Path: ovaries
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
luteal phase
which phase of the ovarian cycle corresponds to the secretory phase of the uterine cycle?
follicular phase
which phase of the ovarian cycle corresponds to the menstrual (days 1-5) and proliferative phase of the uterine cycle?
corpus luteal cyst
PCOS
numerous cystic follicles present in ovary due to hormone imbalance; persistent anovulation, obesity, hirsutism, rarely virilism
increased LH, low FSH
what are the levels of LH and FSH in PCOS?
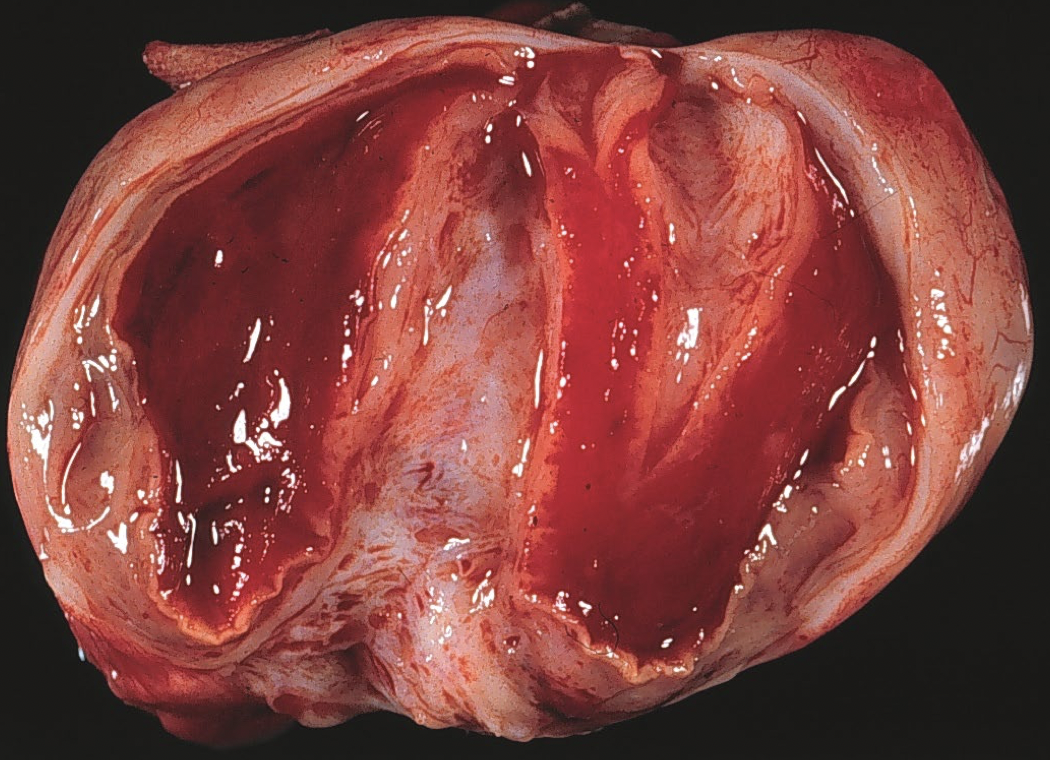
PCOS
