Brain Model FlashCards
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
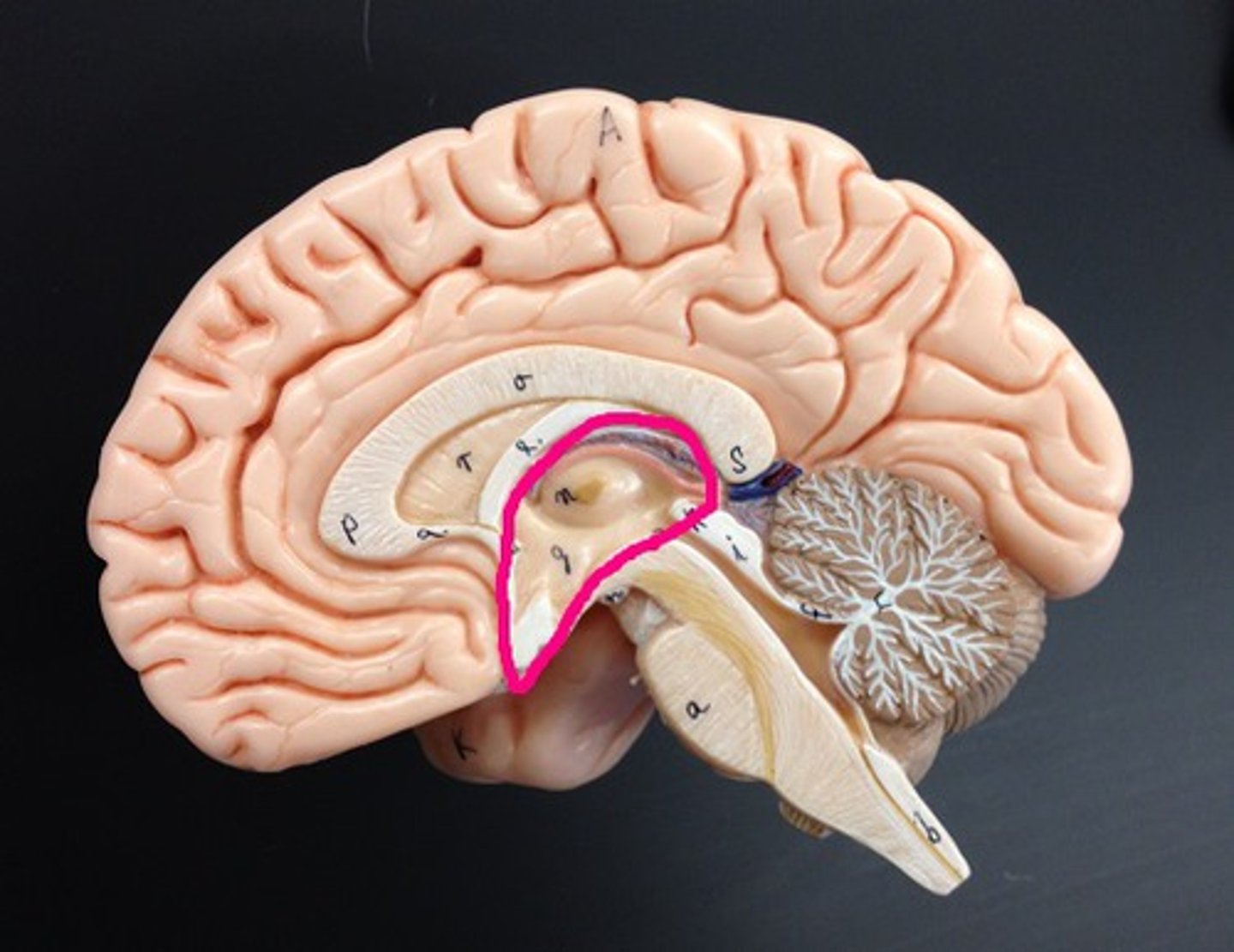
Diencephalon
Contains the thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus (pineal gland/body).
Acts as a primary relay and processing center for sensory information and autonomic control via hormone regulation.
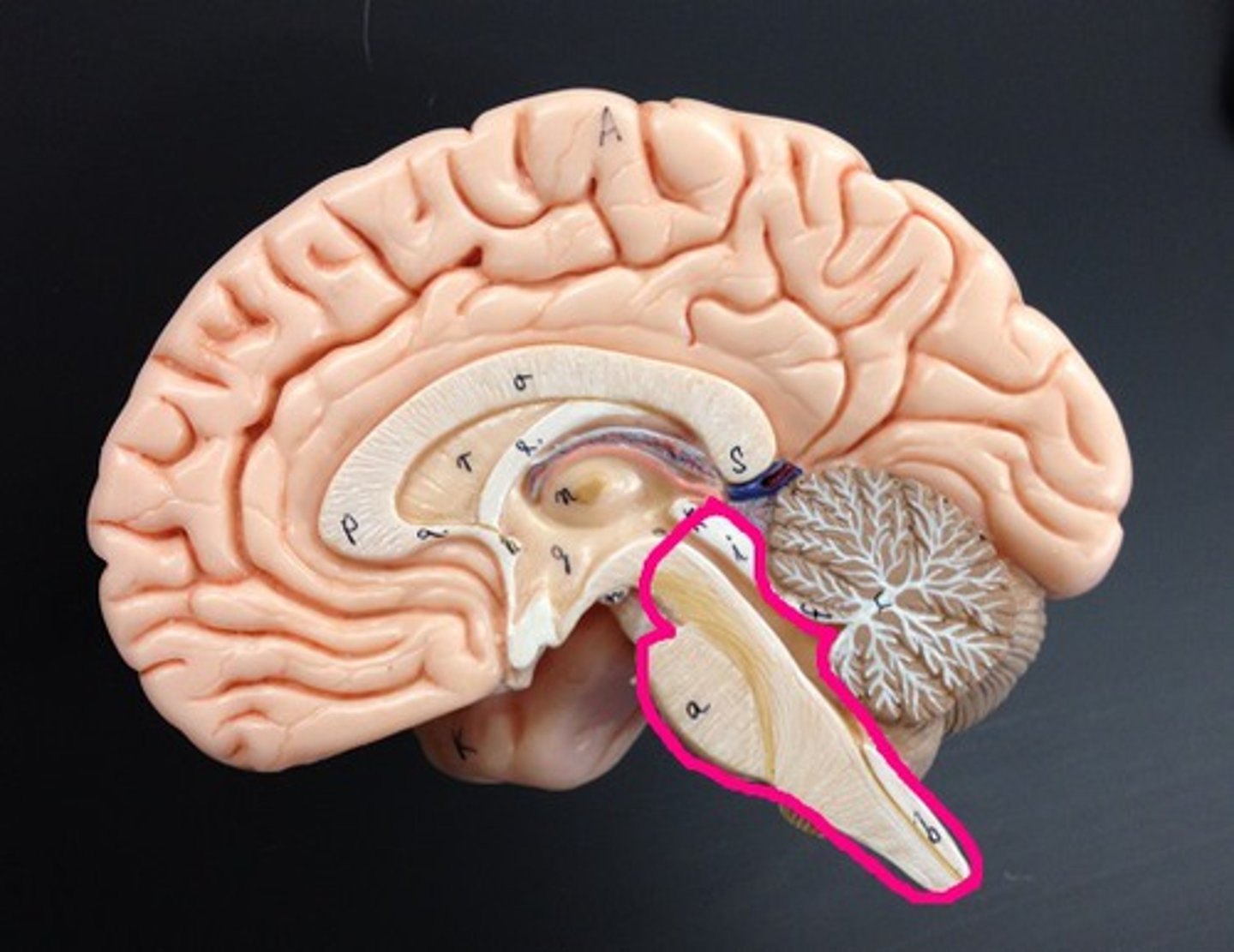
Brainstem
Contains the midbrain, pons and medulla oblongata.
Responsible for many vital functions including arousal, consciousness, sleep-wake cycles, coordination of certain movements, and cardiovascular control.
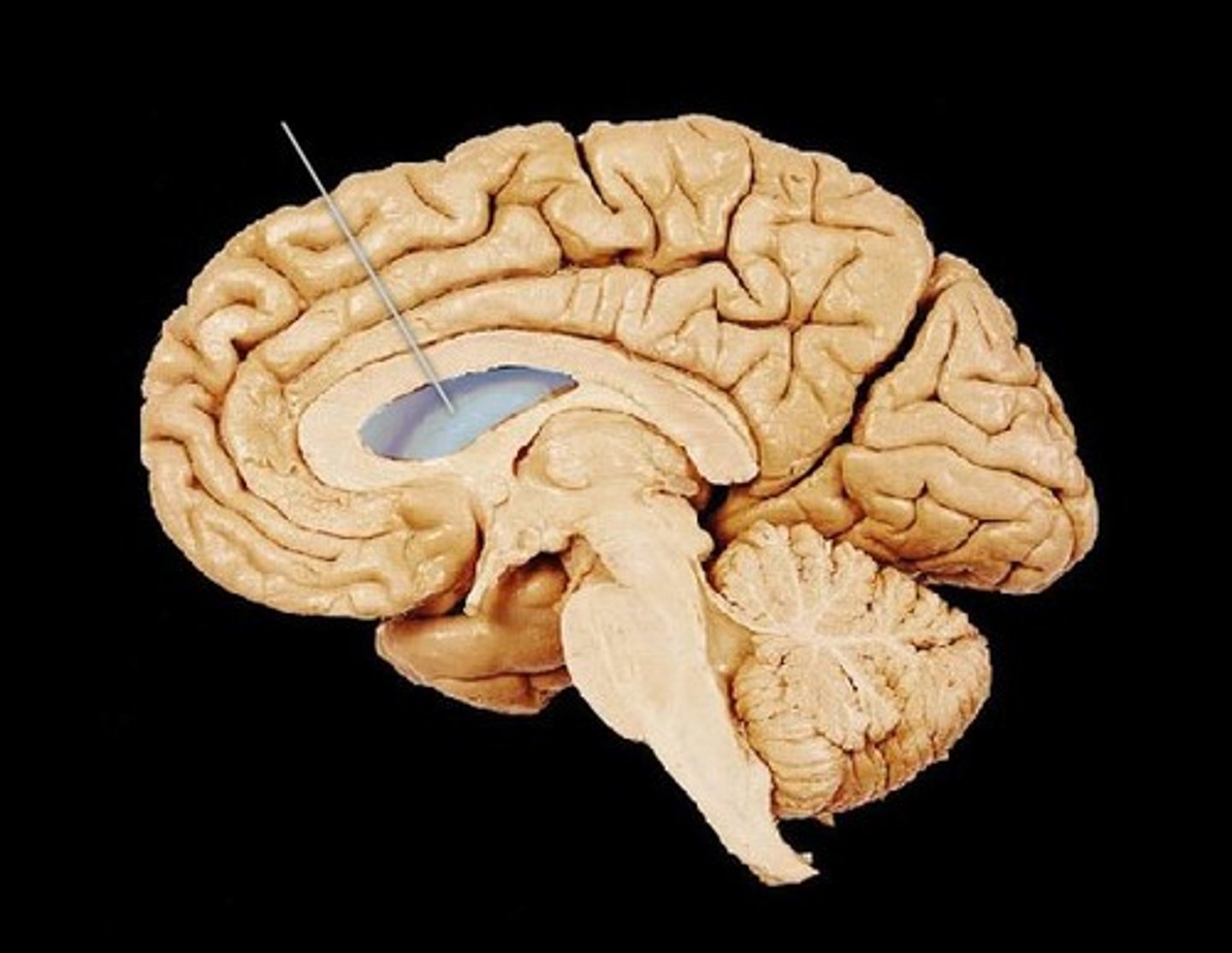
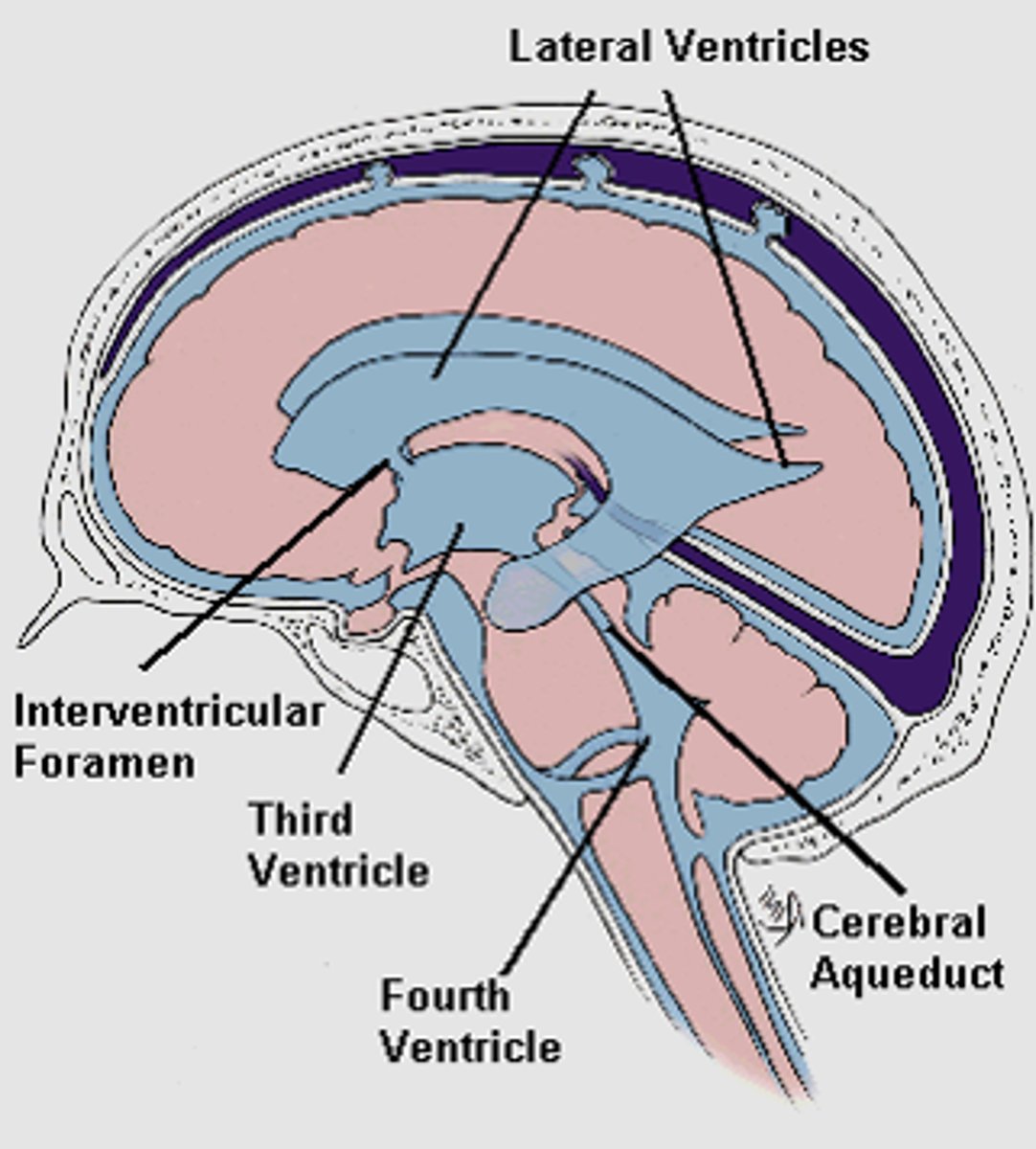
Ventricle
Consist of the lateral (1 and2), third and fourth.
Responsible for protecting the brain through cushioning, producing and circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to nourish the brain and remove waste, and maintaining brain homeostasis
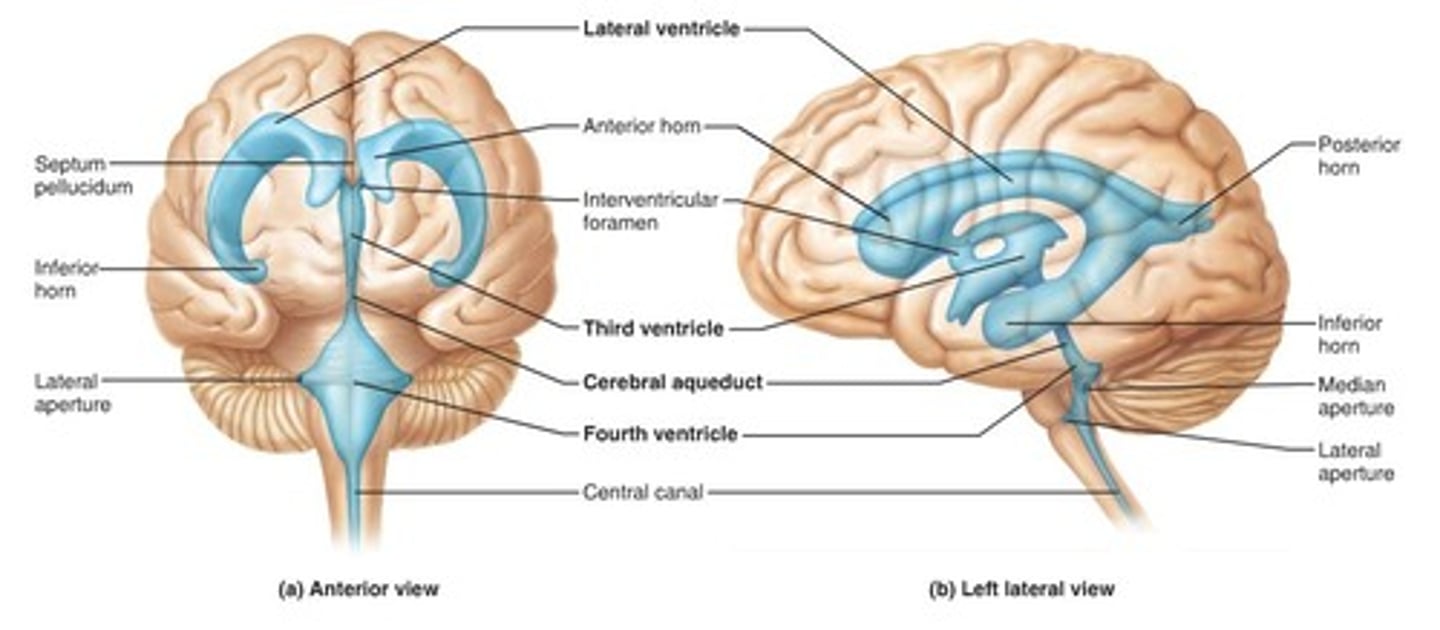
Lateral Ventricles
Producing and circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) via the choroid plexus.
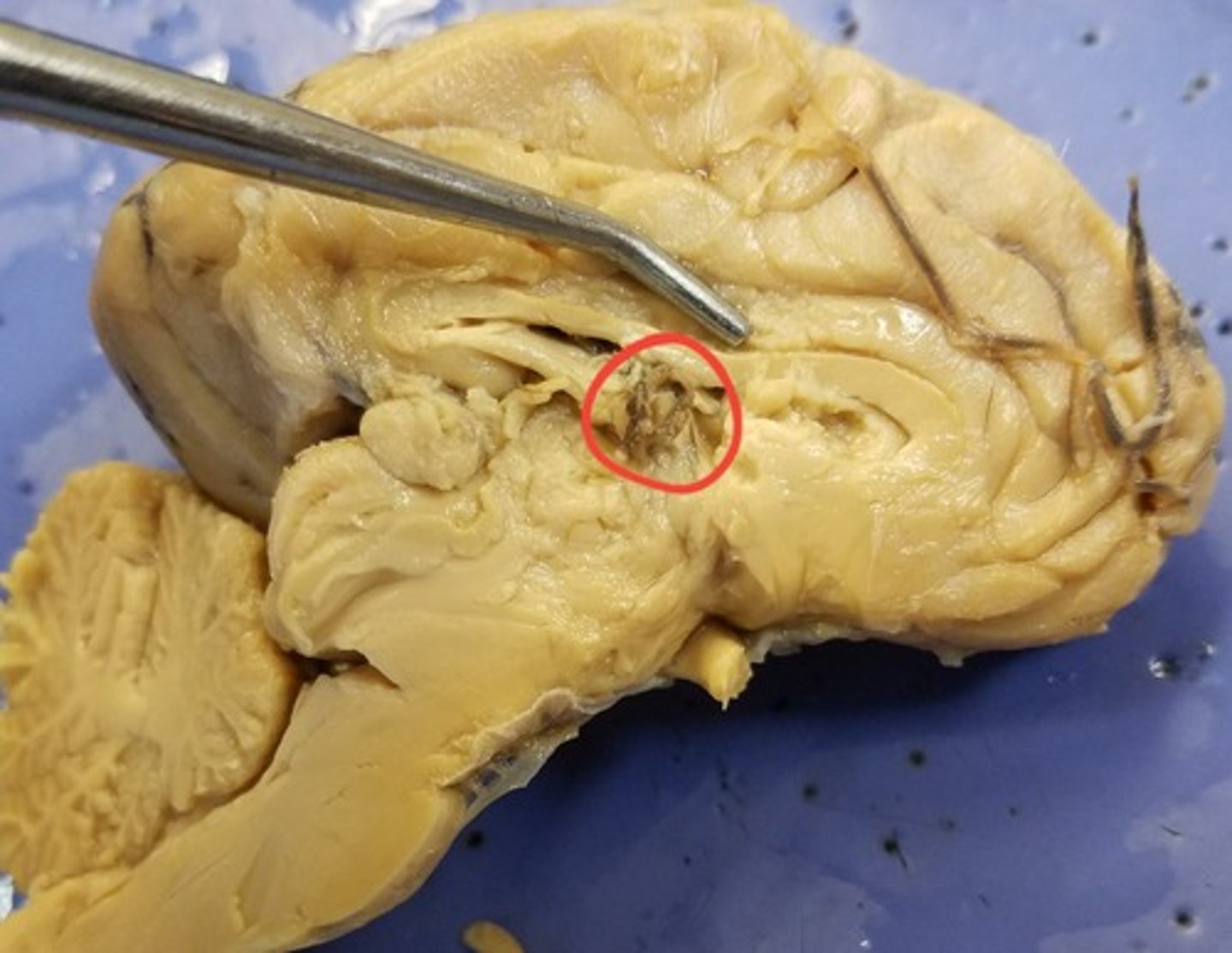
Choroid plexus
Produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) via the ependymal cells that line the ventricles of the brain
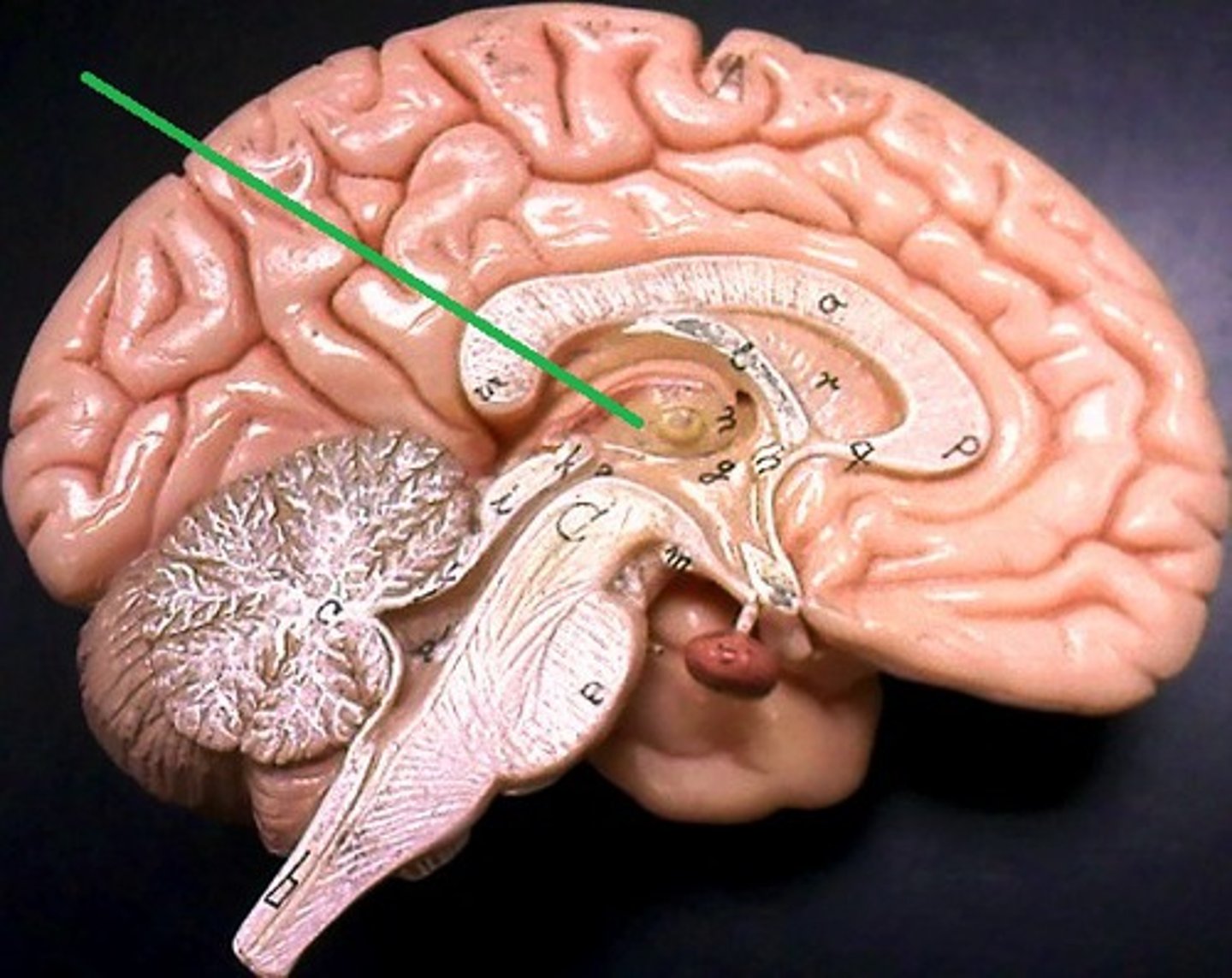
Thalamus
Acts as a central relay station for sensory and motor signals, transmitting them to the cerebral cortex. It is also crucial for regulating consciousness, sleep, emotions, alertness, and wakefulness.
