Lecture 1 -- Small furries (Rodents)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What is the order of rodents?
Rodentia
What is the smallest rodent species?
Pygmy mouse or Pygmy gerboa
What is the largest rodent species?
Capybara
What are the suborders in rodents? Give examples for each order.
Myomorpha
Rat, Mouse, Gerbil, Golden hamster, Russian hamster and Chinese hamster
Hystricomorpha
Guinea pig, Chinchilla, Degu
Sucriomorpha
Chipmunk
Anomarluromorpha
Springhares, scaly tailed squirrels
Castorimorpha
Beavers, Kangaroo mic, Kangaroo rats, Pocket mice
What is the significant dental formula for Myomorpha?
1/1, 0/0, 0/0, 3/3 ×2
Total: 16 teeth
What is the significant dental formula for Hystricomorpha?
1/1, 0/0, 1/1, 3/3 ×2
Total: 20 teeth
What shape are rodent incisors and why?
Chisel-shaped 鑿
Due to hard enamel on one side and softer dentine wearing away faster
What is the key feature of rodent incisors?
Open rooted (Aradacular) = lack fully formed root → Continue to grow throughout the rodent's life
Continually growing (Elodont) → “Elo” = Continuous; “Dont” = Tooth
Hard enamel on rostral surface, with softer dentine behind = Chisel shaped 鑿子
Length of lower incisor is 3 times the length of upper incisor
Do myomorphs and hystricomorphs commonly suffer from molar overgrowth?
Myomorphys:
NO because their molars are anelodont = Grow for a short period then stop erupting
Histricomorphs:
YES because their premolars and molars are elodont = Continuously grow → Make them prone to overgrowth if not worn down properly
Compare the features of myomorph and hystricomorph premolars and molars.
Myomorphs
Absent of premolars
Molars are anelodont = Grow for a short period then cease erupting
Hystricomorphs
Presence of both premolars (1/1)and molars (3/3)
Premolars and molars are elodont = Continue to erupt throughout the life of the animal
How do rodent chew food?
By pulling the lower jaw back → (Lower incisors behind uppers) + Molars align and can grind food
How do rodents gnaw 啃?
By moving the lower jaw forward → Incisors opposed to each other (but molars are not) + Cheeks drann in to diastema
What special features are found in rodent mouth anatomy?
Large diastema
Ability to gnaw without involving molar
They can move the lower jaw forward so the incisors oppose, while the molars do not touch
Ability to chew
They can bring the lower jaw back → Lower incisors behind uppers incisors → Molar oppose for grinding
Why can rodent incisors be safely shortened with a dental burr?
Incisor pulp cavity is small and beneath gumline → Allow crown trimming without hitting the pulp, which contains the blood vessels and nerve
Are rodents monogastric or polygastric?
Monogastric (Except hamsters, which have two compartment stomach)
What are the main gastrointestinal (GI) system adaptations in rodents?
Fore-stomach is non-glandular and tough
Glandular part of the stomach is separated from the fore-stomach by ridge
Large caecum
Elongated colon
Why do rodents have a large caecum?
Rodents often consume high-fiber, plant-based diets → Caecum acts as a fermentation chamber
Why do rodents need an elongated colon?
Prolong hindgut fermentation → Longer fermentation produces more vitamins e.g. vitamins B and K and amino acids → More uptake of vitamins and amino acids through caecotrophy
Do rodents vomit? Why?
No
Strong oesophageal sphincter
Weak diaphragmatic muscle = Unable to have a big contraction of diaphragm to cause vomit
Limited ridge between oesophagus and cardia of stomach (J shaped cardia)
Should rodents be fasted before surgery? Why or why not?
NO
Rodents have fast gut transit and high metabolic rate → Fasting can cause hypoglycemia
What species of rodent is most prone to GI issues and why?