2x ovary size, smooth gray-white outer cortex studded with subcortical, bilateral cysts
benign epithelial
makes up about 80% of ovarian tumors; seen in young women 20-45
malignant epithelial
ovarian tumors that are common in older women, 45-65; most have spread once they are detected
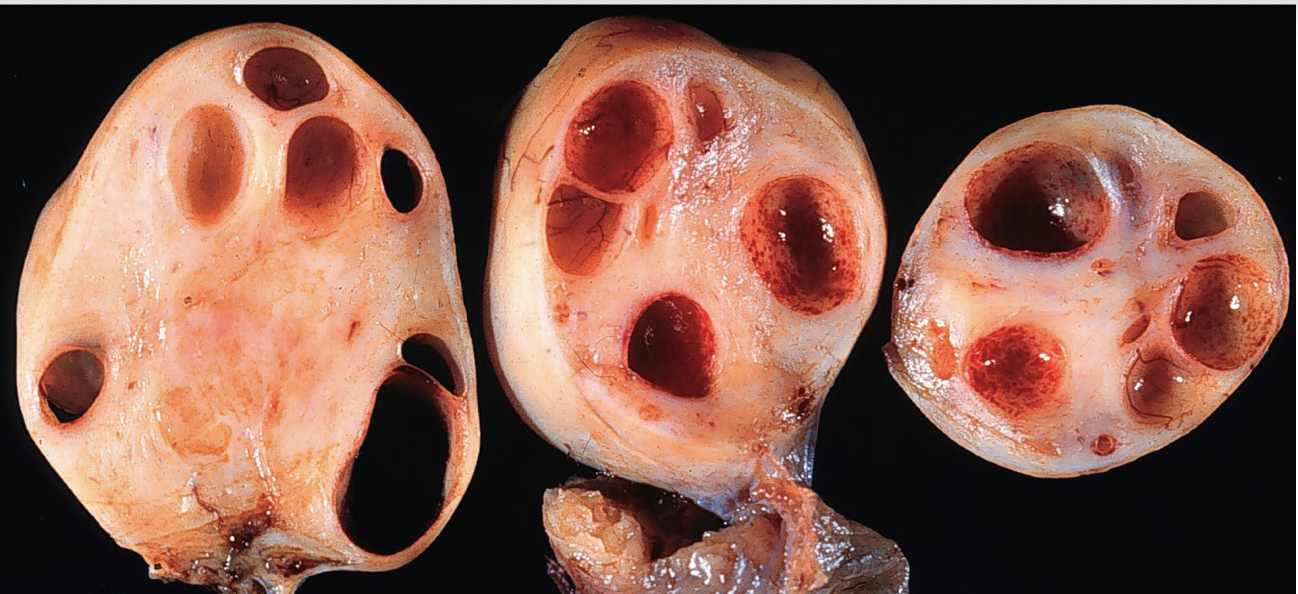
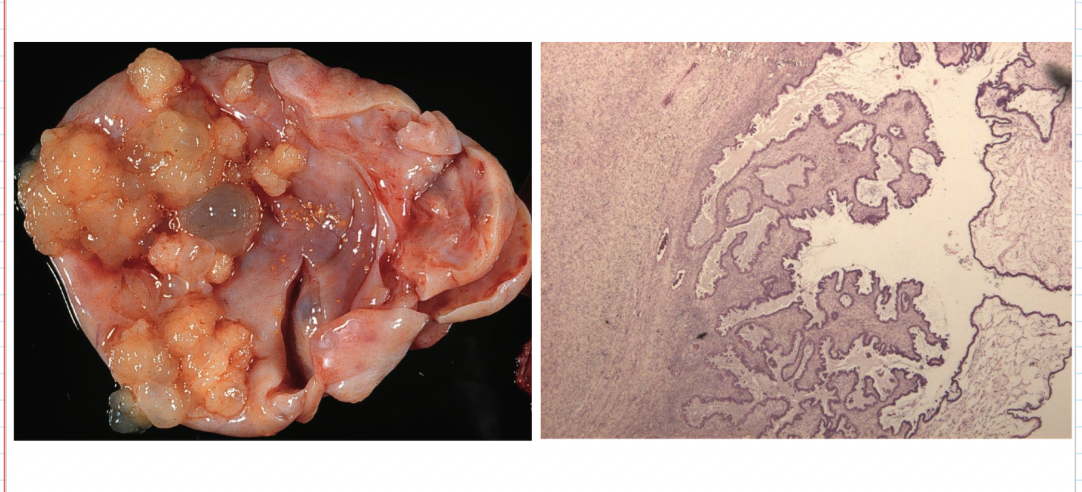
serous
ovarian tumors that are filled with watery fluid; epithelial lining resembles the fallopian tube lining
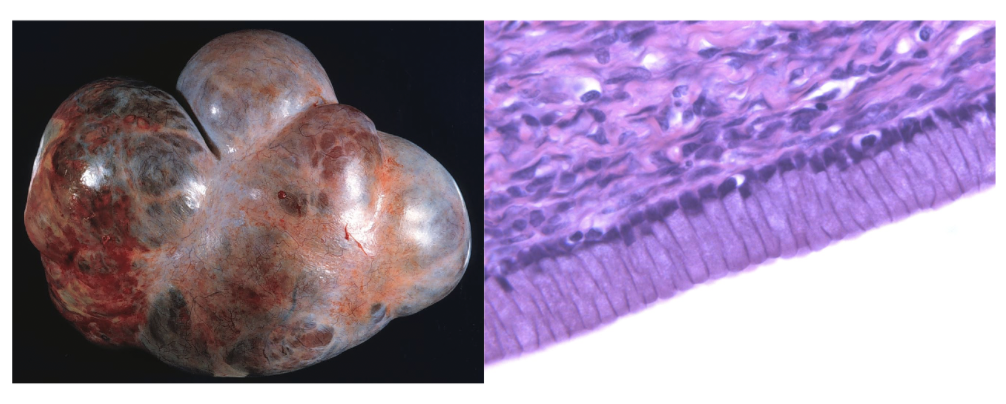
mucinous
ovarian tumors that are full of sticky, gelatinous fluid rich in glycoprotein; tumor epithelial lining resembles endocervix
