Concept 17.3: Eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
alteration to the 5’ end vs 3’ end
5’ end: 5’ cap (modified form of guanine nucleotide) added after first 20-40 nucleotides transcribed
3’ end: poly-A tail of 50-250 adenine nucleotides
purpose of AAUAAA
pre-mRNA is cut and released soon after the polyadenylation signal is transcribed
purpose of 5’ cap and poly-A tail
facilitate the export of mature mRNA from nucleus
protect mRNA from degradation
help ribosomes attach to 5’ end of mRNA
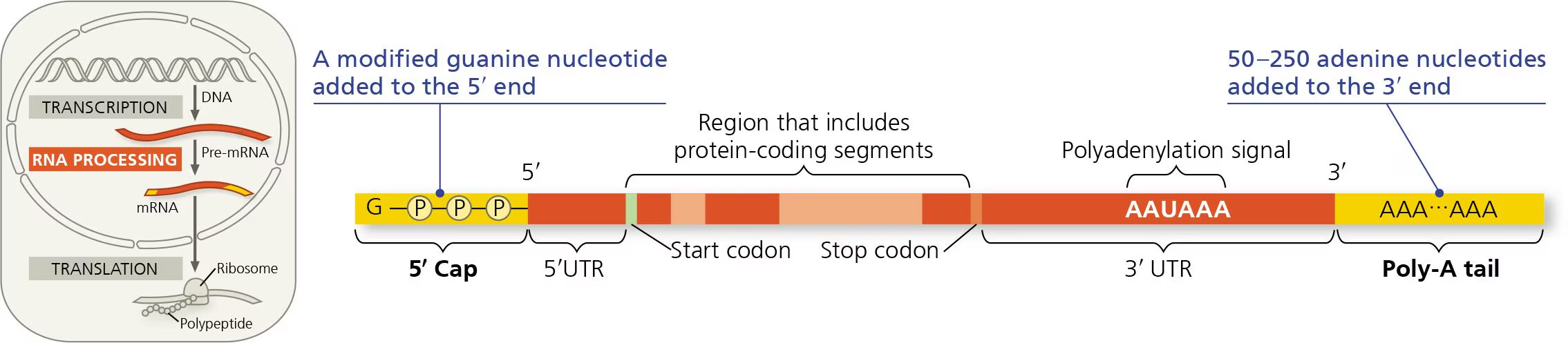
untranslated regions
UTRs are parts of mRNA that aren’t translated into proteins but instead do things like ribosome binding
RNA splicing
large portions of RNA primary transcript molecules are removed and remaining portions are connected
introns vs exons
intron: noncoding segment that lies between coding regions (INtervening sequence)
exon: eventually EXpressed by being translated into amino acid sequences or EXiting the nucleus
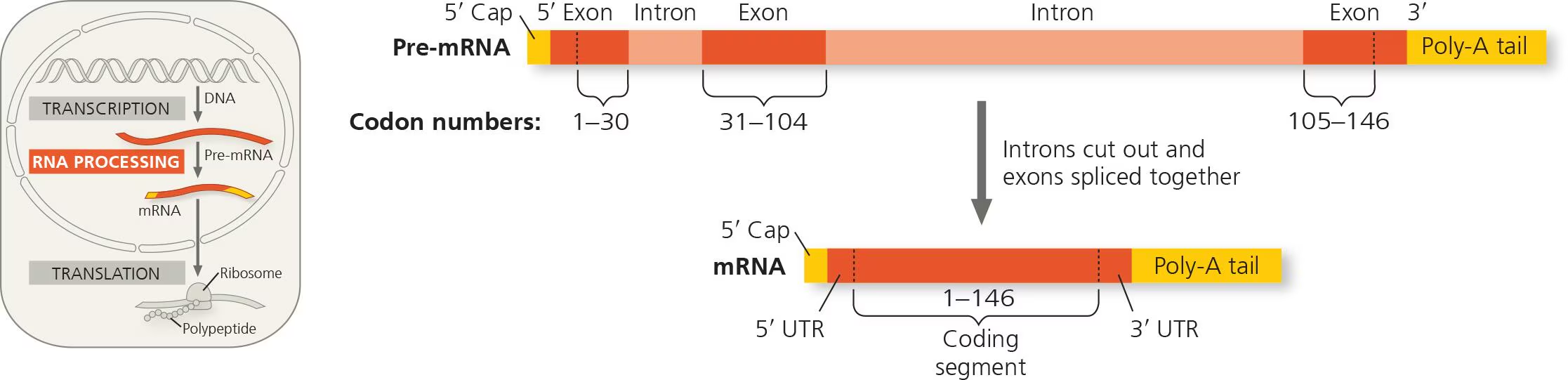
spliceosome
this large complex of proteins and small RNAs accomplishes the removal of introns. when the introns are released and rapidly degraded, the spliceosome joins the two exons together
ribozymes
RNA molecules that function as enzymes (catalytic role)
what can an intron function as
a ribozyme, by catalyzing its own removal in the splicing process
properties that allow some RNA molecules to function as enzymes
RNA is single-stranded so a region of an RNA molecule might base-pair with a complementary region somewhere else in the same molecule (giving it a 3d structure)
like certain amino acids, some bases in RNA contain functional groups that can participate in catalysis
ability of RNA to hydrogen-bond with other nucleic acid molecules adds specificity to its catalytic activity
alternative RNA splicing
eukaryotic gene regulation where different polypeptides can be made depending on which RNA segments are treated as exons vs introns
domains
structural and functional regions of protein architecture (region with active site vs region allowing enzyme to bind to cell membrane)
exon shuffling
when the presence of introns facilitates evolution of new proteins by increasing the probability of crossing over between exons due to more terrain for crossovers