Computer Science - Paper 2
1/326
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
327 Terms
What does TCP/IP stand for?
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol
What does MAC stand for?
Media Access Control
What are the main 4 network layers?
Application
Transport
Network
Link
ATNL — A TuNneL
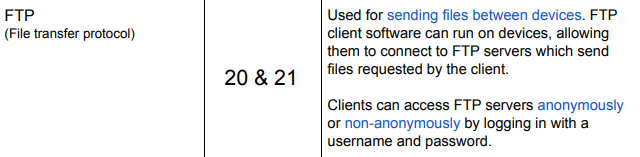
What does FTP stand for?
FTP — (File Transfer Protocol)
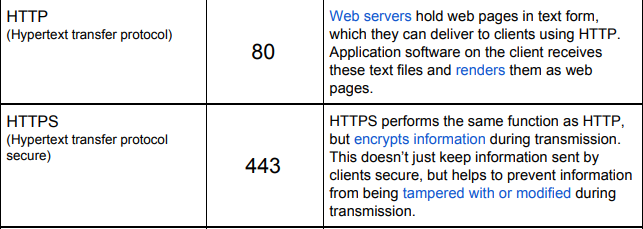
What does HTTP/S stand for?
HTTP/S — (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol / Secure)
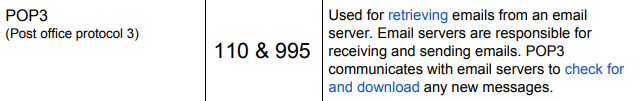
What does POP3 stand for?
POP3 — (Post Office Protocol v3)
What does SMTP stand for?
SMTP — (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)

What does SSH stand for?
SSH — (Secure Shell)
(Allows for Secure Shell Tunnelling Port)

What does DHCP stand for?
DHCP — (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
What does NAT stand for?
Network Address Translation
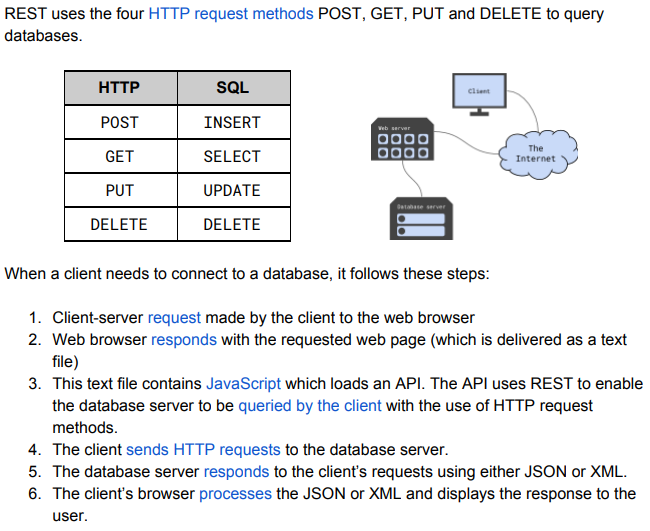
What does CRUD stand for?
Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete
What does REST do?
Allows for CRUD to become available for database mapping functions.
What does the Application layer do?
The Application layer somewhat being featured in the name is responsible for selection and use of correct protocols like using right protocols for User interacted application software.

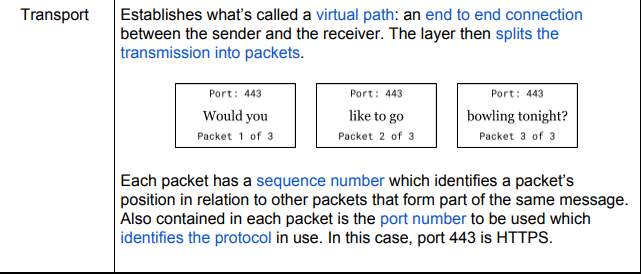
What does the Transport layer do?
The Transport layer establishes Transport funny enough technically making a virtual path and e2e encryption like featured on whatsapp.
in addition of course what’s required for networking is not one massive payload but instead all of the possible millions of packets to be sent according to the size for the data to be transmitted.