Hamsters
Since they have two compartments of stomach, they are more rely on healthy gut flora → When hamsters’ gut bacteria are disrupted, they are more likely to have GI problems
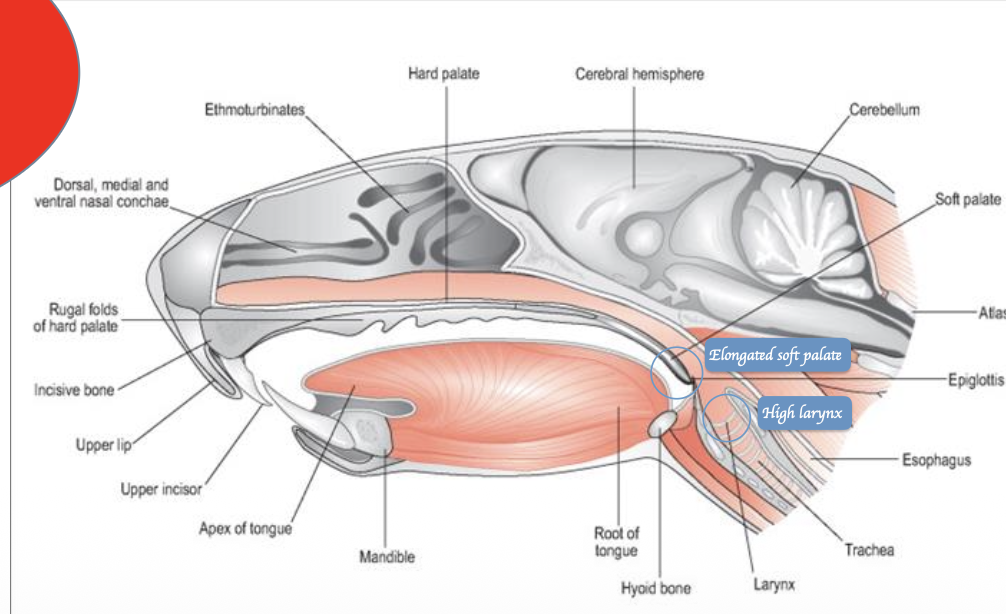
What type of nasal breathers are rodents? What anatomical features make rodents this type of nasal breather?
Rodents are obligate nasal breathers
Anatomical features
Elongated soft palate
High larynx
What types of signs indicate that a rodent is in respiratory distress?
Mouth breathing since rodents are obligate nasal breathers
How many lung lobes do most rodents have? Which species are exceptions?
Left lung: 1 lobe
Right lung: 4 lobes (Cranial, middle, caudal, intermediate)
P.S. Hamsters - Have 5 lobes in right lung (Caudal accessory)
Rodents have high oxygen demands, so what adaptations help them optimise respiration?
Short airways → Increase respiratory rates
More alveoli of thinner diameter → Increase surface area
High chest wall compliance → Increase vital capacity → Reduce residual lung capacity → Optimise lung expansion
O2 dissociation curve is shifted to right = Hemoglobin releases oxygen more readily to tissues
Why rodents require high metabolic rate to maintain body temperature in cold climates?
High surface area to volume ratio → Loss heat easily → Require high metabolic rate to maintain body temperature in cold climates
What are the mechanisms of thermogenesis in rodents in cold environemnt?
Behavioural
Huddling, nest building, tunnelling
Shivering
Peripheral vasoconstriction
Non-shivering thermogenesis
Brown adipose tissue behind scapula and around neck
What are the mechanisms for heat loss in rodents?
Sweat glands (Minimal and on feet)
Evaporation of saliva groomed over body
Arteriovenous shunts in ears, tails and feet
What is the reproductive strategy of myomorph rodents, in terms of litter size, gestation period and youngs?
Large litter size
Short gestation period
Altricial young (Undeveloped at birth)
What is the reproductive strategy of hystricomorph rodents, in terms of little size, gestation period and youngs?
Small litter size
Long gestation period
Precocial young (Well-developed at birth)
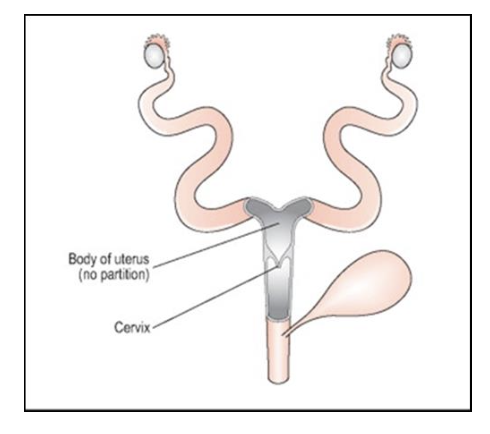
What type of uterus do rodents have, and which species have this type?