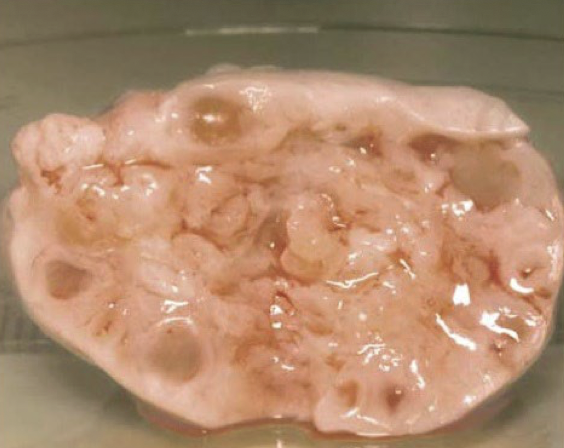
benign ovarian serous cystadenoma
borderline
ovarian tumors that contain an increased number of papillary projection and nuclear atypia with malignant potential, but no invasion into the stroma
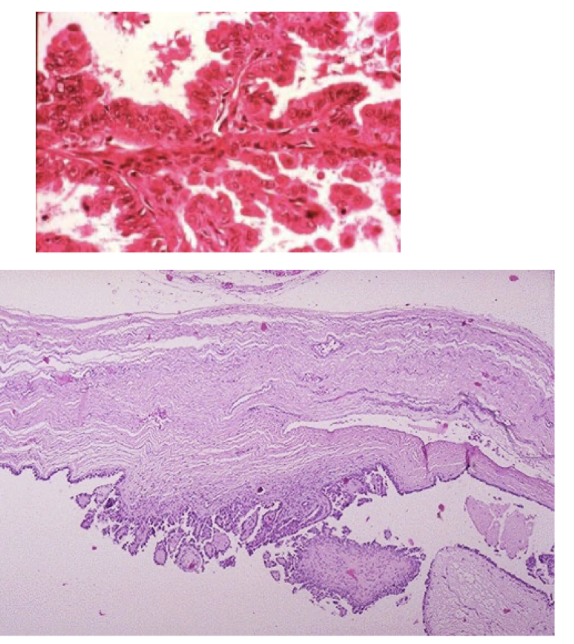
serous borderline tumor
BRCA1, BRCA2, p53
serous ovarian tumors often involve what mutations (3)?
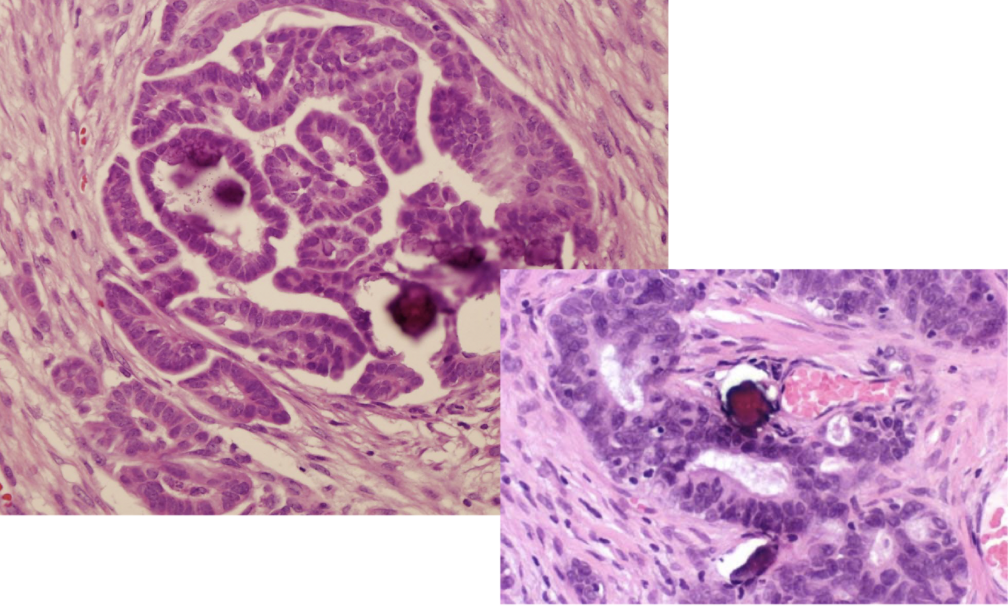
serous carcinoma
buzzword: psammoma bodies in the ovary
serous
are serous or mucinous ovarian tumors more common?