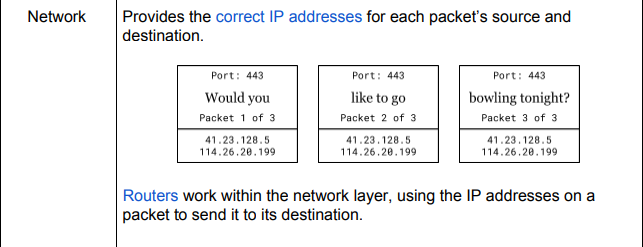
What does the Network layer do?
The Network layer simply is what allows for networking being the provider which assigns the correct IP address to each packet source and destination.
Routers work in Unison here in order to accomplish successful sending to set destinations.
What does the Link layer do?
Finally the link layer once again does exactly as described making the physical link between pieces of hardware then to the network.
This adds the personal MAC to the packets received to the network layer and for security each hop changes to the then brand new corresponding MAC address.
What happens once the user receives their data?
The packet gets stripped of extra detail
link layer removes MAC of course to add the new one
Network removes IP for security
Transport then uses packet port to see correct port to send through and packet number to see if in the correct order.
Finally application layer shows user their requested data.
What is a socket address?
An IP combined with a port number.
Example :
Socket Address : 114.26.20.199:443
IP : 114.26.20.199
Port : 443
What does a Socket Address do?
Identifies what application the packet should get sent to.
What ports do FTP use?
20&21
What port does SSH use?
22
What port does HTTP use?
80
What port does HTTPS use?
443
What ports does POP3 use?
110&995
What port does SMTP use?
25&587&465
What are the 2 parts of an IP Address?
Network Identifier
Host Identifier
What are subnets?
Subnets are broken down networks with the requirement that different network identifiers are used.
How do you find the network identifier?
Through use of the subnet mask.
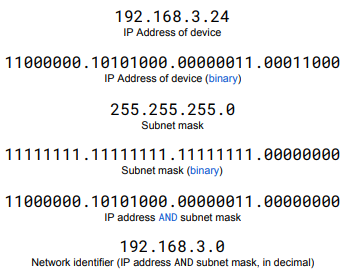
What is the link between Binary and subnets?
They’re similar in the fact that floating point has the choice between Size of precision and this is featured also with subnet IPs where you can either have more networks or more hosts/users.
What are the 2 types of IPs?
IPv4
IPv6
(Internet Protocol version 4/6)
What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6?
The difference between them relates to overall size of IPs that can be stored/used with IPv4 storing over 4 billion while IPV6 is able to use 10^ 37.
This being a requirement because there are 8 billion people on the planet meaning IPv4 is not enough.
How does DHCP work?
For example if a Device turns on but then is forgotten their assigned IP would be wasted making it so that Devices once they leave they lose their IP adding it to a pool of available IPs to be granted to whoever requires. Dynamic IPs
How can a private IP access the internet when its IP is not accessible?
Through the use of a NAT as with a Network Address Translation somewhat like a Hash Table it will store them both separately and technically assign the private IP a public one of which it will remember the conversion for when the time comes to receive the output.
What is port forwarding?
Port forwarding is used when a client is attempting to communicate with a server that is connect to a private network.
Similar to the problem that NAT fixes instead with Port Forwarding it works on a larger level allowing for entire client to gain access to the private network.
What does API stand for?
Application Programming Interface
What is an API?
A set of protocols which handle how different apps talk with each other.
The WebSocket protocol is an example.
What does it mean if a WebSocket protocol is full-duplex?
Means that data can be transmitted in both directions simultaneously.
What does REST stand for?
REpresentational State Transfer
What does XML stand for?
eXtensible Markup Language
What does JSON stand for?
JavaScript Object Notation
What is the difference between XML and JSON?
They are both simply styles of writing HTML with each to their benefit.
What is the difference between Thin and Thick-client networks?
Thin-client networks and thick-client networks are somewhat described in their name with thin-clients stating that they’re pretty thin and don’t really have that much too them being pretty simple and cheap with the main server handling pretty much everything compared to the thick-clients where they’re pretty well supplied and can overall handling everything theirself.
What does URL stand for?
Uniform Resource Locator
What does FQDN stand for?
Fully Qualified Domain Name
What does DNS stand for?
Domain Name Server
What does ISP stand for?
Internet Service Provider
What does TTL stand for?