Bicornuate uterus
Found in guinea pig
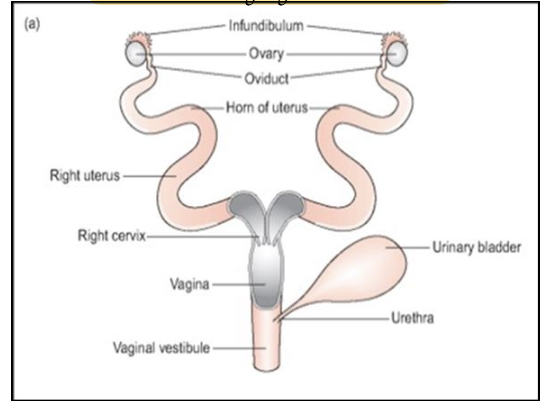
What type of uterus do rodents have, and which species have this type?
Duplex uterus
Found in rat, mouse hamster, gerbil and chincilla
Where are the testes located in most rodents, and how does the chinchilla differ?
Most rodents: Testes descend into the scrotal sac after puberty
Chinchilla: Testes often stay inguinal
Do rodents have an os penis?
Yes
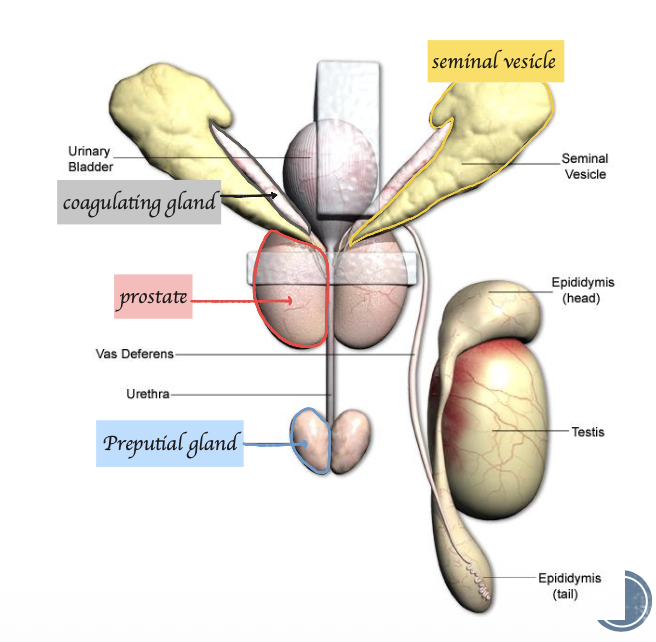
