Transport Part 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/120
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:02 AM on 11/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
1
New cards
ER lumen side
On which side of ER membrane is the receptor of the transmembrane protein located on?
2
New cards
Cytosol side
On which side of the ER membrane are the binding domains of the transmembrane protein located on?
3
New cards
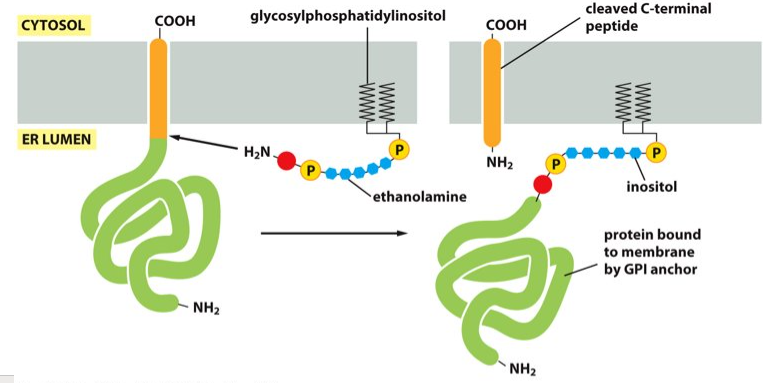
plasma membrane
GPI anchor attaches proteins to the __________.
4
New cards
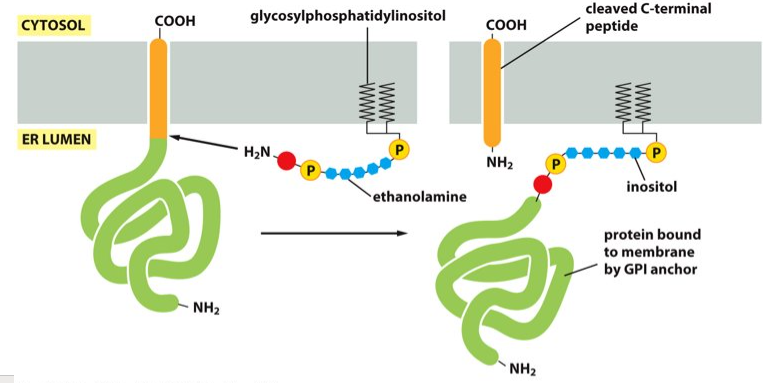
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol
What does GPI stand for?
5
New cards
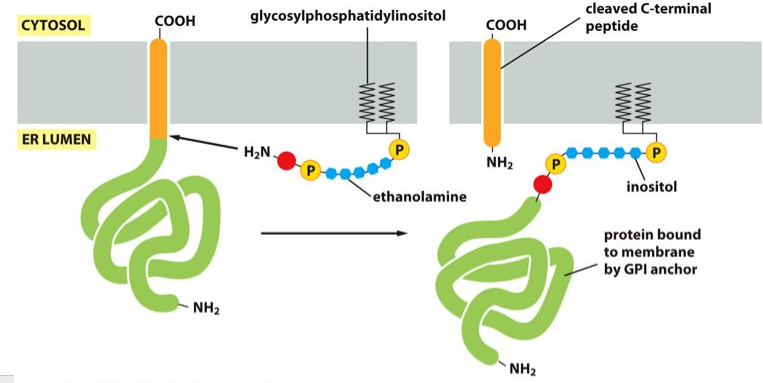
ER enzymes
What catalyzes the GPI anchor?
6
New cards
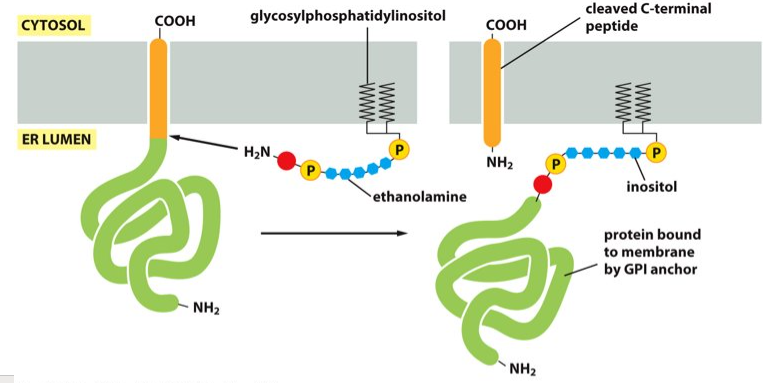
the C-terminus of a protein
What is the GPI anchor covalently attached to?
7
New cards
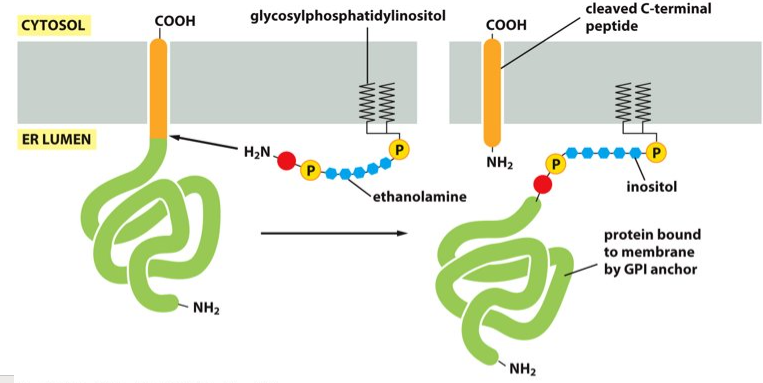
In the ER lumen
Where does the linkage of the GPI to the C-terminus of the protein occur?
8
New cards
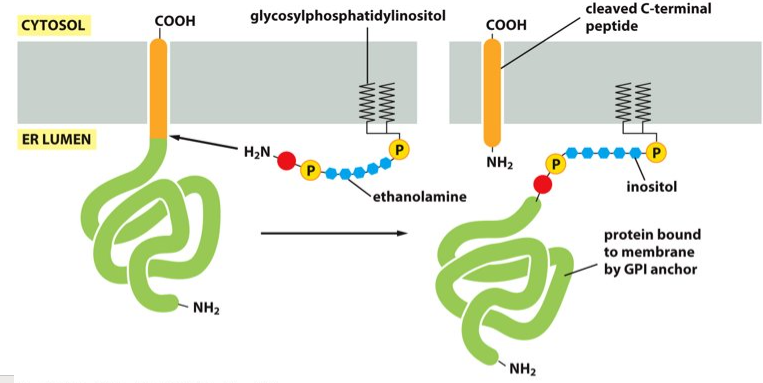
GPI
Protein cut free from the ER membrane and then attaches to the ________, which is membrane bound and eventually travels to the plasma membrane.
9
New cards
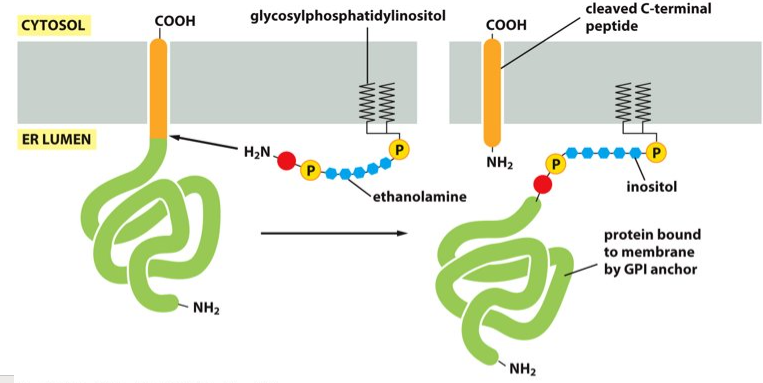
the plasma membrane
What does the GPI anchor attach proteins to?
10
New cards
dynamic
The plasma membrane is very _________, it's always forming and being recycled.
11
New cards
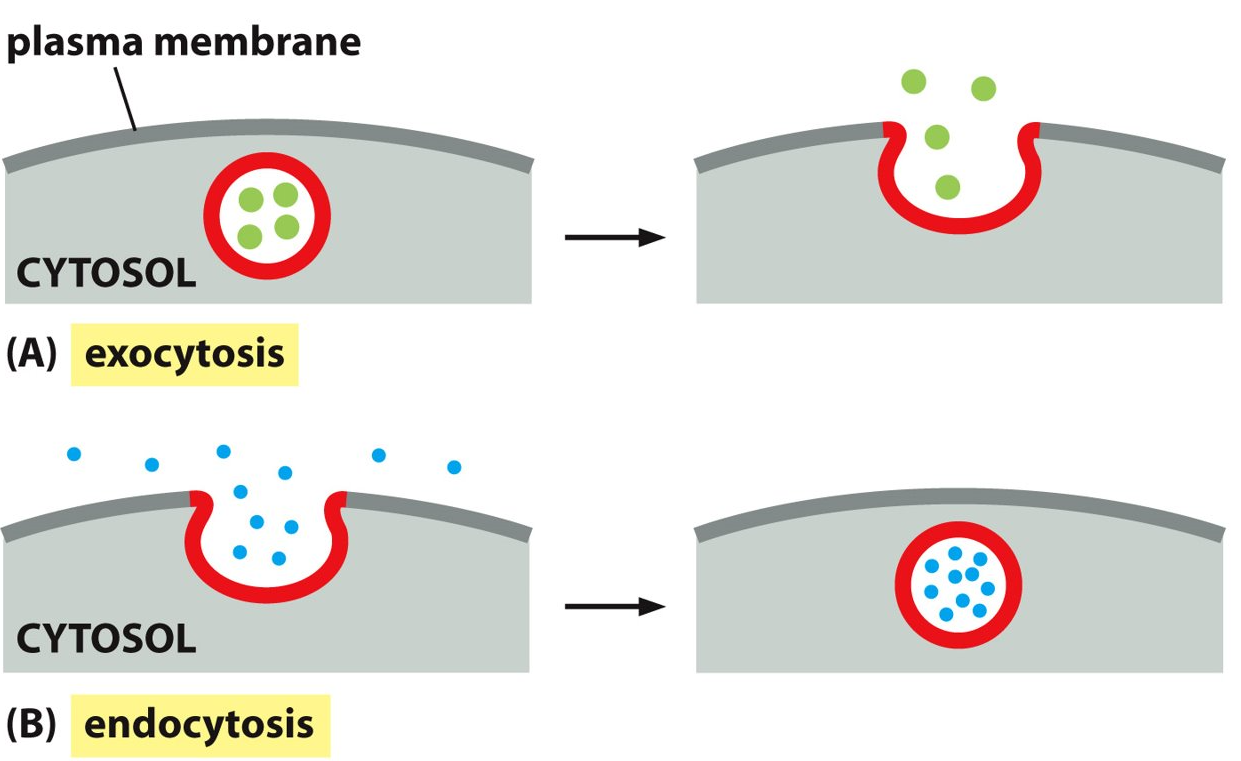
packaging proteins to leave the cell
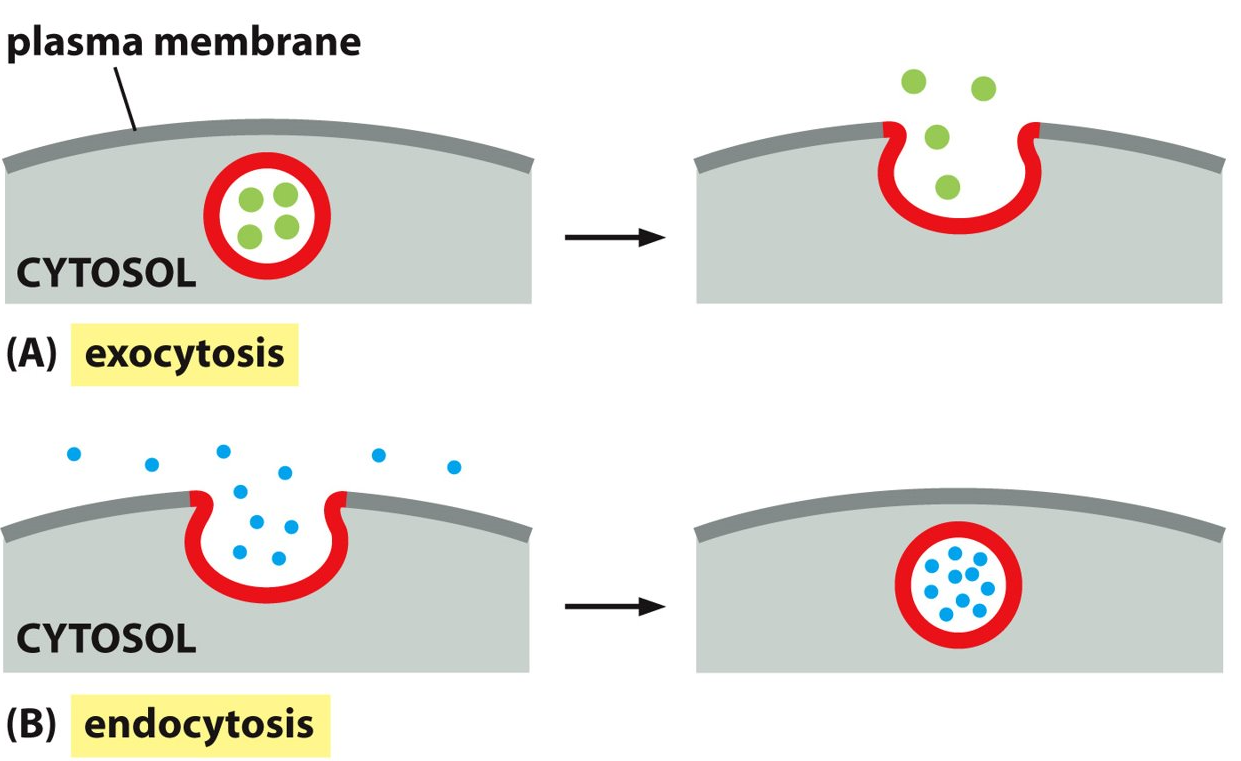
What is exocytosis?