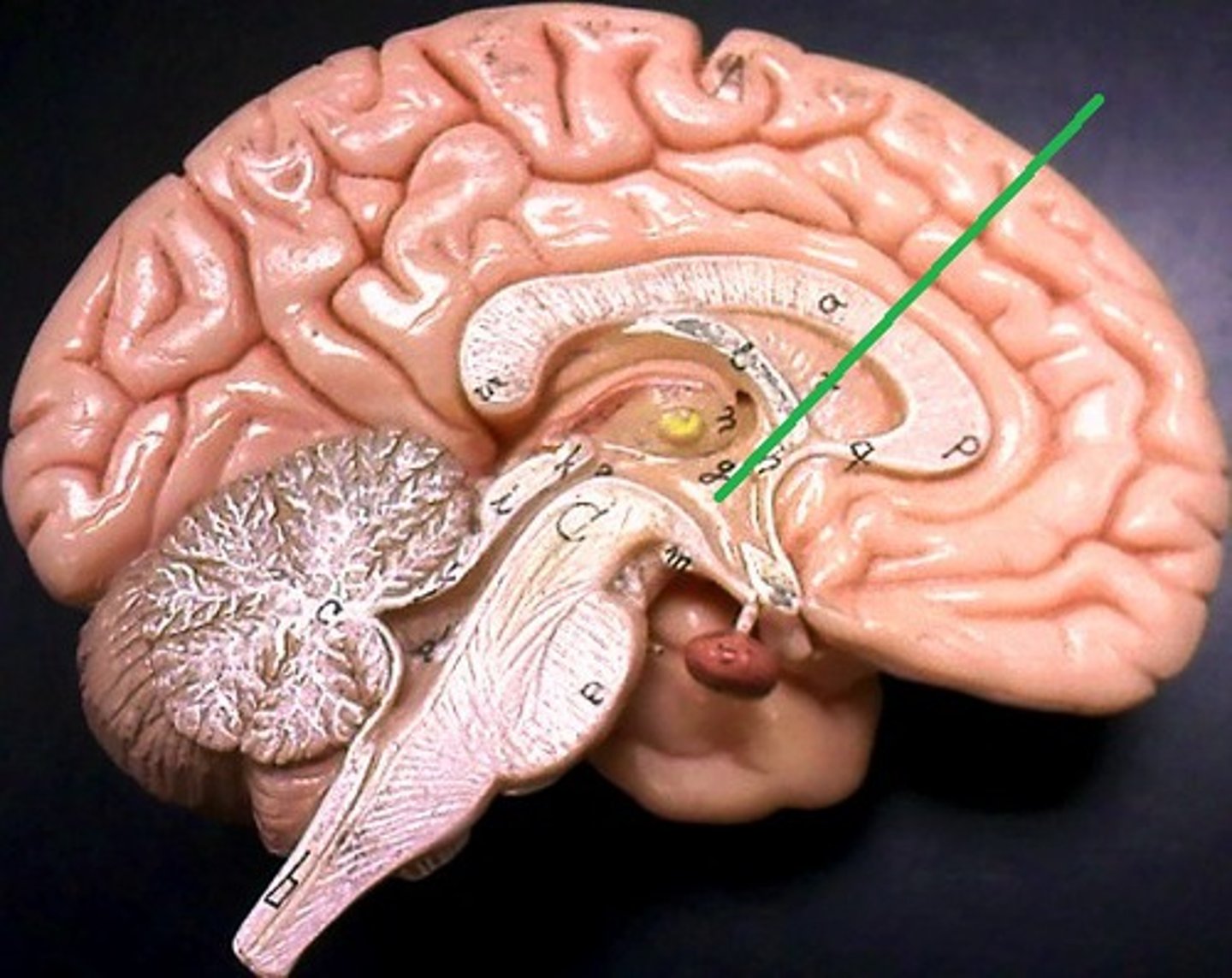
Hypothalamus
Maintain the body's internal balance (homeostasis) by regulating essential functions like body temperature, hunger, thirst, and sleep
Epithalamus (pineal body/gland)
Acts as a connection between the limbic system and other parts of the brain
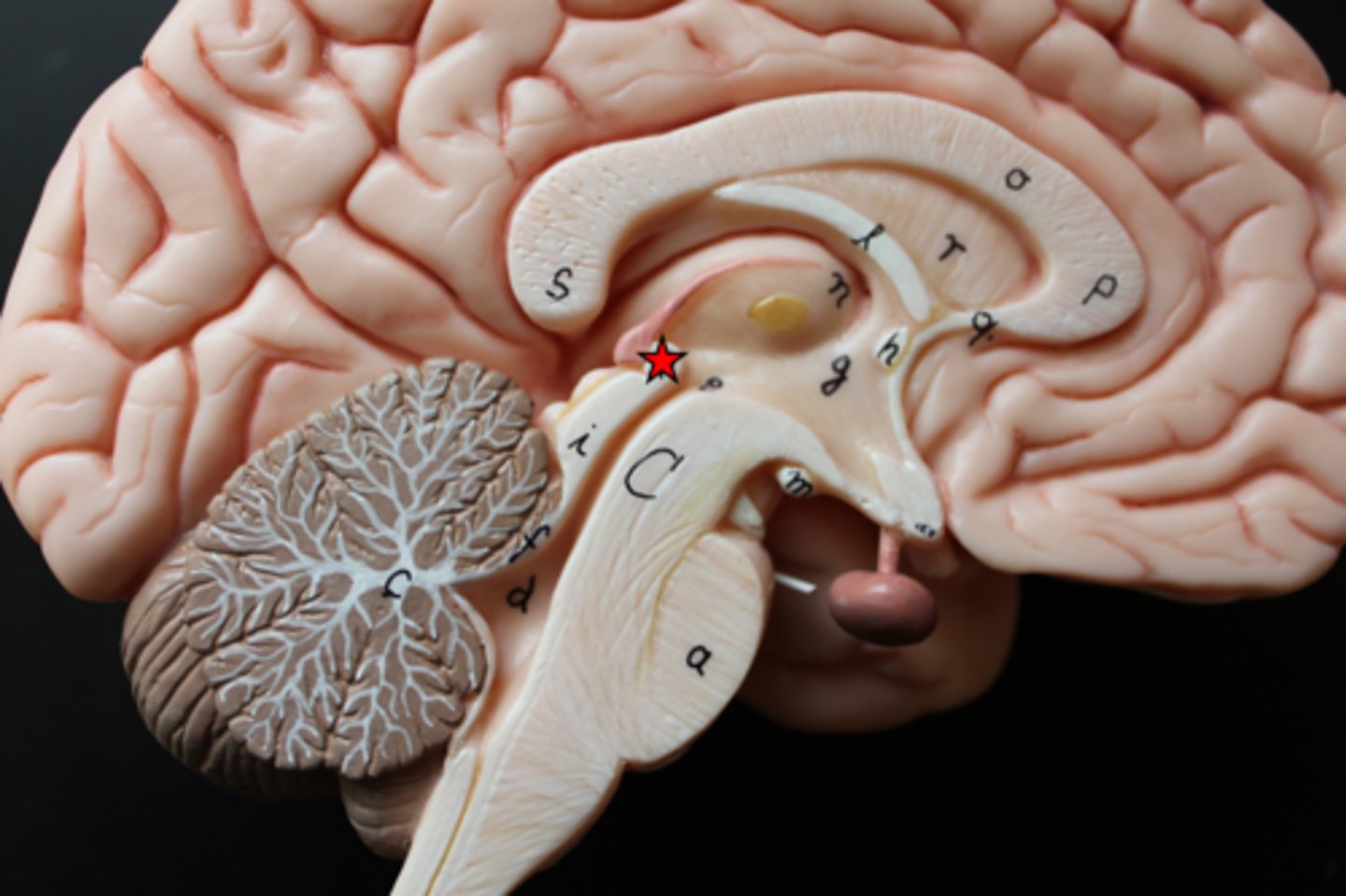
Corpus callosum
Connects the two hemispheres of the brain
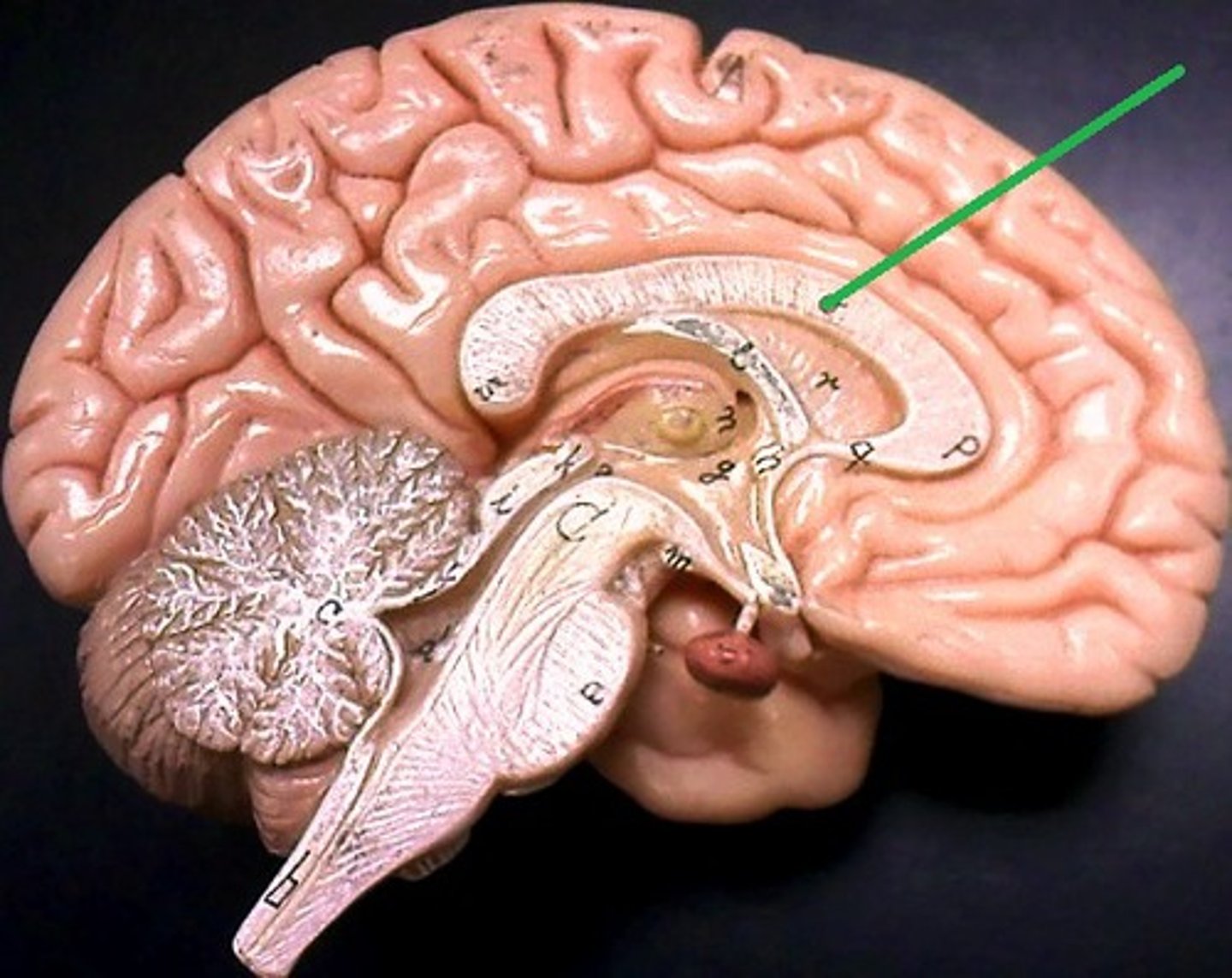
Fornix
A white matter tract in the brain that plays a crucial role in memory and cognitive function.
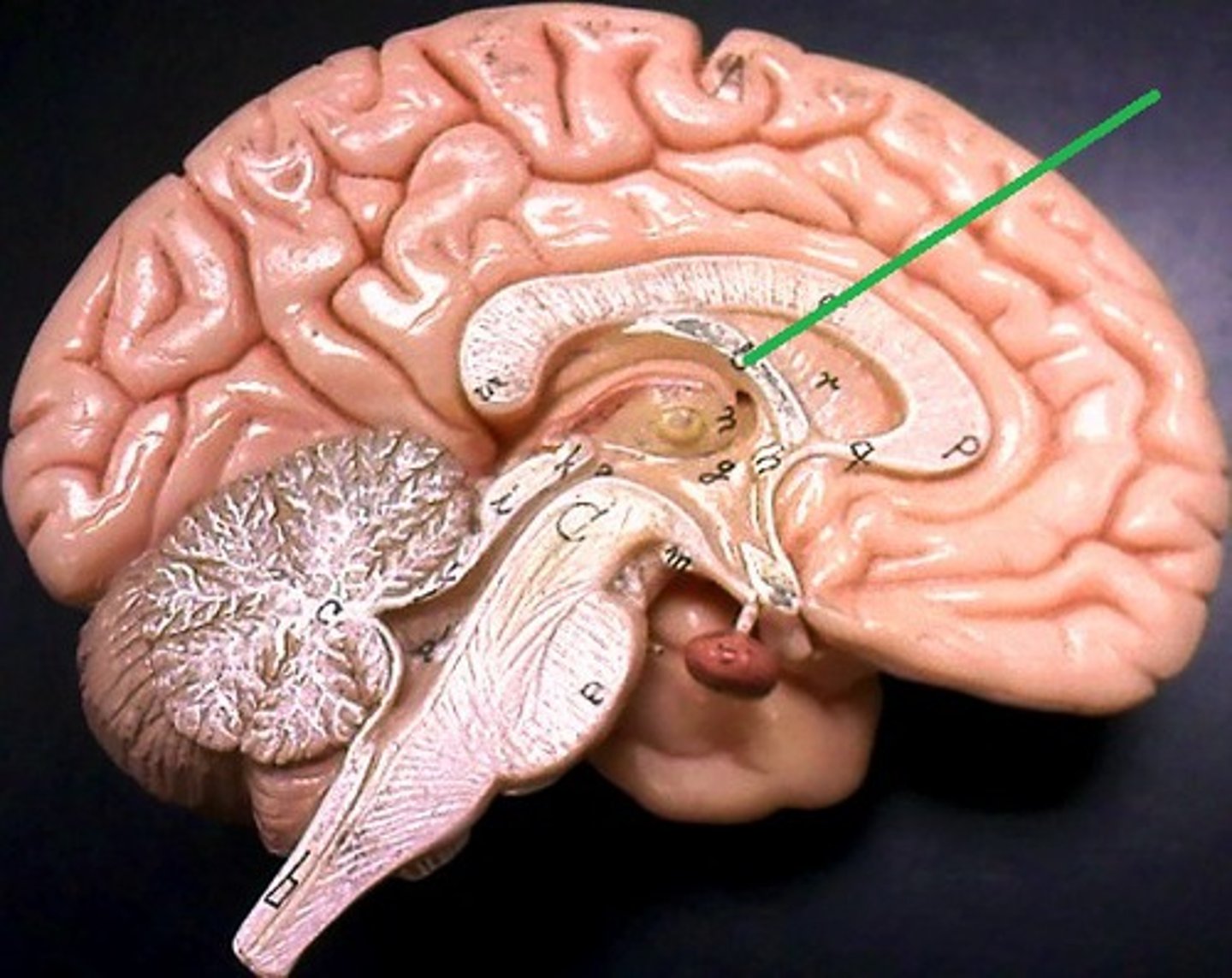
Corpora Quadrigemina
Plays a crucial roles in visual and auditory processing, as well as reflex movements.
