Plant Phys exam 3: 6 photosynthesis- C4/CAM
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What did the evolution of two metabolic pathways lead to and what are they called?
limit photorespiration
C4 Pathway (C4 carbon cycle)
CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism)
When does C4 and CAM occur and what is the consequence?
PRIOR to the Calvin Cycle
physiology is different
anatomy is modified
Calvin cycle STILL occurs!
What are the separation types of the C4 and CAM pathway?
C4- spatial separation with the calvin cycle (different system)
CAM- temporal separation with calvin cycle (day= CAM vs night= calvin)
Describe C4 plants
4% of plant species have a C4 metabolic pathway
maize, sugarcane
75% of agriculture’s worst weeds are C4 plants
this pathway recently evolved= ~25 mil years
30 different times
C3 and C4 plants- some do both
C4 anatomy
ring of bundle sheath cells- tightly associated with vascular bundles (phloem & xylem tissues)
bundle sheath cells: thick walled (impermeable to gases), large/abundant chloroplasts, tightly associated with mesophyll cells
unique anatomy
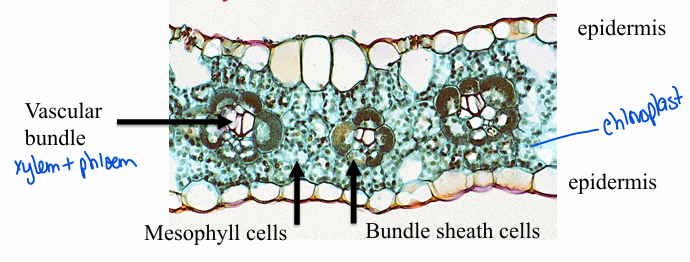
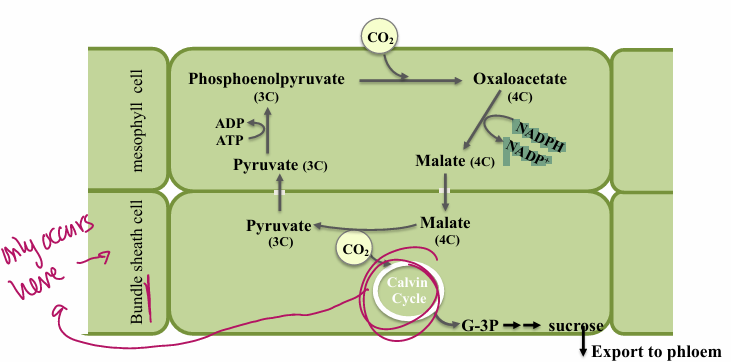
What is unique about the C4 biochemistry in mesophyll cells?
PEP carboxylase (no RuBisCO is present)
Carboxylates 3C PEP & produces 4C acid
Enzyme has no affinity for O2
Very high affinity for CO2
Can bind CO2 at very low conc
4C acid is transported to BSC and is source of CO2 for Calvin cycle
What does PEP stand for?
PEP = phosphoenolpyruvate
How is PEP made?
starch
starch is broken down at night and reformed during the daytime
Describe the Bundle Sheath Cell biochemistry
NADP Malic Enzyme: decarboxylating enzyme
releases CO2 in BSC for Calvin Cycle
CO2 is trapped in cell due to thick cell wall: C4 keeps conc. high
RuBisCO is present in BSC
Pyruvate (3C) is returned to mesophyll cell to reform PEP
requires 2 ATP
Enzyme is pyruvate phosphate dikinase
What is the cost of the C4 pathway?
requires extra energy
All pathways require a minimum of 2 Extra ATP to fix 1 CO2 (overall: 5 ATP/2 NADPH per CO2 fixed)
Some pathways require extra NADPH to fix 1 CO2 (overall: 5 ATP/3 NADPH per CO2 fixed
How do C4 plants do photorespiration?
No/little photorespiration in C4 plants
C3 = photorespiration increases as temps increase
What is the CO2 compensation point in C4 plants?
lower in C4 plants
CO2 compensation point: ambient CO2 concentration when the rate of CO2 uptake for photosynthesis is balanced by rate of respiratory CO2 evoluti
Reason: PEP carboxylase has a much higher binding affinity for CO2
Describe the temperature optima in C4 and C3 plants?
Temperature optima is higher for C4 plants
PEP carboxylase activity is maximal at higher temperatures
At lower temperatures - C3 plants assimilate more CO2 into plant
What is quantum yield?
ratio of light dependent product produced (i.e. sugar or fresh weight) to the # of absorbed photons
C4 = steady as temps increase
C3 = decrease with increasing temps
Why do C3 plants have decrease in quantum yield with increasing temp?
need more O2… photorespiration
Why do C4 plants not change with increasing temperature
water loss- C4 is better at keeping H20
can close guard cells and continue to photorespire
What is the transition ratio in C4 plants?
lower in C4 plants- H20 loss through guard cells
due to PEP Carboxylase; high affinity for CO2 - none for O2
guard cells can change size of stoma, limiting water loss but isn’t affected by changing CO2/O2 ration
transpiration ratio = moles of water lost/ moles of CO2 fixed
C4 = 200-350
C3 = 500-1000
Describe CAM plants
Occurs in at least 23 different families of flowering plants
Most families are not exclusively CAM - exception is the cactus family (Crassulaceae)
can also have species within family that are C3, C4, or CAM
some are facultative: turn CAM on ONLY under stress
example- cacti, pineapple, agave, orchids
** evolved as adaption to hot/dry environments
When do CAM plants photorespire?
later in the afternoon as malate is used up
Grow very, very slowly
But survive in harsh environments where water is limiting (ALOT)

Describe the guard cells in C4 and CAM plants
CAM: Inverted guard cell cycle (open at night-closed during day)
C4 made at night and stored in vacuole (guard cells open)
C4 decarboxylated during day (when guard cells close) to release CO2
Light reactions and Calvin Cycle can occur during day
CAM plants anatomy
thick cuticle (waxy covering on epidermis)
low surface to volume rations
large vacuoles (for storing malate)
stomata with small apertures
tightly packed mesophyll (to help prevent CO2 loss/diffusion during day)
** specialized to limit water loss
Which type of plant has the lowest transpiration ratio?
CAM plants
CAM = 50-100
C4 = 200-350
C3 = 500-1000
** higher ration BUT fixing lower amount of CO2
How does a low transpiration ratio benefit these plants?
Only assimilate about ½ the carbon of C3/C4 plants
Ability to utilize respired CO2 keeps them from losing carbon (they maintain their dry weight)
Energy Requirements/CO2: ≈ 6.5 ATP: 2 NADPH