12
New cards
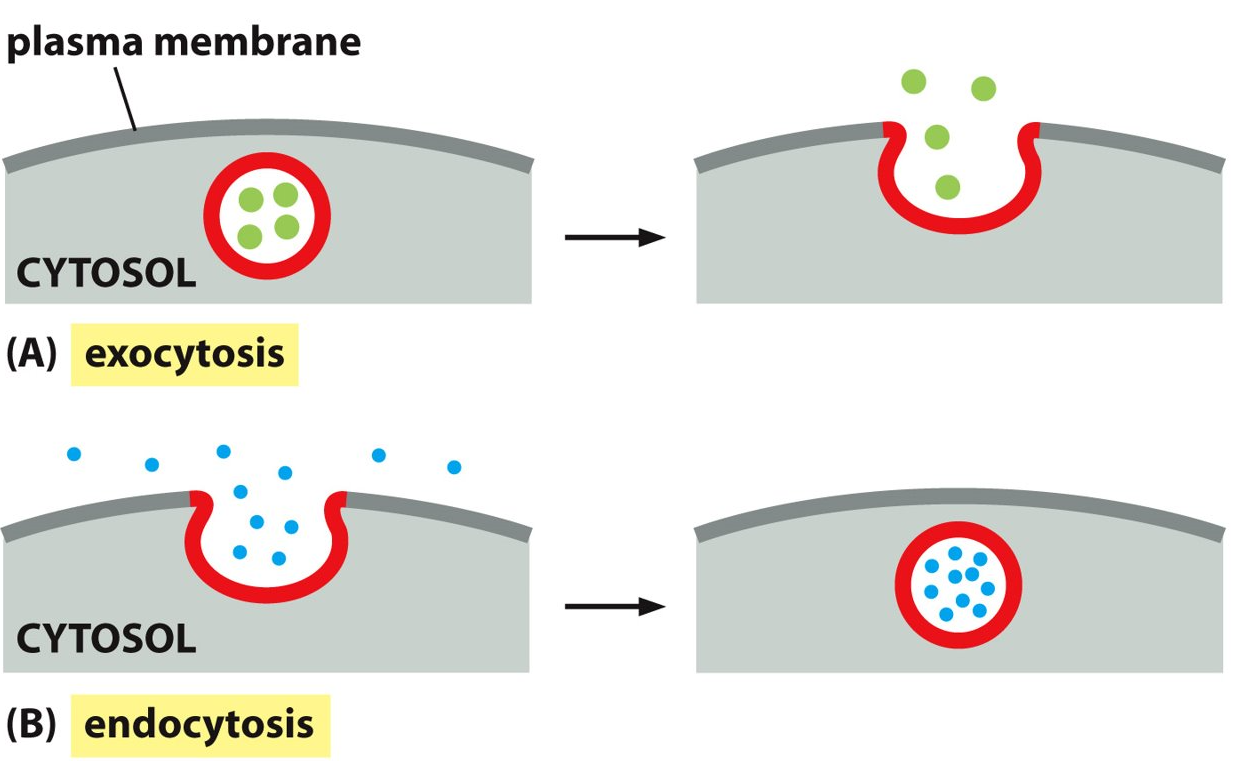
What is endocytosis?
13
New cards
Golgi apparatus
What is known as the mail office of the cell?
14
New cards
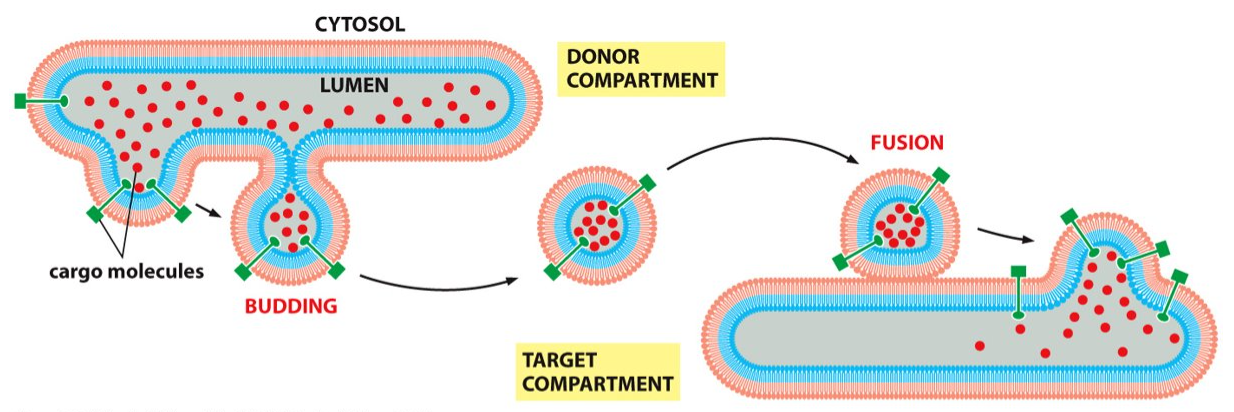
the lumen
What is the interior part of the vesicle called?
15
New cards
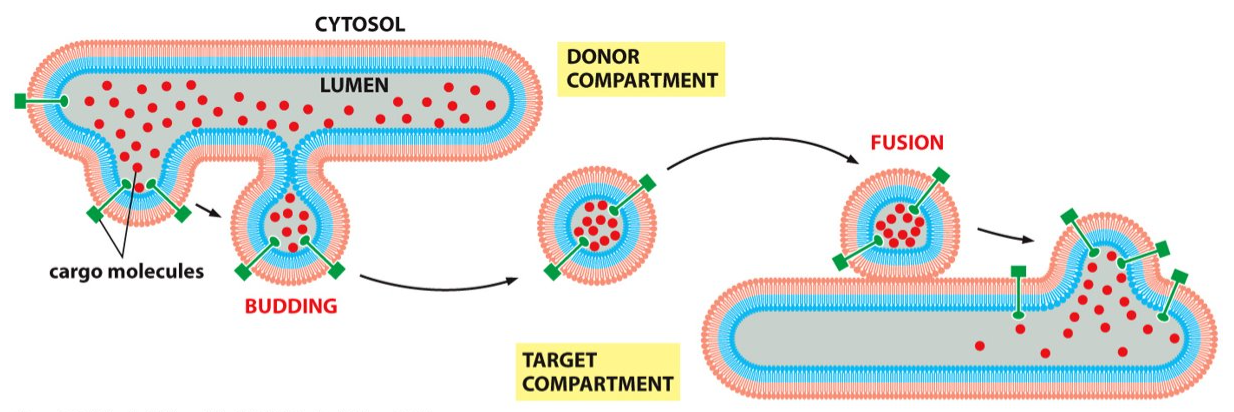
transport vesicle
What allows the travel of a substance without passing through the phospholipid bilayer/ membrane?
16
New cards
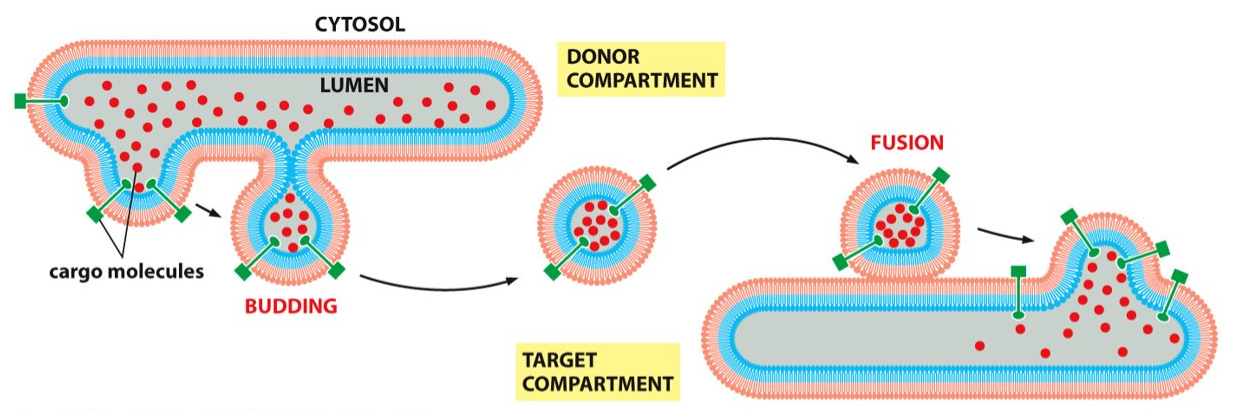
cargo
What are the components of the lumen called?
17
New cards
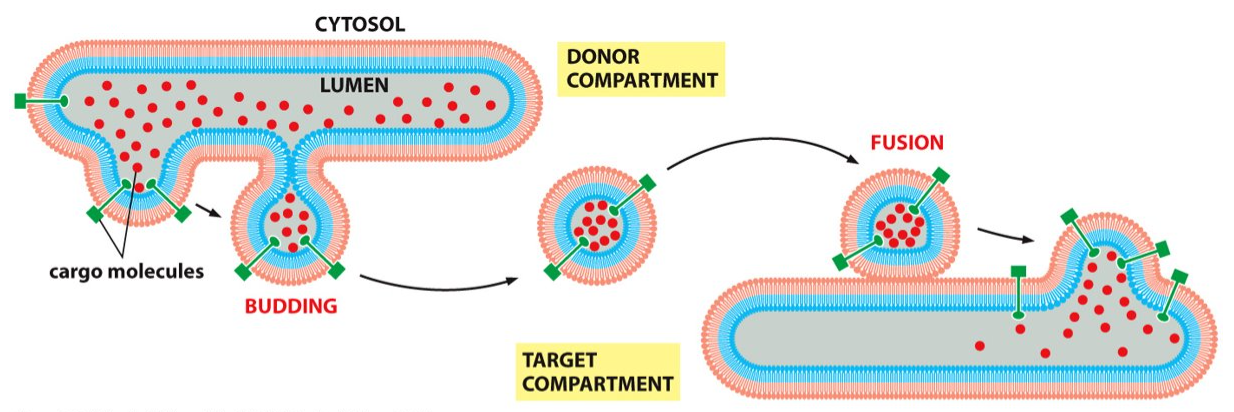
1. they must take up appropriate cargo (budding stage)
2. must fuse with appropriate target membrane (fusion stage)
2. must fuse with appropriate target membrane (fusion stage)
What are the two rules of transport vesicles selectivity?