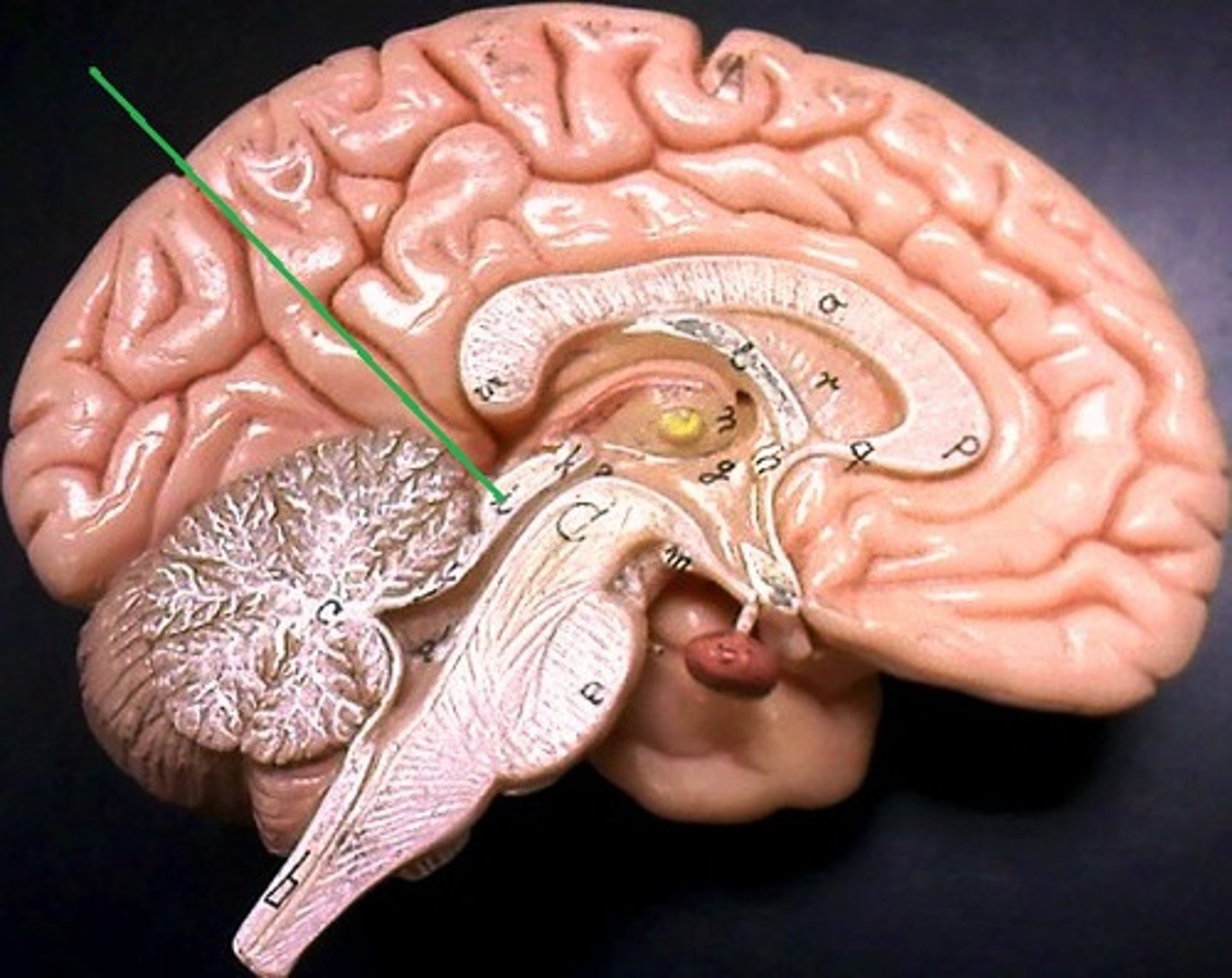
Midbrain
Part of the brainstem serves important functions in motor movement, particularly movements of the eye, and in auditory and visual processing
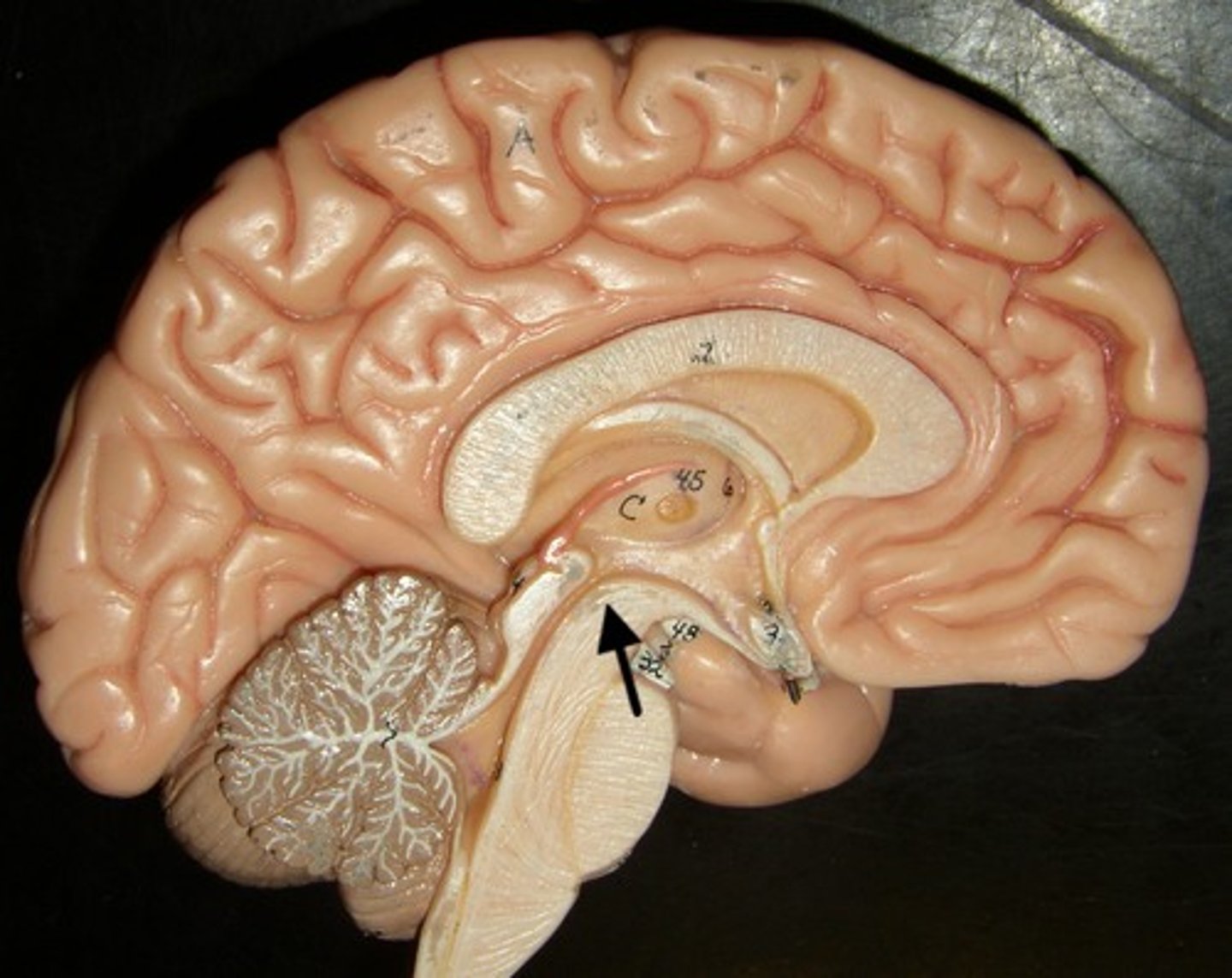
Pons
Part of your midbrain helps with coordination of movement.
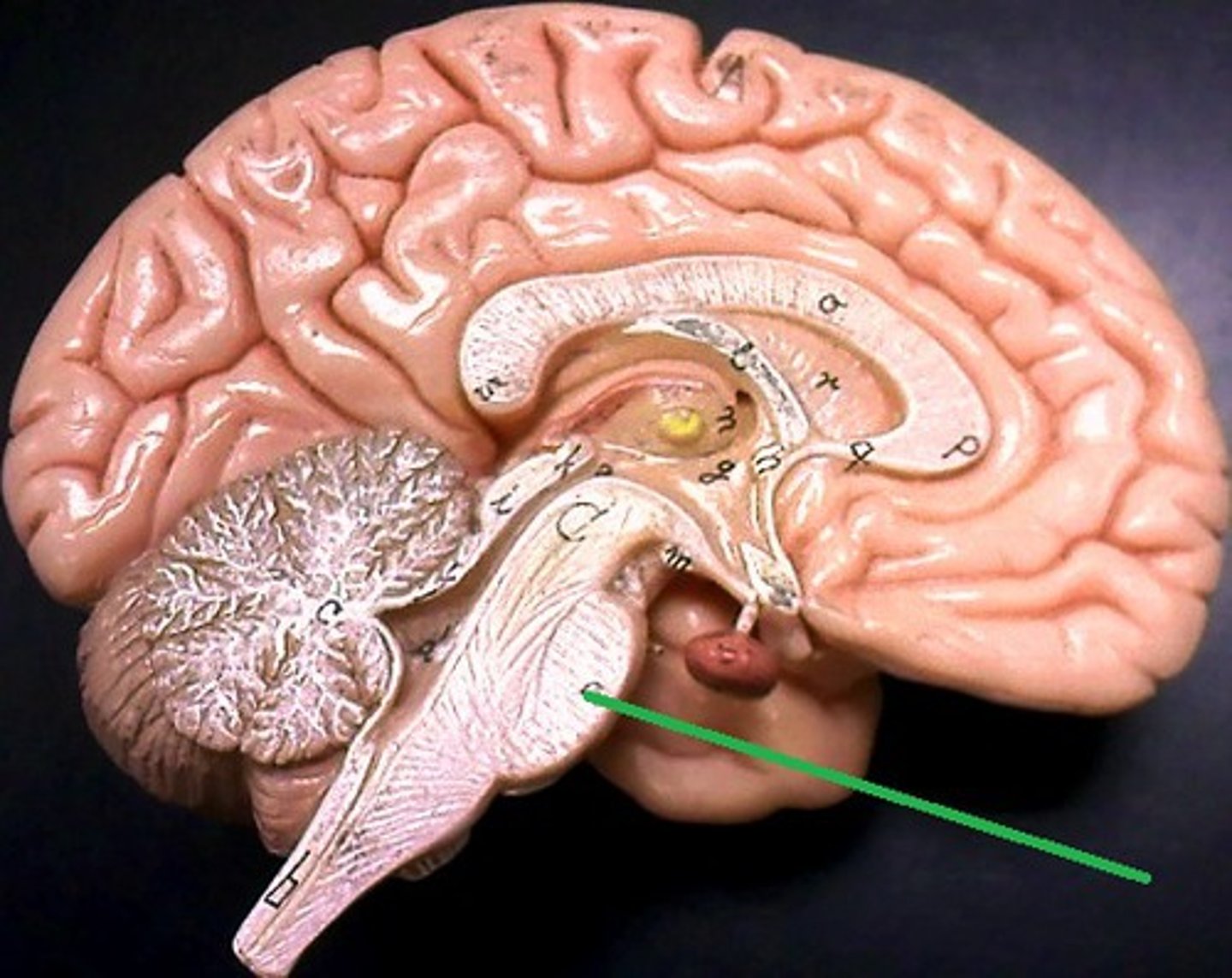
Medulla oblongata
Part of the midbrain plays a key role in controlling involuntary functions, including breathing, digestion, and heart rate.
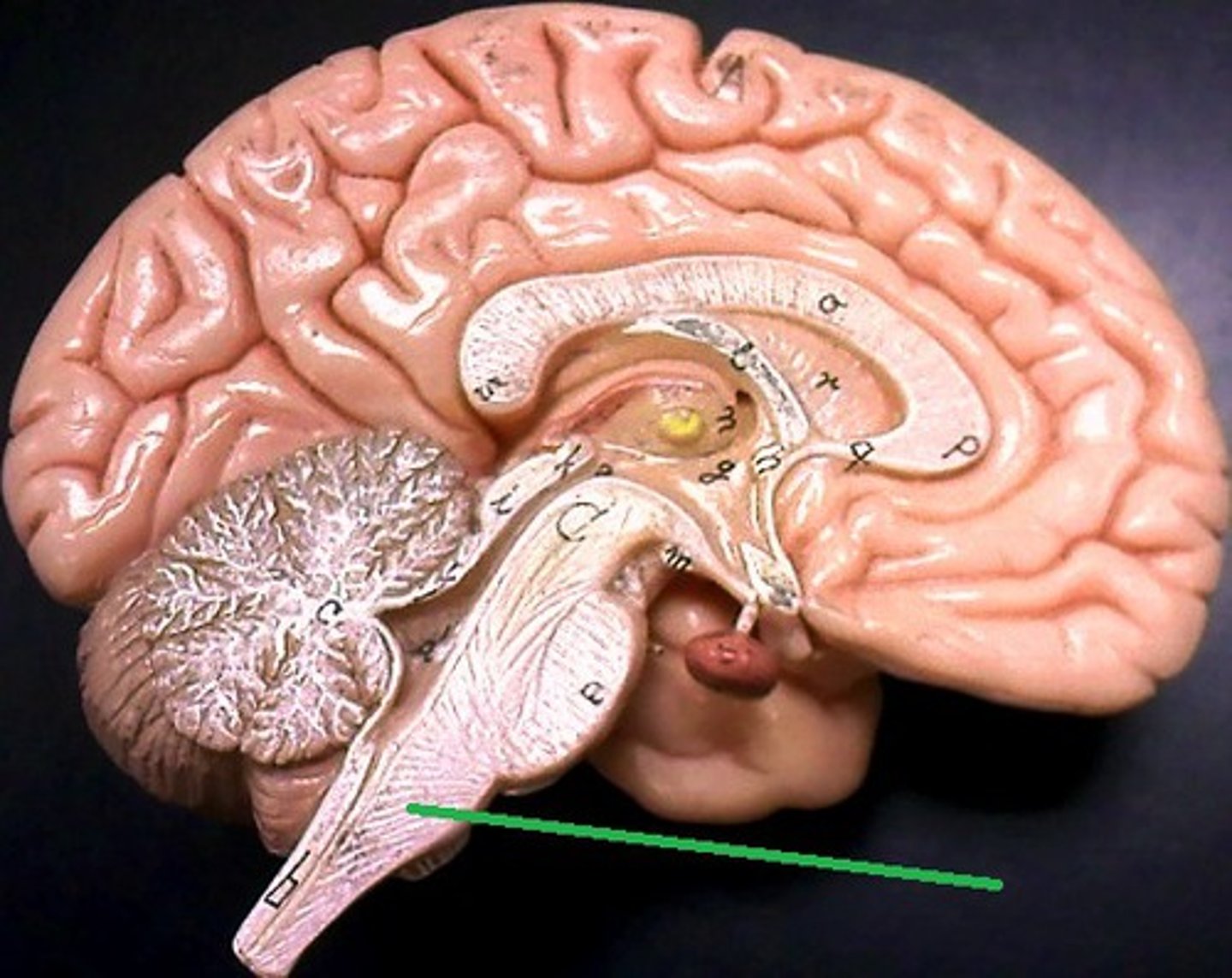
Mammillary body
Located within the hypothalamus, they play a crucial role in memory consolidation and retrieval
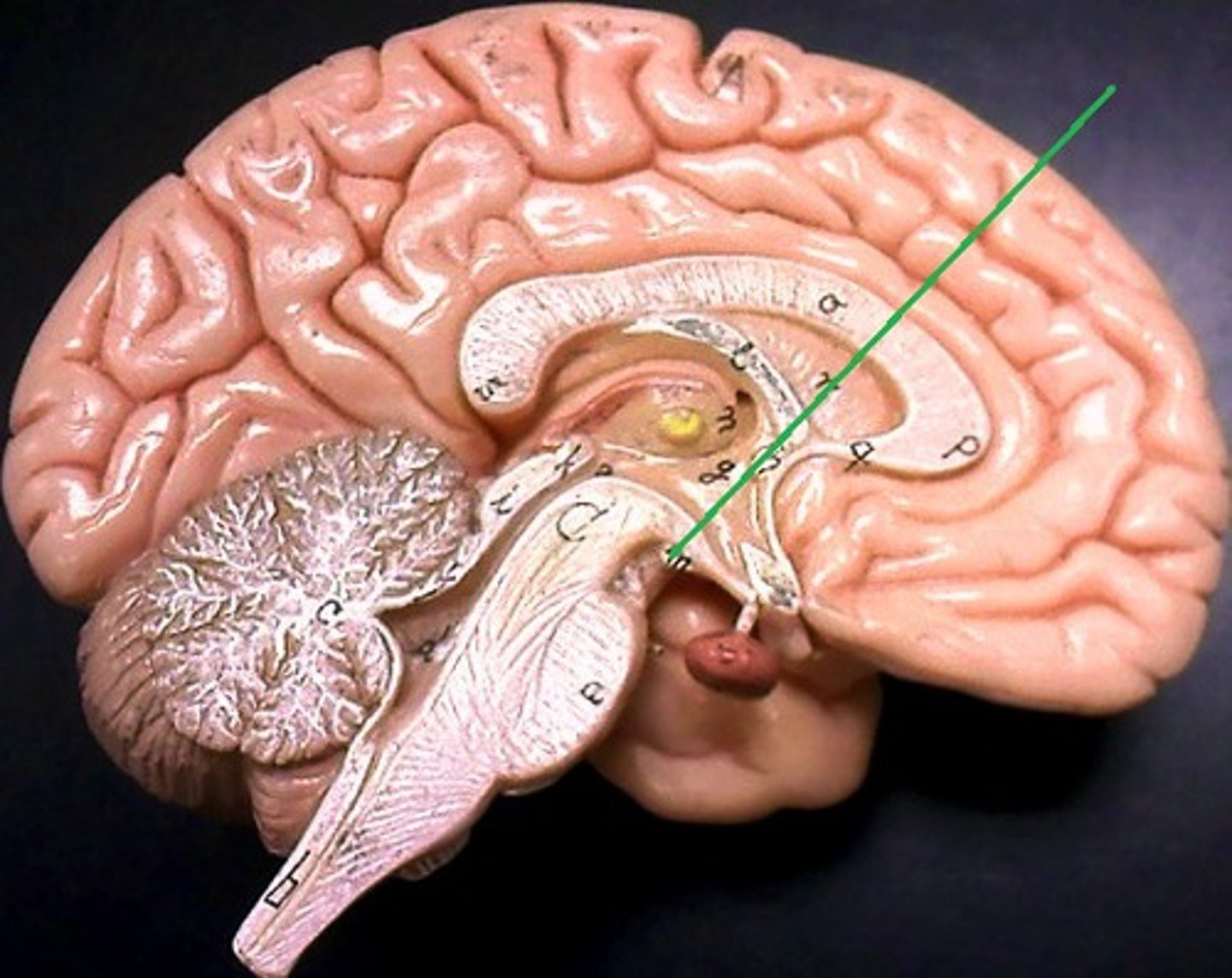
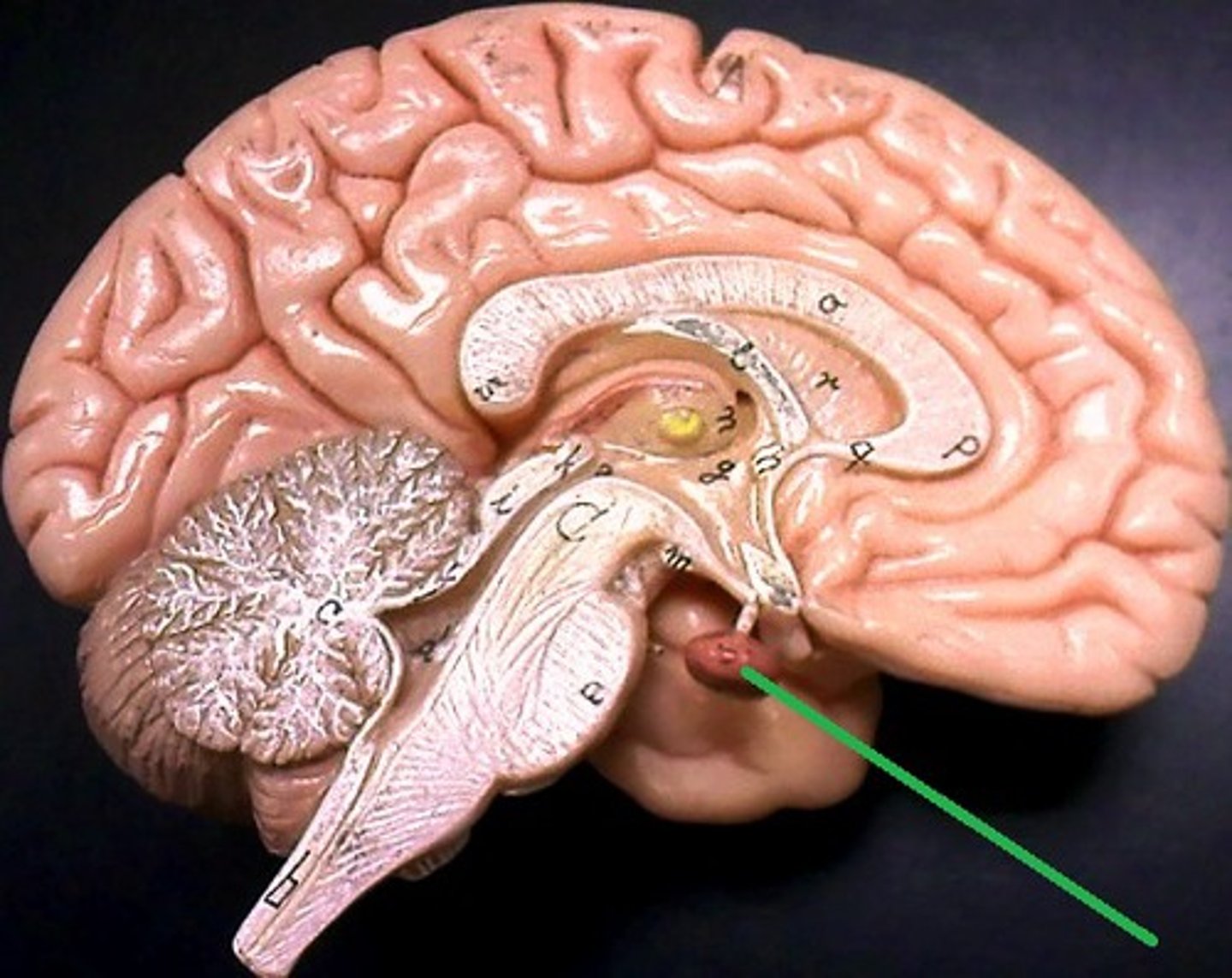
Pituitary gland
Plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions by producing and releasing hormones
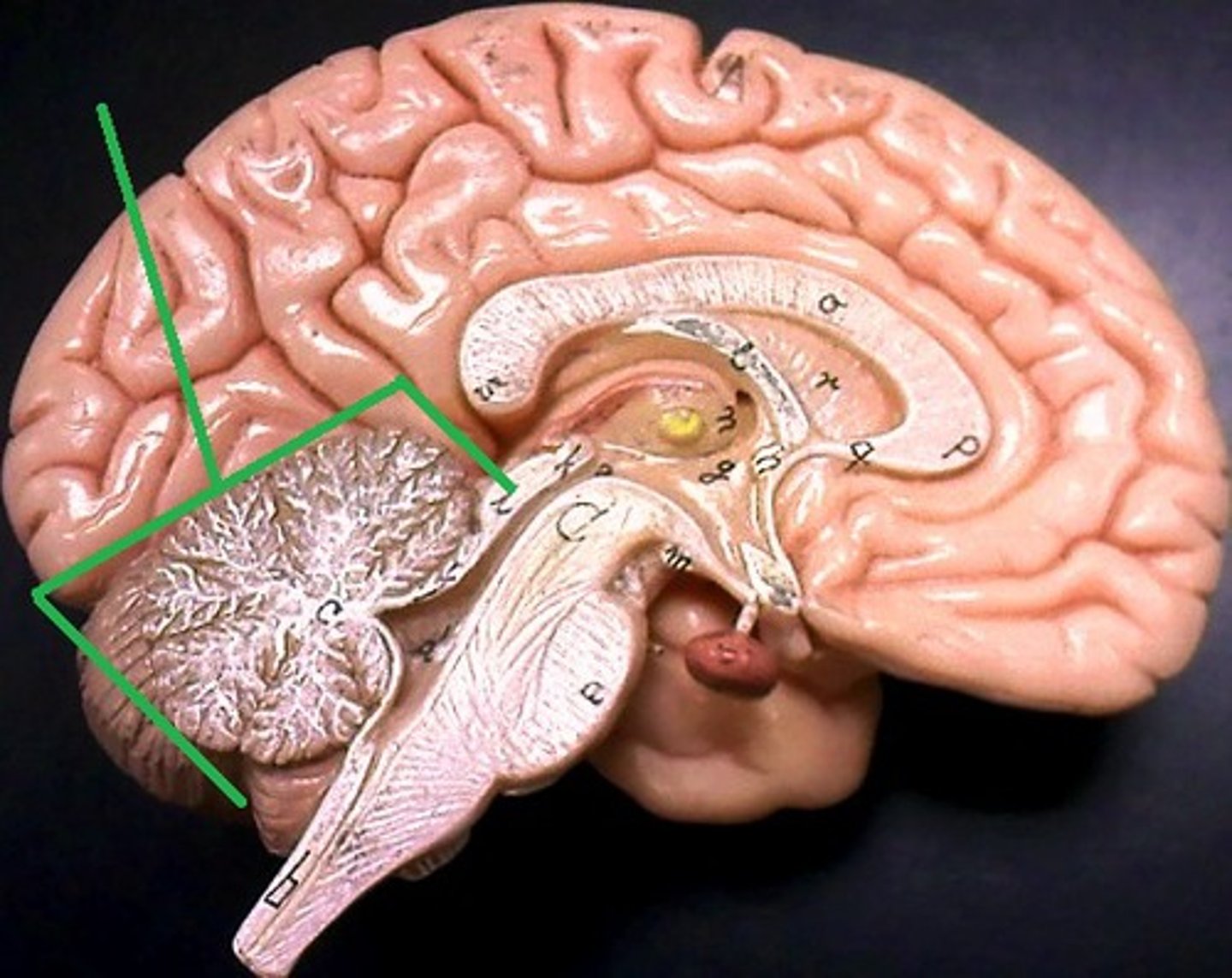
Cerebellum
Primarily responsible for muscle control, including balance and movement
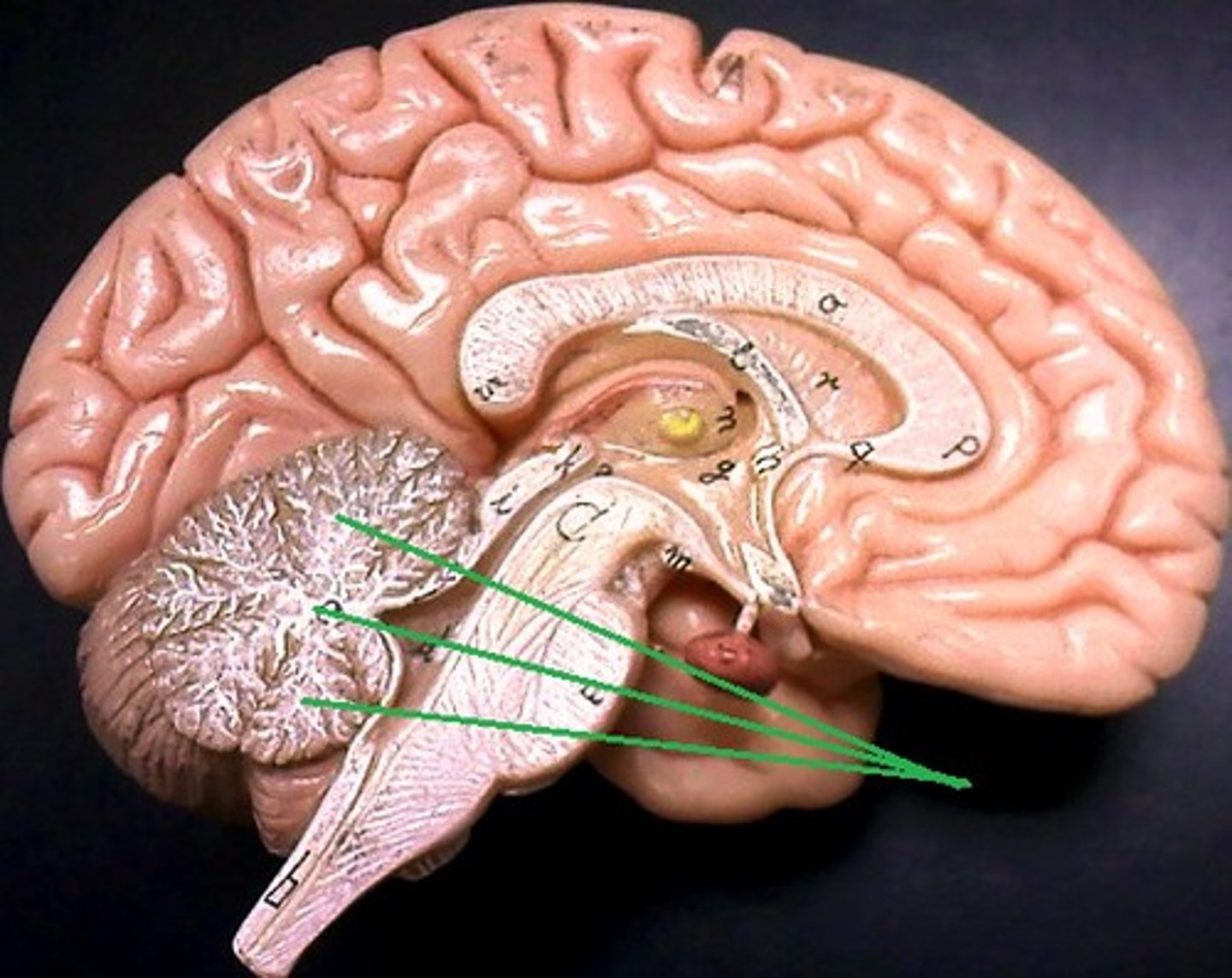
