PHYSMOD_UVR
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
This is shorter than visible light but longer than x-rays; 400-200 nm
UVR
UVR
Freq:
Wavelength:
Freq : 1.65 × 10^15 to 7.5 ×10^14 Hz
Wavelength: shorter than visible light but longer than x-rays
BANDS→ WAVELENGTH→ OTHER NAME → USE
UVA → ________ nm →______ UV → _______
UVB → ________ nm →______ UV →________
UVC → ________ nm → ______ UV →______
UVA → (315) 320-400 nm →Long-wave UV; Near UV → blacklight
UVB → (280) 290-320 nm →Middle-wave UV →skin erythema; sunburn
UVC → (200) < 100-290 nm → Short-wave UV →germicidal; bactericidal
UVR characteristics
Method of transmission: __________
Reflected, refracted, and absorbed
Absorbed within the first ___ mm (0.22 mm) of human skin
___% absorbed in the dermis
_________ property - causes chemical changes or metabolism of superficial skin tissues (closer to visible light = longer wavelengths)
Used for physiologic effects like electron excitation
_________ property - primarily harmful; x-ray; can cause gene mutation, harmful to DNA (closer to x-ray, shorter wavelength)
Radiation (Phototherapy)
1-2mm of human skin
80-90% absorbed in dermis
Non-ionizing; Ionizing 💢
Phototherapy
Excessive natural UVR exposure → DNA damage
Cutaneous _____ melanoma
_____-cell carcinoma
______-cell carcinoma
Excessive natural UVR exposure → DNA damage
Cutaneous malignant melanoma
Vasal-cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinoma
Factors Affecting UV Penetration (read)
Intensity of radiation
Wavelength of radiation
Power of radiation source
Exposure duration
Distance of radiation source
Frequency
Size of area
Thickness of skin
Pigmentation of skin
Pigmentation
Presence of melanin affects penetration
INC/DEC? melanin on skin = ↑ barrier to penetration = ↑ protection
INC ( darker the better)
UVR Equipments
_______________
Small
Emit radiation at constant intensity
Used for smaller areas
Hot Quartz or Cold Quartz
For localized application
Mercury Arc Lamps
Mercury Arc Lamps
______________
Burner (argon gas and mercury)
↑ pressure and temperature
(+) erythema and pigmentation
Applied ____ from the area
Needs warm up ?
Hot Quartz
≥15” from area
NO warm up
Mercury Arc Lamps
_________
Quartz tube with mercury (ionized vapor)
↓ pressure and temperature
Minimal erythema and (-) pigmentation
Application at close proximity (____ inches)
Needs 5 _____ warm-up
Cold Quartz
1-2 inches
needs 5 min warm up
UVR Equipments
Fluorescent Lamps
Long
Emit ____-intensity radiation
Used for ____ areas
Low pressure mercury discharge tubes with phosphor coating inside (_______)
Higher intensity radiation
larger areas
Theraktin
Physiologic Effects of UVR
Erythema Production
Dilation of blood vessels due to ______ release