benign mucinous cystadenoma
pseudomyxoma peritonei
clinical condition defined by extensive mucinous ascites and implants on peritoneal surfaces; associated with mucinous tumors of the ovary and appendix
endometrial carcinoma of the endometrium
15-30% of ovarian endometrioid carcinomas are accompanied by?
endometrioid ovarian tumor
mostly malignant ovarian tumors with tubular glands resembling endometrium; may arise from endometriosis
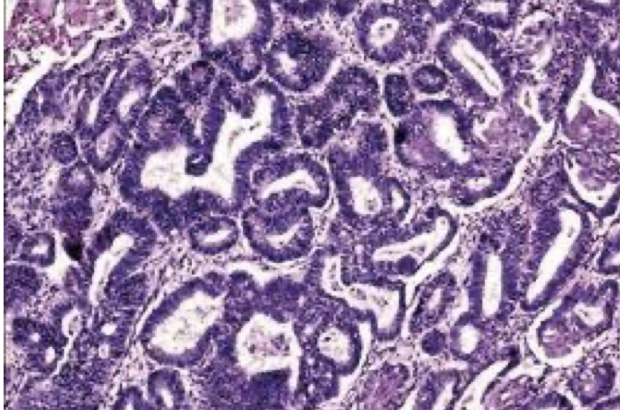
brenner tumor
mostly benign epithelial tumor consisting of nests of transitional cells resembling those lining the urinary bladder
CA-125
what serum marker can be used to monitor disease recurrence/progression after dx of surface epithelial ovarian tumors?
teratoma
ovarian germ cell tumor of fetal tissue
dysgerminoma
ovarian germ cell tumor of oocytes
choriocarcinoma
ovarian germ cell tumor of placental tissue
yolk sac
ovarian germ cell tumor known as an endodermal sinus tumor
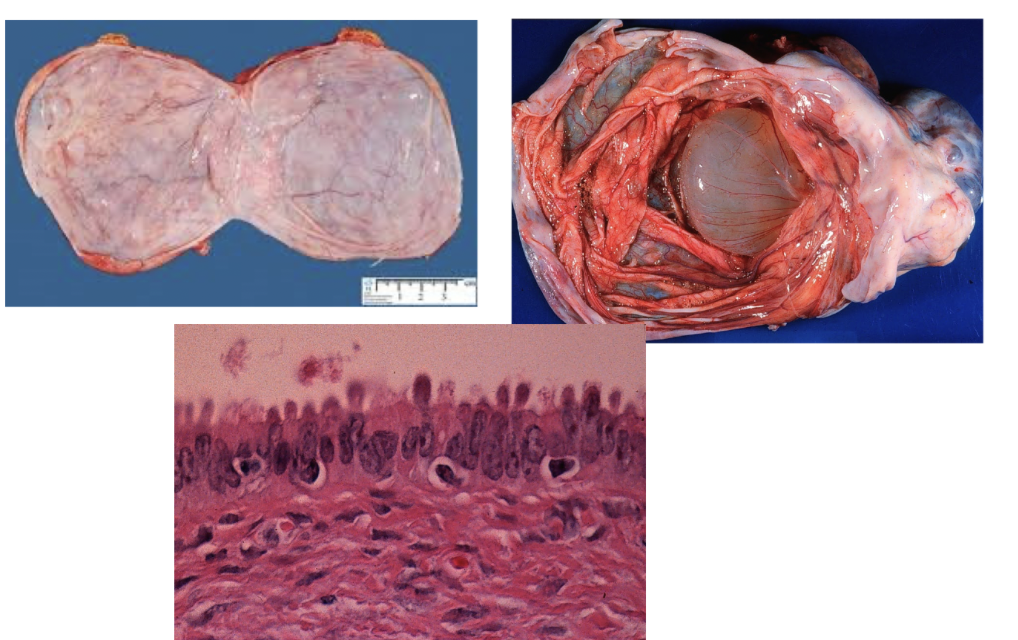
benign mature cystic teratoma