Arbor Vitae
Tree-like white matter inside the cerebellum that carries sensory and motor information to and from the cerebellum
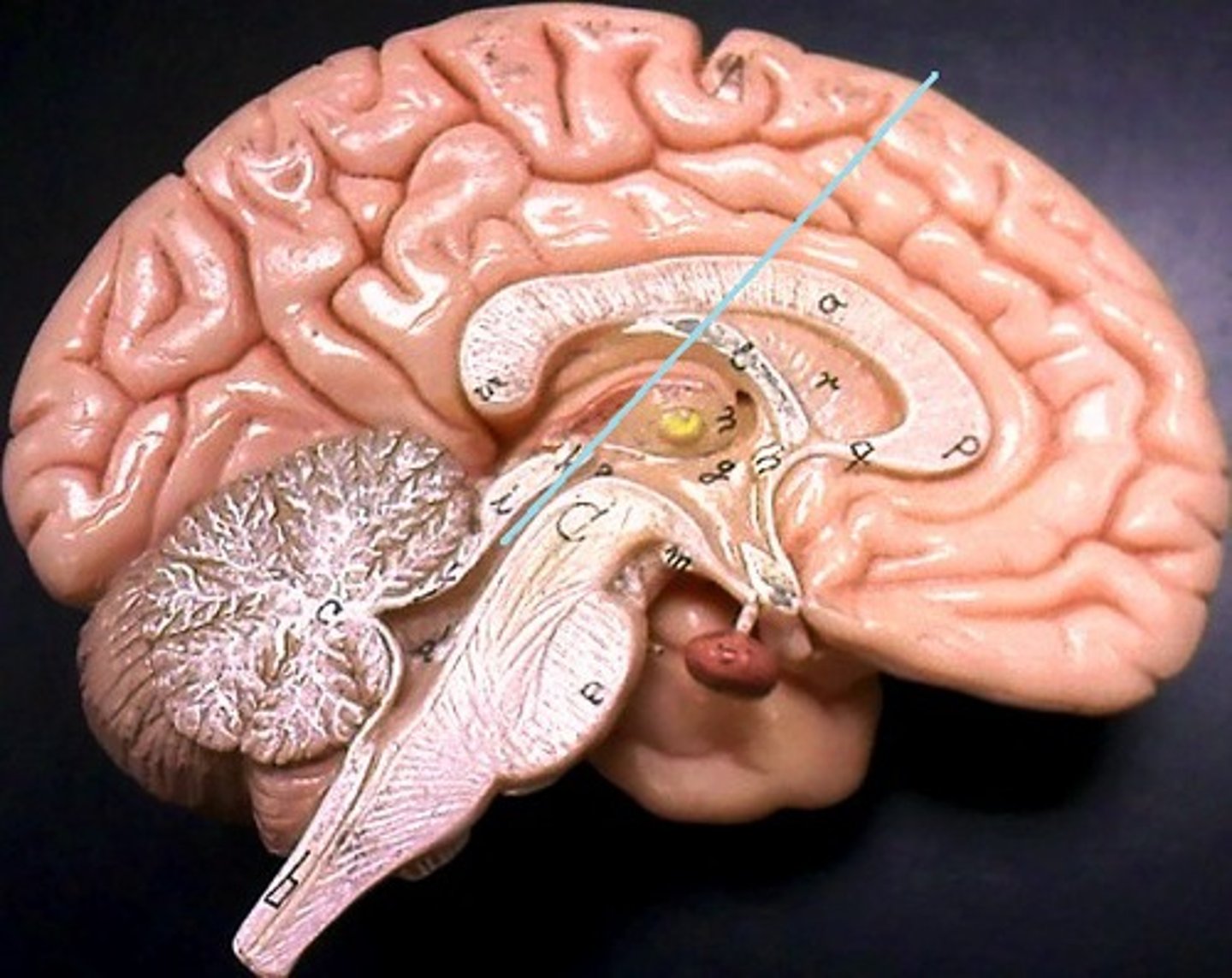
Cerebral aqueduct
Primary function is to facilitate the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) between third and fourth ventricle.
Third ventricle
Main function is to produce and secrete the CSF.
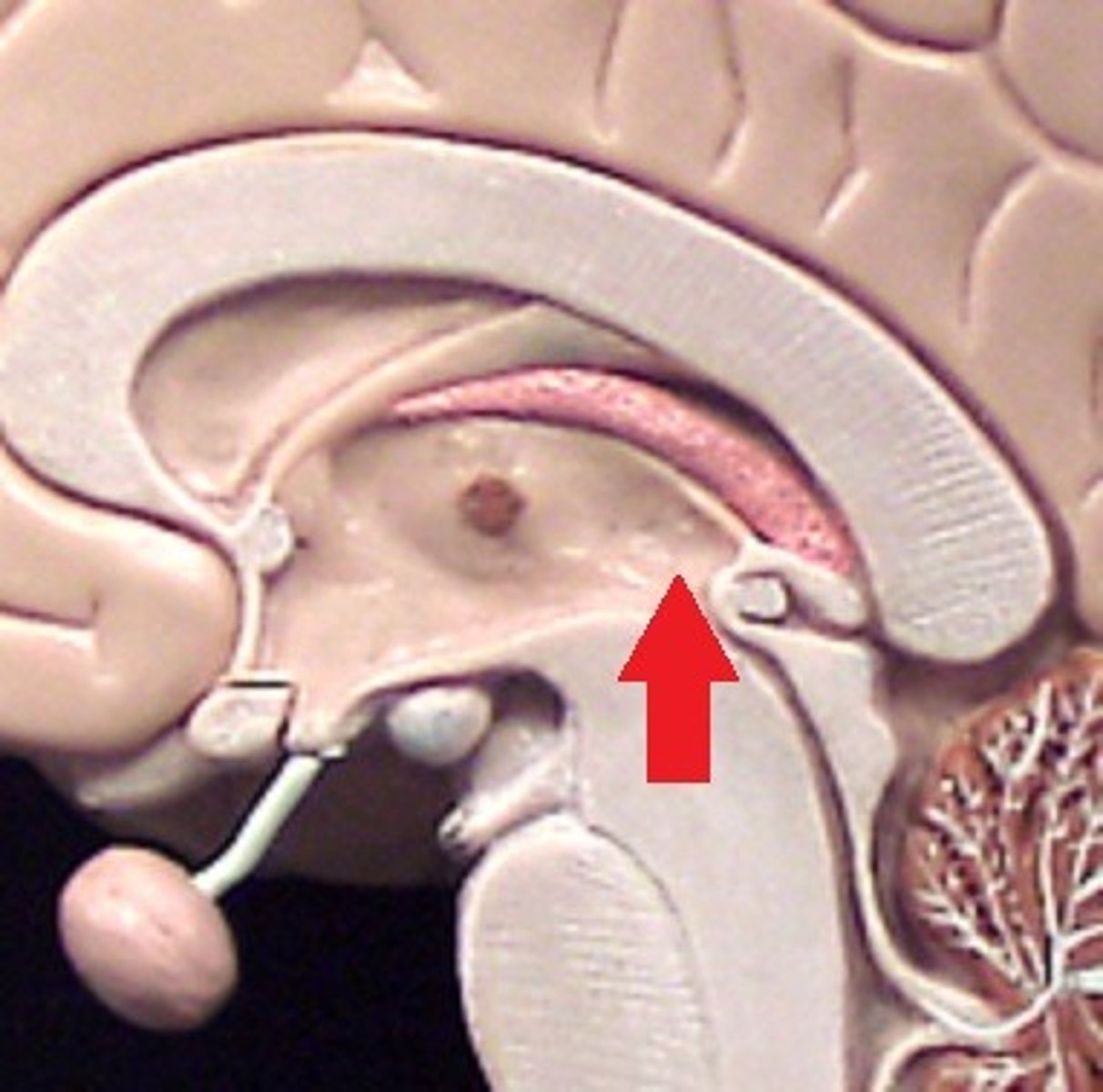
Fourth Ventricle
Main function is to produce and secrete the CSF.
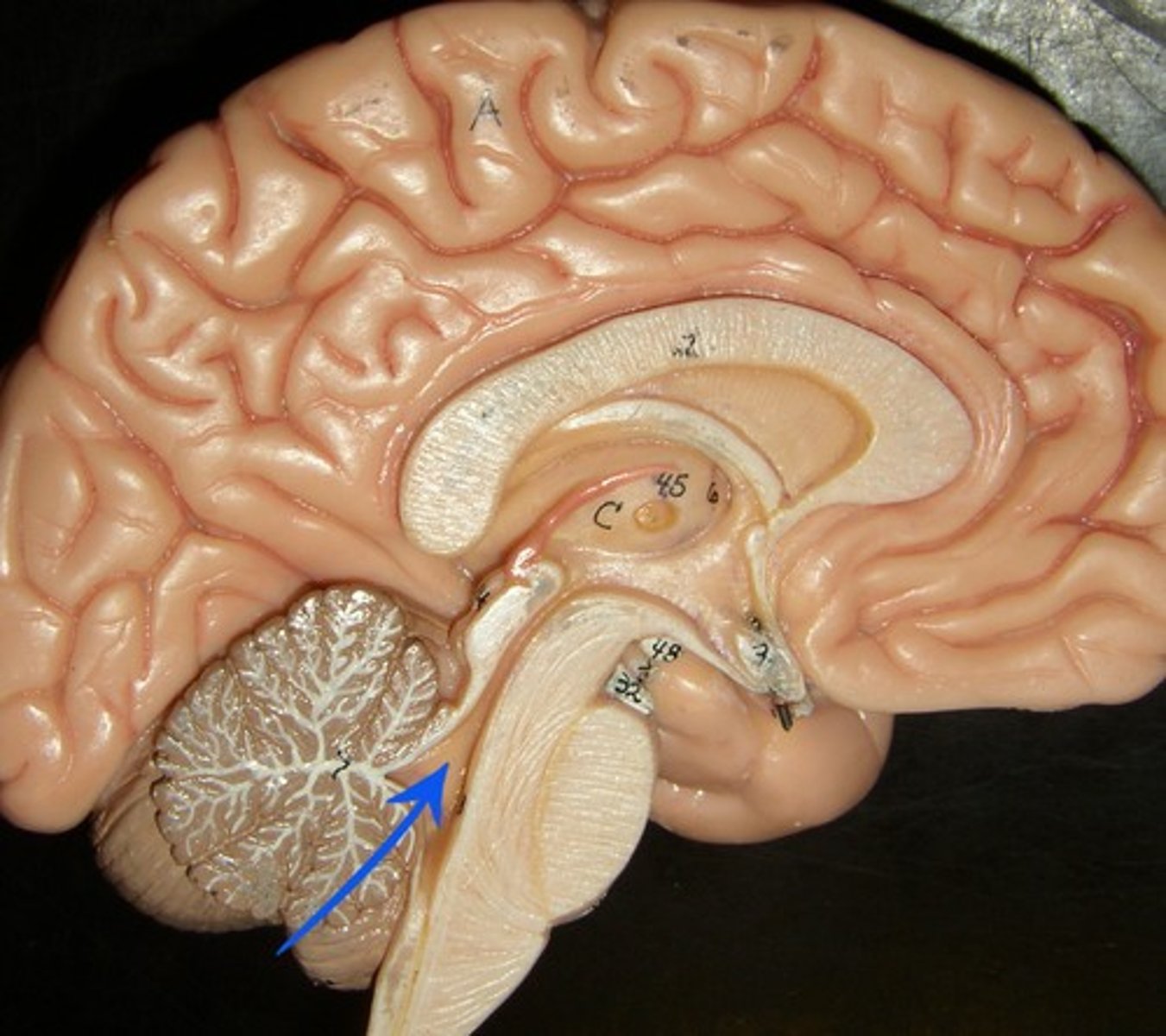
Interventricular foramen
Pathway for CSF to move from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle.
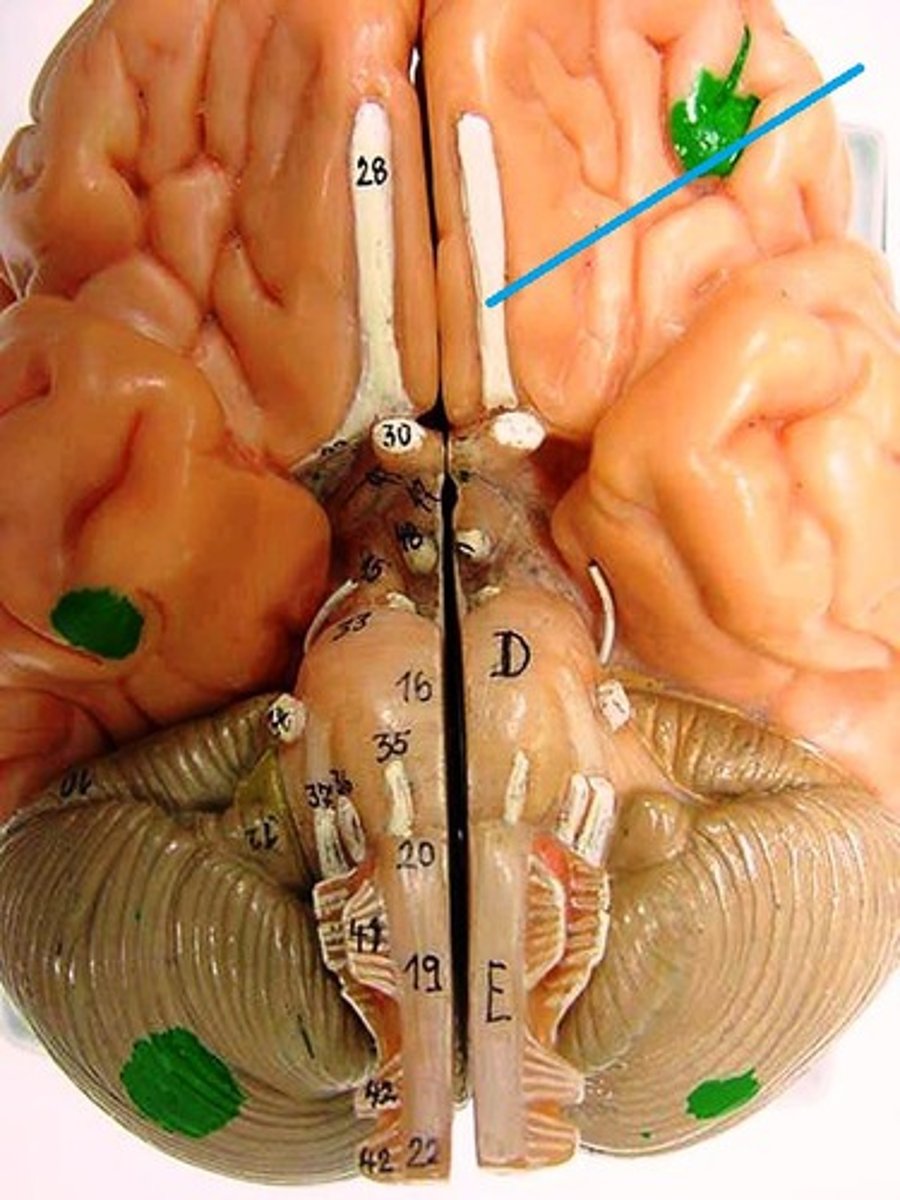
Olfactory Bulbs
Act as a relay station for smells, receiving information from the nose and sending it to the brain for interpretation.
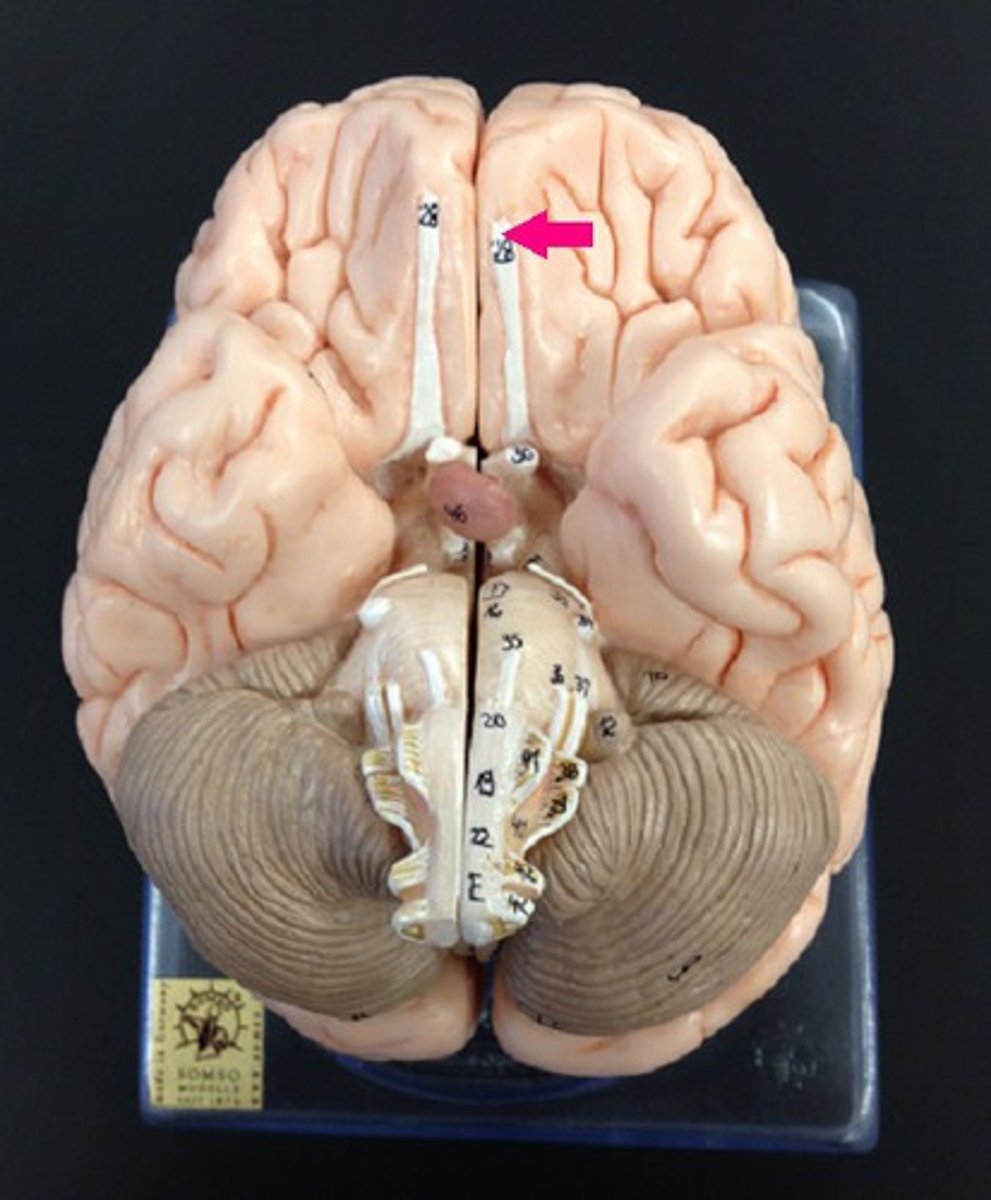
Olfactory Tract
Transmitting sensory information related to smell from the olfactory bulb to other areas of the brain.
