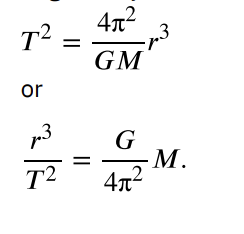Chapter 6: Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
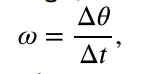
angular velocity (ω)
the rate of change of the angle with which an object moves on a circular path, where change in angle takes place in change in time; units are radians per second (rad/s)
arc length (Δs)
the distance traveled by an object along a circular path
banked curve
the curve in a road that is sloping in a manner that helps a vehicle negotiate the curve
center of mass
the point where the entire mass of an object can be thought to be concentrated
centrifugal force
a fictitious force that tends to throw an object off when the object is rotating in a noninertial frame of reference
centripetal acceleration
the acceleration of an object moving in a circle, directed toward the center; units are m/s2
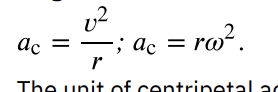
centripetal force
any net force causing uniform circular motion
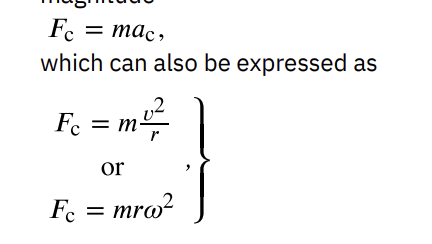
Coriolis force
the fictitious force causing the apparent deflection of moving objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference
fictitious force
a force having no physical origin
gravitational constant, G
a proportionality factor used in the equation for Newton’s universal law of gravitation; it is a universal constant—that is, it is thought to be the same everywhere in the universe
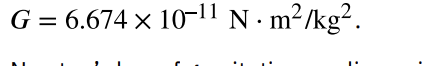
ideal angle
the angle at which a car can turn safely on a steep curve, which is in proportion to the ideal speed
ideal banking
the sloping of a curve in a road, where the angle of the slope allows the vehicle to negotiate the curve at a certain speed without the aid of friction between the tires and the road; the net external force on the vehicle equals the horizontal centripetal force in the absence of friction
ideal speed
the maximum safe speed at which a vehicle can turn on a curve without the aid of friction between the tire and the road
microgravity
an environment in which the apparent net acceleration of a body is small compared with that produced by Earth at its surface
Newton’s universal law of gravitation
every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force along a line joining them; the force is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
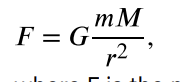
non-inertial frame of reference
an accelerated frame of reference
pit
a tiny indentation on the spiral track moulded into the top of the polycarbonate layer of CD
radians
a unit of angle measurement
radius of curvature
radius of a circular path
rotation angle
the ratio of the arc length to the radius of curvature on a circular path; where 2 radians = 360 degrees = 1 revolution
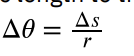
ultracentrifuge
a centrifuge optimized for spinning a rotor at very high speeds
uniform circular motion
the motion of an object in a circular path at constant speed
Conversion of radian to degrees
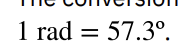
Relationship of Linear velocity (v) and Angular velocity
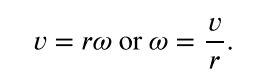
Kepler’s 1st Law
The orbit of each planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
Kepler’s Second Law
Each planet moves so that an imaginary line drawn from the Sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
Kepler’s Third Law
The ratio of the squares of the periods of any two planets about the Sun is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their average distances from the Sun

Relationship between the period and radius of a satelitte’s orbit about a larger body M