What accessory sex glands do rodents have?
Seminal vesicles
Coagulating gland
Prostate gland
Preputial gland
Bulbourethral gland
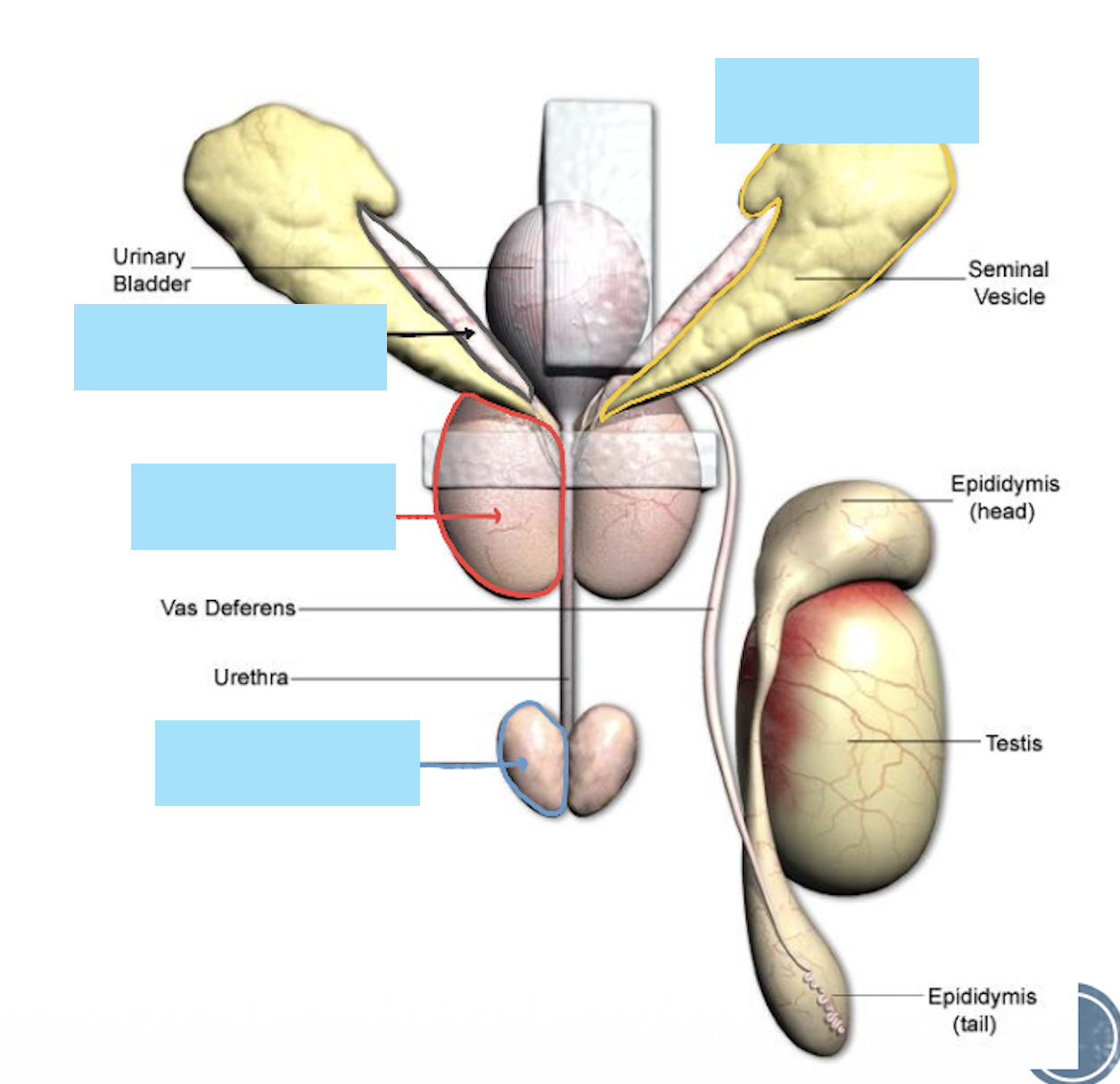
List out the anatomical feature in this picture
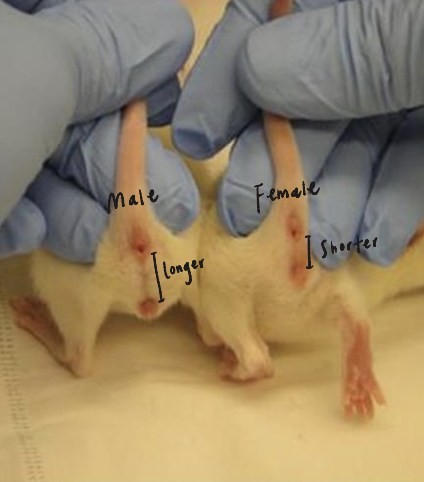
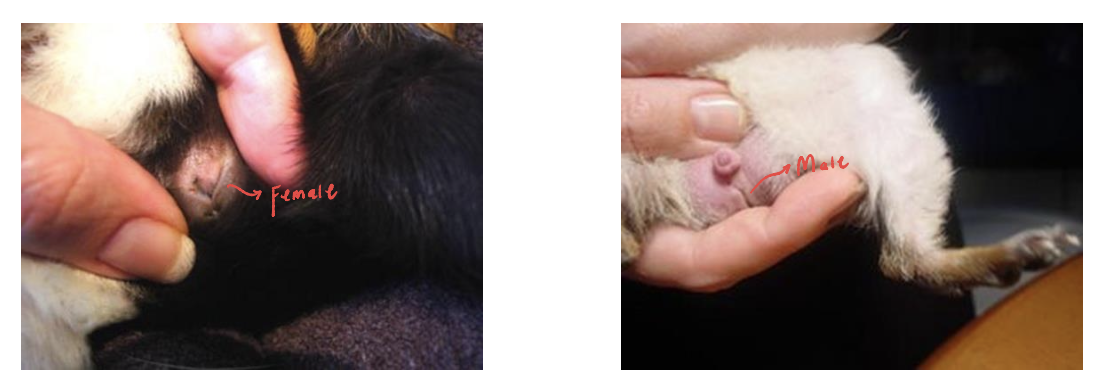
What is the most reliable method for sexing rodents?
Ano-genital distance
Males have longer distance between anus and genitals than females
What are the other method of sexing rodents?