18
New cards
The budding stage
starting to take up the necessary cargo to bud off the vesicle
19
New cards
Fusion stage
The transport vesicle then buds off and after uncoating, tethering and docking, it will fuse to the target membrane.
20
New cards
secretory pathway
What pathway refers to the ER, Golgi apparatus and the vesicles that travel in between them as well as the cell membrane and lysosomes. It's the pathway by which the cell secretes proteins into the extracellular environment.
21
New cards
Exocytosis
a secretory pathway that delivers newly synthesized proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids to the plasma membrane
22
New cards
Endocytosis
the cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell.
23
New cards
Endocytic pathway
Takes things in through the plasma membrane.
The cells remove a region of the plasma membrane and delivers these to the lysosomes where they are degraded in internal compartments.
The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Includes pinocytosis and phagocytosis.
The cells remove a region of the plasma membrane and delivers these to the lysosomes where they are degraded in internal compartments.
The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Includes pinocytosis and phagocytosis.
24
New cards
endosomes
What are these internal compartments called?
25
New cards
formed by the invagination of the plasma membrane and are triggered by the activation of cell surface receptor.
How are endosomes formed?
26
New cards
Invagination
the process of a surface folding in on itself to form a cavity, pouch or tube.
27
New cards
they control the sorting of activated cell surface receptors either to the plasma membrane for further use or to the lysosome for degradation.
Why are endosomes important?
28
New cards
endosomes
membrane bound organelles, internal compartments where things get degraded and can also be used to capture nutrients.
29
New cards
lysosome (digestive organelles)
start with the plasma membrane, which is then removed to bring in the vesicle. Often these vesicles will then fuse with a __________ where the content will then be degraded in the endosome.
30
New cards
coated vesicles
vesicles that bud from membranes and have a coat on their cytosolic surface (surface facing extracellular environment).
31
New cards
shed its coat
After budding, the vesicle will __________, which allows the membrane to interact directly with the target membrane to fuse with it.
32
New cards
where a vesicle is going to fuse
What is a target membrane?
33
New cards
clathrin coated vesicles
these are the most popular type of coated vesicles, their outer coat is made of clathrin
34
New cards
exocytosis of clathrin coated vesicle
they bud from the Golgi apparatus on the outward secretory pathway. What is this process called?
35
New cards
endocytosis of clathrin coated vesicles
bud also from the plasma membrane on the inward path, which creates a clathrin coated pit. What is this process called?
36
New cards
COP coated vesicles
(COPI or COPII)
(COPI or COPII)
Transport vesicles that transport molecules from the ER to the Golgi and the Golgi to the Golgi (exocytosis)
37
New cards
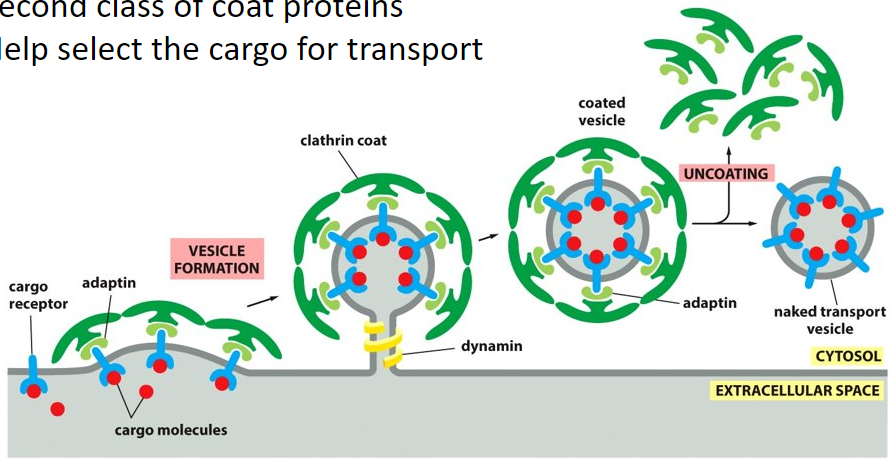
Clathrin
(dark green structure)
(dark green structure)
assemble into basket-like network on the cytosolic surface on the membrane and this starts to shape the membrane into a vesicle
38
New cards
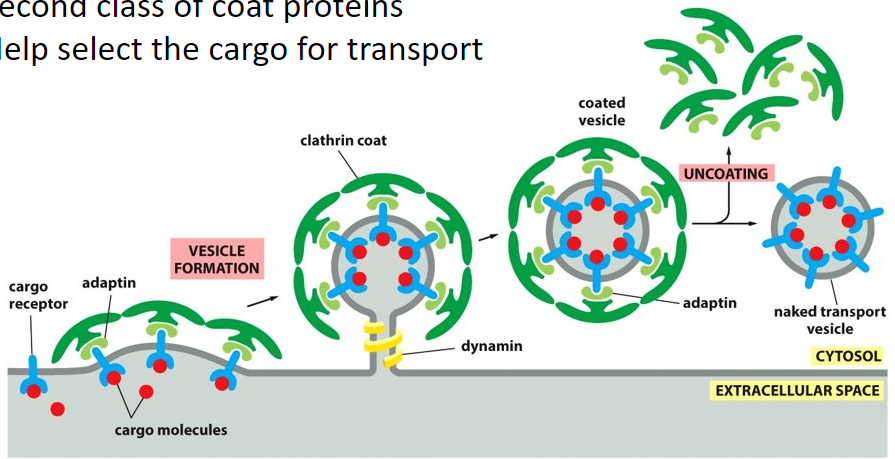
Dynamin
(yellow structure)
(yellow structure)
GTP binding protein that assembles into a ring around the neck of the invaginated pit and pinches off/ constricts the vesicle from the parent membrane. Uses the power from the phosphate to constrict off of the plasma membrane.
39
New cards
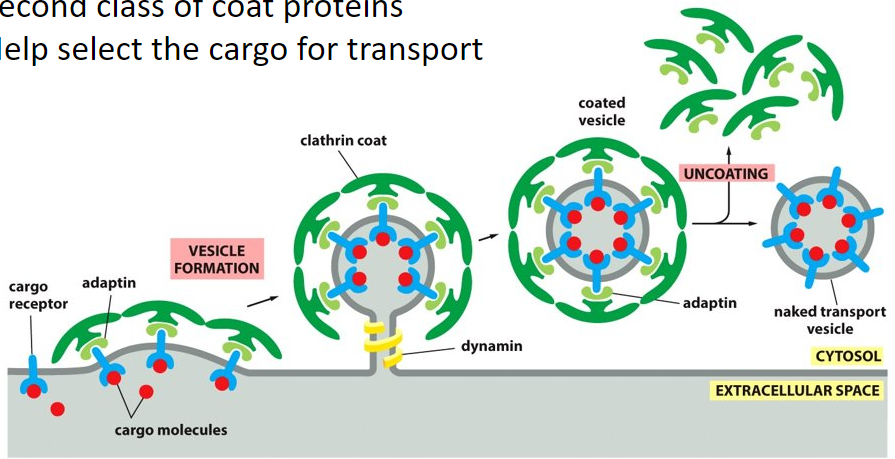
adaptins
(light green structure)
(light green structure)
second class of coat proteins that helps to select the cargo for transport
40
New cards
adaptin
binds to your cargo and these cargo receptors bind to ________ and helps deliver it to your transport vesicle.
41
New cards
adaptin
What binds to clathrin?
42
New cards
in the cytosol
When does the clathrin coat disassemble?
43
New cards
vesicle docking
once the naked vesicle is within the cell, you have to dock the vesicles at a different location. use motor proteins to move vesicles along the cytoskeleton.
44
New cards
Rab proteins
What are the markers on vesicles called?
45
New cards
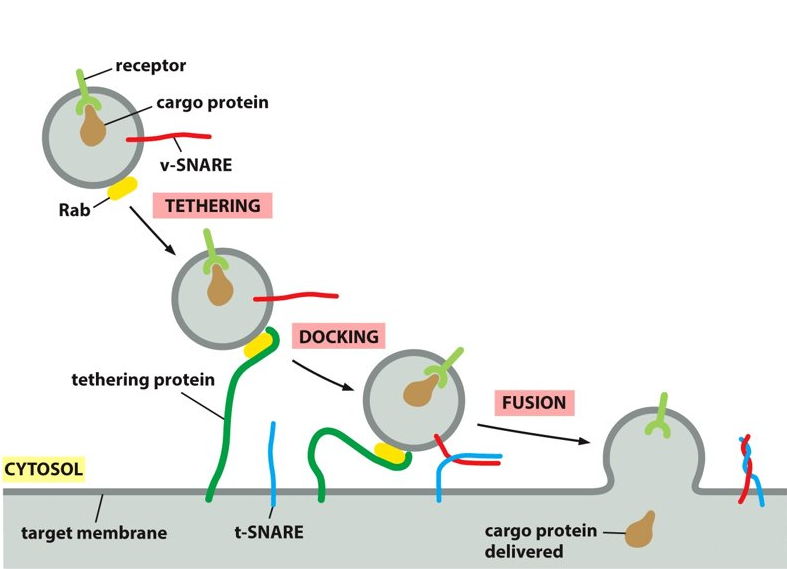
tethering proteins
What are receptors on the organelle called that dock vesicles?
46
New cards
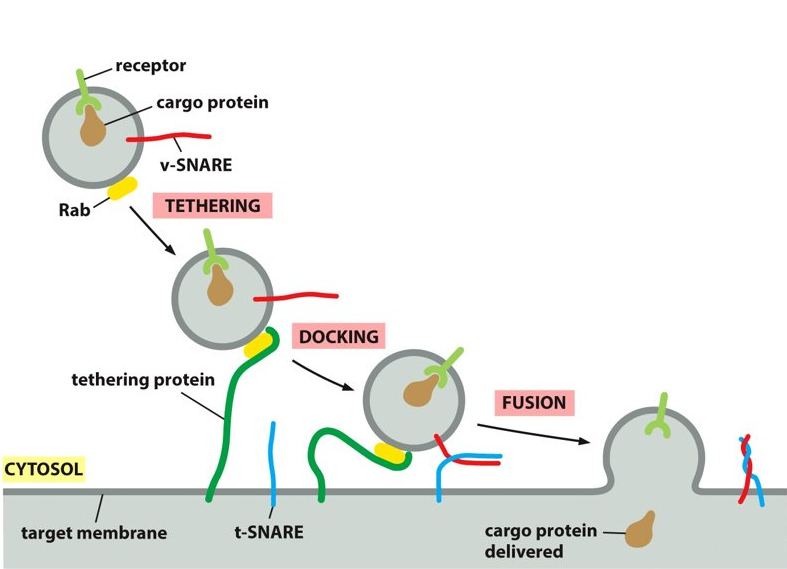
tethering protein
Rab proteins bind to _________ on the target membrane.