Exposure to ____ or _____ after drug sensitization
Skin Redness - _________ release
Dilation of blood vessels due to histamine release
Exposure to UVB or UVA after drug sensitization
Skin Redness - prostaglandin release
Physiologic Effects of UVR
Tanning
Delayed _____ of the skin
Due to exposure
Increased production and upward migration of _____ granules and oxidation of _______
Skin color affects penetration of UV (Tanning = ↓ penetration)
↑ tan = ↑ protection
Fluorescent and hot quartz can both cause tanning or pigmentation
Delayed pigmentation of the skin
Due to exposure
Increased production and upward migration of melanin granules
and oxidation of premelanin
Skin color affects penetration of UV (Tanning = ↓ penetration)
↑ tan = ↑ protection
Fluorescent and hot quartz can both cause tanning or pigmentation
Physiologic Effects of UVR
Epidermal Hyperplasia
Thickening of ______ layer of skin
Thickening of _______ (stratum corneum) due to cell proliferation
Occurs usually after _____ hours after exposure to UVR
Thickening of superficial layer of skin
Thickening of eipdermis (stratum corneum) due to cell proliferation
Occurs usually after 72 hours after exposure to UVR
Physiologic Effects of UVR
Vitamin D Synthesis
Coverts ingested provitamin D to _________
Found to be an effective treatment for ______
Coverts ingested provitamin D to active Vitamin D
Found to be an effective treatment for psoriasis
Physiologic Effects of UVR
Bacterial Effect
____ = bactericidal
Also promotes _____ healing
_______ = slough off (shed off) dead skin cells
UVA & UVB =_______/______
UVC = bectericidal
Also promotes wound healing
Desquamation = slough off (shed off) dead skin cells
UVA & UVB = redness or sunburn
UVR VS IRR
UVR
_______ effect
No _____
Absorbed at _____ mm
_____ source
Delayed ______ (dark)
Lasts for ______ days
Has _____ wavelength (more superficial)
Photochemical effect
No heat
Absorbed at 1-2 mm
Luminous source
Delayed erythema (dark)
Lasts for several days
Has shorter wavelength (more suiperficial)
UVR VS IRR
Infrared
______ Effect
Absorbed as _____
Absorbed at ___ mm
______ and _______
Immediate _____ (light)
Lasts for ___- ____ mins
Has _____ wavelength (deeper penetration)
Infrared
Physical Effect
Absorbed as heat
Absorbed at 3 mm
Luminous and non-luminous
Immediate erythema (light)
Lasts for 20-30 mins
Has longer wavelength (deeper penetration)
Dosimetry
Parameter → Synonym → Formula → Unit
Irradiance (I) → Intensity /Power → ________ → _______
Exposure Duration T → Treatment time → NA → ______
Dose per Treatment(D1) → Amount of energy delivered to skin for a single treatment →_______ → ______
Cumulative Dose (Dc) → Summation of all doses →______ → ______
Irradiance (I) → Intensity or power → Measured by UV sensor on device → mw/cm2