Presence or absence of nipples
In most rodents, only female mice have nipples
Presence or absence of testes penis
Cannot rely on that because rodents have open inguinal canal and often retract testicles back into the abdomen
How is the oestrus cycle assessed in rodents?
Cytology of vaginal secretion
What are the 4 stages of the rodent oestrus cycle?
Proestrus – Mostly round nucleated epithelial cells, few leucocytes
Oestrus – Some nucleated cells, few leucocytes
Metoestrus – +++ leukocytes, non-nucleated epithelial cells
Dioestrus – Some leukocytes, non-nucleated epithelial cells
Why does the number of leukocytes increase in metestrus and diestrus?
Defensive mechanism after mating
What is copulatory plug? What is its function?
Congealed凝結的 sperm, mucus and accessory ejaculatory fluids, which is harden within the cervix
Seal vagina → Make it more likely for mating to be successful
What are the special reproductive features of mice?
Males:
Longer anogenital distance than females
Large testicles relative to body size in adult mice (Not reliable)
Females:
Only female mice have nipples
Why are rat incisors yellow?
Due to iron pigment
Are rats nocturnal or diurnal?
Nocturnal
What is the special gland in rats located behind their eyes? What happens when stressed?
Harderian gland
Red brown gland fills large part of the orbit and lies behind the globe
Increased secretion - porphyrin when stressed = Red tears
What are the common venipuncture sites in rats?
Lateral tail vein
Lateral saphenous vein
Ventral tail artery
Do rats have gall bladder?
No
How many mammary glands do female rats have?
6 pairs
Extensive mammary tissue from axilla to groin
What tumors are common in rats’ mammary tissue? Are these tumours more likely to be benign or malignant?
Fibroadenomas (Majority); Adenocarcinomas (10%)
Benign → Fast growing and prone to ulceration and secondary infection
What are the special reproductive features of rats?
Males:
Longer anogenital distance compared to females
Larger testicles relative to body size, especially in mature males
Females:
Only female rats have nipples
What special structures do hamsters have in their cheeks? What is its function?
Bilateral cheek pouches (Extend caudally as far as the shoulder blades)
Functions:
Food storage
Transport of food
Can inflate → Helps to keep hamster afloat in water
Immunologically privileged site = Don’t tend to get infection in there
How is the hamster stomach structured?
Two compartments:
Forestomch (Like ruminants)
Glandular stomach
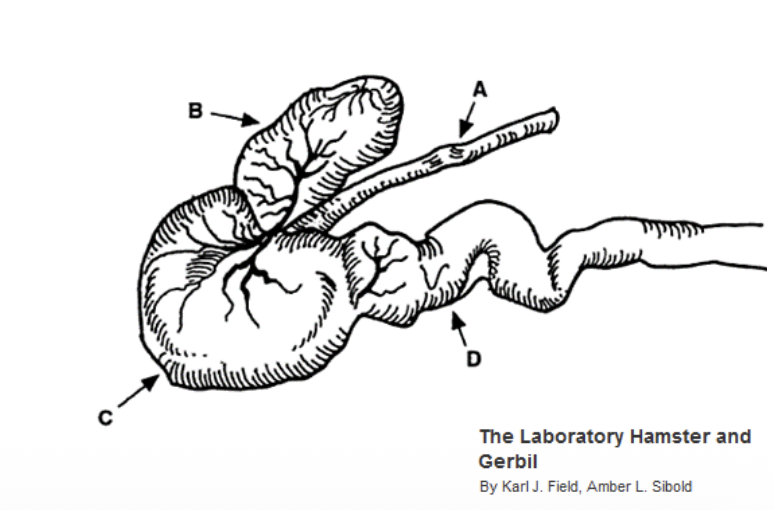
List out the anatomical structure of hamster’s stomach
A: oesophagus
B: Forestomch
C: Glandular stomach
D: Pylorus
What are the special reproductive features of hamsters?
Males:
Longer ano-genital distance compared to females
Large testes in males
Flank gland is more obvious in male
Females
Separate vaginal and urethral opening
Same as gerbils, both sexes have nipples
How long is the gestation of the Syrian hamster?
Shortest gestation length of all eutherian 胎生 mammals
~16days
What are flank glands in hamsters?
Androgen responsive glands
More obvious in males than females
What are the common venipuncture sites in hamsters?
Jugular vein
Cephalic vein
Cranial vena cava (Must be anaesthetise)
Why can’t we use the tail vein to take blood from a hamster?