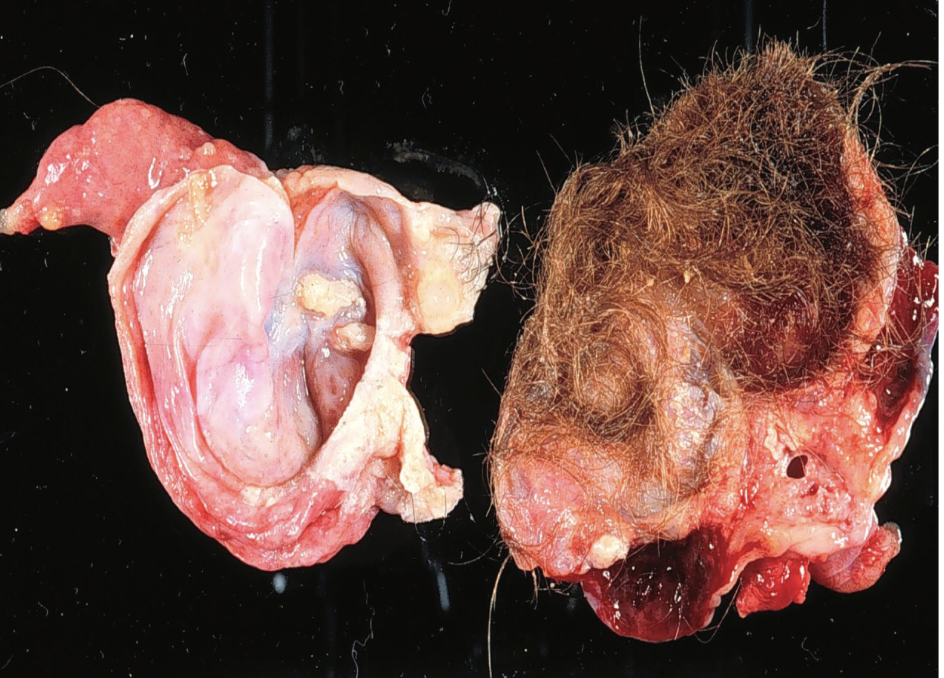
benign mature cystic teratoma
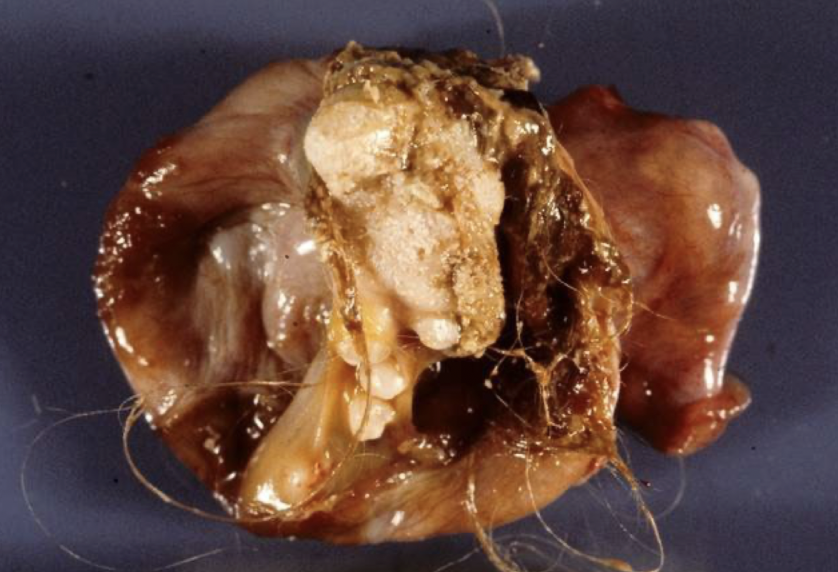
immature malignant teratoma
rare germ cell tumor that resembles embryonal and immature fetal tissue
struma ovarii
monodermal teratoma composed entirely of mature thryoid tissue
dysgerminoma
ovarian counterpart of testicular seminoma; may occur in patients with gonadal dysgenesis; malignant but good prognosis
dysgerminoma
buzzword: Oct3, Oct4, c-KIT
dysgerminoma
cell dispersed in sheets or cords separated by scant fibrous stroma that is infiltrated with mature lymphocytes and occasional granulomas; large cells with clear cytoplasm and central nuclei
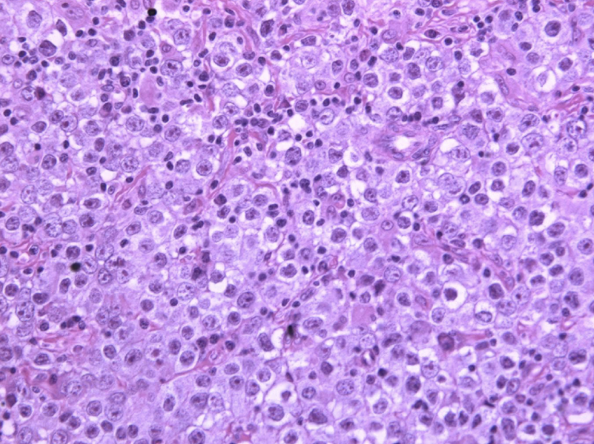
yolk sac
most common germ cell tumor in children
yolk sac
buzzword: rich in alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)
yolk sac
buzzword: schiller-duval body (central blood vessel enveloped by germ cells)
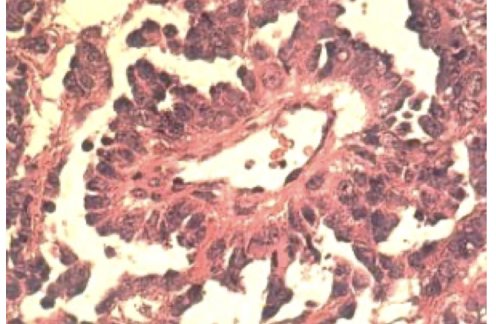
choriocarcinoma
malignant tumor composed of trophoblasts and syncytioblasts; early hematogenous spread and poor response to chemo