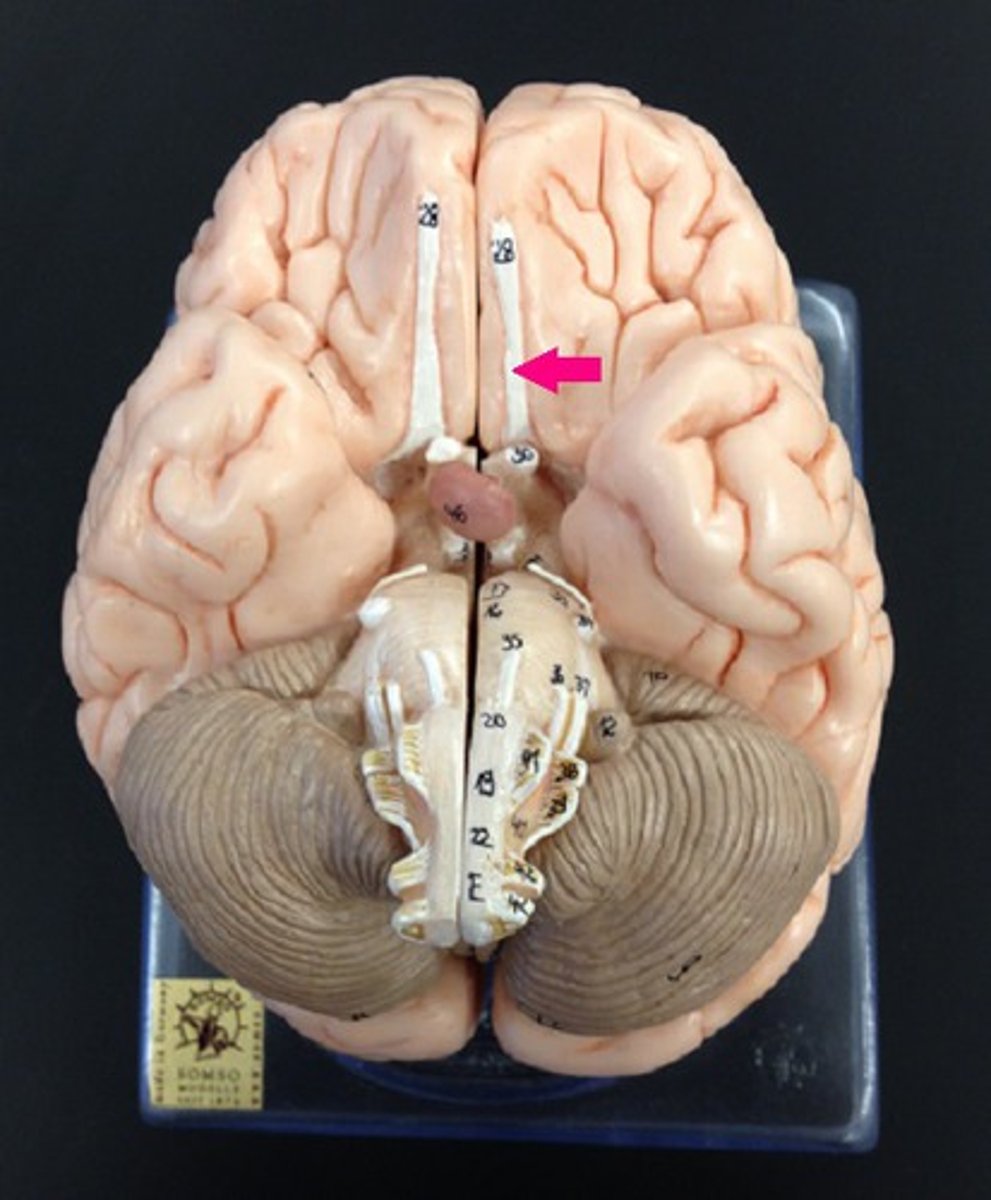
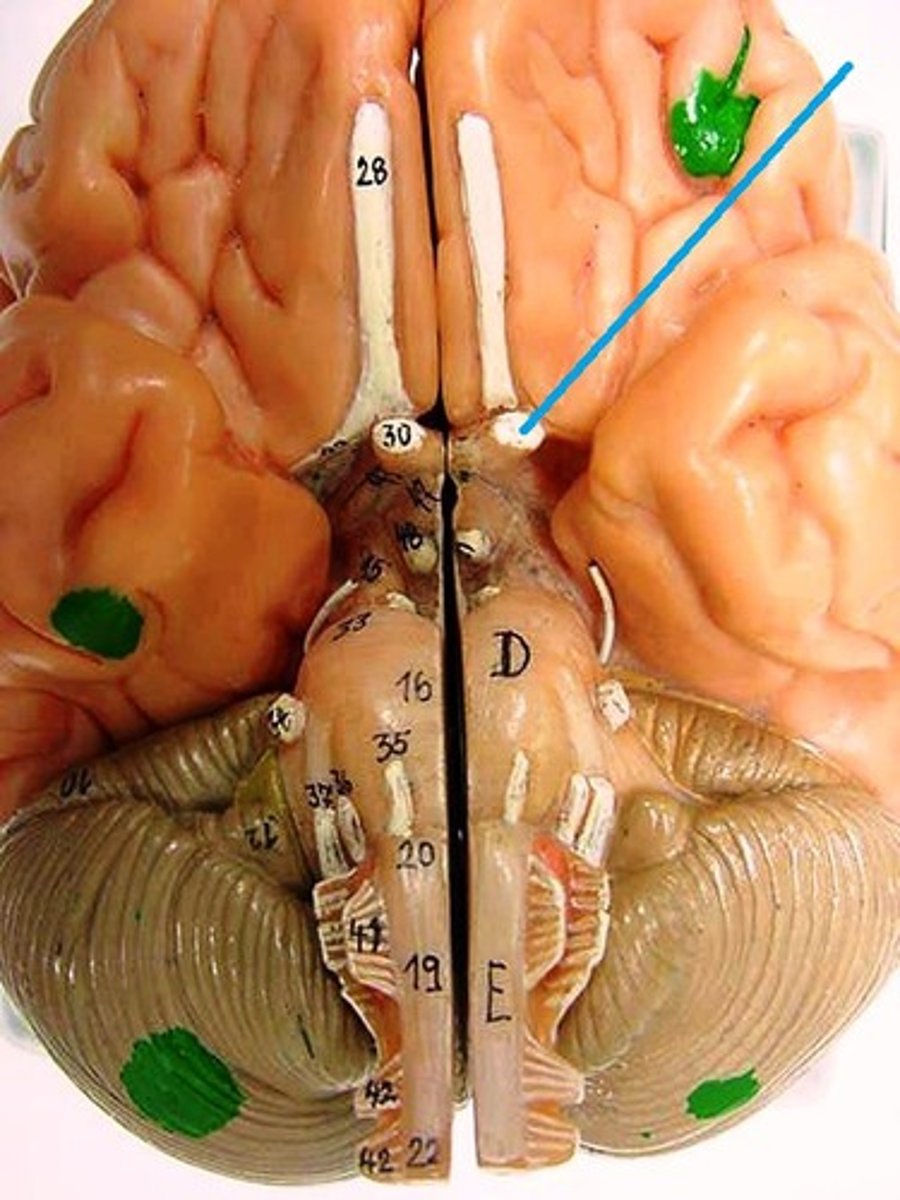
Optic Nerves
Carrying visual information from the retina to the brain, enabling sight.
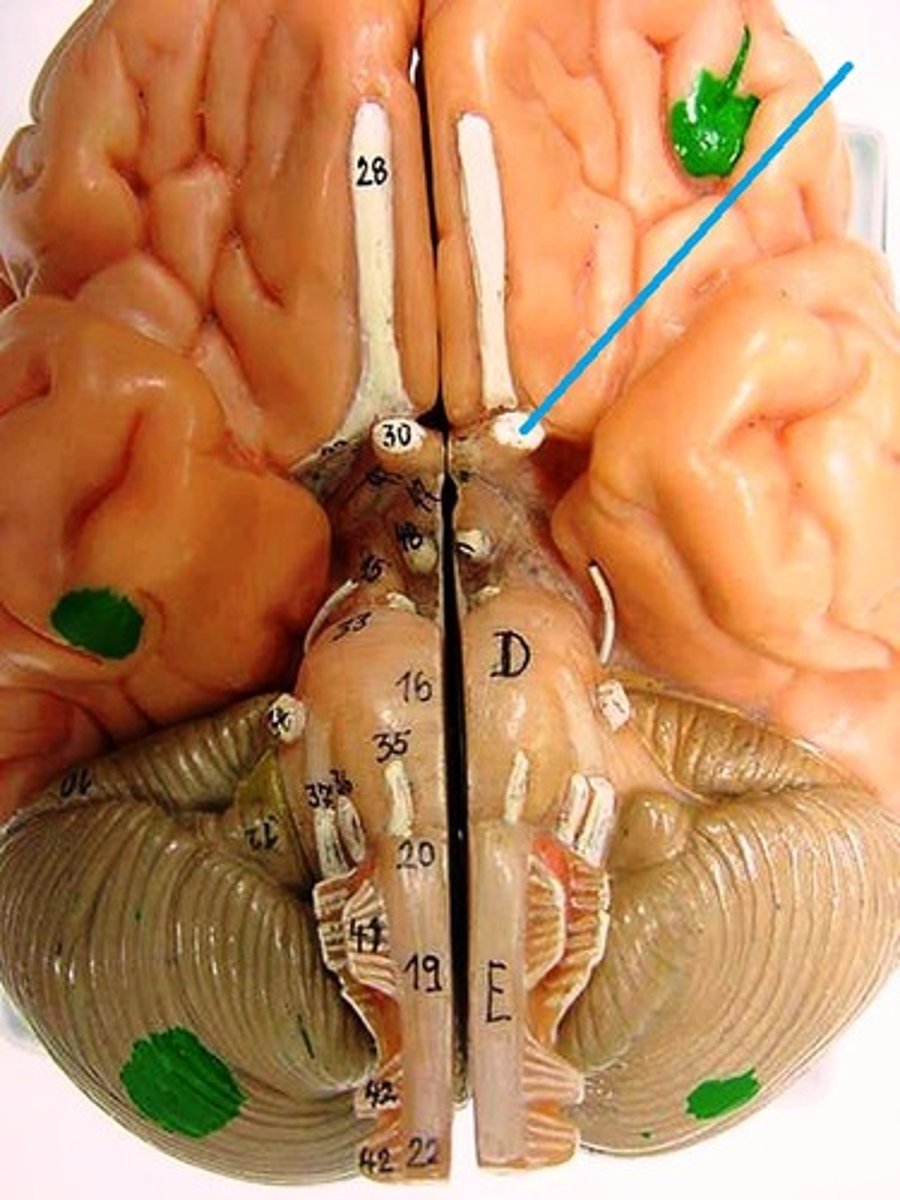
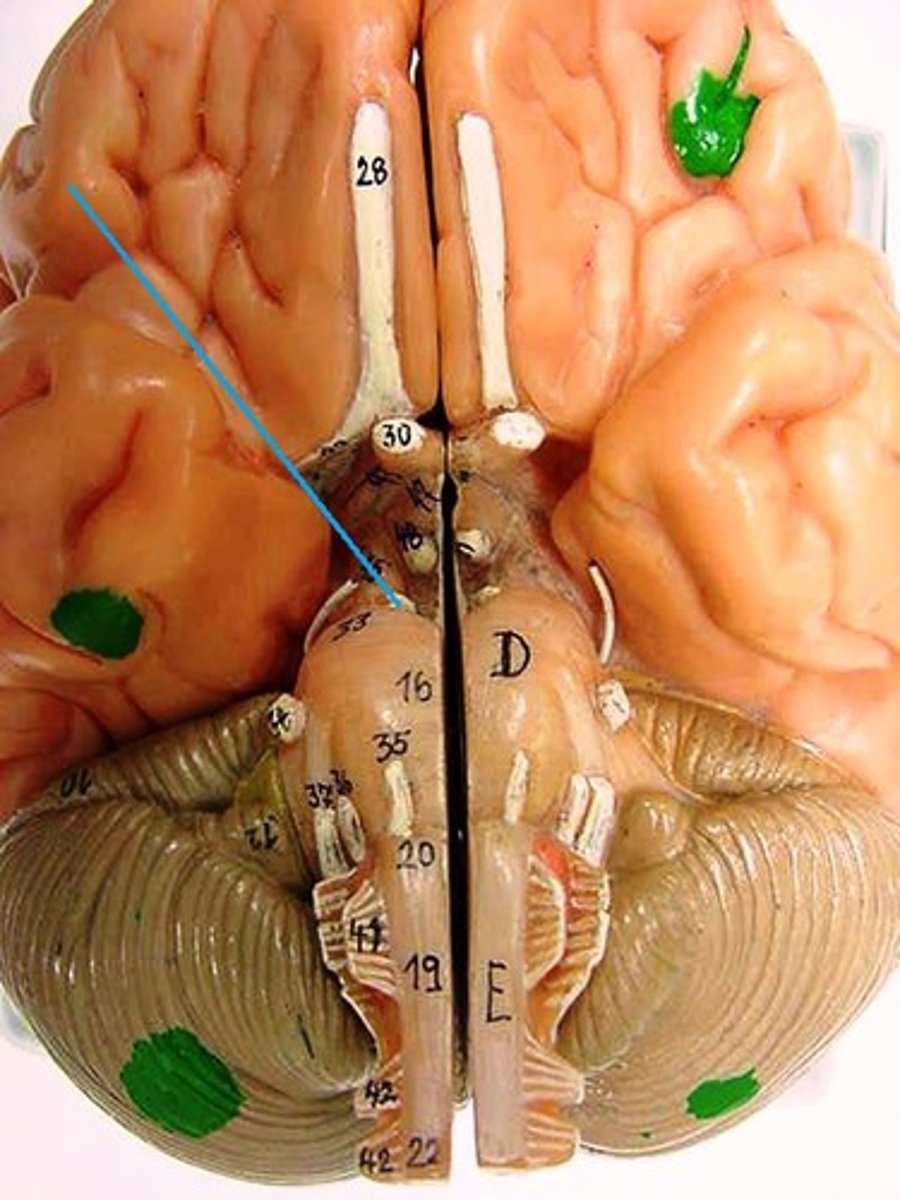
Optic chiasma
Transmitting visual information by crossing nerve fibers from the optic nerves.
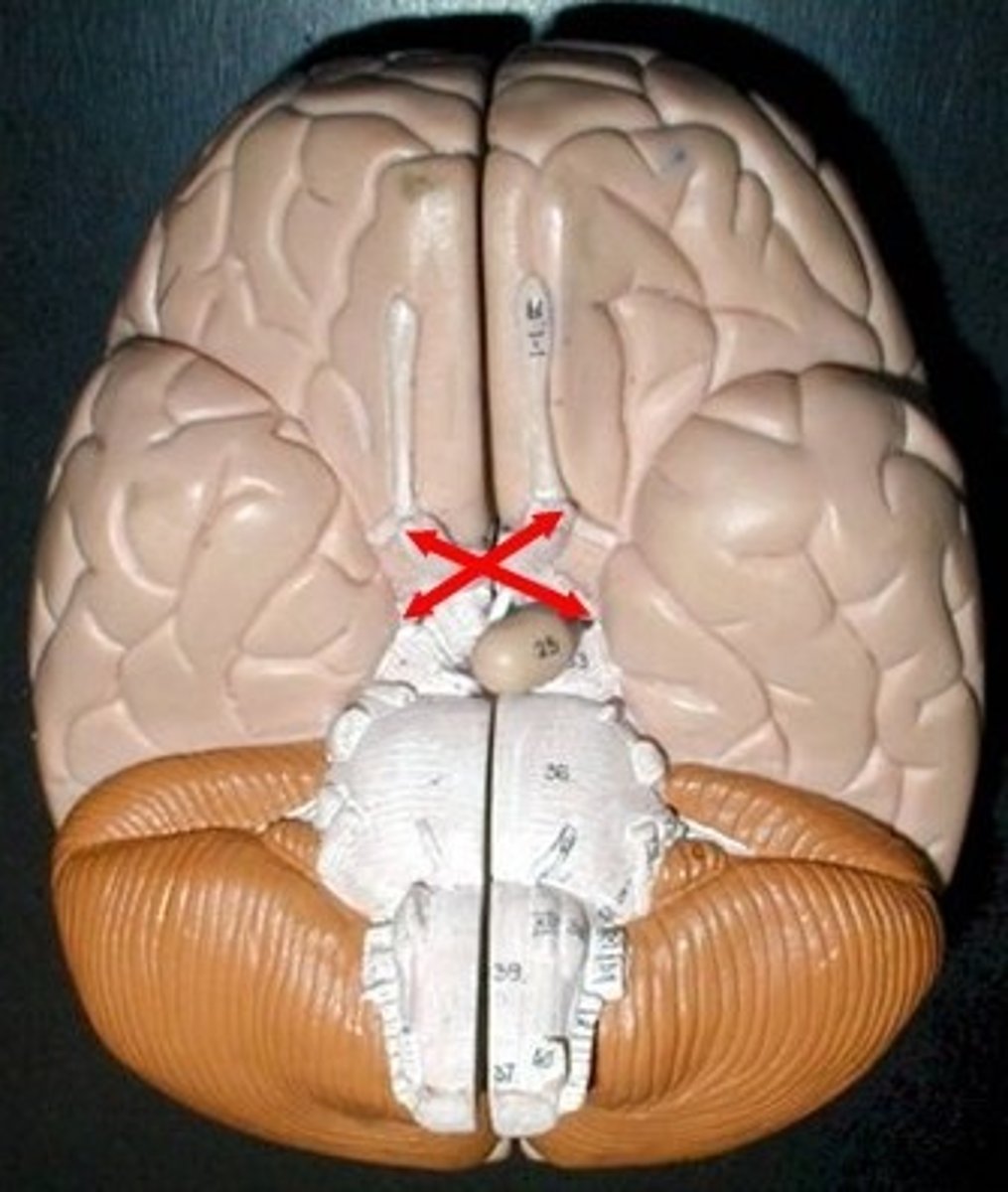
Optic Tracts
Relaying visual information from the optic chiasm to the brain's primary visual centers.