47
New cards
ensures that transport vesicles fuse with the correct membrane
Unique combination of rab proteins/ tethering proteins ensures what?
48
New cards
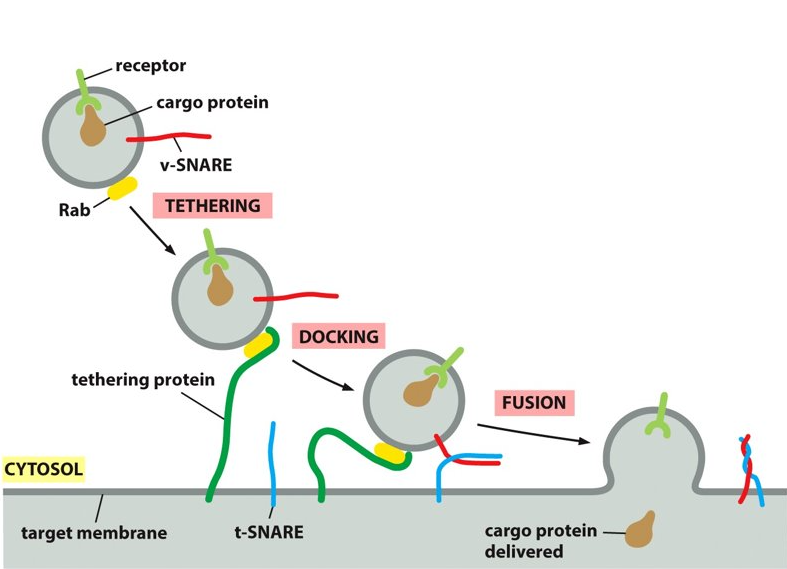
vesicle-SNARE
What does v-SNARE stand for?
49
New cards
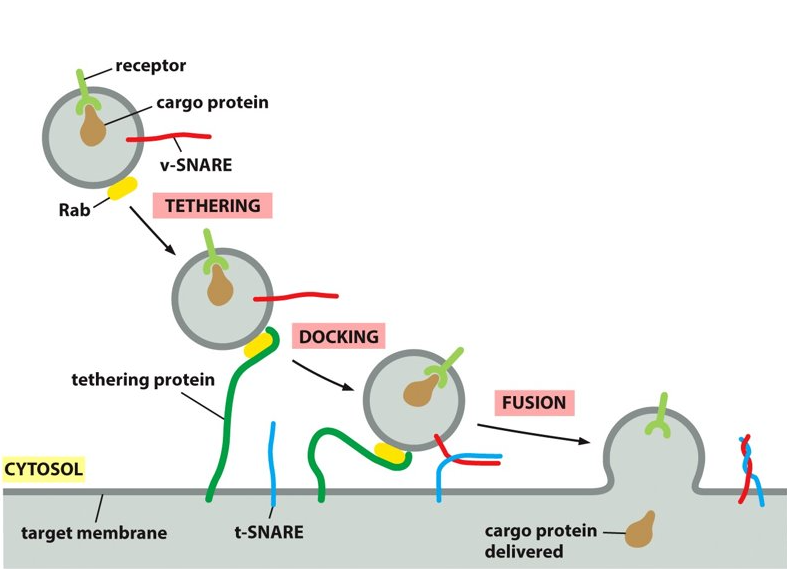
tethering-SNARE
What does t-SNARE stand for?
50
New cards
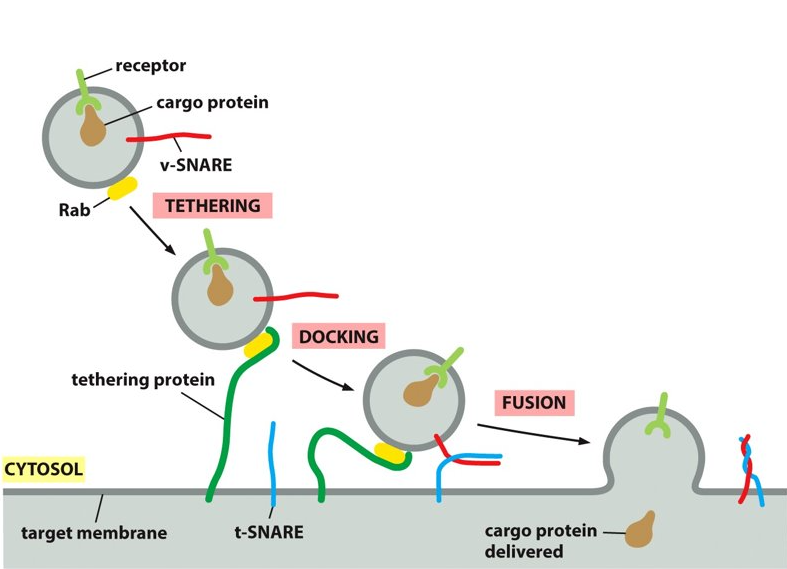
SNARE
provides additional recognition as transmembrane proteins. The tethering protein captures a vesicles by grabbing hold of the Rab protein.
51
New cards
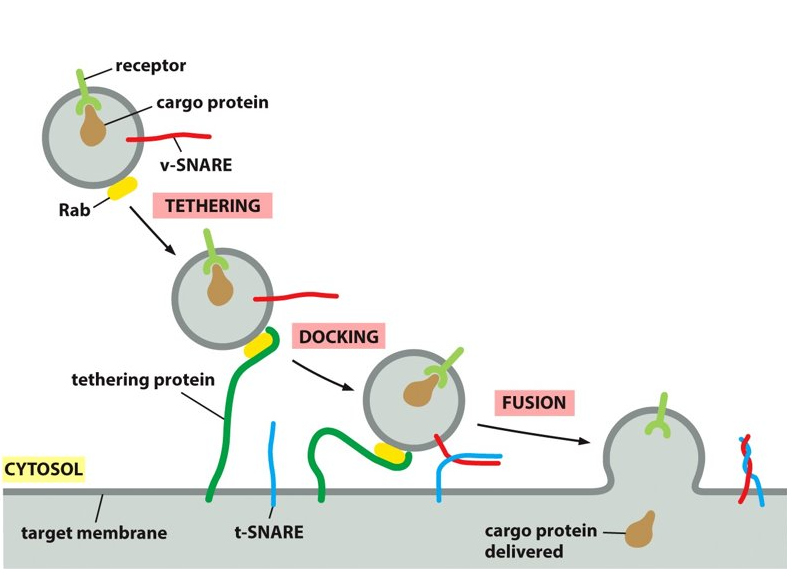
vesicle, target membrane
SNAREs are on the ___________ and the _______.
52
New cards
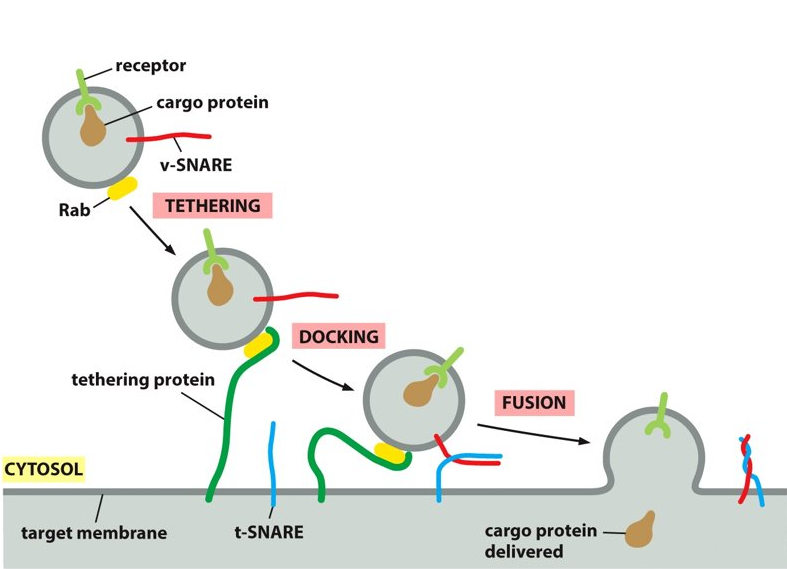
vSNARE, tSNARE
_______ and ______ work together to firmly dock the vesicle in place on the target membrane. They also make sure that the vesicle is binding to the correct membrane.
53
New cards
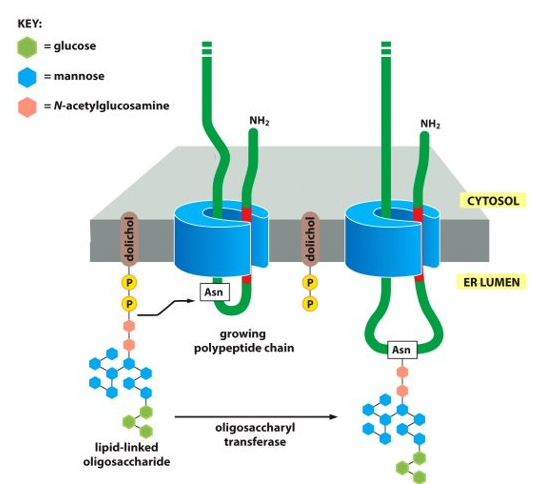
exocytosis
proteins delivered from the ER to the Golgi to the cell surface via transport vesicles
54
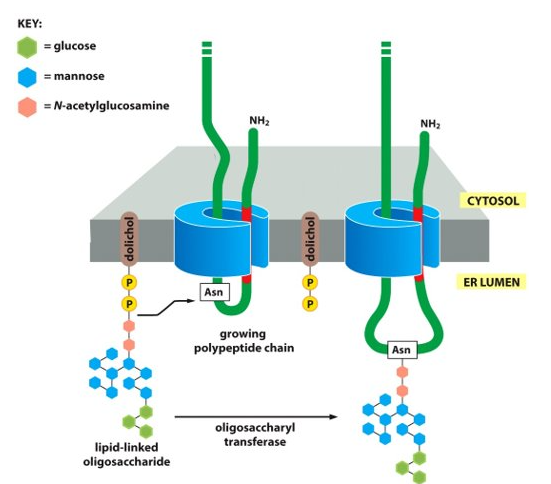
New cards
transport vesicles, ER
These ____________ then fuse with the plasma membrane, and are then covalently modified in the ______ before leaving the cell.
55
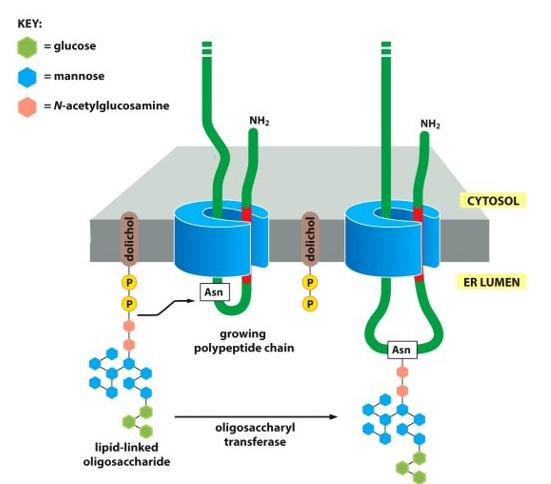
New cards
disulfide bonds, glycosylation, and protein folding
What are examples of some covalent modifications that take place in the ER?