Because hamster has no tail
Do hamsters hibernate? If yes, below what temperature do hamsters enter torpor/hibernation?
<18°C
Are hamsters nocturnal or diurnal?
Nocturnal but very active during hours of darkness
How much water does a hamster consume?
High water consumption → Up to 20ml a day in some large adults
What is unique about gerbil social behavior?
Form monogamous pairs = Male contributes to raise the young and they usually form a single lifelong pair bond with a mate → Aggressive to any newcomers
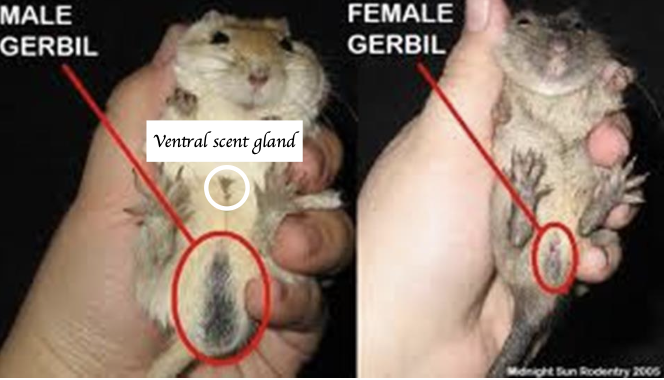
What are the special reproductive features of gerbils?
Males:
Longer ano-genital distance compared to females
Large testes in males
Pigmented scrotum
Both sexes:
Ventral scent gland (Hairless patch) (More obvious in males)
Have nipples (More obvious in female)
What is “degloving” in gerbils?
Tail skin can shed if grabbed
How much water do gerbils drink?
Gerbils are desert species = Excellent urine concentrating abilities → Drink very little (4ml/100g/day)
What are the special reproductive features of guinea pigs?
Males:
i shaped genital opening
Large obvious testicles
Penis can be everted from prepuce
Females:
y shaped genital opening
Both species have inguinal nipples
Which vitamin is an absolute dietary requirement for guinea pigs? Why?
Vitamin C because they cannot synthesize it themselves → Scurvy can develop within 4 days of decreased intake
How much vitamin C is required daily in adult guinea pigs and pregnany females?
Adults: 20–25 mg/kg/day
Pregnant females: 30–40 mg/kg/day.
What is the ideal age for the first breeding of guinea pigs? Why?
Before the age of 6-8months
Since public symphysis starts to fuse after that → It cannot dilate to allow parturition → High risk of dystocia

What is the gland shown in the picture? Are males or females more prominent with this type of gland?
Caudal sebaceous gland
Males have more prominent caudal sebaceous gland than females
What are the blood sampling sites of guinea pig?
Cranial vena cava
Jugular vein
Femoral vein
Lateral saphenous vein
What is the gestation period of guinea pig?
59–72 days (average 63 days)
Are young guinea pigs precocial or altricial?
Precocial
What is the gestation period of chinchillas?
111days
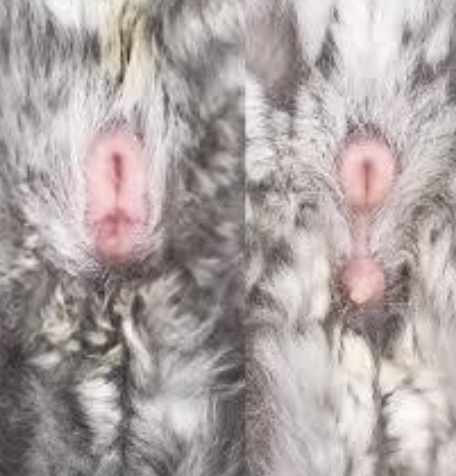
What are the special reproductive features of chinchillas?
Males:
Longer ano-genital distance compared to females
No true scrotum
Testes often stay inguinal
External genitalia look similar to female (Mistake the penis for clitoris)
Are young chinchillas precocial or altricial?
Precocial
Chinchillas have dense fur, which allows them to tolerate what type of weather?
Cold weather (But not wet)
What happens when chinchillas are stressed?
Fur slip = Sudden loss of furs that lets them escape from predators
What are the blood sampling sites of chinchillas?
Cranial vena cava
Lateral saphenous vein
Are chinchillas nocturnal or diurnal?
Nocturnal but can adapt to diurnal lifestyle
Need 12hr :12hr light dark periods
Are young chinchillas precocial or altricial?
Precocial