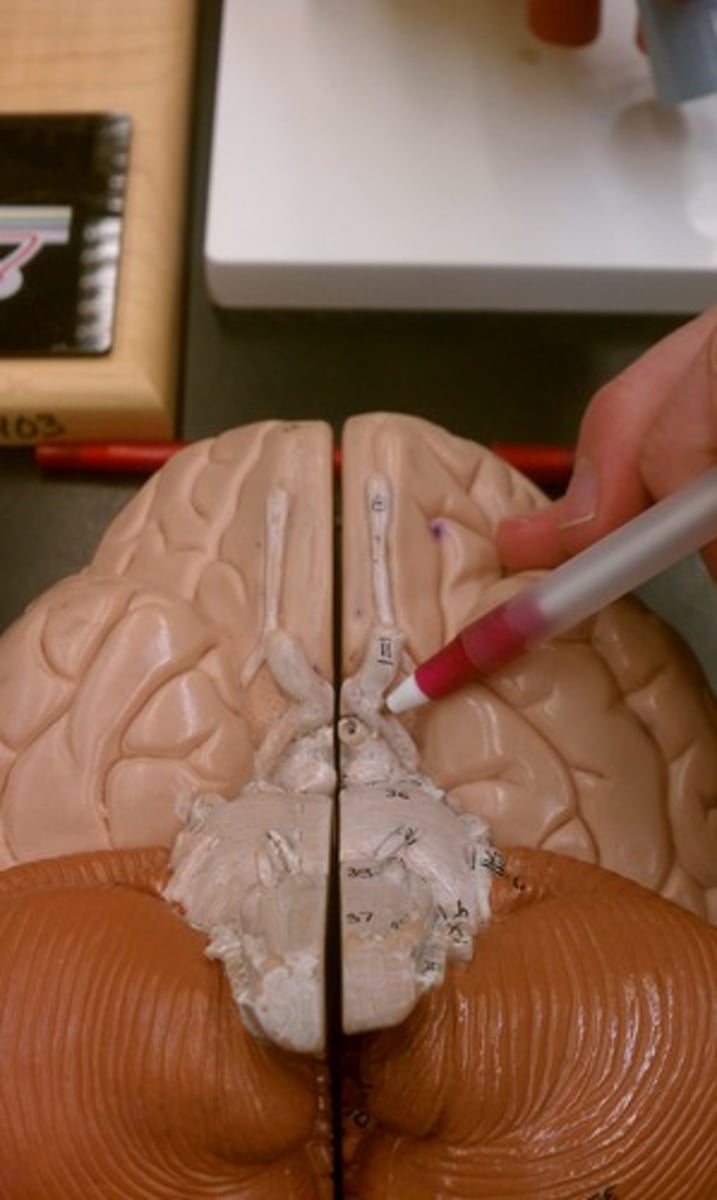
Spinal Cord
Carries nerve signals from your brain to the rest of your body and back
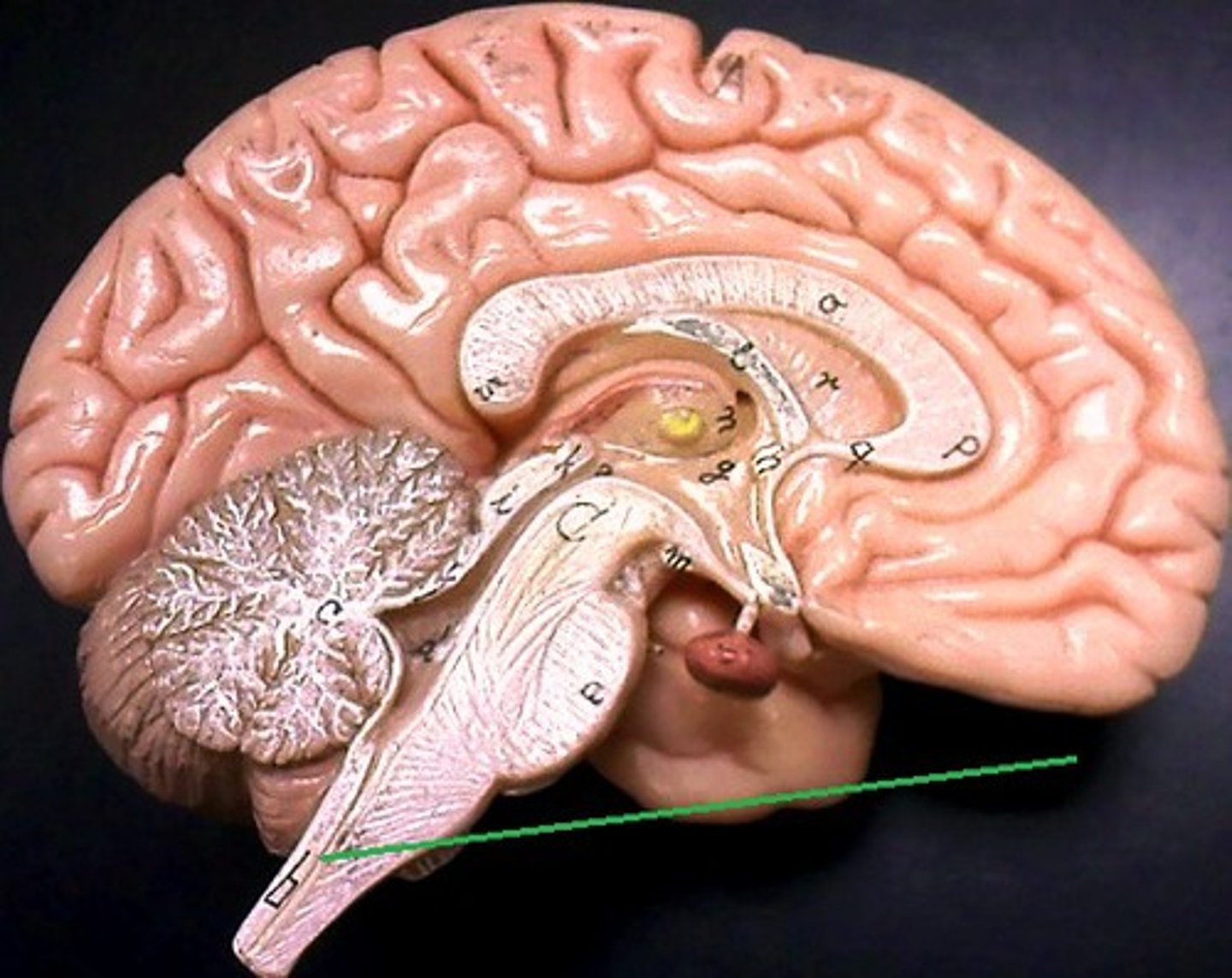
Cranial Nerve 1: Olfactory Nerve
the sense of smell
Cranial Nerve 2: Optic Nerve
transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain
Cranial Nerve 3: Oculomotor Nerve
controlling eye movements, eyelid elevation, and pupil constriction
Cranial Nerve 4: Trochlear Nerve
controlling the movement of the superior oblique eye muscle
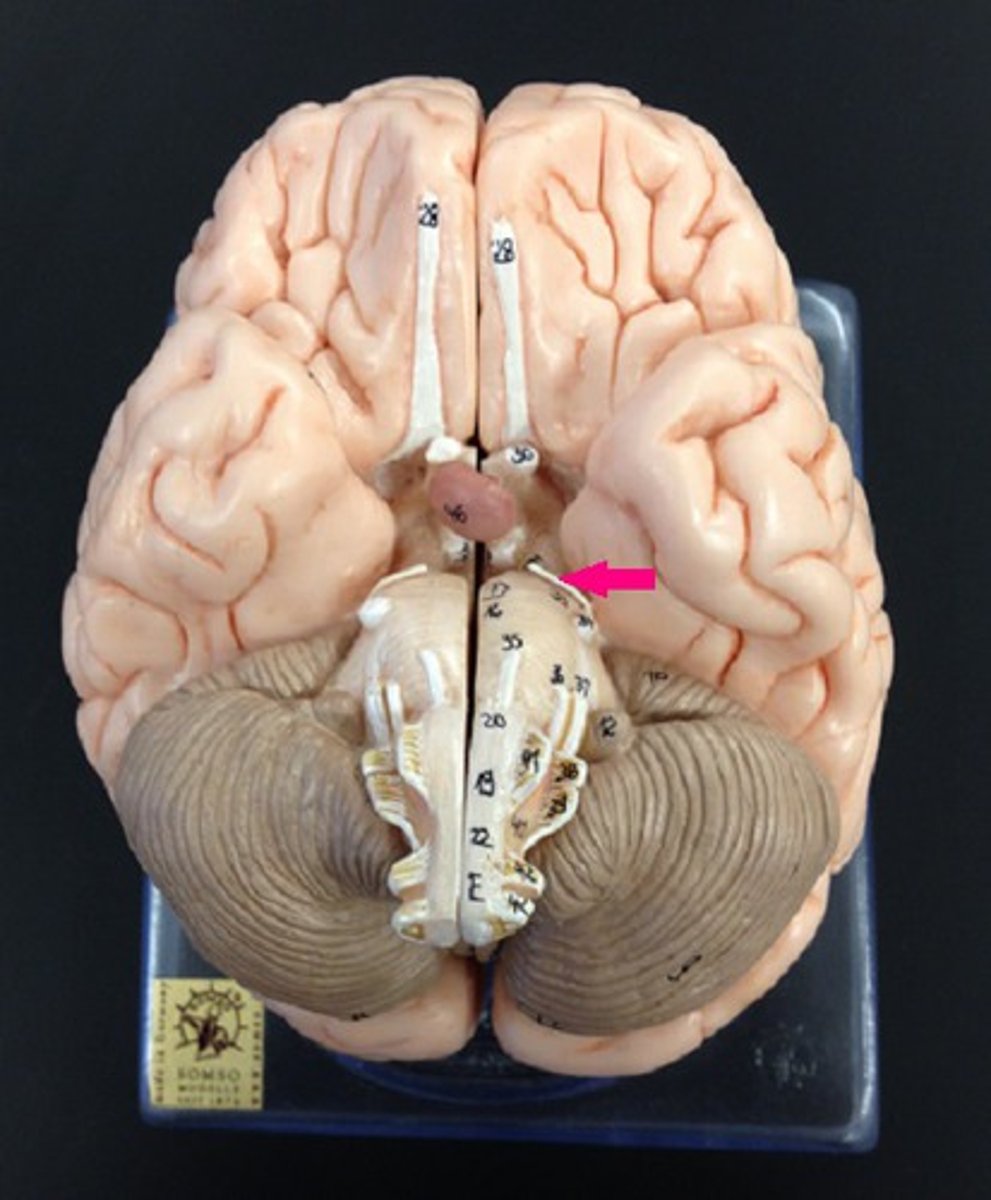
Cranial Nerve 5: Trigeminal Nerve
Sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves
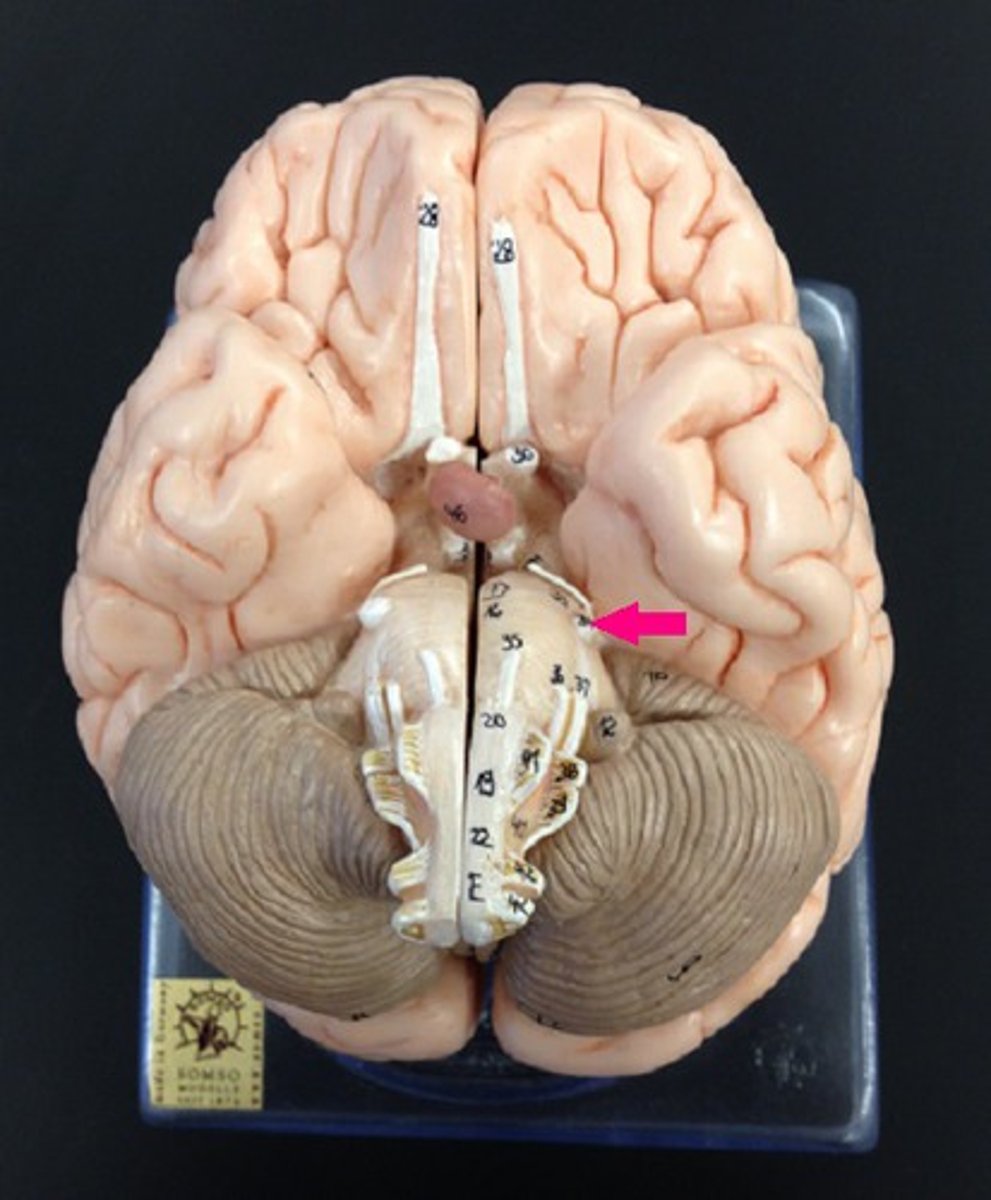
Cranial Nerve 6: Abducent Nerve
Controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle in the eye.
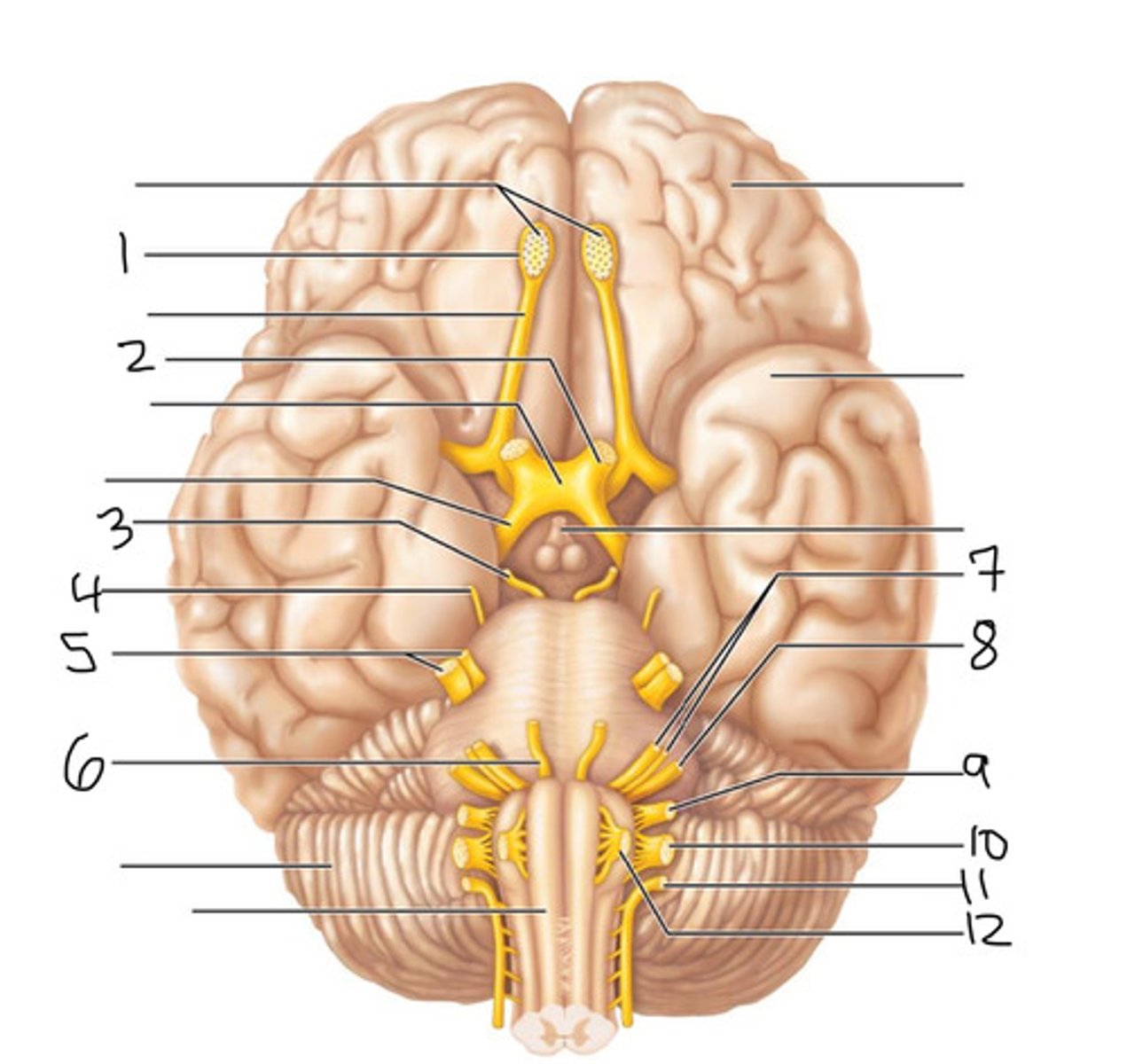
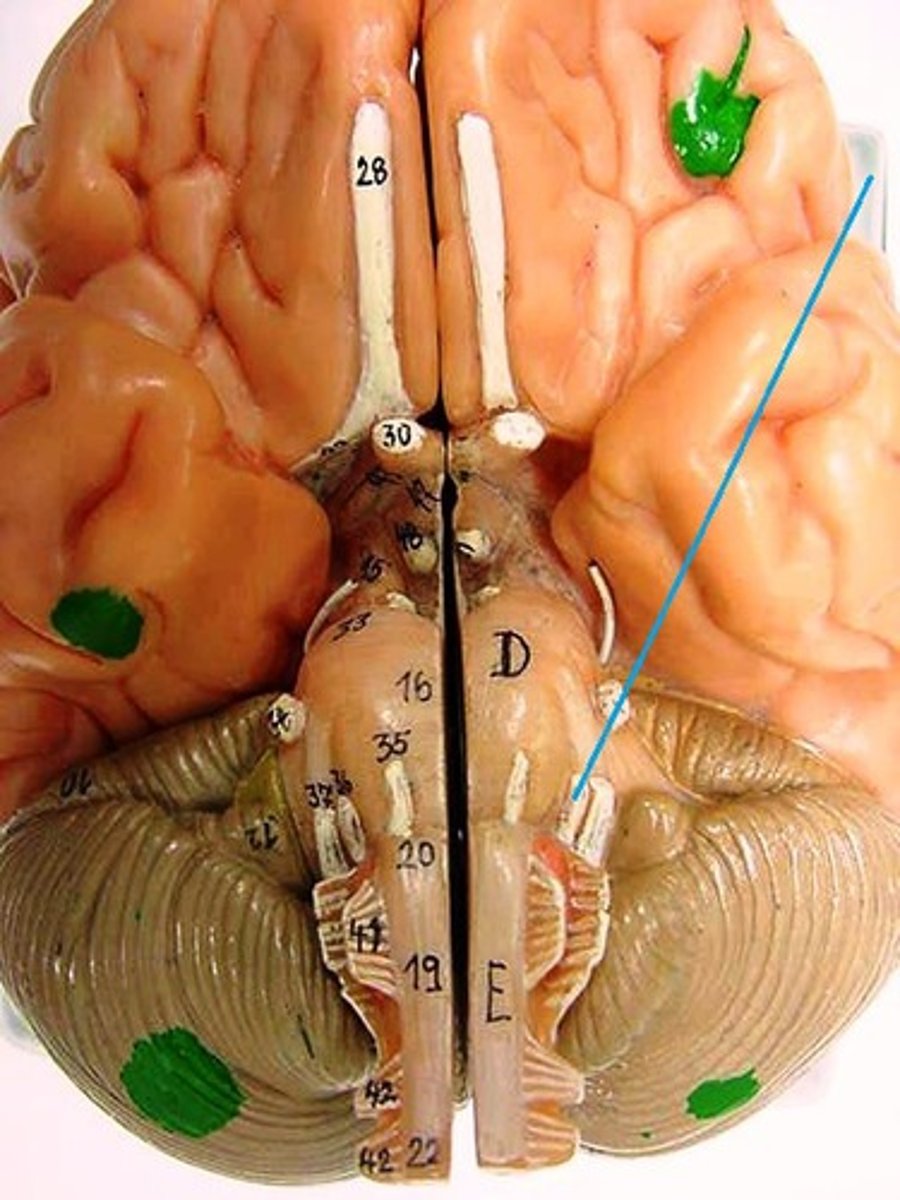
Cranial Nerve 7: Facial Nerve
Responsible for forming facial expressions, communicating orally, tasting and tear production
Cranial Nerve 8: Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Controls hearing and balance.