56
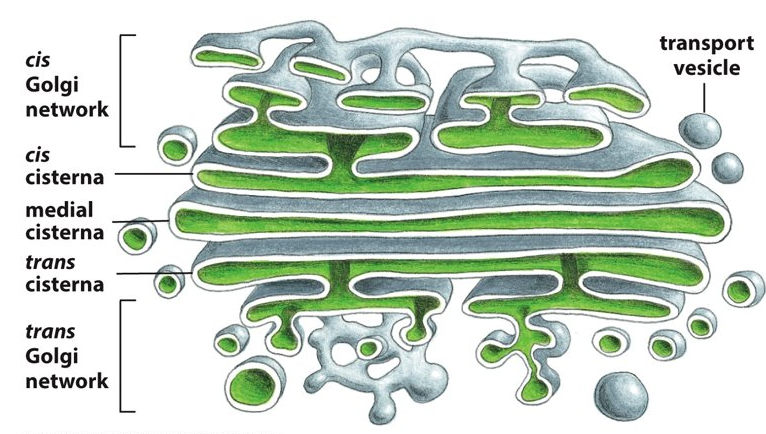
New cards
Golgi apparatus
has a collection of flattened membrane enclosed sacs and each stack consists of two distinct faces
57
New cards
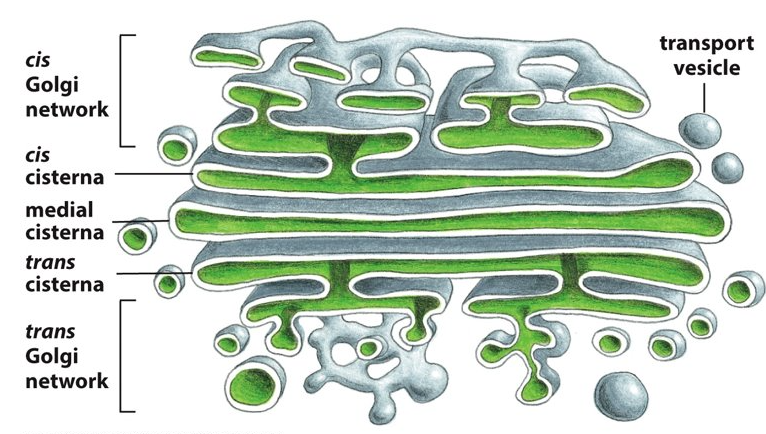
cisternae
What are these flattened membrane enclosed sacs called?
58
New cards
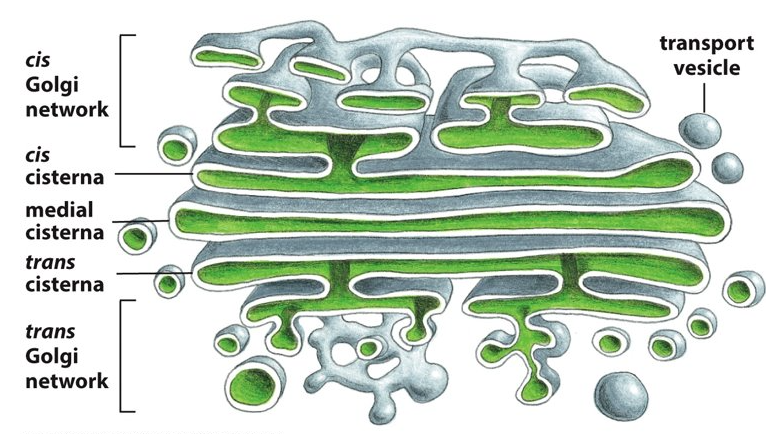
cis face
Which face of the Golgi apparatus is next to the ER and allows entry into the Golgi?
59
New cards
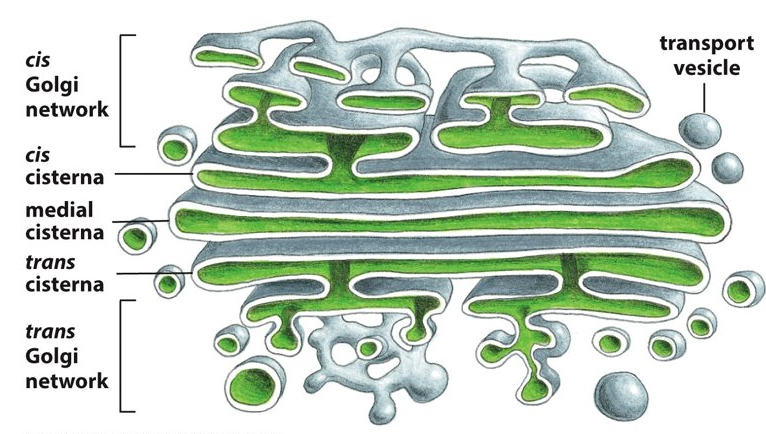
trans face
Which face of the Golgi apparatus points towards the plasma membrane and allows things to exit from the Golgi?
60
New cards
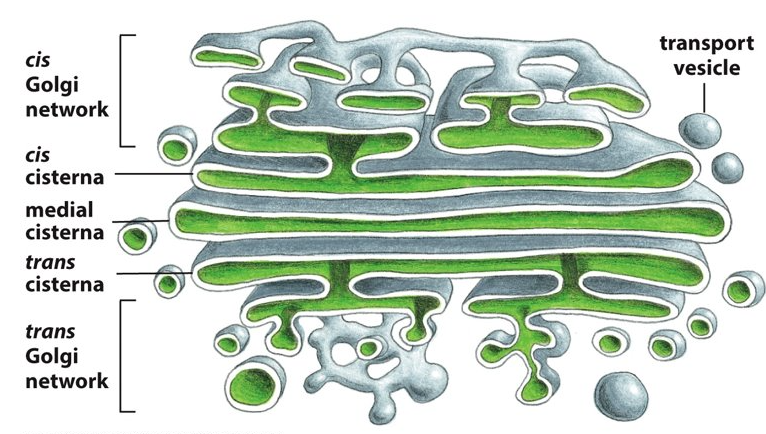
cis, ER
Proteins enter through the _______ face of the Golgi network via transport vesicles from the _______?
61
New cards
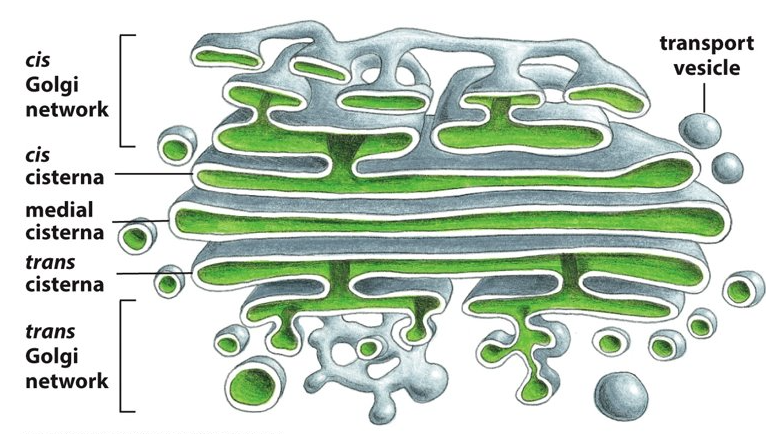
cisternae
Proteins then travel through the ________ through transport vesicles from one cisterna to the next.
62
New cards
trans, plasma membrane
Proteins exit through the _________ face of the Golgi network destined for the _________ or another organelle.
63
New cards
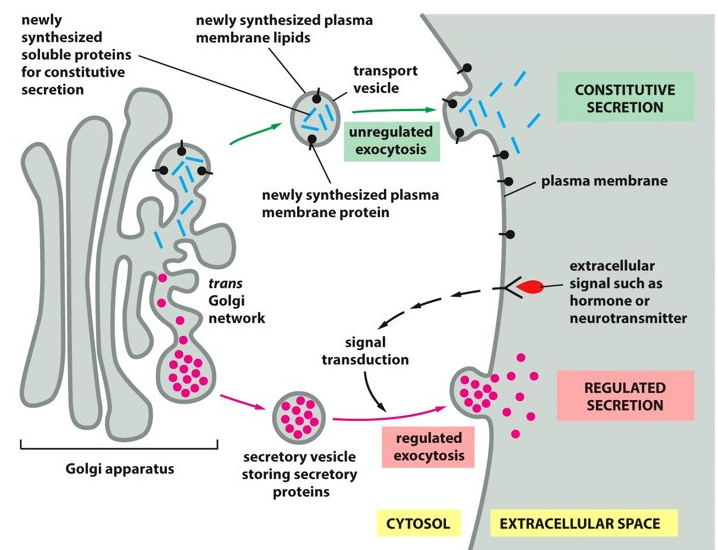
The secretory vesicle
What tells you to release the secretory protein?
64
New cards
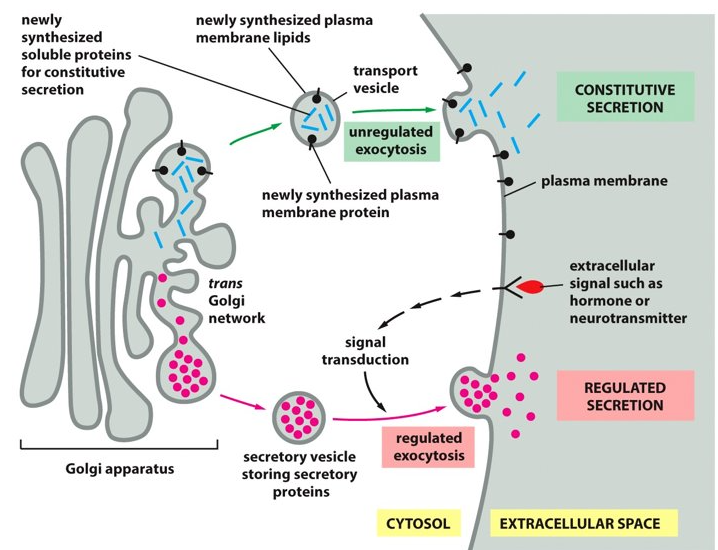
constitutive exocytosis pathway
a steady stream of vesicles bud from the trans Golgi network to the plasma membrane, where the plasma membrane supplies the vesicles with newly made lipids and proteins.
65
New cards
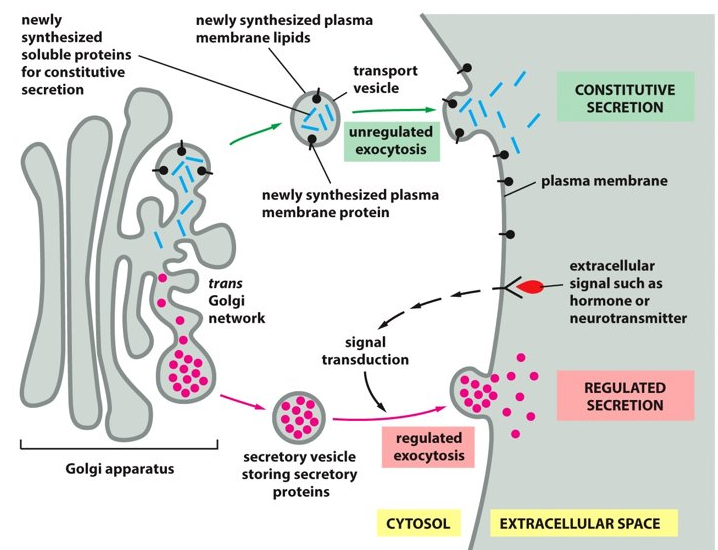
secretion
The vesicle carries soluble proteins to the cell surface to be released in the extra cellular fluid, what is this process called?
*Keep in mind that the vesicle stays attached to the cell surface and that it contributes to the extracellular matrix.
*Keep in mind that the vesicle stays attached to the cell surface and that it contributes to the extracellular matrix.
