, vaginal bleeding, placenta previa, placental abruption, polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios, fetal anomaly, assisted reproductive conception
Risk factors for preterm labor
Respiratory distress syndrome, intraventricular hemorrhage, necrotizing enterocolitis, sepsis, seizures, neurologic impairment
Complications of preterm labor
Cervical dilation 3+ cm, 80%+ effacement, + fetal fibronectin, TVUS
Diagnostics for Preterm labor
R/o infections, Amniocentesis to determine L:S ratio (UNDER 2 means high chance of fucked up lungs)
Workup for preterm labor
Delay with tocolytics + betamethasone (enhance fetal lung) Mg Sulfate (neuroprotection IF 24-32 weeks), Ampicillin for GBS prophylaxis
Management of preterm labor under 34 weeks (anything above just admit for delivery)
Prolapsed umbilical cord
Occurs when the cord extends past the presenting part of the fetus and protrudes into the vagina - results in reduced fetal oxygenation (due to vasospasm or occlusion)
low birth weight, malpresentation, long cord, pelvic deformities, low-lying placentation, polyhydramnios, prematurity
Risk factors for Prolapsed umbilical cord
Sudden onset of severe, prolonged fetal bradycardia or variable decelerations after a previously normal tracing, cord palpable on vaginal exam
Manifestations of Prolapsed umbilical cord
Palpation or visualization, U/S with doppler to clarify
Diagnostics for Prolapsed umbilical cord
EMERGENT C SECTION, preop intrauterine resuscitation (manual elevation of the fetal presenting part until in the OR, trendelenburg or knee to chest), Tocolytics
Management of Prolapsed umbilical cord
32-34 weeks
Nifedipine is the 1st line tocolytic when?
24-32 weeka
Indomethacin is the 1st line tocolytic when?