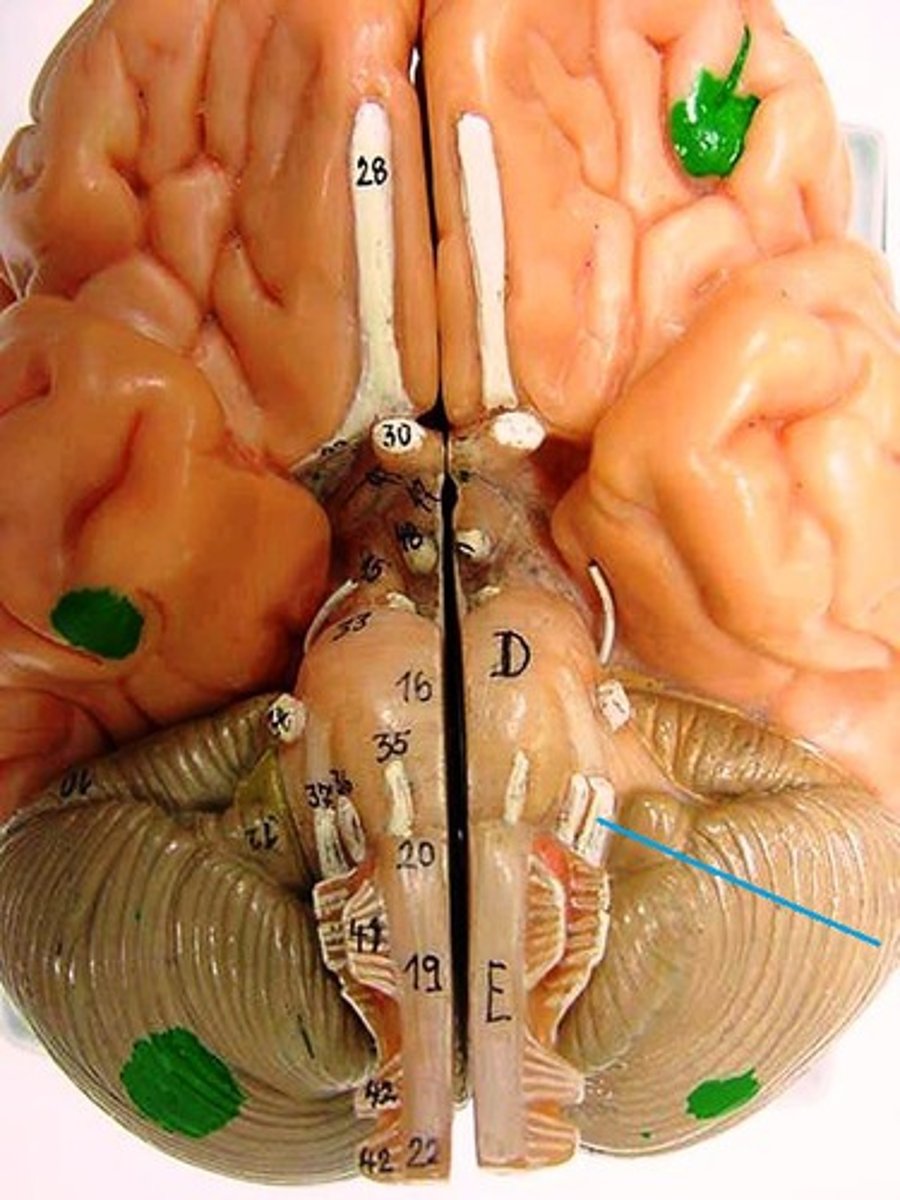
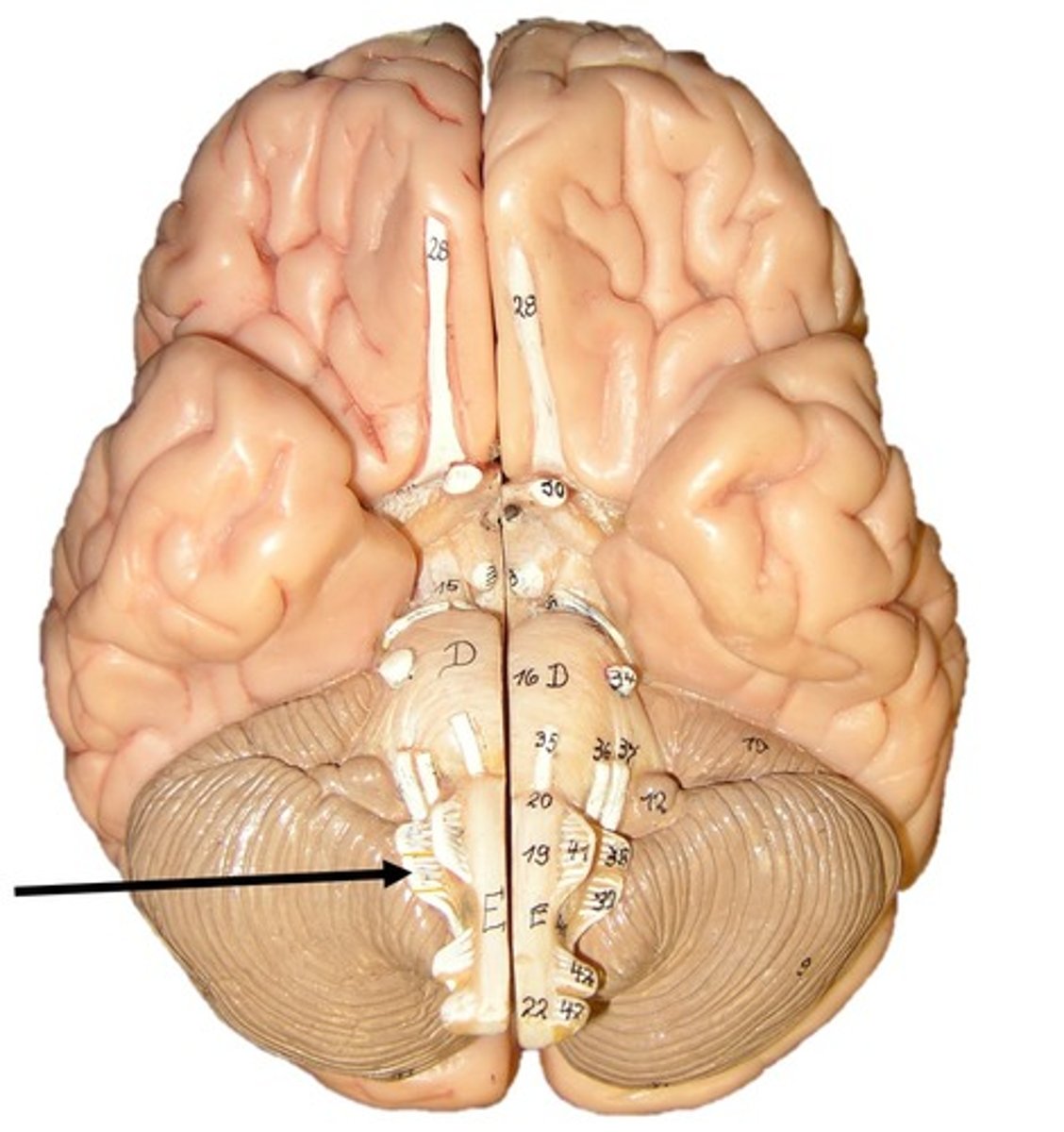
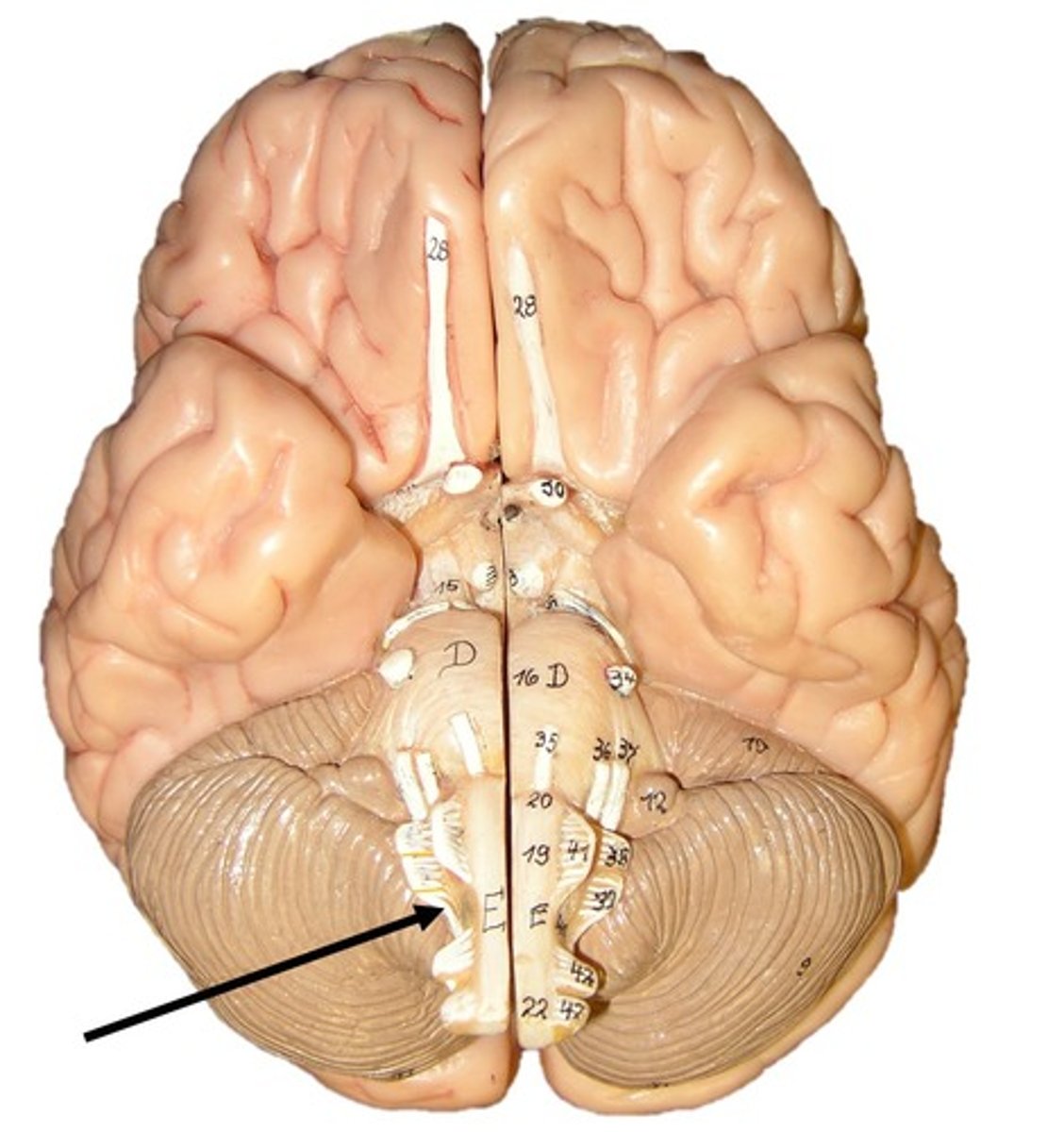
Cranial Nerve 9: Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Controls taste, swallowing, and sensation in the tongue, throat, and ear.
Cranial Nerve 10: Vagus Nerve
Controls your mood, speech, and breathing, among many other vital functions.
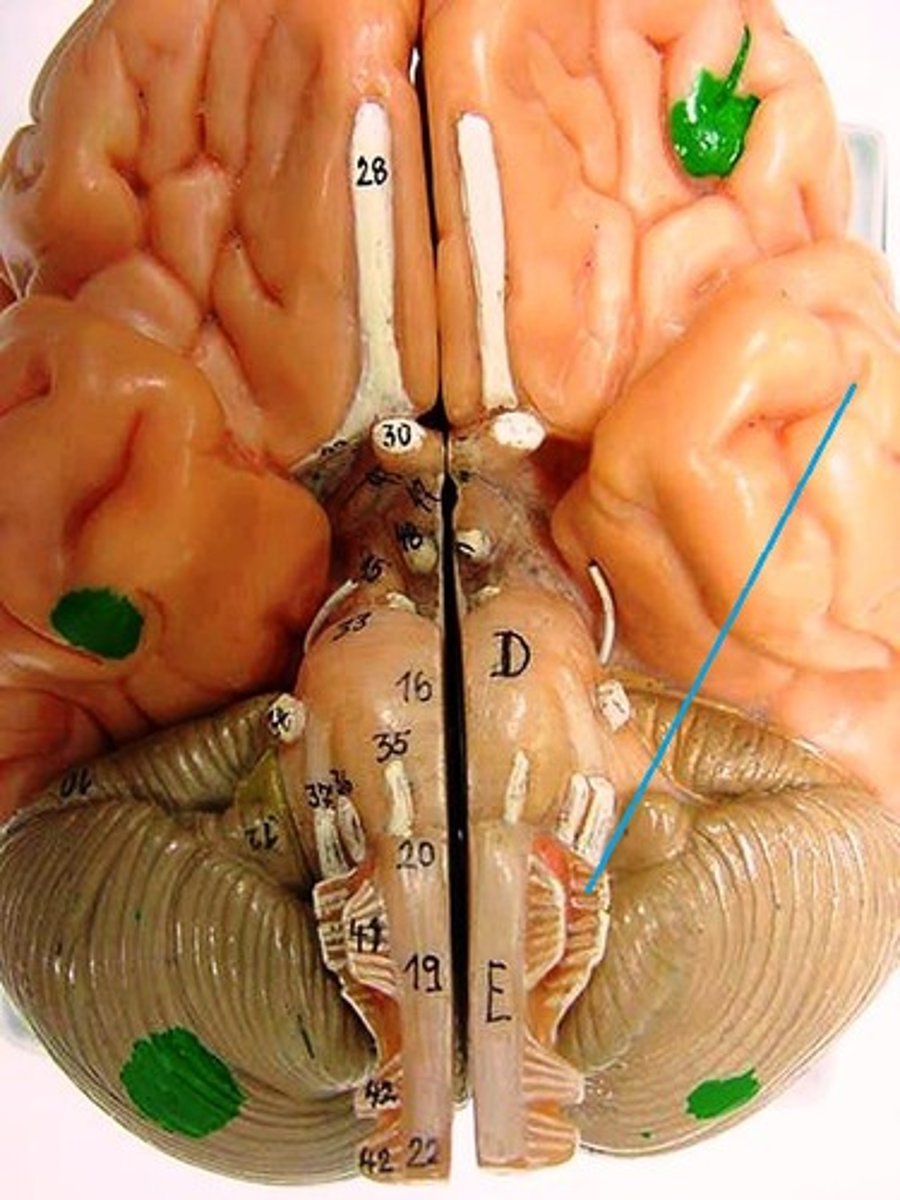
Cranial Nerve 11: Accessory Nerve
Controlling the movements of the neck and shoulders
Cranial Nerve 12: Hypoglossal Nerve
Controlling the muscles of the tongue
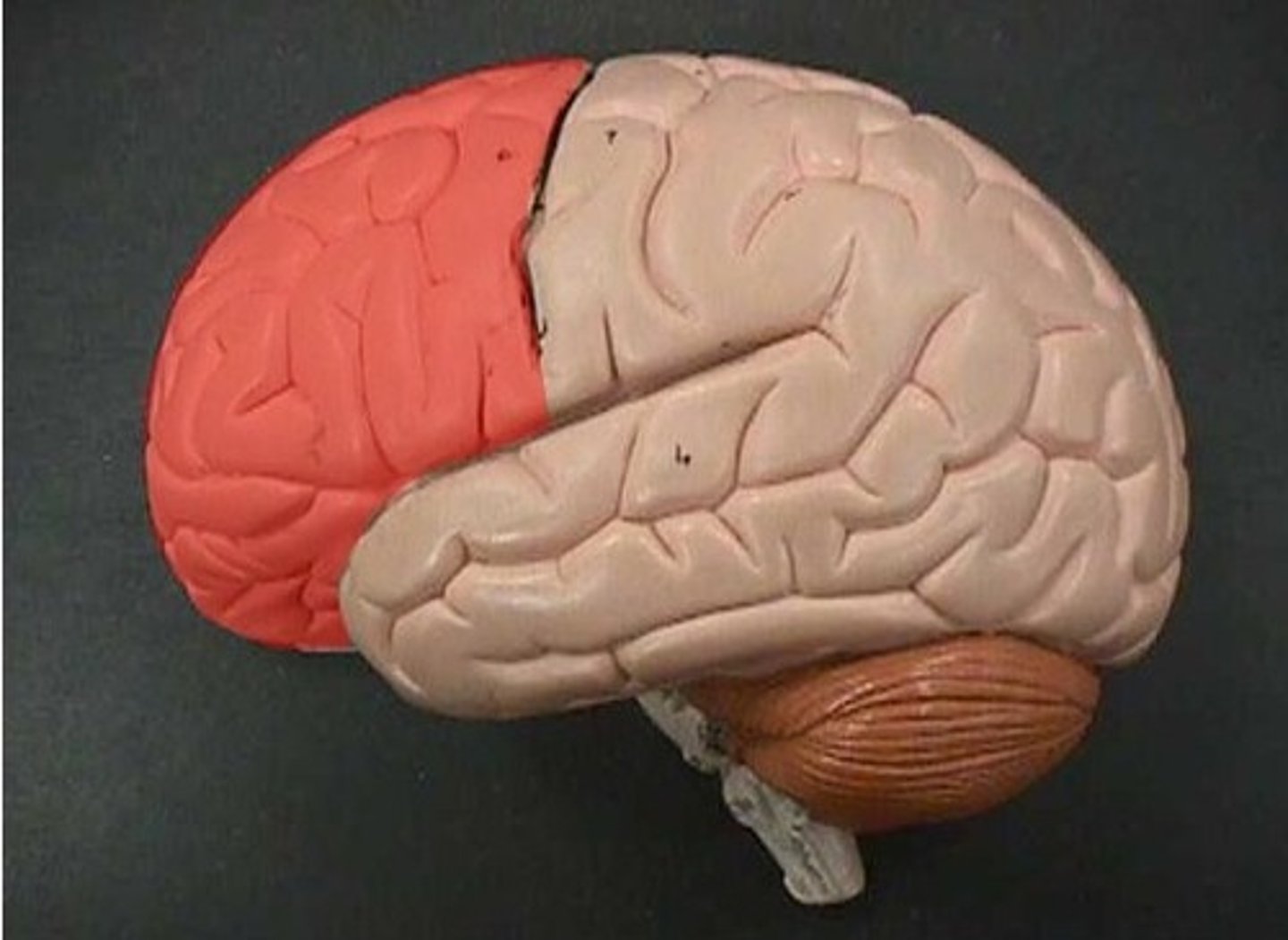
frontal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
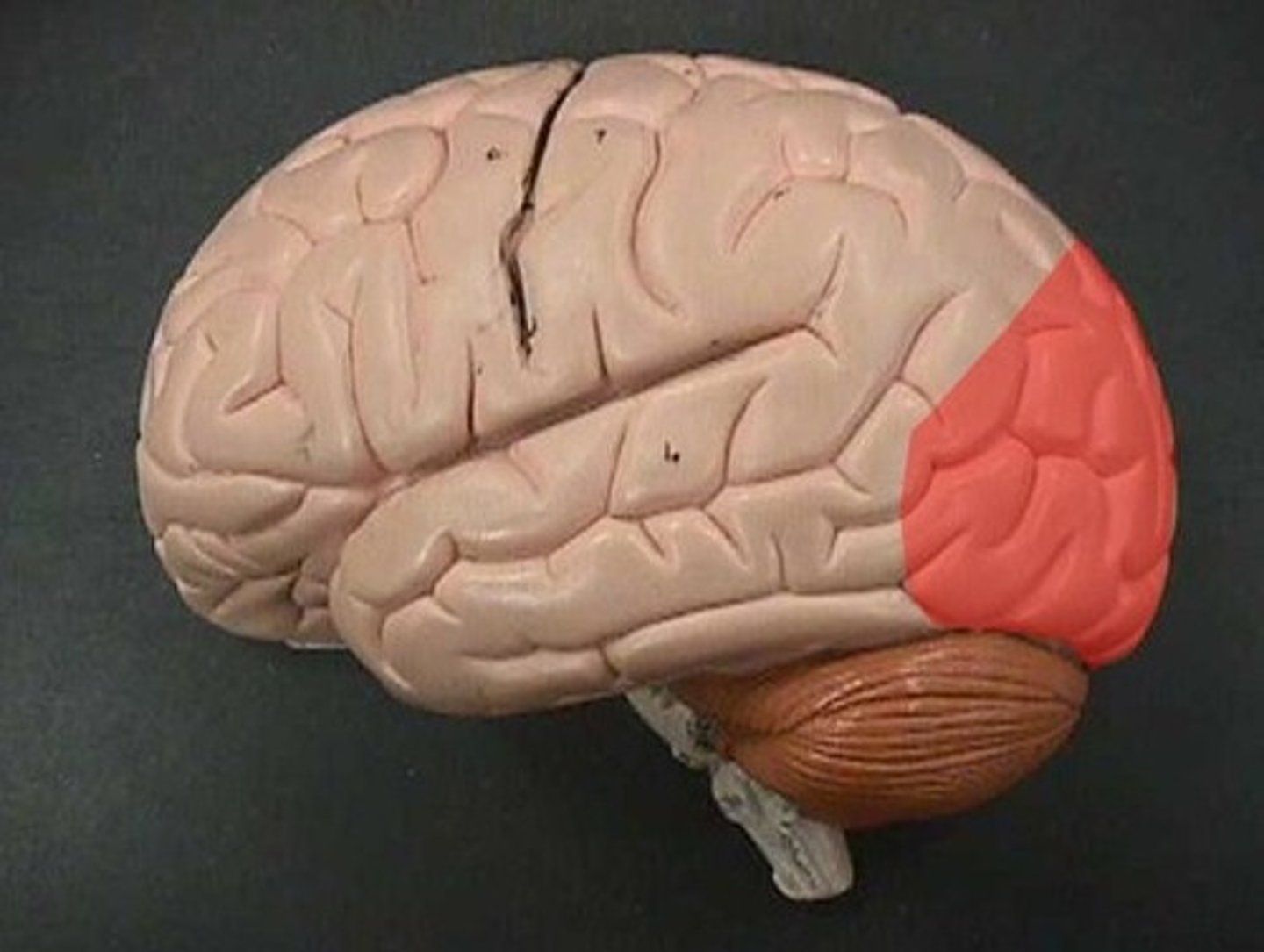
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
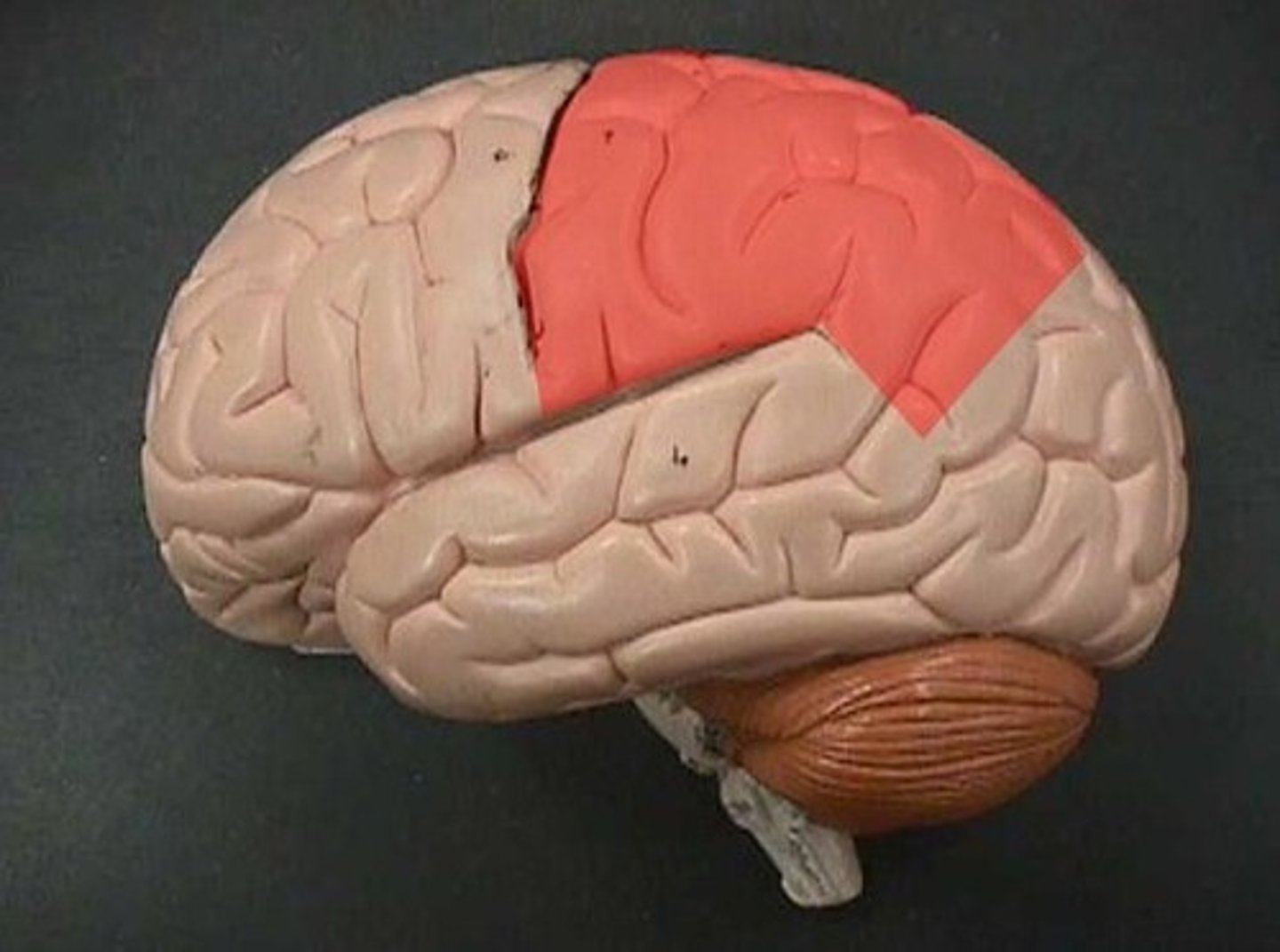