66
New cards
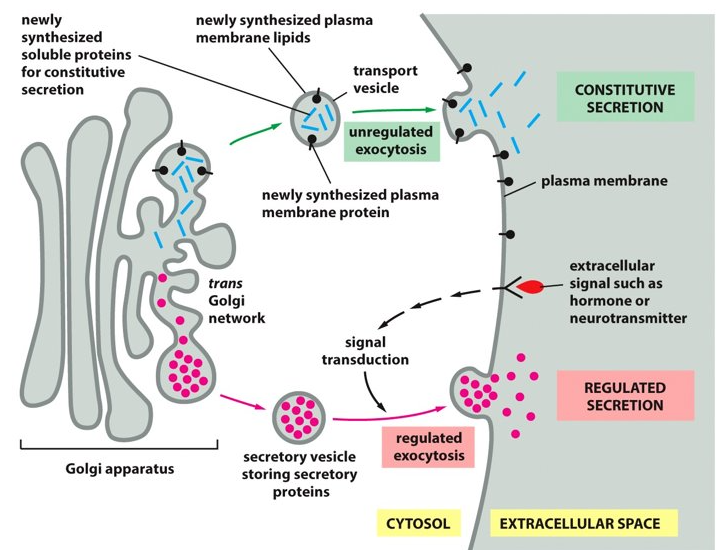
ER, Golgi
For the constitutive exocytosis pathway to occur, there has to be vesicles coming from the _________ to the ________.
67
New cards
regulated exocytosis pathway
This pathway is not always on and is important for secretory cells. This pathway awaits signal instructions before the vesicle leaves the trans Golgi network with the cargo.
68
New cards
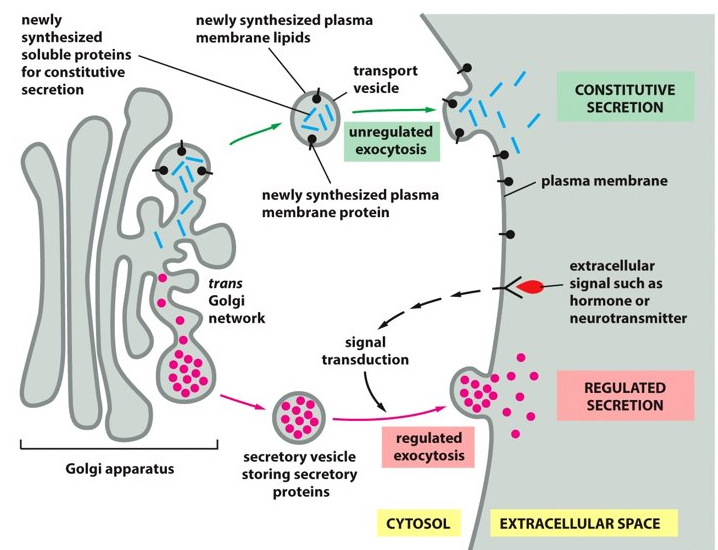
Golgi
The ___________ packages cargo at much higher concentrations.
69
New cards
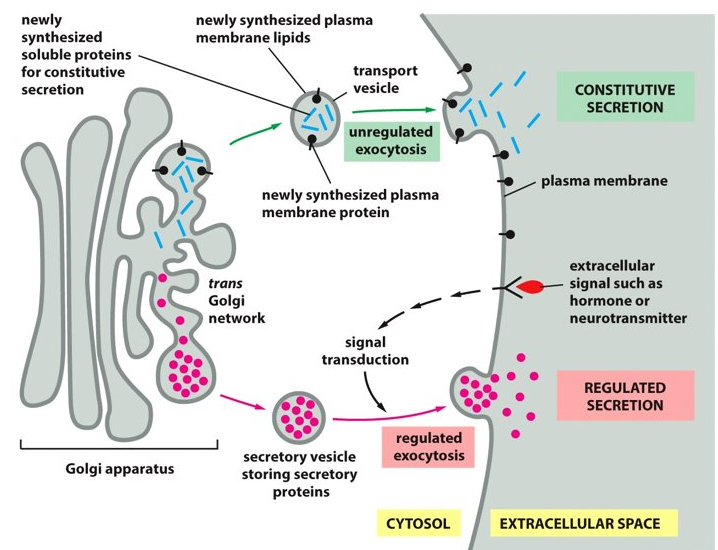
regulated exocytosis pathway
This pathway is important for the secretion or release of hormones, mucus, and digestive enzymes (extracellular signals like hormones or neurotransmitters).
70
New cards
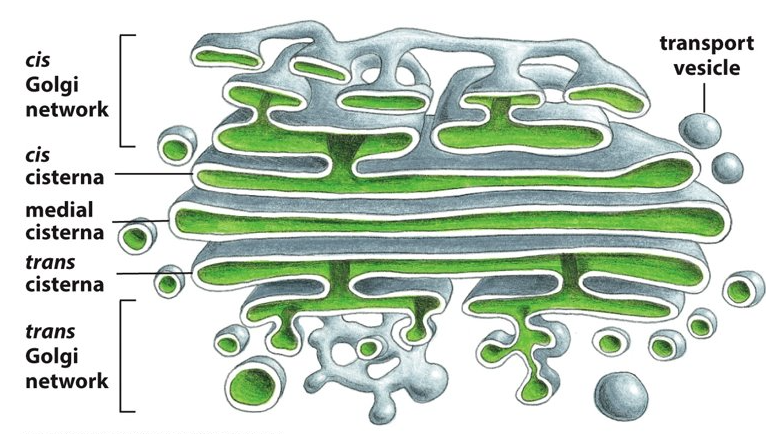
closest to the ER
Where is the cis face of the Golgi located?
71
New cards
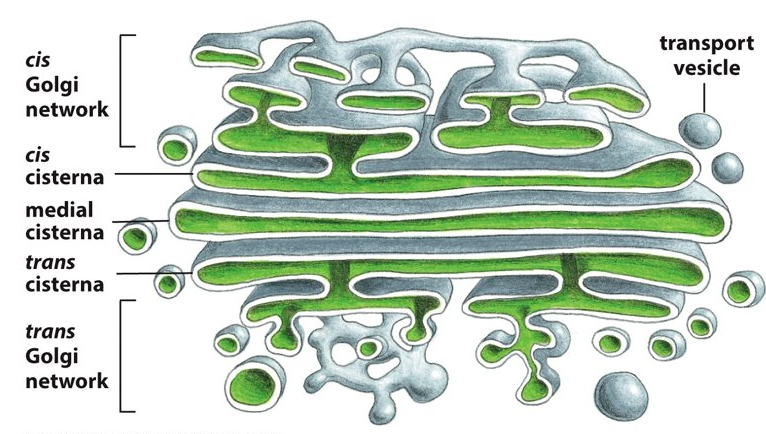
after medial region
Where is the trans face of the Golgi located?
72
New cards
endocytosis
Cells that take up fluid and molecules, small portion of the plasma membrane buds inward and pinched off to form the endocytic vesicle, and many of these become endosomes. This process is called?
73
New cards
the endosome
Where is the ingested material delivered to?
74
New cards
plasma membrane, lysosomes
The ingested material delivered to the endosome is then recycled back to the ___________ or is sent to the ___________(digestive organelle) to be degraded.
75
New cards
Pinocytosis
Pino=drinking
Pino=drinking
cellular drinking for fluid molecules. The ingestion of liquid into a cell by the budding of small vesicles from the cell membrane.
One type of endocytosis.
One type of endocytosis.
76
New cards
Phagocytosis
Phago=eating
Phago=eating
Cellular eating. A process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle, giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome.
One type of endocytosis.
One type of endocytosis.
77
New cards
Phagosomes
Phago = eating
Phago = eating
large vesicles brought in, therefore creating this internal compartment
78
New cards
Phagocytotic cells
Phagocytes (neutrophils and monocytes)
Phagocytes (neutrophils and monocytes)
Immune cells that play a critical role in both the early and late stages of immune responses.
79
New cards
Macrophages
defense mechanisms
engulf or take up smaller cells. They digest and break them down.
*Once they are in the cell, they are then delivered to the endosome.
One type of endocytosis.
a large phagocytic cell found in stationary form in the tissues or as a mobile white blood cell, especially at sites of infection.
engulf or take up smaller cells. They digest and break them down.
*Once they are in the cell, they are then delivered to the endosome.
One type of endocytosis.
a large phagocytic cell found in stationary form in the tissues or as a mobile white blood cell, especially at sites of infection.
80
New cards
Autophagy
the cell recycles components. The mitochondria breaks it down and the plasma membrane recycles it. It's also a lysosome dependent process (digestive organelle).
81
New cards
to promote cell survival
An autophagy performs self-eating ____________. Also known as canabolism of a cell.
82
New cards
development of autophagy
helps reconstruct cells that are differentiating and not dividing, but still need to be maintained
83
New cards
autophagosome
fusion of small vesicles into a double membrane around the organelle and can fuse with the lysosome.
84
New cards
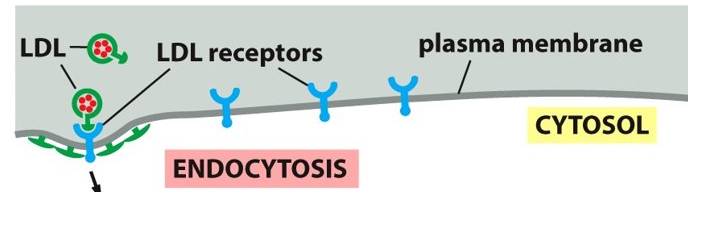
receptor mediated endocytosis
a means to import macromolecules from the extracellular fluid that involves Clathrin coats on the vesicles.
Selectively concentrating material mechanism as the vesicles are brought into the cell.
Uptake of cholesterol needed to make new membranes.
Selectively concentrating material mechanism as the vesicles are brought into the cell.
Uptake of cholesterol needed to make new membranes.
85
New cards
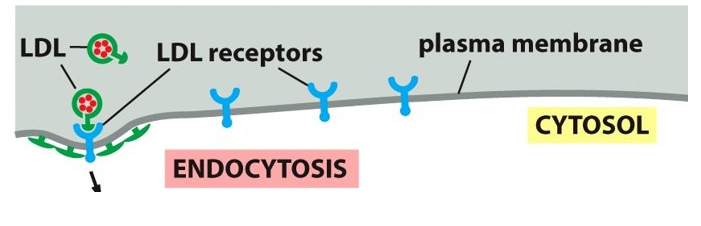
Cholesterol
___________ depends on receptor mediated endocytosis.
86
New cards
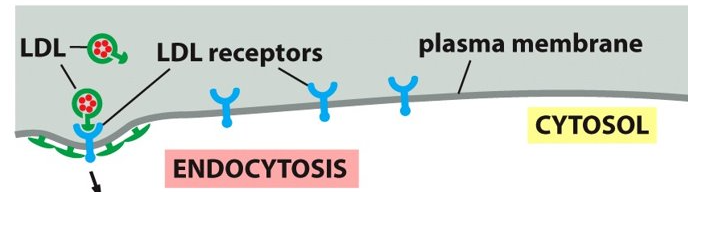
low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
Cholesterol is extremely insoluble, transported to the bloodstream bound to ________________.
87
New cards
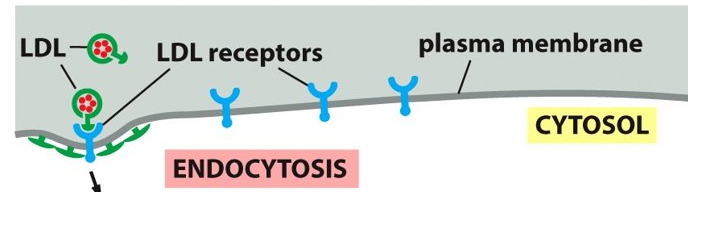
liver
Cholesterol-LDL is secreted by the _______ and binds to receptors on the cell surface.