Time-To Live
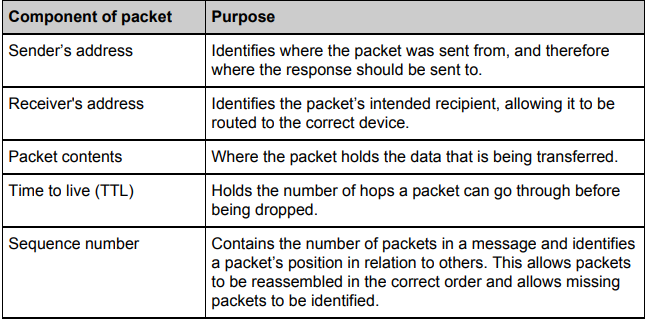
What are key 5 parts of a packet?
Sender Address
Receiver Address
Packet Contents
TTL
Sequence Number
What does hop mean in networking?
It refers to that every time a packet has been passed through a router it counts as a hop which has a limit for security reason designated within each packet.
What is the difference between Routers and Gateways?
Routers working on a smaller level compared to gateways where routers connect computers together and gateways connect entire networks together and one of the possible features of a gateway is to be able to change protocols of packets.
What are the 7 possible parts to a URL?
For example:
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology/index.html — FQDN
https:// — Protocol
www. — Subdomain
bbc.co.uk — Domain
You’ll see this bit looks alot like file management and thats because it is this URL pretty much is accessing a servers folder/file.
/new — Directory
/technology — Sudirectory
/index — Name of file
.html — File extension
What are the main 3 parts of a URL?
Protocol
subdomain
domain
FQDN must contain all these
How does a Domain work?
A Domain name like zedf.co.uk is the English version to where what it actually looks like is a IP Address and the reason we simply don’t just use the address is because you wont remember it compared to a nice domain and how this is all handled is then done through the DNS.
What are 3 types of security featured by a proper firewall?
Packet Filtering
Stateful Inspection
Proxy Server
What does a packet filter do? :D
it simply will filter packets accepting good and blocking bad depending entirely on their IP and protocol which they are using.
Use of a whitelist would also suffice for this.
What does stateful inspection do?
Stateful inspection pretty much will inspect the data being sent for example what data is within a packet to see whether it is harmful or not.
What is a proxy server?
A proxy server is like a substitute server that works for the primary server and acts somewhat as a middle-person / mask
What is the difference between Symmetric and Asymmetric encryption?
Symmetric means that both the sender and receiver obtain the same private key. (able to encrypt and decrypt data) while Asymmetric encryption makes use of four different keys with two coming from each user (a public and private)
How does Symmetric Encryption work?
Firstly both users in the ordeal must agree to sharing their keys each having their own copy which allows for the process to work as then they can both decrypt however if anyone else has this key then they can easily intercept which Asymmetric solves

How does Asymmetric Encryption work?
When a message gets encrypted with a public key then only the corresponding private key is even able to decrypt it vise versa.
This gets done before sending to the recipient of which the recipients public key is used so then only they can view it because only they have access to their corresponding private key.
It acts like those boat transmission things to where they have to place you in that holding place to where then they fill it with water so you can move on.
What does a Digital Signature do?
A Digital Signature allows for Asymmetric encryption to verify the sender of the message so that when they do unbox the sent message with their private key it isn’t something that is malicious.
How does a Digital Signature work?
Message hashed for unique value.
Hash encrypted with private key.
Encrypted hash attached to message.
Recipient decrypts hash with sender's public key.
Compares decrypted hash with rehashed message for verification.
What is a digital certificate?
Quite literally acting like professional paper/documents which get sent along in asymmetric encryption which acts as another step proving whoever is sending is rightful which again shows how it solves the interception problem featured on symmetric encryption.
What are 3 main types of Malware?
Worms
Trojan
Viruses
What does Malware stand for?
Malicious Software
What is a worm?
Worms have the ability to self replicate within a network spreading or rather digging or via users downloading/executing the worm programs.
What is a trojan?
just like the real thing it pretends to be the real thing tricking users to open it and these are usually sent to users through email where it all begins.
What is a virus?