Exposure Duration T → Treatment Time → NA → sec
Dose per Treatment(D1) → Amount of energy delivered to skin for a single treatment → Dt = I x T → mJ/cm2
Cumulative Dose (Dc) → Summation of all doses → Dc=EDt → J/cm2
_______ Law
Inverse relationship of irradiance and exposure time
Bunsen-Roscoe Law / Reciprocity Law
Fitzpatrick Skin Phototype Method
____________ Method
More convenient to use; based on skin color and reaction to sun exposure
Fitzpatrick Skin Phototype Method
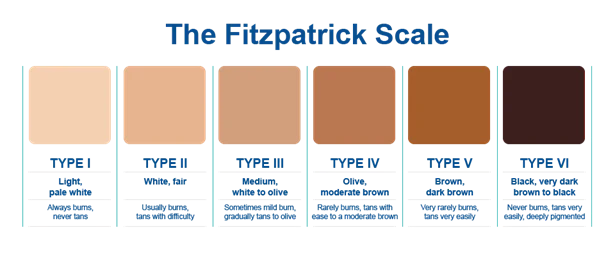
Fitzpatrick Scale
1 → _____ white → ____ easily; never ___
2 → ____ white → burns ____; tans _____
3 → ____ brown → burns ____ ; tans _____
4 → ____ brown → burns ____ ; tans ____
5 → ____ brown → burns ____ ; tans _____
6 → _____ → burns ____ ;intense _____
1 → Lighter white → burns easily; never tans
2 → Darker white → burns easily ;tans minimally
3 → Light brown → burns mod; tans gradually
4 → Moderate brown → burns min; tans well
5 → Dark brown → burns rarely; tans profusely
6 → Black →never burns; intense tanning
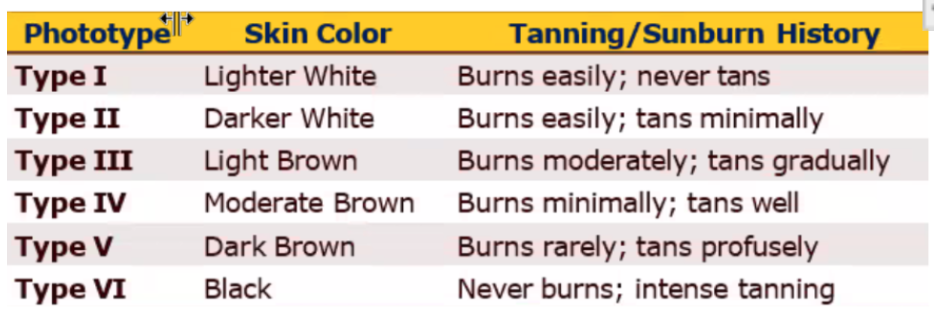
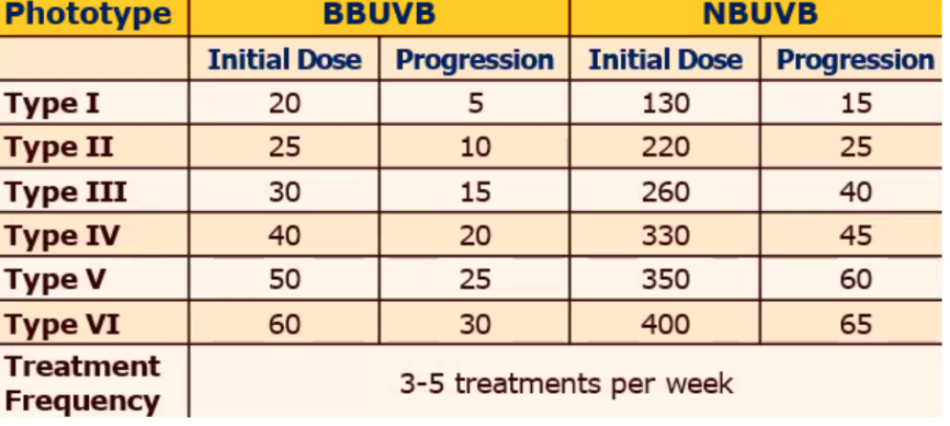
Recommended UV Dosing based on Skin Phototype
Treatment Freq → _____ per week
3-5 treatments per week
______________
UV-induced Erythema - varies on each individual
Dose of UV radiation that will produce a barely detectable erythema about 8-24 hours after exposure
Minimal Erythemal Dose Method
Minimal Erythemal Dose Method : Dose-Response Assessment
Suberythemal Dose (SED)
__________ (MED)
First Degree Erythema (E1)
Second Degree Erythema (E2)
Third Degree Erythema (E3)
______ is the target effect
REMEMBER: to instruct the patient to observe which shape appears last but disappears first (Erythrometer, 15s increments)
Minimal Erythemal Dose
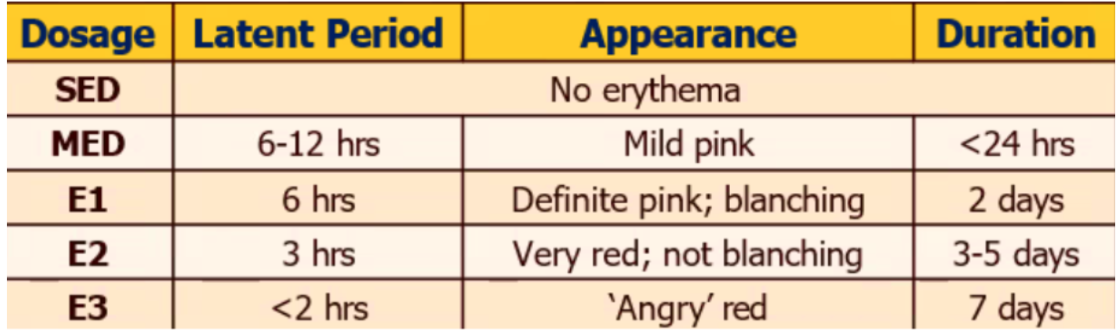
Minimal Erythemal Dose Method
Minimal Erythemal Dose Method
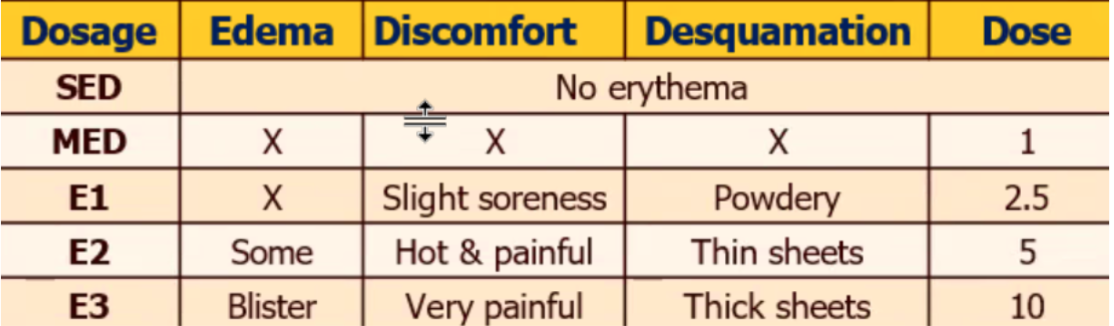
Minimal Erythemal Dose Method
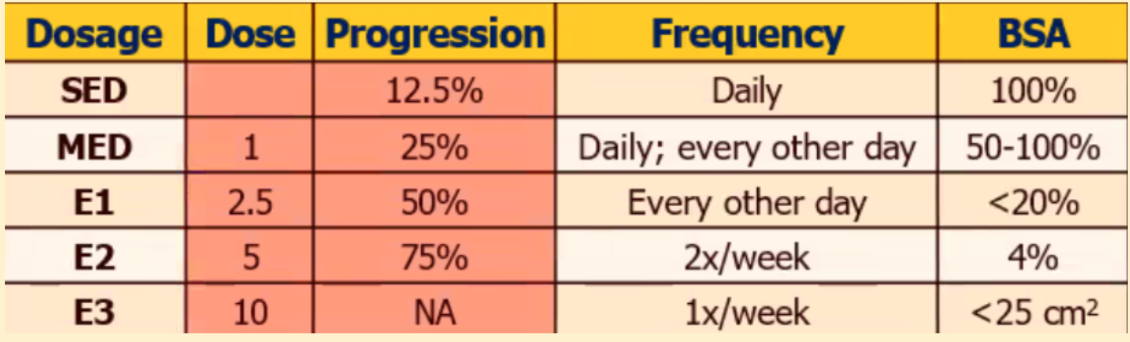
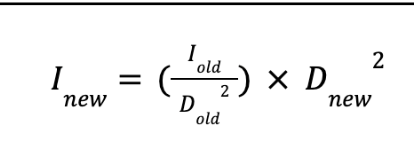
Guidelines in Altering Intensity
For Cold Quartz (Kromayer Lamp), the lamp is applied at least ____ inch away from the wound
For Hot Quartz lamp, the lamp is is initially applied ___-___ cm distance
Distance is altered when duration has reached the maximum ___ minutes
at least 1 inch away
60-80cm distance
5 minutes
Contraindications
|
Precautions
Photosensitivity or Photoallergy
Photosensitizing Medications
Recent x-ray therapy
No dose of UV should be done until the effects of the previous treatmernt have disappeared
Indications
Subacute and Chronic Psoriasis
Narrow-Band UVB (NBUVB)
___ or E__
Also for _____
PUVA (Psoralen + UVA)
Usually, E__ is used
E2 for ____ and ____
Also used for:
Eczema
Urticaria