88
New cards
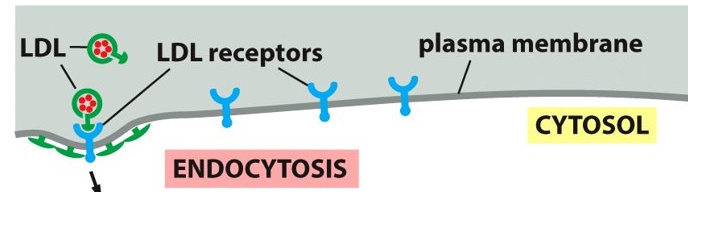
Cholesterol
_____________ is essential to cell membrane health.
89
New cards
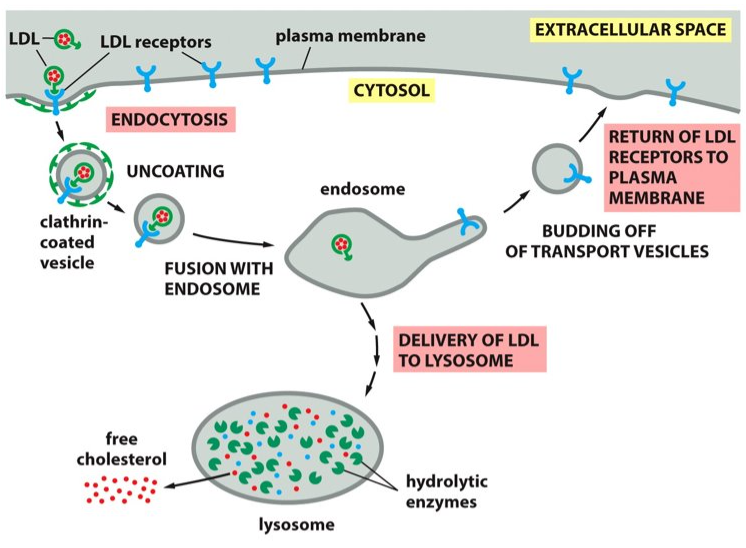
Receptor mediated endocytosis
Ingest receptor-LDL complexes and deliver them to the endosomes. LDL then dissociates from the receptor and the receptor is recycled back to the plasma membrane. What is this process known as?
90
New cards
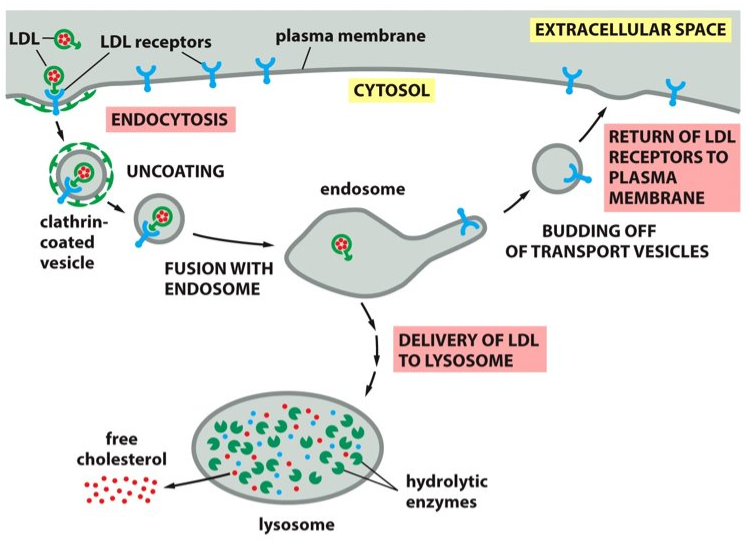
lysosomes
LDL goes back to the _____________.
91
New cards
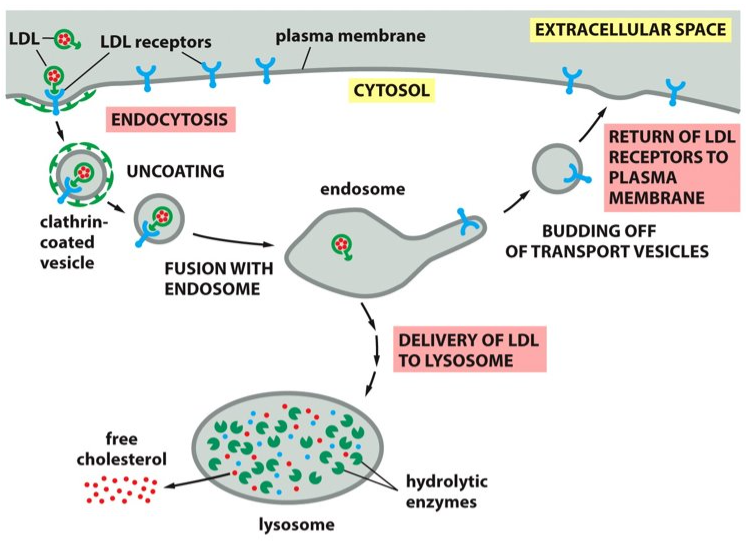
hydrolytic enzymes
LDL is broken down into ___________ in the lysosomes.
92
New cards
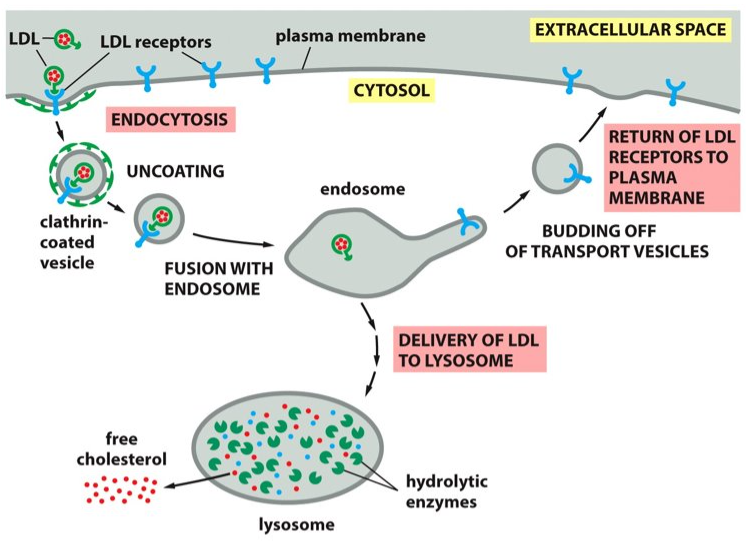
cytosol
Cholesterol is then released from the LDL and will translocate to the ________. Now the LDL is available for membrane synthesis.
93
New cards
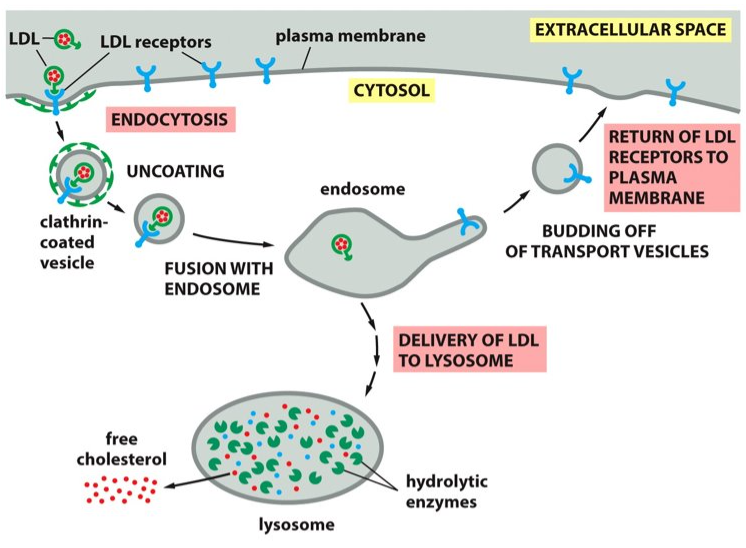
cholesterol
The lysosomes release _______ to be used in the plasma membrane.
94
New cards
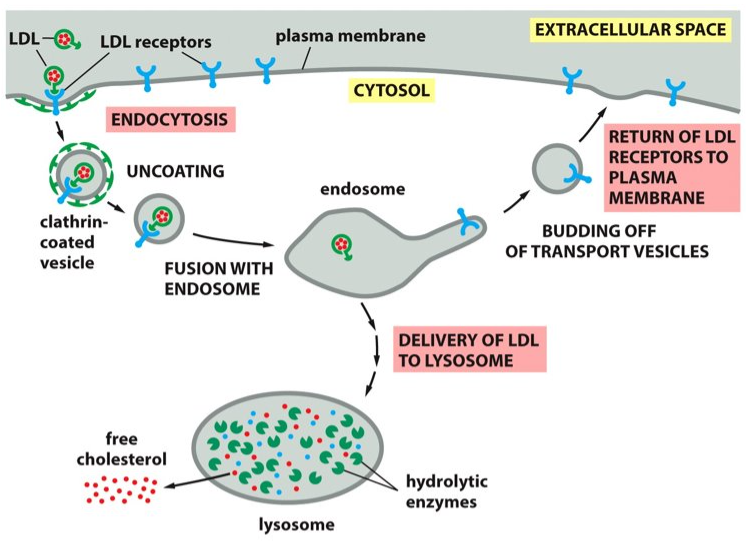
acidic
Lysosomes are very _________ with their hydrolytic enzymes that use water to break down bonds.
95
New cards
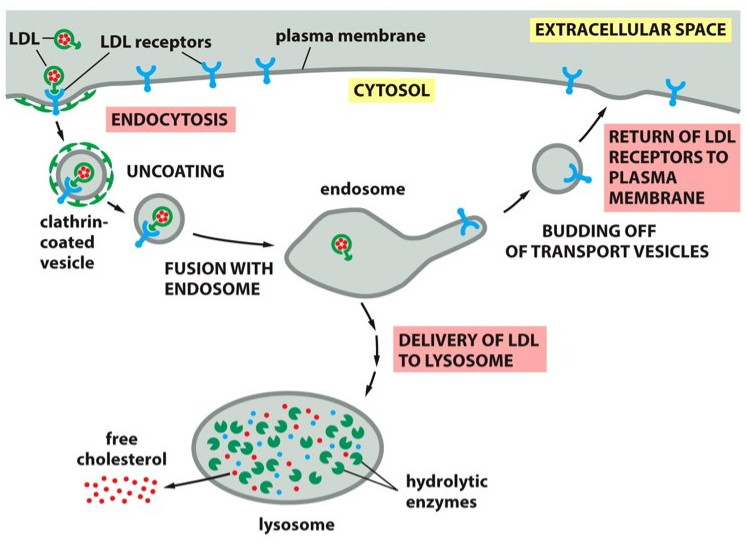
LDL gene
Genetic pre-disposition to high cholesterol means that individuals have inherited defective versions of the _______, which causes the receptor o be missing or non-functional.
96
New cards
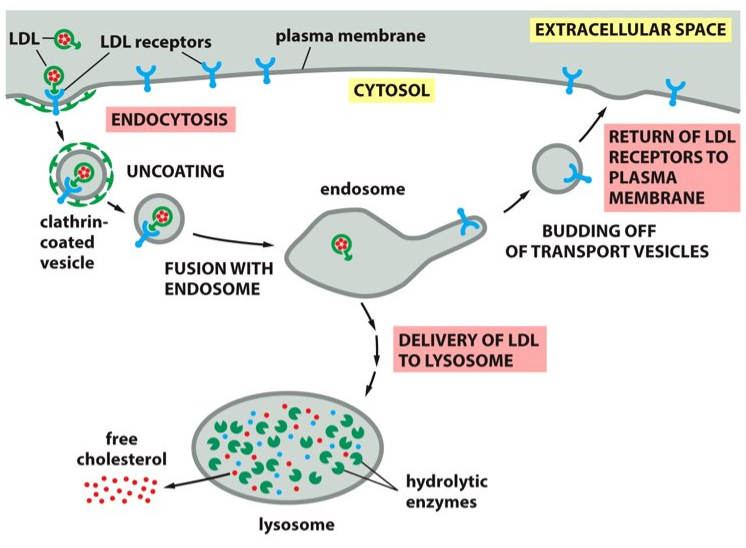
atherosclerosis
Cells deficient in taking up LDL-bound cholesterol, causes cholesterol to stay in the blood or the buildup of cholesterol (leading to higher levels of cholesterol), which leads to a disease called _____________.