choriocarcinoma
buzzword: HCG
granulosa cell tumor
sex cord-stromal tumor composed of cells that resemble a developing ovarian follicle; divided into juvenile and adult; potentially malignant but minimal metastatic risk
granulosa cell tumor
buzzword: produce large amounts of estrogen
thecoma
benign tumor in ovarian stroma composed of plump spindle cells with lipid droplets
fibroma
buzzword: basal cell nevus syndrome
fibroma
hydrothorax
ascites
meigs syndrome (3)
sertoli-leydig cell tumor
buzzword: reinke crystals
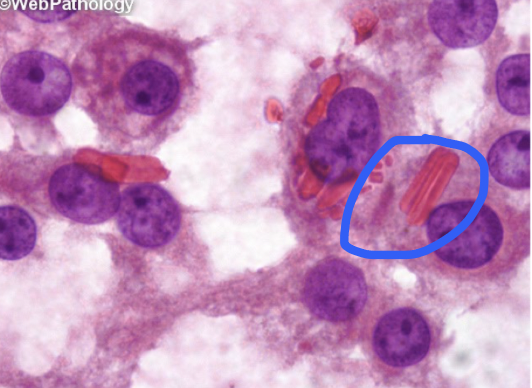
sertoli-leydig cell tumor
sex-cord stromal tumor that commonly produce masculinization (hirsutism and virilization); may have estrogenic effects
fibroma
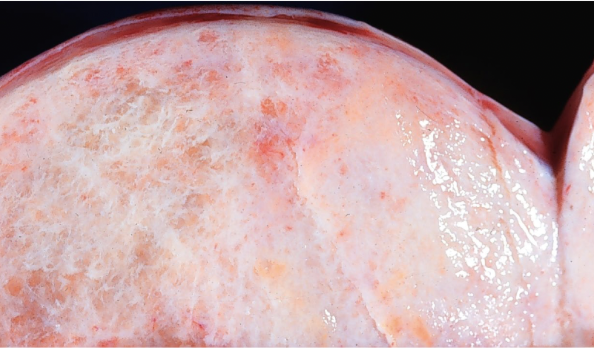
krukenberg tumor
tumors made up of mucin-secreting “signet ring” cells; metastatic to the ovaries, usually from the stomach
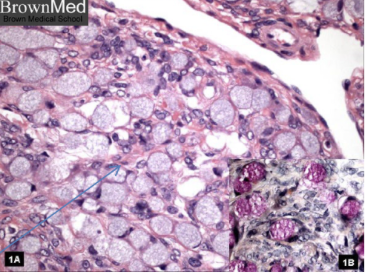
GI, breast, uterus
where do ovarian tumor mets commonly arise from?