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
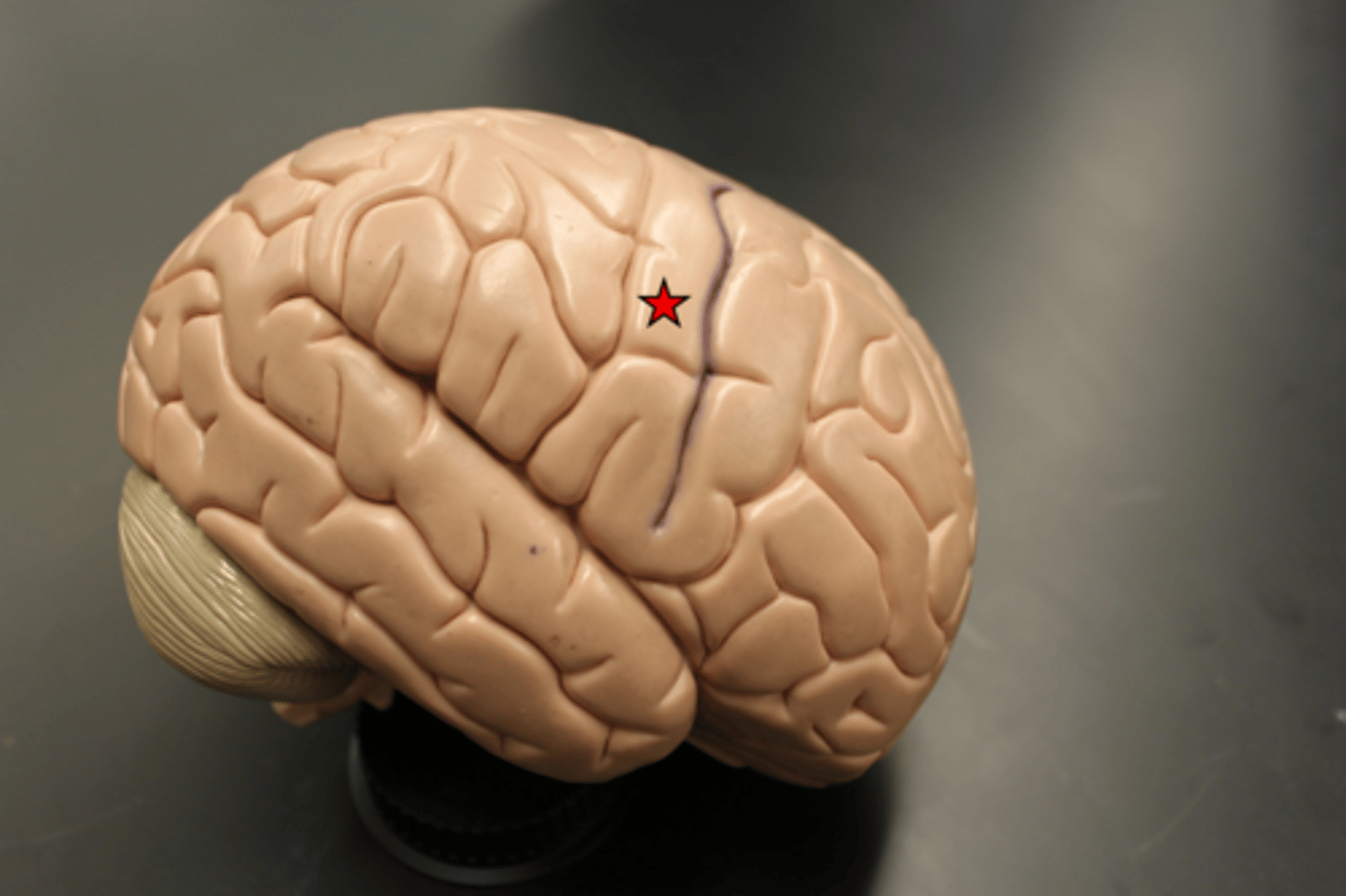
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
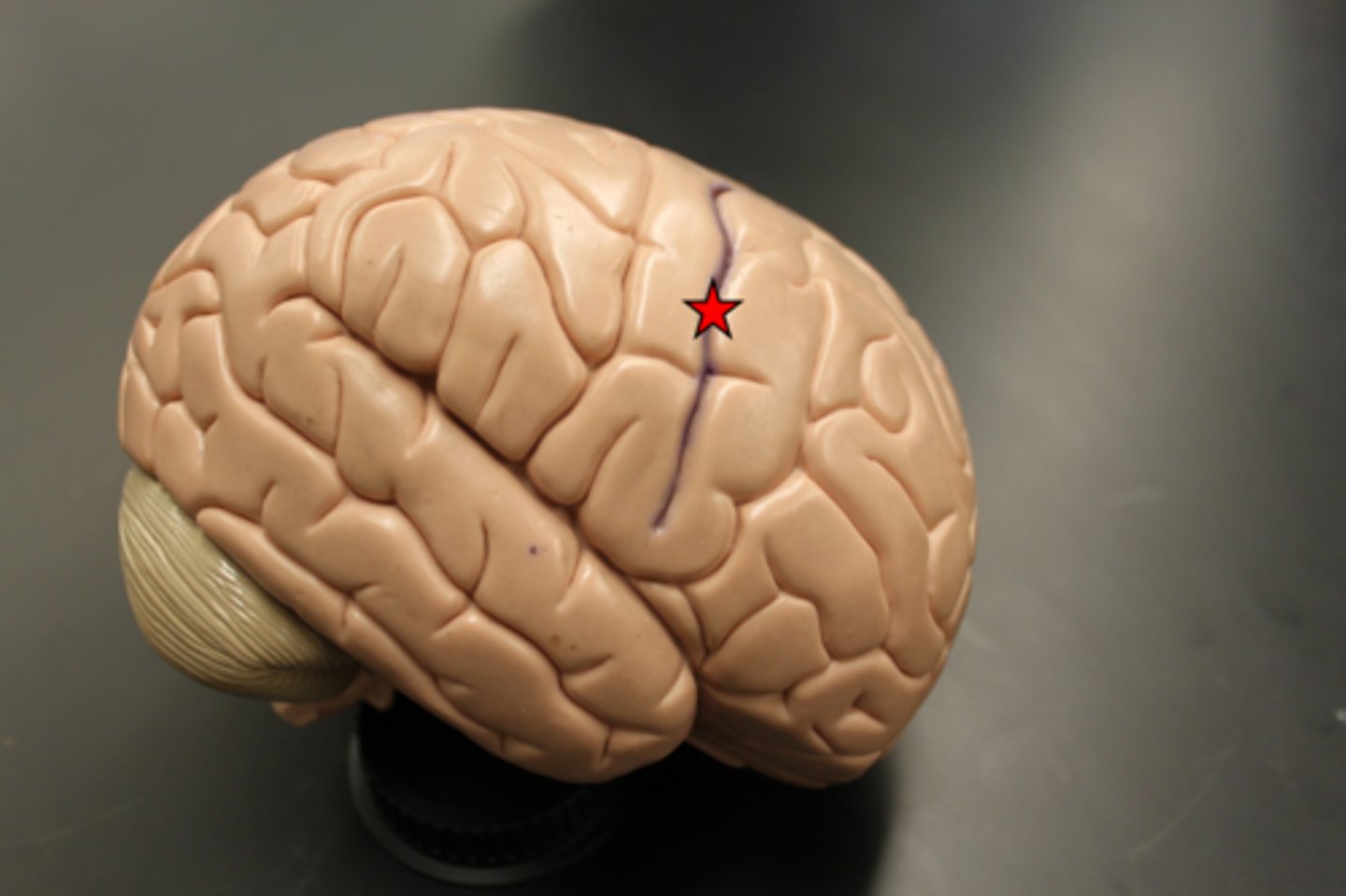
precentral gyrus
the strip of frontal cortex, just in front of the central sulcus, that is crucial for motor control
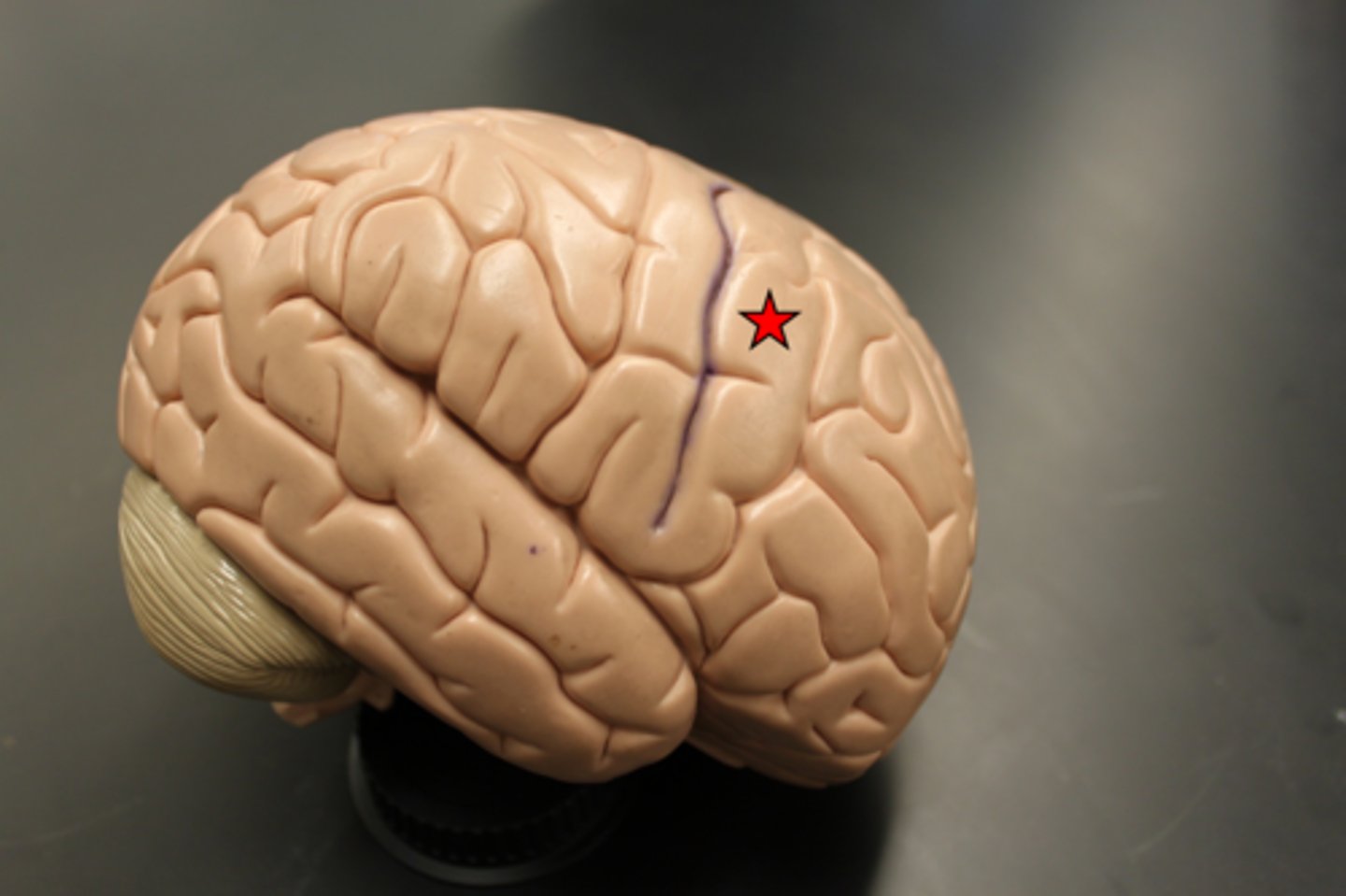
postcentral gyrus
the strip of parietal cortex, just behind the central sulcus, that receives somatosensory information from the entire body
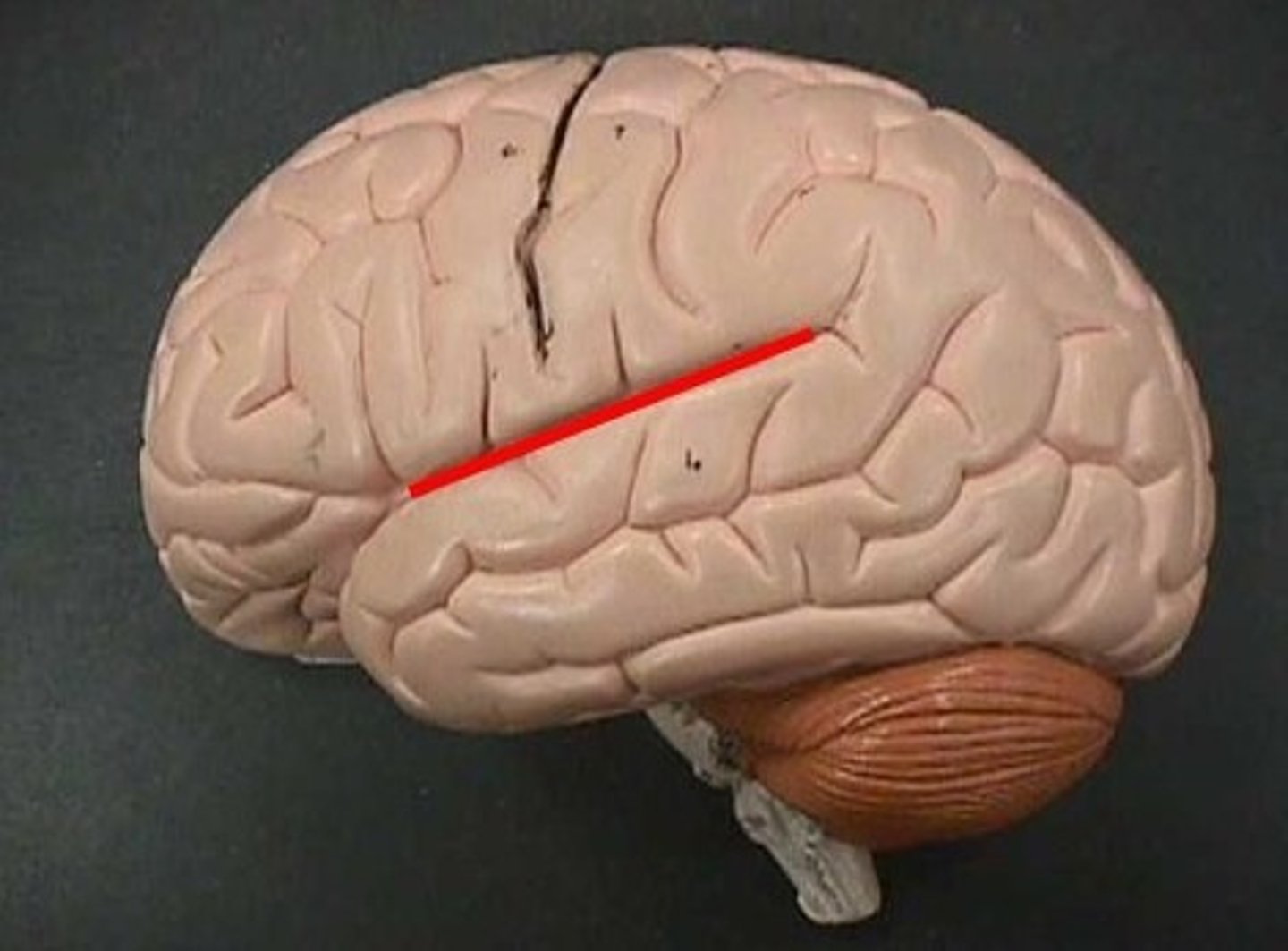
lateral sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from parietal and frontal lobes
insular lobe
The lobe tucked away in the lateral sulcus. Crucial for taste, awareness of internal organs
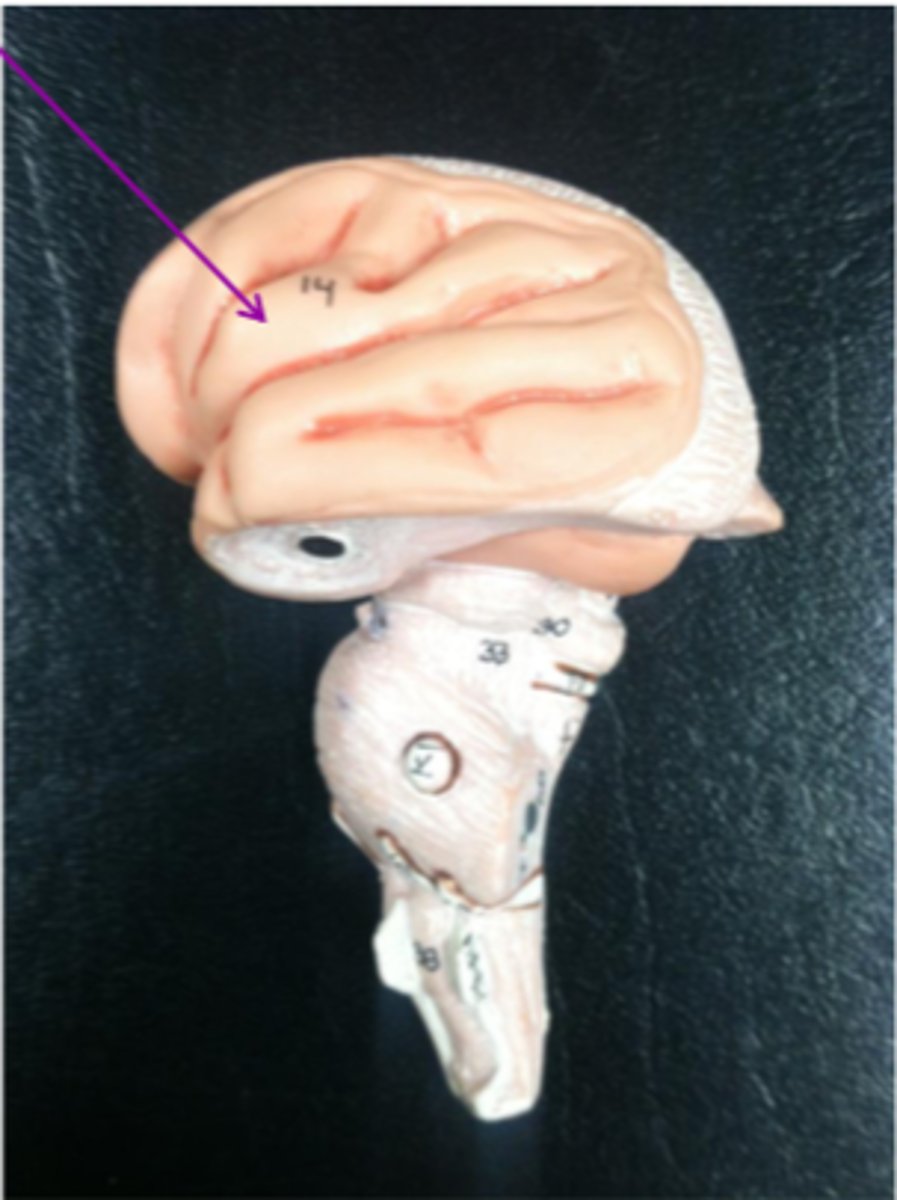
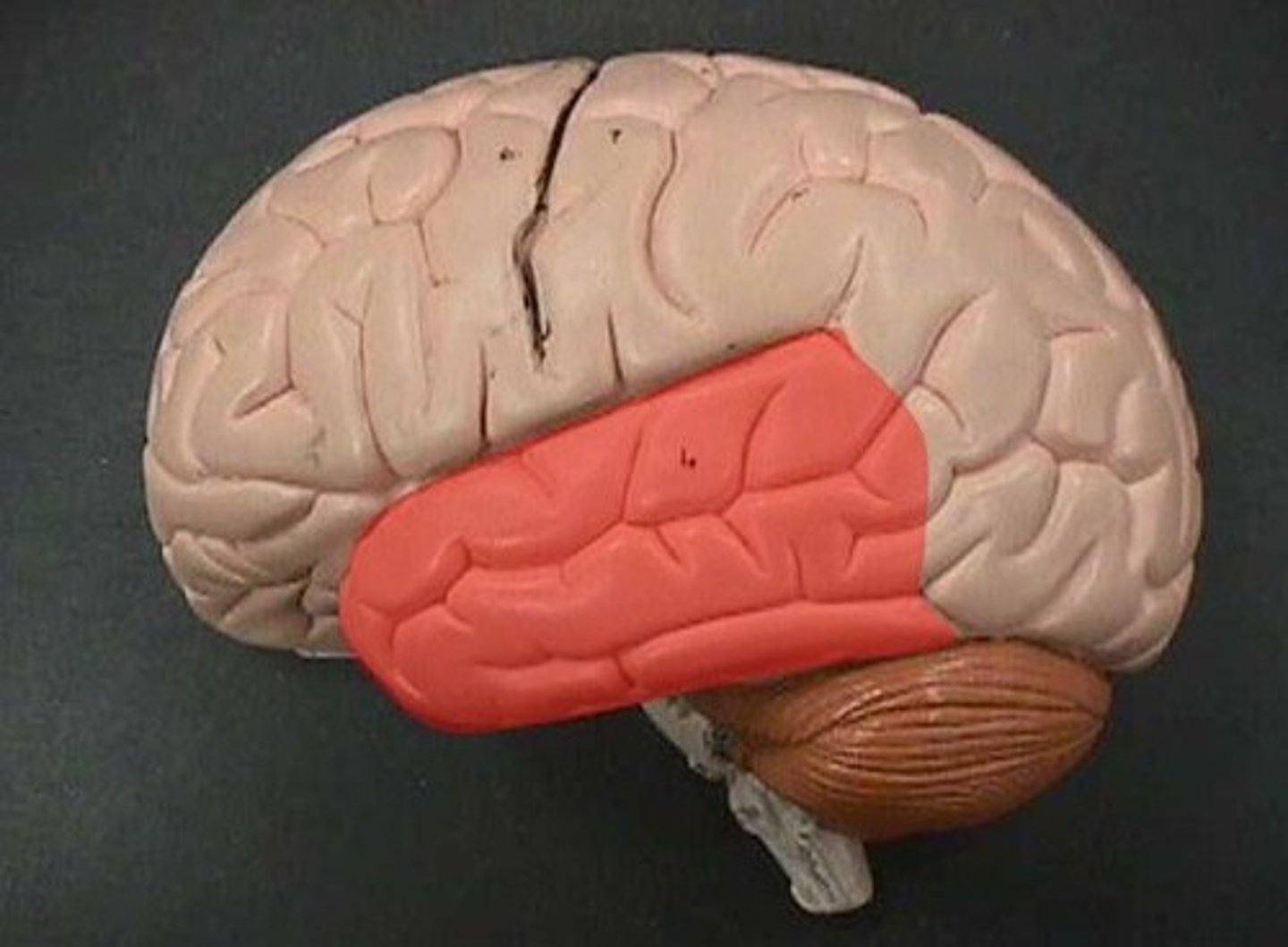
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.