97
New cards
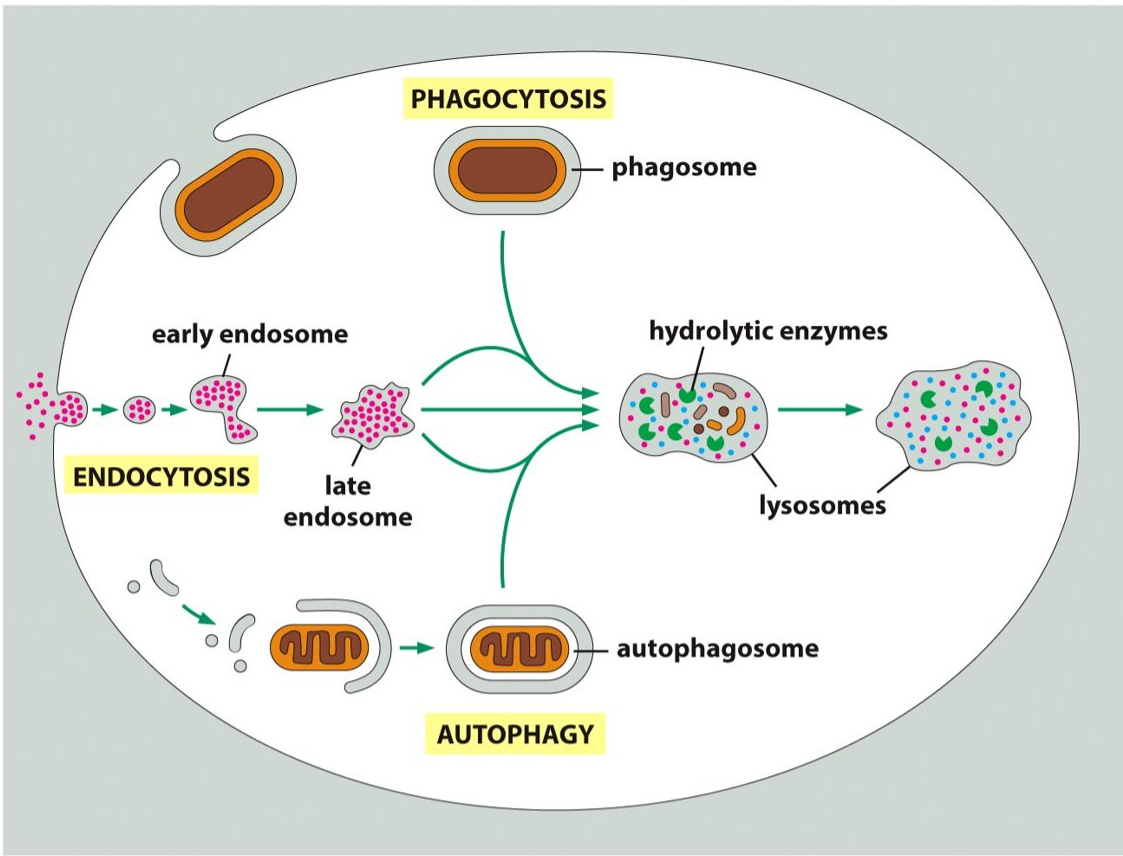
a lysosome-dependent process that recycles components of itself to survive
What is autophagy?
98
New cards
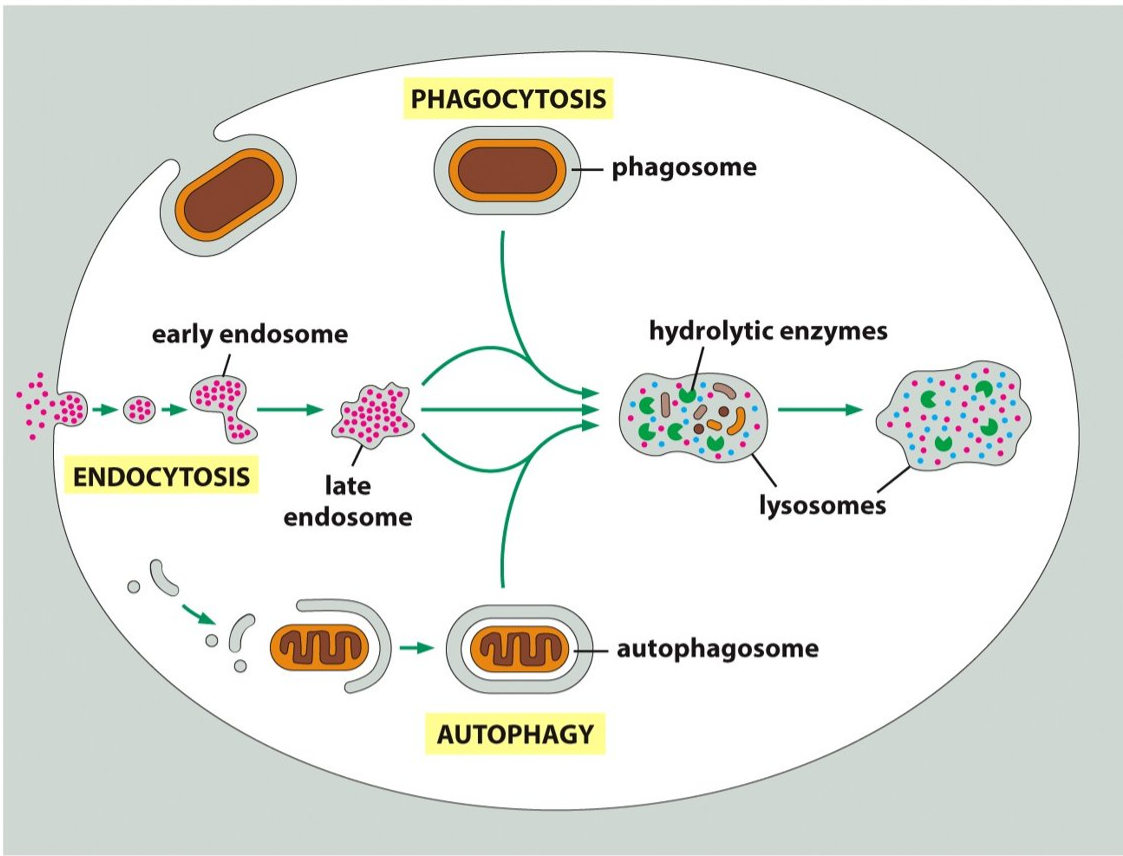
cellular eating
The process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle like bacterial cells or viruses, thus giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome.
The process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle like bacterial cells or viruses, thus giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome.
What is phagocytosis?
99
New cards
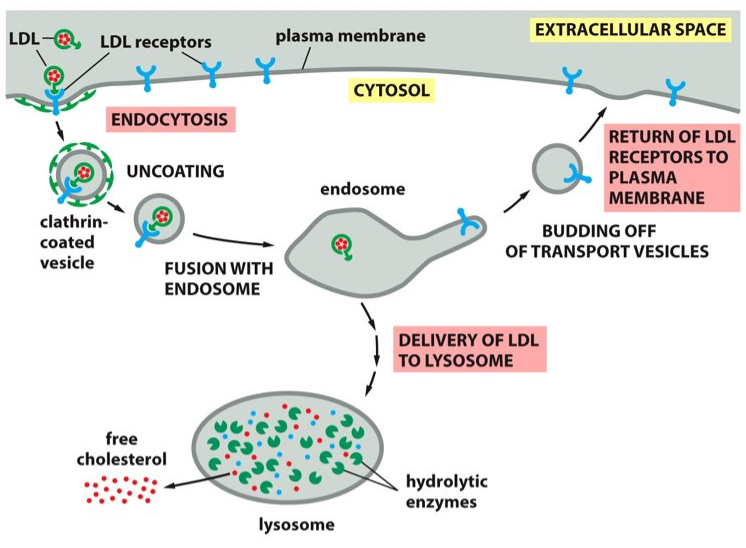
lysosomes
Where can free cholesterol and hydrolytic enzymes be found?
100
New cards
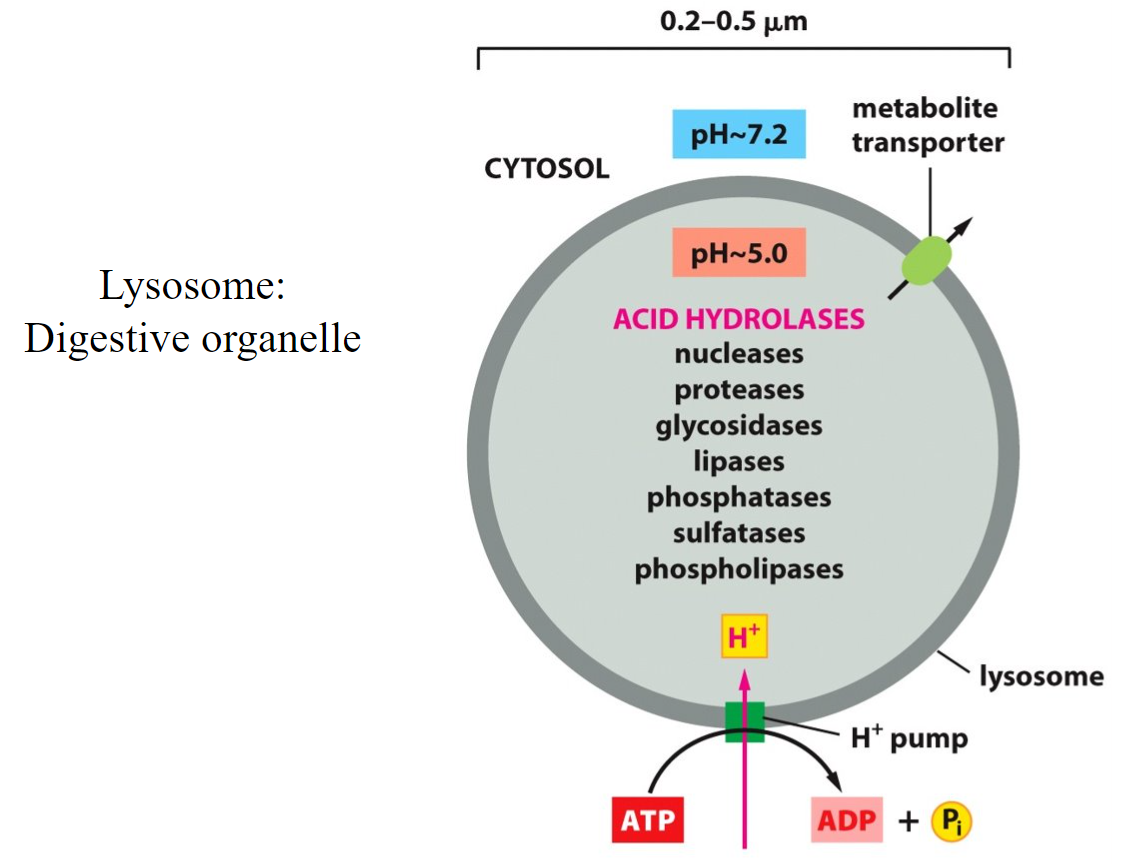
lysosome
This organelle is very acidic, uses a pump to maintain its H+ environment (against the gradient, so it needs ATP).