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Some photosensitive disorders
Narrow-Band UVB (NBUVB)
MED or E1
Also for vitiligo
PUVA (Psoralen + UVA)
Usually, E1 is used
E2 for heels and elbows
Also used for:
Eczema
Urticaria
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Some photosensitive disorders
Indications
Cystic Acne/Acne Vulgaris
E1 for ___, ____ and ____
E2 for ____ and ____
Cystic Acne/Acne Vulgaris
E1 for face, neck and chest
E2 for back and shoulders
Indications
Non-Infected Open Wounds
Such as surgical incisions, pressure/ venous/ arterial ulcers
Use UV___
Granulation Tissue = no treatment or suberythemal dose to ____ only, no progression
Decubitus Ulcers = affecting the epidermis/dermis: __/_
Surrounding skin = _____, daily
Non-Infected Open Wounds
Such as surgical incisions, pressure/ venous/ arterial ulcers
Use UVC
Granulation Tissue = no treatment or suberythemal dose to MED only, no progression
Decubitus Ulcers = affecting the epidermis/dermis: E1/E2
Surrounding skin = MED, daily
Infected Open Wounds
Thin yellowing slough = ____ daily and unprogressed
Definite green or yellow slough = ___ daily and unprogressed
Black Slough = __ daily
Surrounding skin = ____ daily
Thin yellowing slough = E2 daily and unprogressed
Definite green or yellow slough = E3 daily and unprogressed
Black Slough = E3 daily
Surrounding skin = MED daily
Other Indications
Counter-irritation for pain relief (____ applied that the discomfort masks the pain)
Alopecia - UV__ at __ or _
Vitamin D deficiency
Uremic pruritus - ___ UV__
Counter-irritation for pain relief (E3 applied that the discomfort masks the pain)
Alopecia - UVB at E1 or E2
Vitamin D deficiency
Uremic pruritus - SED UVB
PRECAUTIONS
Photosensitizing Medications
_________ = sensitizing agent
Sulphonamides & Tetracyclines = ___
Griseofulvin = ________
Phenothiazine = _______
________ = diuretic
Psoralen = must stay away from the sun because it can cause hyperpigmentation (increases light penetration)
Psoralen = sensitizing agent
Sulphonamides & Tetracyclines = antibiotics
Griseofulvin = antifungal
Phenothiazine = tranquilizer
Chlorothiazide = diuretic
Adverse Effects
Burning
Premature aging of skin (actinic damage)
Carcinogenesis
Eye damage (photokeratitis, conjunctivitis, cataracts)
Documentation
TBD
UV Overdose
IRR for 20 mins every hour for 6-8 hrs
Documentation for Overdose
Date
Lamp used
Distance
Exact area treated (specify pt position)
Time
Reaction obtained
Treatment Considerations
Phototesting for the determination of MED
Time of appearance (last to appear)
Time of disappearance (first to disappear)
Characteristics/description
Calculation of dosage
Area of application
Progression
Steps in Determining Dosage

Trivia:
Define the word “racist”
U