Viruses truly acting like one from biology acts with living hosts just like the real thing where a host cell must emody the virus and once they’ve been caught like an illness its too late to of which they’re usually found as .exe so it may be there for a very long time but until it truly is triggered it will just wait somewhat like cancer.
What are two types of topology?
Physical
Logical
What is a physical network topology?
Considering a physical network topology this refers to the actual architecture of the network.
What are 2 types of physical network topology?
Star
Bus
How does a physical star network topology function?
In a physical star network each client is connected to a central hub and have their own direct connection so they all can receive and talk to the central hub with new connections easily being made and broken however if the central hub goes down they all do.
How does a physical bus network topology function?
A physical bus connects the clients through a single cable quite similar to a star however instead of a central hub they all rely on the cable (Backbone)
What is a logical network topology?
For logical networking this instead of focusing on the actuality instead looks at logically what is actually happening like where the packets are going and how they move within the network.
Are you able to combine/mix topologies?
Yes, a physical star is able to logically even work like a bus even if the hardware doesn’t match all you would need to do for this logical idea is then make use of bus protocols.
What are 2 types of networking between hosts?
Client Sever
P2P (Peer-2-Peer)
What does WPA stand for?
WiFi Protected Access
What does SSID stand for?
Service Set IDentifier
How can Wi-Fi be made more secure?
WPA/WPA2 — any sussy business will not go un-noticed
Disabling SSID Broadcasting making it invisible to the unknowing eye. — only those which know the name can add
Addition of MAC Address filter — Only those allowed may join
What does CSMA/CA stand for?
Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Avoidance
Why is use of CSMA/CA done?
CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Avoidance) is used in order to avoid any possible data collisions
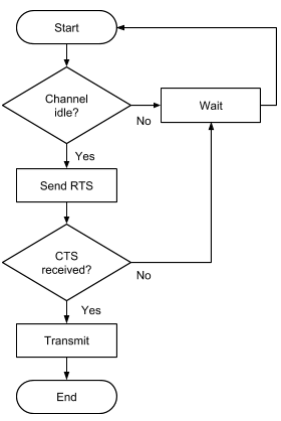
What does RTS stand for?
Request To Send
What does CTS stand for?
Clear To Send
What is Baud Rate?
Baud Rate refers to the overall amount/speed of which channels change every second.
What is Bit Rate?
Bit Rate refers to the overall speed/amount of which bits are being transferred every second.
What is Bandwidth?
Bandwidth refers to the total width of the amount of overall data can be handled/worked with at one single time.
What is Latency?
Latency refers to the time delay between doing something and the actual response then finally ocurring.
What is a Protocol?
A protocol is a rule that is set/used across networking etc. in order to organise/control everything.
What is a symbol?
A symbol is simply a pattern of bits.
How do you calculate the Bit Rate?
Bit Rate - Baud Rate X Number of Bits per signal.
What is the difference between Serial and Parallel Data Transmission?
overall its the abilities provided from both with Serial being able to work over longer distances and parallel working with more at one single time.
What are two possible issues caused by Parallel Data Transmission?
Skew
Crosstalk
What is skew?
Skew refers to the wires used in a parallel data transmission because as not everything can be perfect by trying to perfectly make a set of wires to be used within a parallel transmission is incredibly difficult and this effects the overall quality being a feature it relies on with all supposedly arriving at the same time but if one wire is off then this is all wrong.
What is crosstalk?
Crosstalk refers to these wires being so close together that it is possible the frequencies could overlap ending up crosstalking and overriding the data only getting worse over longer distances.
What is the difference between Synchronous and Asynchronous transmission?
Synchronous transmission and asynchronous overall refers to how data is sent with when it is done in sync it means that the data is sent inline with the clock pulse meaning that it can be slower but is overall more ordered which then compared to being asynchronous which will just send data as soon as possible whenever possible which could get messy but also pretty fast.
What are the 5 main components of the CPU?
Arithmetic & Logical Unit (ALU)
Control Unit
Clock
General-Purpose Registers
Dedicated Registers
What does CU stand for?
Control Unit
What does ALU stand for?
Arithmetic & Logical Unit
What does CPU stand for?
Central Processing Unit
What are the key 5 dedicated registers?
Program Counter
CIR — Current Instruction Register
MAR — Memory Address Register
MDR or MBR — Memory Data or Buffer Register
Status Register