Bio 110: Exam 2
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Who is credited with the discovery of DNA
watson and crick
Who actually discovered DNA
Rosalind Franklin
Genome
Full set of DNA present in a individual
Chromosomes
Linear of circular strand of DNA (makes up the genome)
Gene
Sequence of bases that contain instructions for making a specific protein; section of chromosome
How many genes and bases do humans have
25,000 genes and 3,000 bases long
Allele
alternative form of a gene that codes for the same trait
Trait
Any single feature of an organism
Examples of traits
hair color, eye color
How many copies of chromosome do you inherit from your parents
one copy each
Do all DNA code for protein
No
How much human DNA codes for protein
2%
Who has the most amount of junk DNA
E.coli
Genotype
All the genes an organism has (genetic makeup)
Phenotype
Physical expression of genotype (outward appearance)
Transcription
Synthesis of an RNA copy of a segment of DNA
Steps of DNA into protein
DNA to transcription to RNA to translation to protein
RNA polymerase
Recognizes the start of a gene on the DNA strand and attaches RNA match
Transcription happens where
nucleus
Central dogma
Framework for understanding the sequential transfer of genetic info
Translation
mRNA is translated into protein
3 materials needed for translation
amino acids, ribosomes, and tRNA
Codon
group of 3 nucleotide bases in mRNA that specify a particular amino acid to be incorporated into a protein
Translation happens where
cytoplasm
Mutation
Alteration of the sequence of bases in DNA which can have a range of effects
Types of mutations
nucleotide substitutions and nucleotide deletions or insertions
Frameshift mutation
Nucletide insertion and Nucletide deletion
chromosomal aberrations
gene deletion, gene relocation, gene duplication
Mutation diseases are caused by what
translation of a non functioning protein
What makes fireflies light up
luciferase protein
Transgenic organism
transplanting genes from one organism to another organism
What chops up DNA via binding
restriction enzymes
Two applications of biotech
healthcare and agriculture
Polymerase does what
amplify DNA and creates two copies of interest DNA
What did biotech cure
SCID using stem cells
Process of gene therapy
replaces non functioning gene with working one using vectors
Example of a vector
virus
Can vectors reproduce
no
Difficulties with gene therapy
immune response, transfer DNA going into wrong cell, & virus wake up
Ethical dilemmas of biotech/screening
health insurance and discrimination
Who was the first recorded clone
dolly the sheep
Telomere
protective cap at the end of DNA, made of nucleotide bases, and gets shorter each cell division
Up to how many times can a cell divide
50
Hutchinson Gilford progeria
shortened telomeres which ages cells
Do eukaryotes replicate through mitosis or meiosis
both
What do somatic cells go through
mitosis
What do gametes go through
meiosis
Gap 1 (interphase)
cell makes proteins and rids waste
Gap 2 (interphase)
second period of growth and division prep
S phase
DNA synthesis and division prep
What replicates DNA
DNA polymerase
What does m phase stand for
mitosis phase
Apoptosis
programmed cell death to stop damage from the cell
Homologues
two chromosomes from each parent that code for same gene but are not genetically identical
DNA + Histones =
chromatin
DNA replication
2 copies to 2 chromosomes to sister chromatids connected by centromere
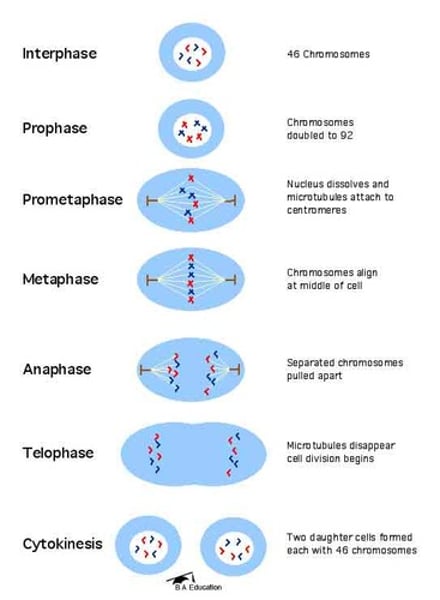
Prophase
nuclear membrane breaks down, sister chromatids condense, and spindle forms
Metaphase
sister chromatids line up at center of cell
Anaphase
sister chromatids are pulled apart to each pole
Telophase
Chromosomes uncoil, nuclear membrane reassembles and cell pinches in 2
Reasons for mitosis
growth and repair
What happens at the G1 checkpoint?
The cell checks that the chemicals needed for replication are present and for any damage to the DNA before entering S-phase
G2 checkpoint
Did DNA replicate correctly?
Spindle assembly checkpoint
Are the spindle fibers properly built and attached?
What happens to the length of telomeres on a cancer cell
Stays the same length
Benign tumor
localized non harmful mass of normal cells
Malignant tumor
cancerous cells that continuously replicate and are harmful
Metastasis tumor
Cancer is spreading to other parts of the body and is harmful
What does cancer interfere with
DNA and cell regulation
Phases of Mitosis
....
asexual reproduction
Daughter cells inherit full set of identical DNA from 1 parent cell
sexual reproduction
combination of DNA from 2 separate individuals that is passed on
Diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
Haploid
having only one complete set of chromosomes.
Homologues (meiosis)
maternal and paternal copies of a chromosome
Crossing over creates what
genetic variation
Prophase 1
chromosomes condense, homologous chromosome crossover and unite, nuclear membrane disappears
Metaphase 1
each pair of homologous chromosome moves to the middle
Anaphase 1
homologues are pulled apart, random assortment happens
Telophase 1
chromosomes get to poles, cytoplasm divides, and pinches into 2 daughter cells
Prophase 2
chromosomes condense, spindles form and no crossing over
Does crossing over happen in prophase 2
no
Metaphase 2
sister chromatids move to the middle
Are the sister chromatids identical in metaphase 2
no
Anaphase 2
pulls sister chromatids apart and one set goes to each pole
Telophase 2
cytoplasm divides, cell pinches into 2 and there's 4 haploid cells total
How many haploid cells does meiosis produce?
4
Why does meiosis have one large egg and one polar body
unequal division of cytoplasm
Sexual reproduction disadvantages
mate competition, parent only contributes half, and higher risk of disease
Asexual reproduction disadvantages
little genetic variability and more vulnerable to change
Meiosis starts with how many chromatids
92
Autosomes
carry genes for non sex specific traits
How many chromosomes are autosomes
22 pairs
How many chromosomes are sex chromosomes
1 pair
Who determines sex of the baby
father
Karyotype
a display of an individual's complete set of chromosomes performed on fetus
What do karyotypes show?
sex and chromosomal abnormalities
extra copy of chromosome 21
Down syndrome
Nondisjunction
the unequal distribution of chromosomes during meiosis
Turner syndrome
only one X chromosome